实验5
1
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 5
void input(int x[], int n);
void output(int x[], int n);
void find_min_max(int x[], int n, int* pmin, int* pmax);
int main() {
int a[N];
int min, max;
printf("录入%d个数据:\n", N);
input(a, N);
printf("数据是: \n");
output(a, N);
printf("数据处理...\n");
find_min_max(a, N, &min, &max);
printf("输出结果:\n");
printf("min = %d, max = %d\n", min, max);
return 0;
}
void input(int x[], int n) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
scanf_s("%d", &x[i]);
}
void output(int x[], int n) {
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
printf("%d ", x[i]);
printf("\n");
}
void find_min_max(int x[], int n, int* pmin, int* pmax) {
int i;
*pmin = *pmax = x[0];
for (i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if (x[i] < *pmin)
*pmin = x[i];
else if (x[i] > *pmax)
*pmax = x[i];
}问题一:是在给定的整数数组x中,通过指针pmin和pmax来找到数组中的最小值和最大值,并通过指针返回最值
问题二:pmin和pmax分别指向函数调用时实参传递给它们的用于存储最小值和最大值的地址,且它们所指向的内存单元被赋值为x【0】
1.2
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 5
void input(int x[], int n);
void output(int x[], int n);
int *find_max(int x[], int n);
int main() {
int a[N];
int *pmax;
printf("录入%d个数据:\n", N);
input(a, N);
printf("数据是: \n");
output(a, N);
printf("数据处理...\n");
pmax = find_max(a, N);
printf("输出结果:\n");
printf("max = %d\n", *pmax);
return 0;
}
void input(int x[], int n) {
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
scanf("%d", &x[i]);
}
void output(int x[], int n) {
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
printf("%d ", x[i]);
printf("\n");
}
int *find_max(int x[], int n) {
int max_index = 0;
int i;
for(i = 0; i < n; ++i)
if(x[i] > x[max_index])
max_index = i;
return &x[max_index];
}1.在一个数组中寻找最大值,并通过指针返回
2,可以
2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 80
int main() {
char s1[N] = "Learning makes me happy";
char s2[N] = "Learning makes me sleepy";
char tmp[N];
printf("sizeof(s1) vs. strlen(s1): \n");
printf("sizeof(s1) = %d\n", sizeof(s1));
printf("strlen(s1) = %d\n", strlen(s1));
printf("\nbefore swap: \n");
printf("s1: %s\n", s1);
printf("s2: %s\n", s2);
printf("\nswapping...\n");
strcpy(tmp, s1);
strcpy(s1, s2);
strcpy(s2, tmp);
printf("\nafter swap: \n");
printf("s1: %s\n", s1);
printf("s2: %s\n", s2);
return 0;
}1.80个字节 s1占用的字节数· 字符串中的个数
2.不可以 改变了s1的指向
2.2
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#define N 80
int main() {
char *s1 = "Learning makes me happy";
char *s2 = "Learning makes me sleepy";
char *tmp;
printf("sizeof(s1) vs. strlen(s1): \n");
printf("sizeof(s1) = %d\n", sizeof(s1));
printf("strlen(s1) = %d\n", strlen(s1));
printf("\nbefore swap: \n");
printf("s1: %s\n", s1);
printf("s2: %s\n", s2);
printf("\nswapping...\n");
tmp = s1;
s1 = s2;
s2 = tmp;
printf("\nafter swap: \n");
printf("s1: %s\n", s1);
printf("s2: %s\n", s2);
return 0;
}3.s1s2存放的地址值 没有
3
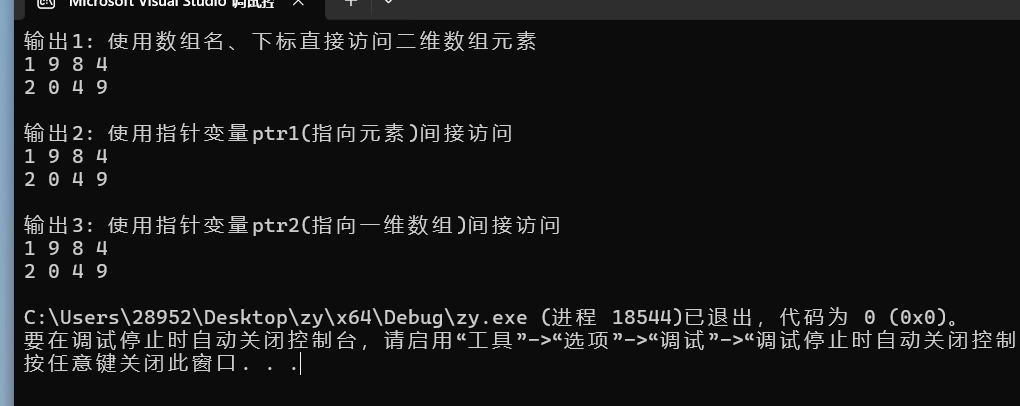
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int x[2][4] = {{1, 9, 8, 4}, {2, 0, 4, 9}};
int i, j;
int *ptr1; // 指针变量,存放int类型数据的地址
int(*ptr2)[4]; // 指针变量,指向包含4个int元素的一维数组
printf("输出1: 使用数组名、下标直接访问二维数组元素\n");
for (i = 0; i < 2; ++i) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j)
printf("%d ", x[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n输出2: 使用指针变量ptr1(指向元素)间接访问\n");
for (ptr1 = &x[0][0], i = 0; ptr1 < &x[0][0] + 8; ++ptr1, ++i) {
printf("%d ", *ptr1);
if ((i + 1) % 4 == 0)
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n输出3: 使用指针变量ptr2(指向一维数组)间接访问\n");
for (ptr2 = x; ptr2 < x + 2; ++ptr2) {
for (j = 0; j < 4; ++j)
printf("%d ", *(*ptr2 + j));
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
4
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 80
void replace(char *str, char old_char, char new_char); // 函数声明
int main() {
char text[N] = "Programming is difficult or not, it is a question.";
printf("原始文本: \n");
printf("%s\n", text);
replace(text, 'i', '*'); // 函数调用 注意字符形参写法,单引号不能少
printf("处理后文本: \n");
printf("%s\n", text);
return 0;
}
// 函数定义
void replace(char *str, char old_char, char new_char) {
int i;
while(*str) {
if(*str == old_char)
*str = new_char;
str++;
}
}1.将所有等于old_char的字符改为new_char
2.可以
5
#include <stdio.h>
#define N 80
char* str_trunc(char* str, char x);
int main() {
char str[N];
char ch;
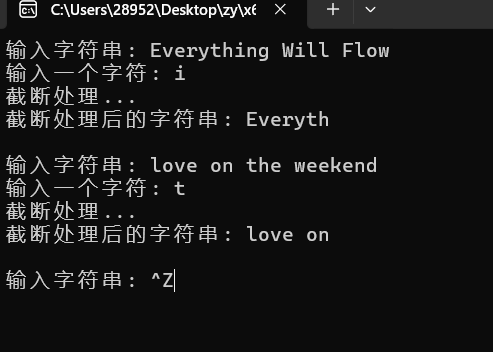
while (printf("输入字符串: "), gets(str) != NULL) {
printf("输入一个字符: ");
ch = getchar();
printf("截断处理...\n");
str_trunc(str, ch); // 函数调用
printf("截断处理后的字符串: %s\n\n", str);
getchar();
}
return 0;
}
// 函数str_trunc定义
// 功能: 对字符串作截断处理,把指定字符自第一次出现及其后的字符全部删除, 并返回字符串地址
char* str_trunc(char* str, char x) {
char* p = str;
while (*p != '\0') {
if (*p == x) {
*p = '\0';
break;
}
p++;
}
return str;
}
作用是读取并清除输入缓冲区中的换行符
6
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 5
int check_id(char* str); // 函数声明
int main()
{
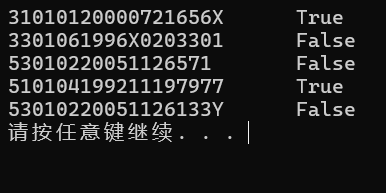
char* pid[N] = { "31010120000721656X",
"3301061996X0203301",
"53010220051126571",
"510104199211197977",
"53010220051126133Y" };
int i;
for (i = 0; i < N; ++i)
if (check_id(pid[i])) // 函数调用
printf("%s\tTrue\n", pid[i]);
else
printf("%s\tFalse\n", pid[i]);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
// 函数定义
// 功能: 检查指针str指向的身份证号码串形式上是否合法
// 形式合法,返回1,否则,返回0
int check_id(char* str) {
int len = strlen(str);
int i;
if (len != 18) {
return 0;
}
for (i = 0; i < 17; i++) {
if (!(str[i] >= '0' && str[i] <= '9')) {
return 0;
}
}
if (str[17] != 'X' && !(str[17] >= '0' && str[17] <= '9')) {
return 0;
}
return 1;
}
7.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define N 80
void encoder(char* str, int n); // 函数声明
void decoder(char* str, int n); // 函数声明
int main() {
char words[N];
int n;
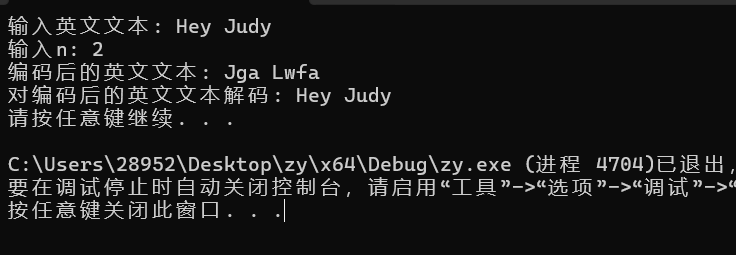
printf("输入英文文本: ");
gets(words);
printf("输入n: ");
scanf_s("%d", &n);
printf("编码后的英文文本: ");
encoder(words, n); // 函数调用
printf("%s\n", words);
printf("对编码后的英文文本解码: ");
decoder(words, n); // 函数调用
printf("%s\n", words);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
// 函数定义
// 功能:对s指向的字符串进行编码处理
// 编码规则:对于a~z或A~Z之间的字母字符,用其后第n个字符替换;其它非字母字符,保持不变
void encoder(char* str, int n) {
while (*str != '\0') {
if ((*str >= 'a' && *str <= 'z') || (*str >= 'A' && *str <= 'Z')) {
char base = (*str >= 'a' && *str <= 'z') ? 'a' : 'A';
*str = (base + ((*str - base + n) % 26));
}
str++;
}
}
// 函数定义
// 功能:对s指向的字符串进行解码处理
// 解码规则:对于a~z或A~Z之间的字母字符,用其前面第n个字符替换;其它非字母字符,保持不变
void decoder(char* str, int n) {
while (*str != '\0') {
if ((*str >= 'a' && *str <= 'z') || (*str >= 'A' && *str <= 'Z')) {
char base = (*str >= 'a' && *str <= 'z') ? 'a' : 'A';
*str = (base + ((*str - base - n + 26) % 26));
}
str++;
}
}
8
#include <stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) {
int i;
for(i = 1; i < argc; ++i)
printf("hello, %s\n", argv[i]);
system("pause");
return 0;
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号