ThreadLocal
1. 是什么?
threadlocal而是一个线程内部的存储类,可以在指定线程内存储数据,数据存储以后,只有指定线程可以得到存储数据,官方解释如下
/** * This class provides thread-local variables. These variables differ from * their normal counterparts in that each thread that accesses one (via its * {@code get} or {@code set} method) has its own, independently initialized * copy of the variable. {@code ThreadLocal} instances are typically private * static fields in classes that wish to associate state with a thread (e.g., * a user ID or Transaction ID). */
大致意思就是ThreadLocal提供了线程内存储变量的能力,这些变量不同之处在于每一个线程读取的变量是对应的互相独立的。通过get和set方法就可以得到当前线程对应的值。
做个不恰当的比喻,从表面上看ThreadLocal相当于维护了一个map,key就是当前的线程,value就是需要存储的对象。
这里的这个比喻是不恰当的,实际上是ThreadLocal的静态内部类ThreadLocalMap为每个Thread都维护了一个数组table,ThreadLocal确定了一个数组下标,而这个下标就是value存储的对应位置。
2. 怎么用?
public void test1() { ThreadLocal<String> tl1 = new ThreadLocal<>(); ThreadLocal<String> tl2 = new ThreadLocal<>(); for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { new Thread(() -> { tl1.set(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->TL1"); tl2.set(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"->TL2"); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+tl1.get()); System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+" "+tl2.get()); tl1.remove(); tl2.remove(); }, "thread"+i).start(); } } //打印结果 thread1 thread1->TL1 thread1 thread1->TL2 thread0 thread0->TL1 thread0 thread0->TL2 thread2 thread2->TL1 thread3 thread3->TL1 thread4 thread4->TL1 thread4 thread4->TL2 thread2 thread2->TL2 thread3 thread3->TL2
分析:每个ThreadLocal实例为每个线程维护一个变量(各线程间独立),get/set/remove 对当前线程的值进行操作
相关操作源码
public T get() { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); // 该方法返回线程的 hreadlocals(下文) if (map != null) { ThreadLocalMap.Entry e = map.getEntry(this); if (e != null) { @SuppressWarnings("unchecked") T result = (T)e.value; return result; } } return setInitialValue(); } /** * Get the map associated with a ThreadLocal. Overridden in * InheritableThreadLocal. * * @param t the current thread * @return the map */ ThreadLocalMap getMap(Thread t) { return t.threadLocals; } public void set(T value) { Thread t = Thread.currentThread(); ThreadLocalMap map = getMap(t); if (map != null) map.set(this, value); else createMap(t, value); } public void remove() { ThreadLocalMap m = getMap(Thread.currentThread()); if (m != null) m.remove(this); }
3. 为什么?
-
每个Thread有一个初始值为null的 ThreadLocalMap 实例,初始化时 key 为当前线程,value为存储的值。 即所有的操作都是针对当前线程的 threadlocals.

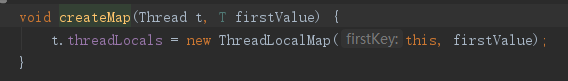
-
ThreadLocalMap 为 ThreadLocal 的静态内部类, ThreadLocalMap 中有 Entry 数组,Entry 为最终存储值的结构,之所以用数组是因为有多个 ThreadLocal, 利用Hash 在Entry中存储不同ThreadLocal 对应的value
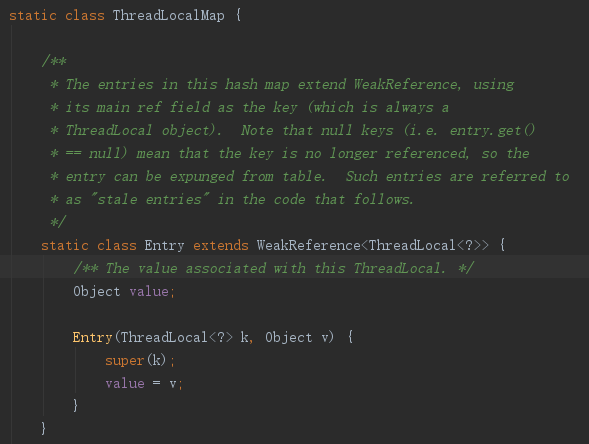
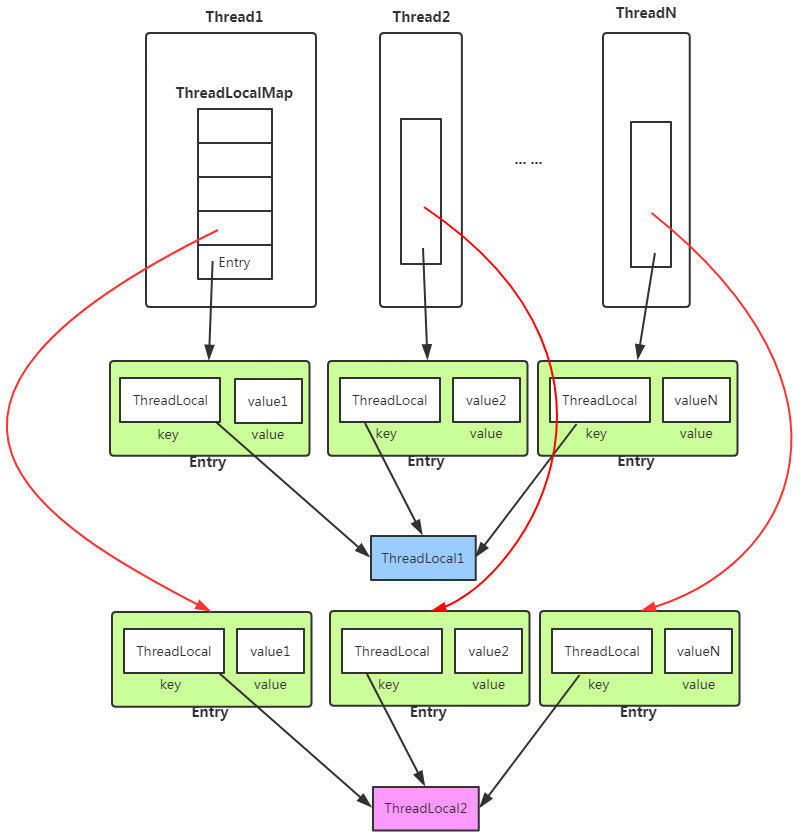
白话:每个线程有个map(ThreadLocalMap), 这个map 有个数组(Entry),数组利用Hash进行地址索引,对应不同的 ThreadLocal
注意: Entry继承了WeakRefrence(如上代码),下次GC后 key(ThreadLocal)就没了,如果线程没有销毁,value还在,就有内存泄露的情况。
所以一般用 try{} finally{ remove()} 的结构
set方法本身有优化,判断当前弱引用(ThreadLocal)是否为空,为空则替换
/** * Set the value associated with key. * * @param key the thread local object * @param value the value to be set */ private void set(ThreadLocal key, Object value) { // We don't use a fast path as with get() because it is at // least as common to use set() to create new entries as // it is to replace existing ones, in which case, a fast // path would fail more often than not. Entry[] tab = table; int len = tab.length; int i = key.threadLocalHashCode & (len-1); for (Entry e = tab[i]; e != null; e = tab[i = nextIndex(i, len)]) { ThreadLocal k = e.get(); if (k == key) { e.value = value; return; } if (k == null) { replaceStaleEntry(key, value, i); return; } } tab[i] = new Entry(key, value); int sz = ++size; if (!cleanSomeSlots(i, sz) && sz >= threshold) rehash(); }
4. 用在哪儿
多个方法嵌套调用相同参数,单线程中用 static 修饰变量即可,多线程会出问题,此时用 ThreadLocal 可实现线程间变量的隔离。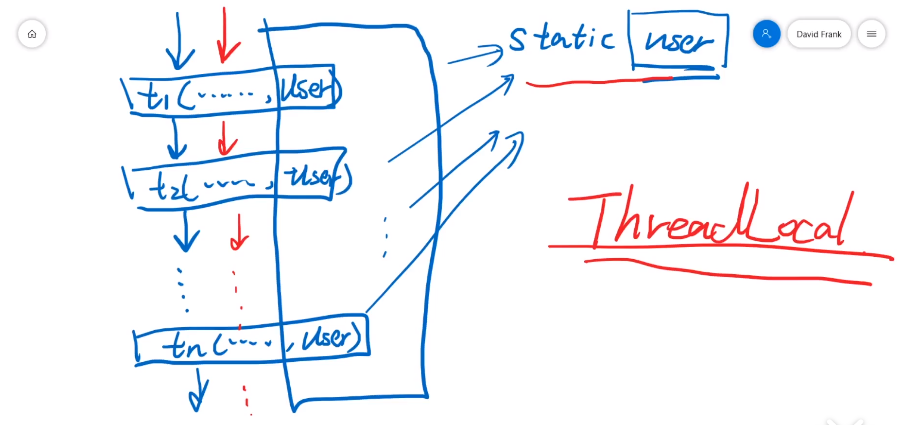
参考:
https://www.cnblogs.com/yinbiao/p/10728909.html
https://www.jianshu.com/p/3c5d7f09dfbd
https://www.jianshu.com/p/1a5d288bdaee
https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1SJ41157oF?from=search&seid=1014931581670395880


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号