PTA题目集4、5以及期中考试的总结性Blog
(1)前言:总结之前所涉及到的知识点、题量、难度等情况
每次打作业的题量不大,对于所学学的知识点运用很紧密。难度大且实现过程比较繁琐。
知识点:字符串处理:需要对输入的字符串进行切割、拼接等操作,比如使用String类的substring()方法或split()方法。;集合类:可以使用ArrayList或HashMap等集合类来存储菜品信息、点餐记录信息等,并进行增删改查等操作。;类与对象:可以定义各种类来描述菜品信息、点餐记录信息等。其中,点餐记录信息可以设计为一个类,包含序号、菜名、份额、份数等属性,并提供计算价格的方法。;输入输出、异常处理:需要使用Scanner类读入输入,并根据不同情况进行异常处理和输出结果。;时间日期处理:需要对输入的日期、时间进行处理,并计算折扣。;条件控制、循环、方法调用等基本语法:需要使用if-else语句、for循环、while循环等实现流程控制,并调用各种方法实现具体的功能。此外,还需要了解Java的面向对象特性,如封装、继承、多态等。
(2)设计与分析:重点对题目的提交源码进行分析,可参考SourceMonitor的生成报表内容以及PowerDesigner的相应类图,要有相应的解释和心得(做到有图有真相),本次Blog主要分析PTA中的菜单计价系列的题目以及期中考试的三道题目
7-4题目分析
class Menu//菜单类
{
int i=0;
Dish[] dishes=new Dish[10];
public void add(String dishName,int price)
{
dishes[i] = new Dish(dishName,price);
i++;
}
public Dish searchDish(Menu menu, String dishName)
{
for (int j=i-1;j>=0;j--)//循环每一种菜
if (dishes[j].name.equals(dishName))//输入的菜是否在菜单上
return dishes[j];//返回找到的菜名
return null;//没找到返回空
}
public boolean searchPortion(int portion){
if(portion==3||portion==2||portion==1)
return false;
else return true;
}
public boolean searchfenshu(int fs){
return fs > 15;
}
}
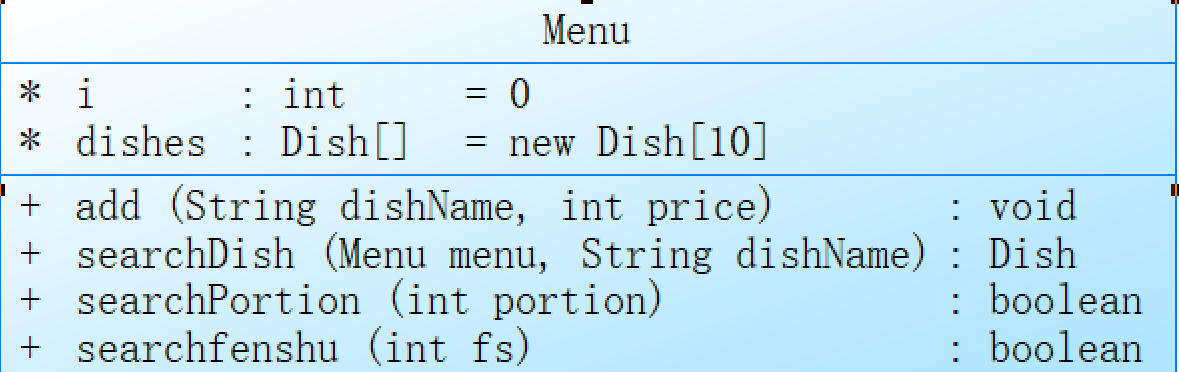
Menu类,其中包含了菜单项(Dish)的数组,以及添加菜单项、查找菜单项的方法和两个验证方法。
可以发现,在add方法中,通过创建Dish的实例并将其存储在dishes数组中,实现了添加菜单项的功能。
在searchDish方法中,通过遍历dishes数组并比较目标菜名和每个Dish对象的名称是否一致,最终返回匹配到的菜品对象,或者返回null表示未找到对应的菜品。
searchPortion和searchfenshu方法则用于验证输入的份额和数量是否合法,如果不合法则返回true,否则返回false。
class Dish//菜
{
String name;//菜名属性
int money;//菜价属性
public Dish(String name, int money) {
this.name = name;
this.money = money;
}
public int getPrice(int portion)//菜钱(actually)
{
double p=1;
switch(portion)
{
case 1:p=money*1;break;
case 2:p=money*1.5;break;
case 3:p=money*2;break;
}
return (int) Math.round(p);
}
}
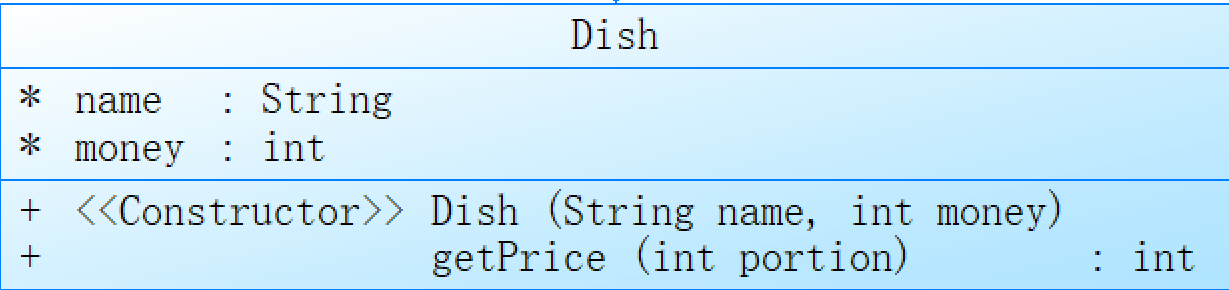
Dish类,其中包含了菜名和价格两个属性,以及获取某个份量的菜品价格的方法。
在Dish类的构造器中,通过传入菜名和价格的参数对菜品进行初始化,定义了一个全局变量name和money。
在getPrice方法中,接收一个参数portion,表示选购的菜品份数,通过switch语句根据份数进行不同的价格计算,返回计算后的菜品价格。具体计算方法为:小份为原价,中份为原价的1.5倍,大份为原价的2倍,返回值需要进行四舍五入。
需要注意的是,Dish类只是菜品信息的存储封装类,不涉及具体的菜品记录操作和菜单的构建,这与前面的Menu类的作用不同。
class DC {
int year, month, day;
int fen, miao, shi;
public boolean judge(String date, String time) {
String[] tb = date.split("/");
year = Integer.valueOf(tb[0]);
month = Integer.valueOf(tb[1]);
day = Integer.valueOf(tb[2]);
String[] k = time.split("/");
shi = Integer.valueOf(k[0]);
fen = Integer.valueOf(k[1]);
miao = Integer.valueOf(k[2]);
if(shi>24||fen>60||miao>60){
return false;
}
if (day < 1 || day > 31 || month > 12 || month < 1) {
return false;
} else {
switch (month) {
case 1: case 3: case 5: case 7: case 8: case 10: case 12:
if (day > 31) return false;break;
case 2:
if ((year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0){
if(day>29) return false;}
else if(day>28) return false;
else return true;break;
case 4:case 6: case 9: case 11:
if (day > 30) return false;break;
}
}
return true;
}
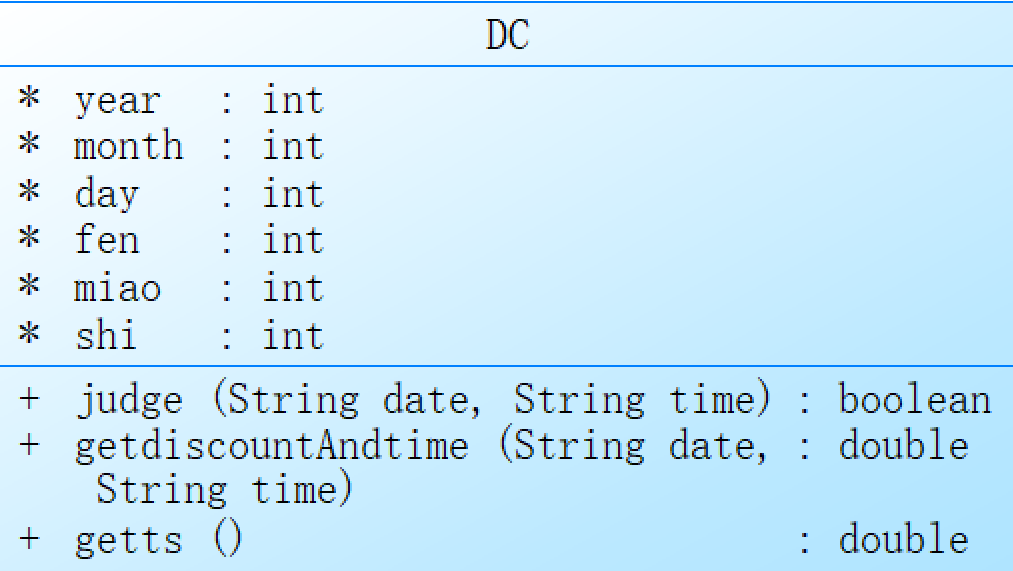
DC类,其中包含了judge方法,用于判断日期和时间格式是否合法。
在judge方法中,通过对传入的日期和时间进行字符串的拆分得到年月日时分秒的变量值,然后依次进行判断。首先对时分秒进行简单的合法性判断,如果超出范围,直接返回false。然后对日期进行判断,首先对1~31的日期范围进行判断,如果不在范围内,则返回false。在日期范围内,则需要进一步进行月份的判断。通过switch语句根据月份进行判断,对于31天的月份,如果日期超出31天,返回false;2月份需要特殊判断是否是闰年,如果日期超出29天(闰年)或28天(非闰年),返回false;对于30天的月份,如果日期超出30天,返回false。
class Table
{
double discount=0;
int totalPrice;
int realPrice;
}
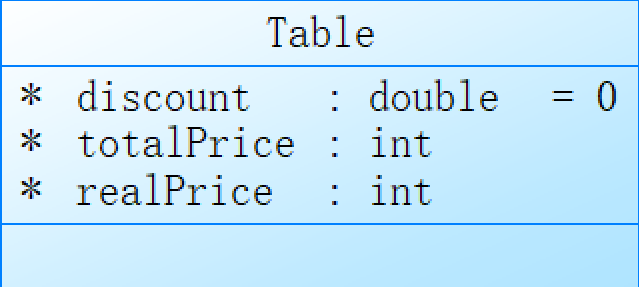
Table类,其中包含了打折折扣和菜品总价以及折扣后的实际价格两个属性。
在Table类中,discount表示打折的折扣值,可以通过设置该属性实现不同桌号的折扣优惠策略;totalPrice表示点餐总价,可以根据所有点的菜品搭配计算得到;realPrice表示经过打折折扣后的实际价格,可以根据打折折扣值和总价计算得到。
需要注意的是,该代码片段中的Table类只定义了属性而没有定义方法,因此需要在具体的业务逻辑中编写方法来对Table对象进行操作,如计算折扣后价格、设置折扣等。
7-5题目总结
本题的类图如下
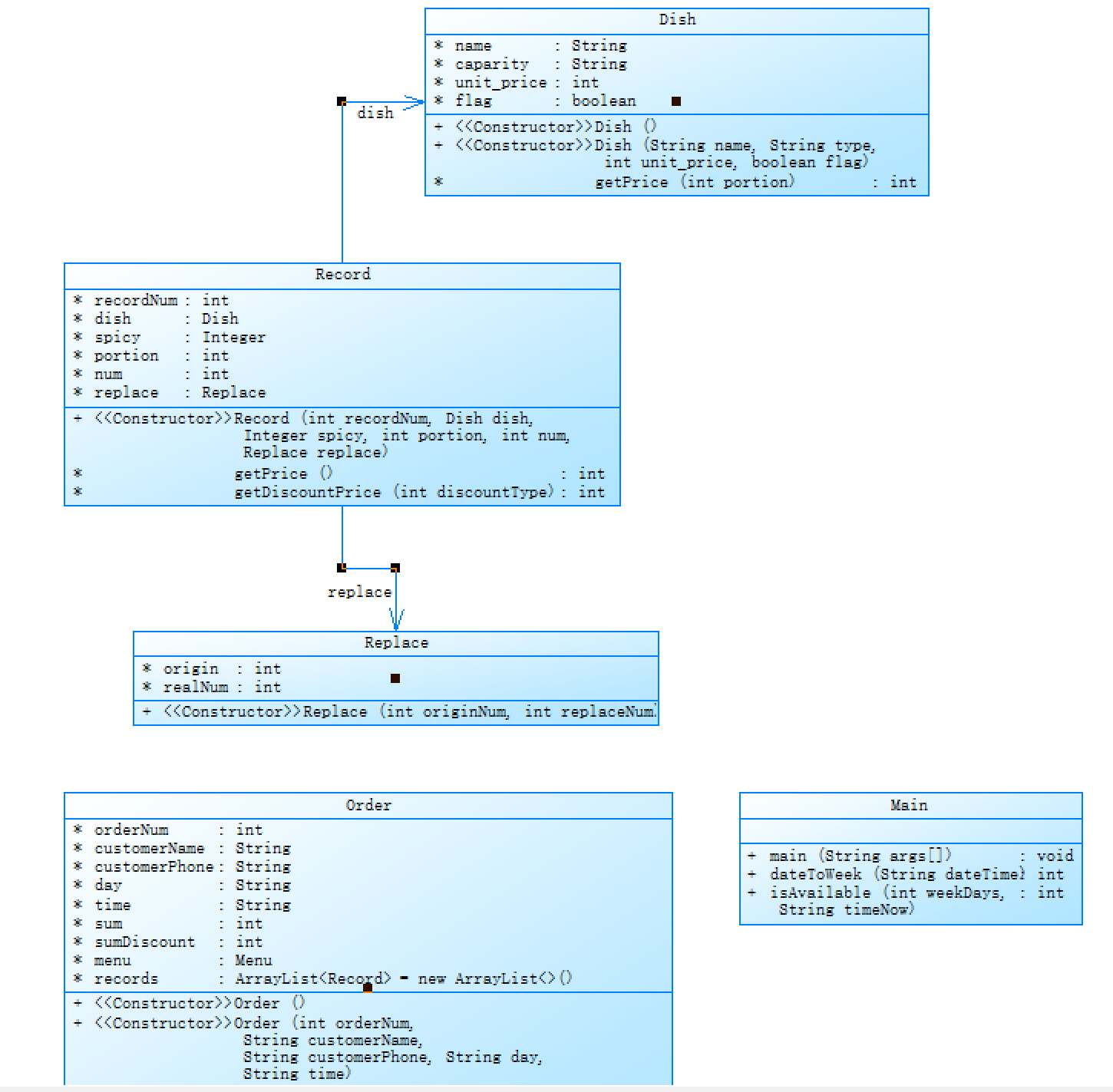
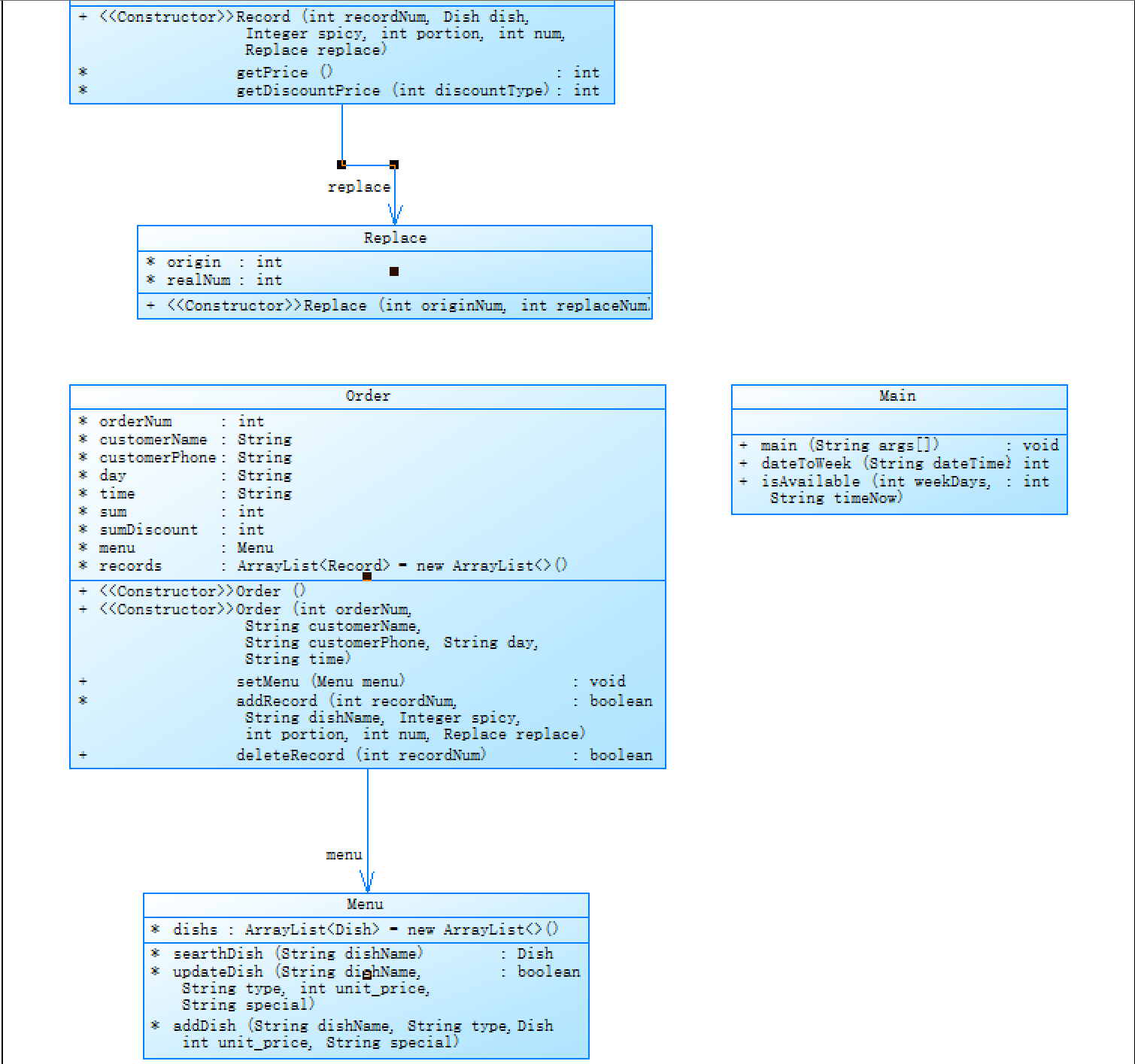
class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
Menu menu = new Menu();
Order[] orders = new Order[1000];
Record[] ss= new Record[1000];
int t = 0, r = 0, c = 0;
String temp = null;
while (true) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
String[] strs = s.split(" ");
if (strs[0].equals("table")) {
temp = s;
orders[t++] = new Order(Integer.valueOf(strs[1]), strs[3], strs[4], strs[5], strs[6]);
break;
} else {
if (strs.length == 2) {
if (menu.searthDish(strs[0]) != null) menu.updateDish(strs[0],null,Integer.valueOf(strs[1]),null);
else menu.addDish(strs[0],null,Integer.valueOf(strs[1]),null);
} else if(strs.length == 4) {
if (menu.searthDish(strs[0]) != null) menu.updateDish(strs[0],strs[1],Integer.valueOf(strs[2]),strs[3]);
else menu.addDish(strs[0],strs[1],Integer.valueOf(strs[2]),strs[3]);
} else {
System.out.println("wrong format");
}
}
}
orders[0].setMenu(menu);
String[] oneS = temp.split(" ");
String phoneN = "180、181、189、133、135、136";
if (oneS [3].length() > 10 || oneS [4].length() != 11 || !phoneN.contains(oneS [4].substring(0, 3))) {
System.out.print("wrong format");
orders[0].setMenu(null);
}
if (isAvailable(dateToWeek(oneS [5]), oneS [6]) == 0) {
System.out.println("table "+ oneS [1] +" out of opening hours");
orders[0].setMenu(null);
}
if (orders[0].menu != null) {
System.out.println("table " + oneS [1] + ": ");
}
while (true) {
String s = sc.nextLine();
String[] strs = s.split(" ");
if (s.equals("end")) {
if (t == 0) return;
else break;
} else {
if (strs[0].equals("table")) {
orders[t++] = new Order(Integer.valueOf(strs[1]), strs[3], strs[4], strs[5], strs[6]);
orders[t - 1].setMenu(menu);
if (strs[3].length() > 10 || strs[4].length() != 11 || !phoneN.contains(strs[4].substring(0, 3))) {
System.out.print("wrong format");
orders[t - 1].setMenu(null);
}
if (isAvailable(dateToWeek(strs[5]), strs[6]) == 0) {
System.out.println("table "+ strs[1] +" out of opening hours");
orders[t - 1].setMenu(null);
}
if (orders[t - 1].menu != null) {
System.out.println("table " + strs[1] + ": ");
}
r = 0;
} else {
if (orders[t - 1].menu != null) {
try {
boolean flag = false, replaceFlag = false;
if (strs.length == 5) flag = orders[t - 1].addRecord(Integer.valueOf(strs[0]), strs[1], Integer.valueOf(strs[2]), Integer.valueOf(strs[3]), Integer.valueOf(strs[4]), null);
else if (strs.length == 4) flag = orders[t - 1].addRecord(Integer.valueOf(strs[0]), strs[1], null, Integer.valueOf(strs[2]), Integer.valueOf(strs[3]), null);
else if(strs.length == 6) {
replaceFlag = true;
flag = orders[t - 1].addRecord(Integer.valueOf(strs[0]), strs[2], Integer.valueOf(strs[3]), Integer.valueOf(strs[4]), Integer.valueOf(strs[5]), new Replace(Integer.valueOf(orders[t - 1].orderNum), Integer.valueOf(strs[1])));
} else if(strs.length == 2) {
orders[t - 1].deleteRecord(Integer.valueOf(strs[0]));
continue;
} else {
System.out.print("wrong format");
}
if (flag) {
if (replaceFlag) System.out.println(strs[0] + " table " + orders[t - 1].orderNum + " pay for table " + strs[1] + " " + orders[t - 1].records.get(r++).getPrice());
else System.out.println(strs[0] + " " + strs[1] + " " +orders[t - 1].records.get(r++).getPrice());
}
} catch(Exception e) {
System.out.print("wrong format");
}
}
}
}
}
int count = 0;
while (orders[count] != null) {
if (orders[count].menu != null) {
int sum = 0;
int sumDiscount = 0;
for (Record record : orders[count].records) {
sum += record.getPrice();
sumDiscount += record.getDiscountPrice(isAvailable(dateToWeek(orders[count].day), orders[count].time));
if (record.replace != null){
ss[c++] = record;
}
}
orders[count].sum = sum;
orders[count].sumDiscount = sumDiscount;
}
count++;
}
count = 0;
TreeMap<String, Integer> map = new TreeMap<>();
while (orders[count] != null) {
if (orders[count].menu != null) {
int sumTaste1 = 0, sumTaste2 = 0, sumTaste3 = 0;
int n1 = 0, n2 = 0, n3 = 0;
int nn1 = 0, nn2 = 0, nn3 = 0;
for (Record record : orders[count].records) {
if (record.spicy != null) {
if ("川菜".equals(record.dish.caparity)) {
n1++;
nn1 += record.num;
sumTaste1 += record.spicy * record.num;
}
if ("晋菜".equals(record.dish.caparity)) {
n2++;
nn2 += record.num;
sumTaste2 += record.spicy * record.num;
}
if ("浙菜".equals(record.dish.caparity)) {
n3++;
nn3 += record.num;
sumTaste3 += record.spicy * record.num;
}
}
}
System.out.print("table " + orders[count].orderNum + ": " + orders[count].sum + " " + orders[count].sumDiscount);
for (Record record : ss) {
if (record != null) {
if (record.replace.origin - 1 == count) {
if ("川菜".equals(record.dish.caparity)) {
n1--;
nn1 -= record.num;
sumTaste1 -= record.spicy * record.num;
}
if ("晋菜".equals(record.dish.caparity)) {
n2--;
nn2 -= record.num;
sumTaste2 -= record.spicy * record.num;
}
if ("浙菜".equals(record.dish.caparity)) {
n3--;
nn3 -= record.num;
sumTaste3 -= record.spicy * record.num;
}
}
if (record.replace.realNum - 1 == count) {
if ("川菜".equals(record.dish.caparity)) {
n1++;
nn1 += record.num;
sumTaste1 += record.spicy * record.num;
}
if ("晋菜".equals(record.dish.caparity)) {
n2++;
nn2 += record.num;
sumTaste2 += record.spicy * record.num;
}
if ("浙菜".equals(record.dish.caparity)) {
n3++;
nn3 += record.num;
sumTaste3 += record.spicy * record.num;
}
}
} else {
break;
}
}
String[] spicyArr = {"不辣", "微辣", "稍辣", "辣", "很辣", "爆辣"};
String[] acidityArr = {"不酸", "微酸", "稍酸", "酸", "很酸"};
String[] sweetnessArr = {"不甜", "微甜", "稍甜", "甜"};
if (n1 != 0) System.out.print(" 川菜 " + nn1 + " " + spicyArr[(int) Math.round((double)sumTaste1 / nn1)]);
if (n2 != 0) System.out.print(" 晋菜 " + nn2 + " " + acidityArr[(int) Math.round((double)sumTaste2 / nn2)]);
if (n3 != 0) System.out.print(" 浙菜 " + nn3 + " " + sweetnessArr[(int) Math.round((double)sumTaste3 / nn3)]);
System.out.println();
if (map.containsKey(orders[count].customerName)) {
map.put(orders[count].customerName, map.get(orders[count].customerName) + orders[count].sumDiscount);
} else {
map.put(orders[count].customerName, orders[count].sumDiscount);
}
}
count++;
}
Iterator<Map.Entry<String, Integer>> it = map.entrySet().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
String e = it.next().getKey();
String phoneNum = null;
count = 0;
while (orders[count] != null) {
if (e.equals(orders[count].customerName)) {
phoneNum = orders[count].customerPhone;
break;
}
count++;
}
if (it.hasNext()) {
System.out.println(e + " " + phoneNum + " " + map.get(e));
} else {
System.out.print(e + " " + phoneNum + " " + map.get(e));
}
}
}
class Dish {
String name;//菜品名称
String caparity;
int unit_price;//单价
boolean flag;
public Dish() {
}
public Dish(String name, String type, int unit_price, boolean flag) {
this.name = name;
this.caparity = type;
this.unit_price = unit_price;
this.flag = flag;
}
//计算菜品价格的方法,输入参数是点菜的份额(输入数据只能是1/2/3,代表小/中/大份)
int getPrice(int portion) {
if (portion == 1) {
return unit_price;
} else if (portion == 2) {
return (int) Math.round(unit_price * 1.5);
} else if (portion == 3) {
return unit_price * 2;
} else {
System.out.println("portion out of range :" + portion);
return 0;
}
}
}
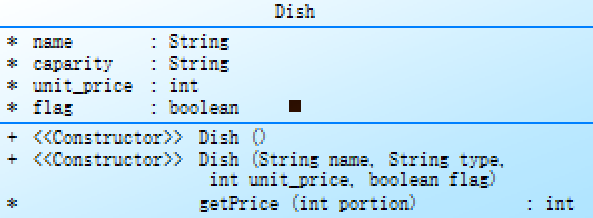
Dish类,其中包含了菜品名称、容量、单价以及是否是特色菜的属性,以及获取菜品价格的方法。
在Dish类的构造函数中,通过传入菜品名称、容量、单价以及是否是特色菜的参数对菜品进行初始化,定义了全局变量name、caparity、unit_price以及flag。
在getPrice方法中,接收一个参数portion,表示点餐的份额。通过if-else语句对小、中、大份的价格进行不同的计算,并返回计算后的菜品价格。具体计算方法为:小份为原价,中份为原价的1.5倍,大份为原价的2倍,返回值需要进行四舍五入。
class Menu {
ArrayList<Dish> dishs = new ArrayList<>();//菜品数组,保存所有菜品信息
Dish searthDish(String dishName) {
if (dishName != null) {
for (Dish dish : dishs) {
if (dishName.equals(dish.name)) {
return dish;
}
}
return null;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("Wrong format!");
}
}
boolean updateDish(String dishName, String type, int unit_price, String special) {
if (dishName != null) {
for (int i = 0; i < dishs.size(); i++) {
if (dishName.equals(dishs.get(i).name)) {
boolean flag = false;
if (type != null && special != null && special.equals("T")) {
flag = true;
}
dishs.set(i, new Dish(dishName, type, unit_price, flag));
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
//添加一道菜品信息
Dish addDish(String dishName, String type, int unit_price, String special) {
boolean flag = false;
if (type != null && special != null && special.equals("T")) {
flag = true;
}
Dish newDish = new Dish(dishName, type, unit_price, flag);
dishs.add(newDish);
return newDish;
}
}
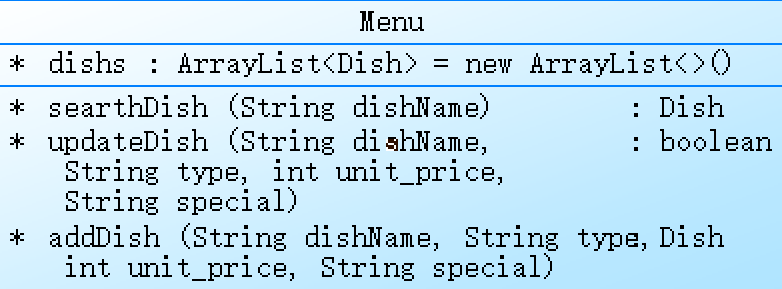
Menu类,用以管理菜单中的菜品信息,包含了查询、更新和添加菜品的方法。
在Menu类中定义了一个ArrayList类型的dishs变量用来保存菜品信息,这个变量可以用来动态添加和删除菜品信息。
searthDish方法接收一个参数dishName,用来查询菜单中是否存在指定的菜品。这个方法遍历了dishs数组,对比传入的dishName和数组元素的name属性值,如果找到了匹配的菜品则返回这个菜品对象,否则返回null。需要注意的是,如果传入的dishName是null,则会抛出异常。
updateDish方法用来更新菜品信息,它接收四个参数:dishName、type、unit_price、special。这个方法遍历了dishs数组,对比传入的dishName和数组元素的name属性值,如果找到了匹配的菜品则更新这个菜品的type、unit_price、flag属性,并返回true。如果没找到匹配的菜品,则返回false。需要注意的是,当传入的参数dishName为null时,这个方法没有任何响应。
addDish方法用来添加菜品信息,它接收四个参数:dishName、type、unit_price、special。这个方法首先通过type、special参数计算出flag属性的值,然后创建一个新的Dish对象,并将它添加到dishs数组中。最后返回这个新创建的Dish对象。
class Record {
int recordNum;//序号
Dish dish;//菜品
Integer spicy;//只有特色菜有辣度
int portion;//份额(1/2/3代表小/中/大份)
int num;//份数
Replace replace;
public Record(int recordNum, Dish dish, Integer spicy, int portion, int num, Replace replace) {
this.recordNum = recordNum;
this.dish = dish;
this.spicy = spicy;
this.portion = portion;
this.num = num;
this.replace = replace;
}
//计价,计算本条记录的价格
int getPrice() {
return dish.getPrice(portion) * num;
}
int getDiscountPrice(int discountType) {
if (dish.flag) {
if (discountType == 1 || discountType == 2) {
return (int) Math.round(dish.getPrice(portion) * num * 0.7);
} else if (discountType == 3) {
return dish.getPrice(portion) * num;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("输入的折扣类型错误!");
}
} else {
if (discountType == 1) {
return (int) Math.round(dish.getPrice(portion) * num * 0.6);
} else if (discountType == 2) {
return (int) Math.round(dish.getPrice(portion) * num * 0.8);
} else if (discountType == 3) {
return dish.getPrice(portion) * num;
} else {
throw new RuntimeException("输入的折扣类型错误!");
}
}
}
}
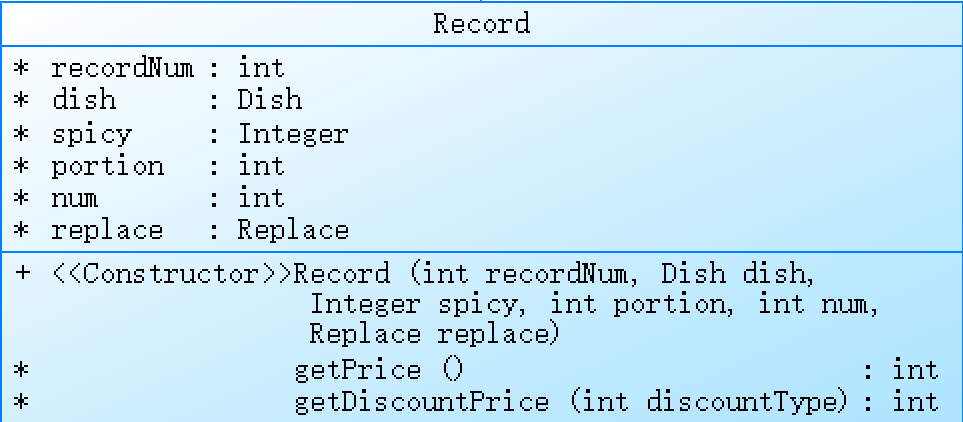
Record类,用来表示订单中的一条记录信息。
Record类包含了多个属性:recordNum表示记录的序号,dish表示所点的菜品,spicy表示辣度(对特色菜有效),portion表示份额,num表示份数,replace表示是否有替换。
getPrice方法用来计算本条记录的价格,它通过调用dish对象的getPrice方法计算菜品价格,并乘以份数得到最终价格。
getDiscountPrice方法用来计算折扣后的价格,它接收一个discountType参数,表示折扣类型。对于特色菜,如果折扣类型是1或2,则打七折,否则不打折;对于非特色菜,如果折扣类型是1,则打六折,如果是2,则打八折,否则不打折。最后根据份额和份数计算折扣后的价格,并返回结果。
class Order {
int orderNum;//序号
String customerName;//用户名
String customerPhone;//手机号码
String day;
String time;
int sum;
int sumDiscount;
Menu menu;//菜单
ArrayList<Record> records = new ArrayList<>();//保存订单上每一道的记录
public Order() {
}
public Order(int orderNum, String customerName, String customerPhone, String day, String time) {
this.orderNum = orderNum;
this.customerName = customerName;
this.customerPhone = customerPhone;
this.day = day;
this.time = time;
}
public void setMenu(Menu menu) {
this.menu = menu;
}
//添加一条菜品信息到订单中。
boolean addRecord(int recordNum, String dishName, Integer spicy, int portion, int num, Replace replace) {
if (menu != null) {
Dish dish = menu.searthDish(dishName);
if (dish != null) {
if ("川菜".equals(dish.caparity) && (spicy < 0 || spicy > 5)) {
System.out.println("spicy num out of range : " + spicy);
return false;
}
if ("晋菜".equals(dish.caparity) && (spicy < 0 || spicy > 4)) {
System.out.println("acidity num out of range : " + spicy);
return false;
}
if ("浙菜".equals(dish.caparity) && (spicy < 0 || spicy > 3)) {
System.out.println("sweetness num out of range : " + spicy);
return false;
}
records.add(new Record(recordNum, dish, spicy, portion, num, replace));
return true;
} else {
System.out.println(dishName + " does not exist");
return false;
}
} else {
return false;
}
}
public boolean deleteRecord(int recordNum) {
for (Record record : records) {
if (record.recordNum == recordNum) {
records.remove(record);
return true;
}
}
System.out.println("delete error");
return false;
}
}
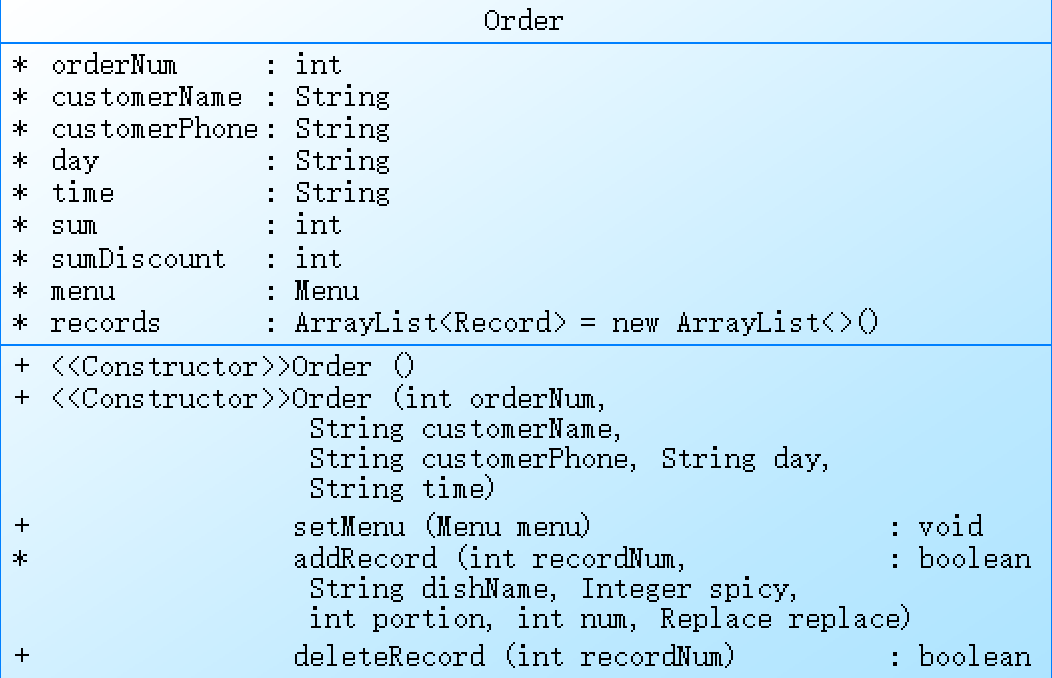
Order类,用来表示用户的订单信息。
Order类包含了多个属性:orderNum表示订单的序号,customerName表示用户名,customerPhone表示手机号码,day表示订单日期,time表示订单时间,sum表示订单总金额,sumDiscount表示折扣后的订单总金额,menu表示菜单信息,records表示订单中每一条记录的信息。
setMenu方法用来设置菜单信息。
addRecord方法用来向订单中添加一条记录,它接收多个参数:recordNum表示记录的序号,dishName表示菜品名称,spicy表示辣度(对特色菜有效),portion表示份额,num表示份数,replace表示是否有替换。该方法首先判断菜单信息是否存在,如果存在则在菜单中查找菜品,如果找到了,则判断辣度等级是否在允许的范围内,如果符合要求,则创建一条记录,并添加到订单中。
deleteRecord方法用来删除订单中的一条记录,它接收一个参数recordNum表示要删除记录的序号,方法遍历记录列表,找到对应的记录并删除。
class Replace {
int origin;//本号码
int realNum;//代点菜号码
public Replace(int originNum, int replaceNum) {
this.origin = originNum;
this.realNum = replaceNum;
}
}
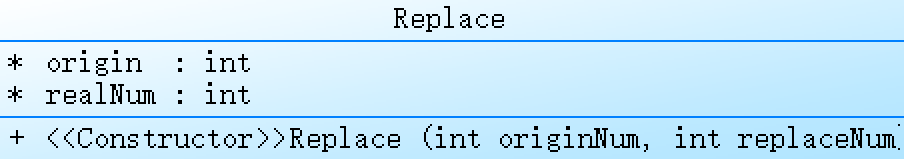
Replace的类,用来表示菜品替换信息。
Replace类包含了两个属性:origin表示原始的菜品编号,realNum表示实际点餐的菜品编号。
该类还包含一个构造方法,接收两个参数:originNum表示原始菜品的编号,replaceNum表示实际点餐的菜品编号,用来初始化该类的属性。
期中考试-1
import java.util.Scanner;
class Circle {
private double radius; // 私有属性 - 圆的半径
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
public double getArea() {
double area = Math.PI * radius * radius;
return area;
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
double radius;
try {
radius = Double.parseDouble(input.nextLine().trim());
if (radius <= 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
return;
}
Circle circle = new Circle(radius);
double area = circle.getArea();
System.out.println(String.format("%.2f", area));
}
}
类图为
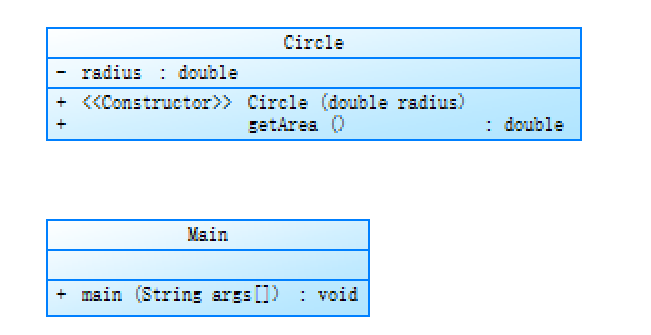
这段代码实现了输入圆的半径并输出圆的面积的功能。
该代码定义了一个Circle类,描述了一个圆的属性和方法,其中,私有属性radius表示圆的半径,构造方法Circle(double radius)用来初始化圆的半径,公有方法getArea()用来计算圆的面积。
在主方法中,首先创建了一个Scanner对象用来读取用户输入的半径,然后通过try-catch语句进行异常处理,如果用户输入不是一个合法的数值,则输出"Wrong Format"并终止程序,否则就使用用户输入的半径创建一个Circle对象,并计算这个圆的面积,最后使用String.format()方法输出面积值,保留两位小数。
期中考试-2
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
double x1 = scanner.nextDouble();
double y1 = scanner.nextDouble();
double x2 = scanner.nextDouble();
double y2 = scanner.nextDouble();
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(x1, y1, x2, y2);
System.out.printf("%.2f", rectangle.getArea());
}
}
class Rectangle {
private double x1, y1, x2, y2;
public Rectangle(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2) {
this.x1 = x1;
this.y1 = y1;
this.x2 = x2;
this.y2 = y2;
}
public double getArea() {
return Math.abs(x1 - x2) * Math.abs(y1 - y2);
}
}
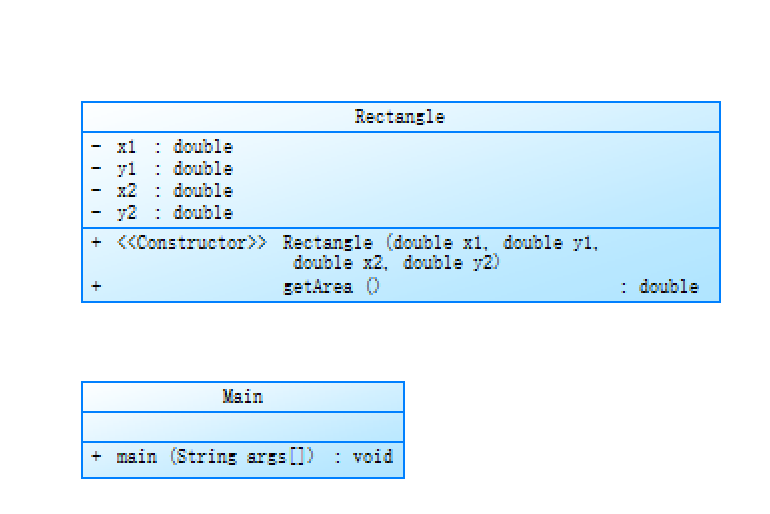
本程序的计算方式是用矩形左上角和右下角的坐标差的绝对值乘积来计算矩形的面积,但应该注意到这种方法只能适用于矩形,不能用于其他类型的四边形。
定义了一个名为Rectangle的类和一个名为Main的主类,主要功能是计算由两个坐标点确定的矩形的面积。
Rectangle类有四个私有属性:x1, y1, x2, y2,它们分别表示矩形的两个顶点的横纵坐标。构造方法Rectangle(double x1, double y1, double x2, double y2)用来初始化这四个属性,getArea()方法则用来计算矩形的面积,返回值是一个double类型的数值。
Main类定义了一个main方法,它首先创建了一个Scanner对象用来读取用户输入的四个坐标值,然后根据这四个坐标值创建了一个Rectangle对象,并调用该对象的getArea()方法计算矩形的面积,最后输出结果。
期中考试-3
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
int choice = scanner.nextInt();
switch (choice) {
case 1: // Circle
double radius = scanner.nextDouble();
Shape circle = new Circle(radius);
printArea(circle);
break;
case 2: // Rectangle
double x1 = scanner.nextDouble();
double y1 = scanner.nextDouble();
double x2 = scanner.nextDouble();
double y2 = scanner.nextDouble();
Point leftTop = new Point(x1, y1);
Point lowerRight = new Point(x2, y2);
Shape rectangle = new Rectangle(leftTop, lowerRight);
printArea(rectangle);
break;
default:
System.out.println("Wrong Input");
break;
}
}
private static void printArea(Shape shape) {
System.out.printf("%.2f", shape.getArea());
}
}
abstract class Shape {
public abstract double getArea();
}
class Circle extends Shape {
private double radius;
public Circle(double radius) {
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private Point leftTop;
private Point lowerRight;
public Rectangle(Point leftTop, Point lowerRight) {
this.leftTop = leftTop;
this.lowerRight = lowerRight;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
double width = Math.abs(lowerRight.getX() - leftTop.getX());
double height = Math.abs(lowerRight.getY() - leftTop.getY());
return width * height;
}
}
class Point {
private double x;
private double y;
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public double getX() {
return x;
}
public double getY() {
return y;
}
}
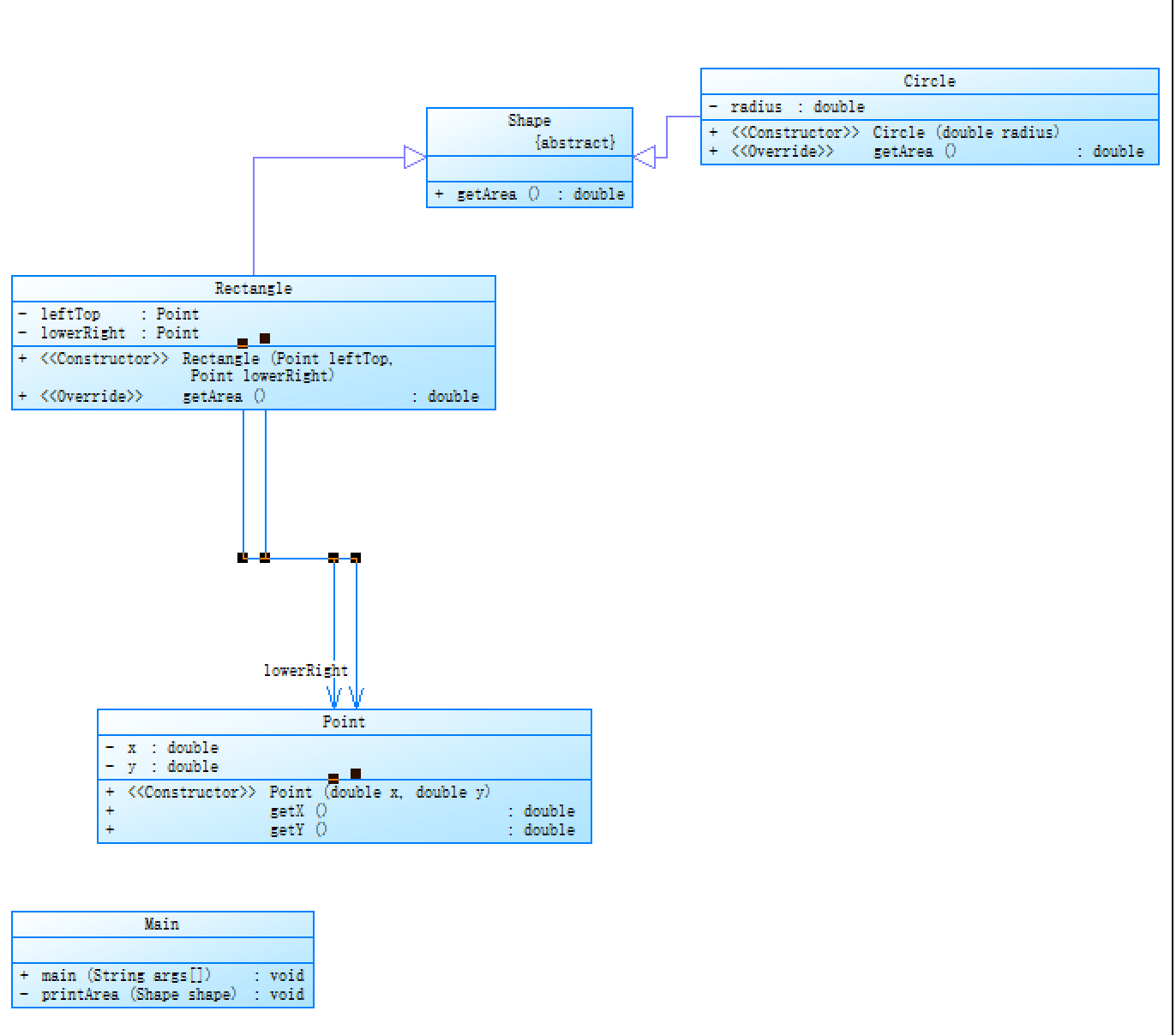
在Main类中,使用Collections.sort方法对列表进行排序,这里的sort方法默认按照Comparable接口实现的Comparable.compareTo比较方法进行排序,因此我们只需要在Shape类中实现compareTo方法即可按面积排序。排序完毕后,按顺序输出各图形的面积即可。补充完善代码中我们定义了更多的类,以便更好地表示圆形和矩形的属性。
添加了Point类,用于表示坐标点,Rectangle类同时引用了左上角和右下角的Point,用于表示矩形的两个端点。Shape类和Circle类基本保持不变,只是添加了@param注释。
Main类的执行过程则是:首先从输入中读取一个整数表示图形类型。如果是1,表示要计算圆形面积,此时读入一个半径值,并根据该半径创建Circle对象;如果是2,表示要计算矩形面积,此时需要读取两个点的坐标,创建Rectangle对象。最后调用printArea()方法打印出图形的面积。
期中考试-4
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
ArrayList<Shape> list = new ArrayList<>();
int choice = input.nextInt();
while(choice != 0) {
switch(choice) {
case 1://Circle
double radiums = input.nextDouble();
Shape circle = new Circle(radiums);
list.add(circle);
break;
case 2://Rectangle
double x1 = input.nextDouble();
double y1 = input.nextDouble();
double x2 = input.nextDouble();
double y2 = input.nextDouble();
Point leftTopPoint = new Point(x1,y1);
Point lowerRightPoint = new Point(x2,y2);
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(leftTopPoint,lowerRightPoint);
list.add(rectangle);
break;
}
choice = input.nextInt();
}
list.sort(Comparator.naturalOrder());//正向排序
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", list.get(i).getArea()) + " ");
}
}
}
interface Shape extends Comparable<Shape>{
double getArea();
String toString();
}
class Point implements Comparable<Point>{
double x;
double y;
public Point(double x, double y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int compareTo(Point o) {
if(this.y != o.y)
return this.y > o.y ? -1 : 1;//y坐标较大的点在y坐标较小点之前
else
return this.x > o.x ? 1 : -1;//x坐标较小的点放在x坐标较大的点之前。
}
}
//圆
class Circle implements Shape{
double radiums;
public Circle(double radiums) {
this.radiums = radiums;
}
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI * radiums * radiums;
}
public String toString() {
return "Circle: " + String.format("%.2f", getArea());
}
//升序排序
public int compareTo(Shape o) {
if(o instanceof Circle)
return getArea() > o.getArea() ? 1 : -1;
else
return -1;
}
}
//矩形
class Rectangle implements Shape{
Point leftTopPoint;
Point lowerRightPoint;
public Rectangle(Point leftTopPoint, Point lowerRightPoint) {
this.leftTopPoint = leftTopPoint;
this.lowerRightPoint = lowerRightPoint;
}
public double getArea() {
return Math.abs(lowerRightPoint.x - leftTopPoint.x) * Math.abs(leftTopPoint.y - lowerRightPoint.y);
}
public String toString() {
return "Rectangle: " + String.format("%.2f", getArea());
}
//升序排序
public int compareTo(Shape o) {
if(o instanceof Circle)
return 1;
else {
Rectangle rectangle = (Rectangle)o;
if(getArea() == rectangle.getArea())
return 0;
else
return getArea() > rectangle.getArea() ? 1 : -1;
}
}
}
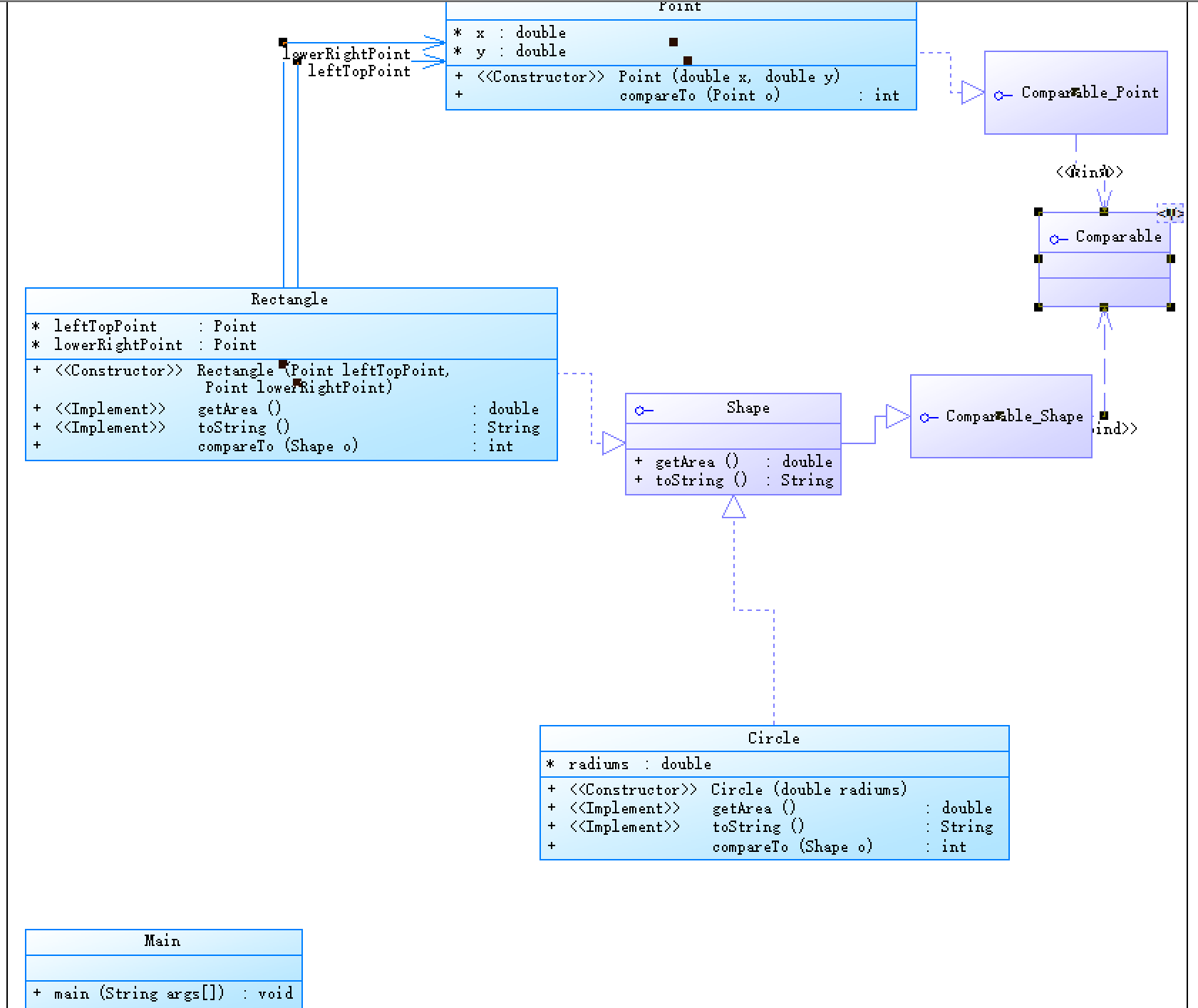
(3)采坑心得:

该错误表示非静态变量this不能在静态上下文中使用,因为它只与类的实例相关联,而静态上下文没有实例。因此,解决方法是将shapes列表和calculateTotalArea()方法声明为static:
第三题中出现了半径输入错误的问题,原因是,没有控制输入半径的范围
修改方法为:添加以下代码:
double radius = input.nextDouble();
if (radius < 0) {
System.out.println(“Error: Invalid input. Radius should be non-negative.”);
continue;
}
Shape circle = new Circle(radius);
list.add(circle);
这样就可以在用户输入不合法的值时,再次提示用户重新输入,避免程序崩溃或输出错误结果。其他输入值的部分也可类似修改。
(4)改进建议:添加更多的形状类:除了圆形和矩形,还可以添加更多的形状类,如三角形、正方形、菱形等等。这些类可以继承自“形状”类,实现相应的抽象方法和属性。优化排序算法:当前代码中使用的排序算法是冒泡排序,可以考虑使用更加高效的排序算法来进行排序。例如可以使用快速排序或归并排序等高效的算法来优化排序操作。
(5)总结:学到的有以下几点
-
面向对象的类设计和实现:本题涉及到“形状”、“圆形”和“矩形”等类的设计和实现。在类中需要定义相应的属性和方法,并通过构造函数进行初始化。
-
抽象类和抽象方法:许多类和方法都是以抽象类和抽象方法的形式定义的。抽象类和方法是一种基于继承的机制,使得子类必须实现抽象类和方法中定义的方法或属性,从而确保了代码的统一和可维护性。
-
继承和多态:本题中的“圆形”、“矩形”等类都是从“形状”类中继承而来的,从而使得这些类可以使用“形状”类中定义好的一些方法和属性。同时,这些类也可以进行类型转换和多态的应用,使得程序更加灵活和可扩展。
-
接口的定义和实现:本题中定义了一个“可比较的”接口,即Comparable接口。这个接口的实现使得“形状”类可以进行比较和排序操作,从而使得形状列表的排序操作得以简化和优化。
-
集合类的使用:本题涉及到了Java中的ArrayList集合类的使用。这个集合类是一种动态数组,可以自动进行扩容和缩容,非常方便和实用。同时,在List集合类中也提供了sort方法,使得对列表中的元素进行排序操作更加便捷和高效。



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号