Java String学习
0、String构造器
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
String() |
Initializes a newly created String object so that it represents an empty character sequence. |
String(byte[] bytes) |
Constructs a new String by decoding the specified array of bytes using the platform's default charset. |
String(byte[] ascii, int hibyte) |
Deprecated. This method does not properly convert bytes into characters. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the String constructors that take a |
String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length) |
Constructs a new String by decoding the specified subarray of bytes using the platform's default charset. |
String(byte[] ascii, int hibyte, int offset, int count) |
Deprecated. This method does not properly convert bytes into characters. As of JDK 1.1, the preferred way to do this is via the String constructors that take a |
String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length, String charsetName) |
Constructs a new String by decoding the specified subarray of bytes using the specified charset. |
String(byte[] bytes, int offset, int length, Charset charset) |
Constructs a new String by decoding the specified subarray of bytes using the specified |
String(byte[] bytes, String charsetName) |
Constructs a new String by decoding the specified array of bytes using the specified |
String(byte[] bytes, Charset charset) |
Constructs a new String by decoding the specified array of bytes using the specified |
String(char[] value) |
Allocates a new String so that it represents the sequence of characters currently contained in the character array argument. |
String(char[] value, int offset, int count) |
Allocates a new String that contains characters from a subarray of the character array argument. |
String(int[] codePoints, int offset, int count) |
Allocates a new String that contains characters from a subarray of the |
String(String original) |
Initializes a newly created String object so that it represents the same sequence of characters as the argument; in other words, the newly created string is a copy of the argument string. |
String(StringBuffer buffer) |
Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters currently contained in the string buffer argument. |
String(StringBuilder builder) |
Allocates a new string that contains the sequence of characters currently contained in the string builder argument. |
1、String的一个特性
String 类是不可改变的,所以你一旦创建了 String 对象,那它的值就无法改变了!
简单理解(想要深入理解涉及到JVM,以后再深入学习):
首先,String对象的创建有两种方式,使用String关键字以及使用构造函数。无论哪种构造方式,String对象一旦被创立是无法改变的。
两种创建的不同点:String 创建的字符串存储在公共池中,而 new 创建的字符串对象在堆上
String s1 = "Runoob"; // String 直接创建
String s2 = "Runoob"; // String 直接创建
String s3 = s1; // 相同引用
String s4 = new String("Runoob"); // String 对象创建
String s5 = new String("Runoob"); // String 对象创建
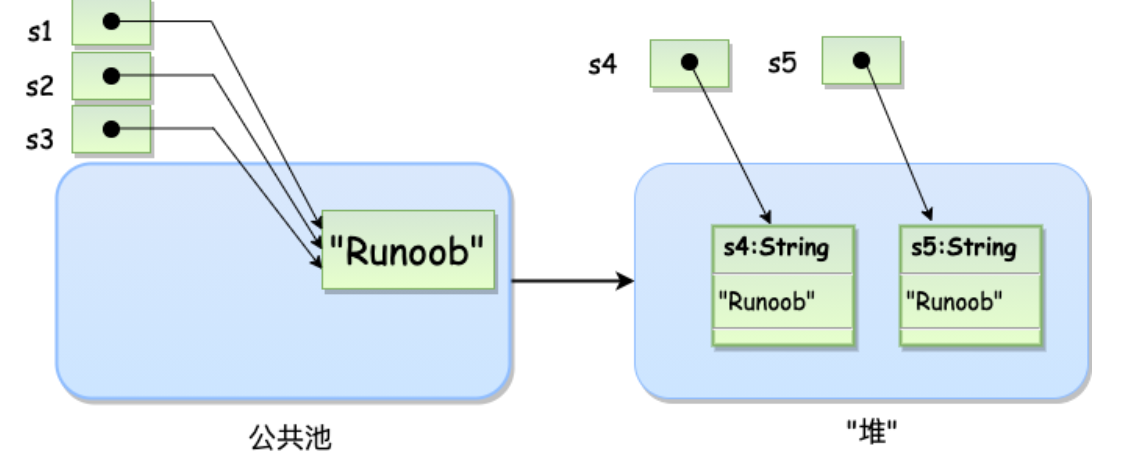
注:公共池即字符串常量池,有这个东西的目的是为了节省空间,不然由于String的不可变性,s1,s2,s3将会指向三块内存。堆没有这个特性
为什么要把String设计成不可变呢?因为Java对象参数传的是引用(c函数传参一般是传的值,这也是Java和c的一个不同点?),这样在不经意间值就被改变了,为了安全,把Sting设计成不可变(可以理解为值传递,值传递就相当于传进去一个分身。)。
String不可变性和StringBuilder可变性的体现
1 // 方法类 2 public class StringLearning { 3 /** 4 * 测试String类型的不可变性 5 * @param s 6 * @return 7 */ 8 public static String appendStr(String s){ 9 s += "bbb"; 10 return s; 11 } 12 13 /** 14 * 测试StringBuilder的可变性 15 * @param sb 16 * @return 17 */ 18 public static StringBuilder appendSb(StringBuilder sb){ 19 return sb.append("bbb"); 20 } 21 } 22 23 // 测试类 24 public class StringTest { 25 @Test 26 public void stringTest(){ 27 String s = new String("aaa"); 28 String appendStr = StringLearning.appendStr(s); 29 System.out.println("s = " + s); 30 31 StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("aaa"); 32 StringBuilder appendSb = StringLearning.appendSb(sb); 33 System.out.println("sb = " + sb); 34 } 35 }
结果:
s = aaa
sb = aaabbb
代码理解:String类型的s和StringBuilder类型的sb分别传入字符串增加方法,结果发现s没有变,sb变了,由此可体现String的不可变性(安全性)。
扩展:关于Java的参数传递
-
传递值的数据类型:八种基本数据类型和String(这样理解可以,但是事实上String也是传递的地址,只是string对象和其他对象是不同的,string对象是不能被改变的,内容改变就会产生新对象。那么StringBuffer就可以了,但只是改变其内容。不能改变外部变量所指向的内存地址)。
-
传递地址值的数据类型:除String以外的所有复合数据类型,包括数组、类和接口
2、可变的StringBuilder/StringBuffer
二者的关系
StringBuilder 类在 Java 5 中被提出,它和 StringBuffer 之间的最大不同在于 StringBuilder 的方法不是线程安全的(不能同步访问)。
由于 StringBuilder 相较于 StringBuffer 有速度优势,所以多数情况下建议使用 StringBuilder 类。
然而在应用程序要求线程安全的情况下,则必须使用 StringBuffer 类。
构造器
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
StringBuilder() |
Constructs a string builder with no characters in it and an initial capacity of 16 characters. |
StringBuilder(int capacity) |
Constructs a string builder with no characters in it and an initial capacity specified by the capacity argument. |
StringBuilder(CharSequence seq) |
Constructs a string builder that contains the same characters as the specified CharSequence. |
StringBuilder(String str) |
Constructs a string builder initialized to the contents of the specified string. |
常见方法:
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
StringBuilder |
append(String str) |
Appends the specified string to this character sequence. |
char |
charAt(int index) |
Returns the char value in this sequence at the specified index. |
StringBuilder |
delete(int start, int end) |
Removes the characters in a substring of this sequence. |
StringBuilder |
reverse() |
Causes this character sequence to be replaced by the reverse of the sequence. |
String |
substring(int start, int end) |
Returns a new String that contains a subsequence of characters currently contained in this sequence. |
String |
toString() |
Returns a string representing the data in this sequence. |
void |
trimToSize() |
Attempts to reduce storage used for the character sequence. |
StringBuffer类似:
public void AnyTest() {
StringBuffer sBuffer = new StringBuffer();
// 链式调用
sBuffer.append("hello").append(" world").append("!");
system.out.println(sBuffer);
}
// 输出
hello world!以下是 StringBuffer 类支持的主要方法:
| 序号 | 方法描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | public StringBuffer append(String s) 将指定的字符串追加到此字符序列。 |
| 2 | public StringBuffer reverse() 将此字符序列用其反转形式取代。 |
| 3 | public delete(int start, int end) 移除此序列的子字符串中的字符。 |
| 4 | public insert(int offset, int i) 将 int 参数的字符串表示形式插入此序列中。 |
| 5 | replace(int start, int end, String str) 使用给定 String 中的字符替换此序列的子字符串中的字符。 |
3、String的常见方法
1 public class StringMethod { 2 @Test 3 public void stringMethodTest(){ 4 String str = "hello world !"; 5 // 1、charAt() 方法用于返回指定索引处的字符。索引范围为从 0 到 length() - 1。 6 char c = str.charAt(4);// c = o 7 // 2、compareTo() 方法用于两种方式的比较: 8 /* 9 int compareTo(Object o)或int compareTo(String anotherString) 10 返回值:如果参数字符串等于此字符串,则返回值 0; 11 如果此字符串小于字符串参数,则返回一个小于 0 的值(长度差值); 12 如果此字符串大于字符串参数,则返回一个大于 0 的值。 13 */ 14 String str1 = "Strings"; 15 String str2 = "Strings"; 16 String str3 = "Strings123"; 17 18 int result = str1.compareTo( str2 ); 19 20 result = str2.compareTo( str3 ); 21 22 result = str3.compareTo( str1 ); 23 /* 24 运行结果:0 25 -3 26 3 27 */ 28 // 3、compareToIgnoreCase() 方法用于按字典顺序比较两个字符串,不考虑大小写。 29 result = str1.compareToIgnoreCase( str2 );// 0 30 31 // 4、concat() 方法用于将指定的字符串参数连接到字符串上。 32 String s = str1.concat(str2); //s = StringsStrings 33 // 5、contentEquals() 方法用于将此字符串与指定的 StringBuffer 比较。 34 String str4 = "String"; 35 String str5 = "String1"; 36 StringBuffer stringBuffer = new StringBuffer("String"); 37 boolean b = str4.contentEquals(stringBuffer);//true 38 boolean b1 = str5.contentEquals(stringBuffer);//false 39 // 6、copyValueOf() 40 /* 41 public static String (char[] data): 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的字符串。 42 43 public static String copyValueOf(char[] data, int offset, int count): 44 返回指定数组中表示该字符序列的 字符串。 45 offset -- 子数组的初始偏移量 count -- 子数组的长度。 46 */ 47 char[] Str6 = {'h', 'e', 'l', 'l', 'o', ' ', 'r', 'u', 'n', 'o', 'o', 'b'}; 48 String Str7 = ""; 49 50 Str7 = String.copyValueOf( Str6 );//返回结果:hello runoob 51 52 Str7 = String.copyValueOf( Str6, 2, 6 );//返回结果:llo ru 53 // 7、endsWith() 方法用于测试字符串是否以指定的后缀结束。 54 String str8 = "hello world"; 55 boolean ends1 = str8.endsWith("hello");// false 56 boolean ends2 = str8.endsWith("world");// true 57 // 8、equals() 方法用于将字符串与指定的对象比较。(重写了Object方法,比较的是内容) 58 str4.equals(str5);// false 59 str4.equals("String");// true 60 // 9、equalsIgnoreCase() 方法用于将字符串与指定的对象比较,不考虑大小写。用法同8(略) 61 // 10、getBytes(); 62 /* 63 * getBytes(String charsetName): 使用指定的字符集将字符串编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。 64 getBytes(): 使用平台的默认字符集将字符串编码为 byte 序列,并将结果存储到一个新的 byte 数组中。*/ 65 String str9 = "hello"; 66 try{ 67 byte[] bytes1 = str9.getBytes();// 直接输出是一个对象[B@7852e922 68 // for循环输出就是ASCII 69 // 想要输出字符new String(bytes1); 70 byte[] bytes2 = str9.getBytes("UTF-8"); 71 72 byte[] bytes3 = str9.getBytes("ISO-8859-1"); 73 74 } catch (UnsupportedEncodingException e){ 75 System.out.println("找不到字符集"); 76 } 77 // 11、getChars() 方法将字符从字符串复制到目标字符数组。 78 /* 79 public void getChars(int srcBegin, int srcEnd, char[] dst, int dstBegin) 80 81 srcBegin -- 字符串中要复制的第一个字符的索引。 82 83 srcEnd -- 字符串中要复制的最后一个字符之后的索引。 84 85 dst -- 目标数组。 86 87 dstBegin -- 目标数组中的起始偏移量。 88 */ 89 String str10 = "hello java!"; 90 char[] chars = new char[4]; 91 str10.getChars(6,10,chars,0);// java 92 // 12、hashCode() 方法用于返回字符串的哈希码。 93 int hashCode = str10.hashCode();// 1781686641 94 95 // 13、indexOf() 96 /* 97 public int indexOf(int ch): 返回指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。 98 99 public int indexOf(int ch, int fromIndex): 返回从 fromIndex 位置开始查找指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。 100 101 int indexOf(String str): 返回指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。 102 103 int indexOf(String str, int fromIndex): 返回从 fromIndex 位置开始查找指定字符在字符串中第一次出现处的索引,如果此字符串中没有这样的字符,则返回 -1。 104 */ 105 String str11 = "abc123abc"; 106 int indexOf1 = str11.indexOf('c'); // 2 107 int indexOf2 = str11.indexOf('c',3); // 8 108 // 14、intern() 方法返回字符串对象的规范化表示形式。(涉及到jvm字符串常量池和堆) 109 /* 110 尽管在输出中调用intern方法并没有什么效果,但是实际上后台这个方法会做一系列的动作和操作。 111 在调用”ab”.intern()方法的时候会返回”ab”,但是这个方法会首先检查字符串池中是否有”ab”这个字符串, 112 如果存在则返回这个字符串的引用,否则就将这个字符串添加到字符串池中,然会返回这个字符串的引用。 113 */ 114 String str12 = "a"; 115 String str13 = "b"; 116 String str14 = "ab"; 117 String str15 = str12 + str13; 118 String str16 = "a" + "b"; 119 String str17 = new String("ab"); 120 121 System.out.println(str17.equals(str14));// true 比较的是内容,没什么好说的 122 System.out.println(str17 == str14);// false 比较的是地址,一个是堆一个是字符串常量池 123 System.out.println(str17.intern() == str14);// true intern()之后,返回的是常量池的引用 124 System.out.println(str17.intern() == str15);// false 只要有一个参数未知,地址都是在堆中 125 System.out.println(str17.intern() == str16);// true 两个都已知,引用在常量池中 126 // 15、lastIndexOf()返回指定字符在此字符串中最后一次出现处的索引。同indexOf() (略) 127 // 16、length() 方法用于返回字符串的长度。 128 int length = str.length(); // 13 129 // 17、matches() 方法用于检测字符串是否匹配给定的正则表达式。 130 String str18 = "www.runoob.com"; 131 str18.matches("(.*)runoob(.*)"); // true 132 str18.matches("(.*)google(.*)"); // false 133 // 18、regionMatches() 方法用于检测两个字符串在一个区域内是否相等。 134 /* 135 public boolean regionMatches(boolean ignoreCase(可省略), 136 int toffset, 137 String other, 138 int ooffset, 139 int len) 140 ignoreCase -- 如果为 true,则比较字符时忽略大小写。 141 142 toffset -- 此字符串中子区域的起始偏移量。 143 144 other -- 字符串参数。 145 146 ooffset -- 字符串参数中子区域的起始偏移量。 147 148 len -- 要比较的字符数。 149 */ 150 String str19 = "runoob"; 151 String str20 = "RUNOOB"; 152 str18.regionMatches(4, str19, 0, 6);// true 153 str18.regionMatches(4, str20, 0, 6);// false 154 str18.regionMatches(true,4, str20, 0, 6);// true 155 // 19、replace() 方法通过用 newChar 字符替换字符串中出现的所有 oldChar 字符,并返回替换后的新字符串。 156 String str21 = "happy new year"; 157 String replace = str21.replace('e', 'x');// happy nxw yxar 158 // 20、replaceAll() 方法使用给定的参数 replacement 替换字符串所有匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。(略) 159 // replaceFirst() 方法使用给定的参数 replacement 替换字符串第一个匹配给定的正则表达式的子字符串。(略) 160 // 21、split() 方法根据匹配给定的正则表达式(就是分隔符)来拆分字符串。 161 /* 162 注意: . 、 $、 | 和 * 等转义字符,必须得加 \\。 163 注意:多个分隔符,可以用 | 作为连字符。 164 public String[] split(String regex, int limit) 165 regex -- 正则表达式分隔符。 166 limit -- 分割的份数。 167 */ 168 String str22 = "www.micro-soft.com"; 169 String[] split1 = str22.split("\\.", 3);// 注意加双反斜杠!! 170 // 结果:www 171 // microsoft 172 // com 173 String[] split2 = str22.split("-|\\.", 3);// 多个分隔符 174 /* 175 结果: 176 www 177 micro 178 soft.com 179 */ 180 // 22、startsWith() 方法用于检测字符串是否以指定的前缀开始。 181 /* 182 public boolean startsWith(String prefix, int toffset) 183 prefix -- 前缀。 184 toffset -- 字符串中开始查找的位置。 185 */ 186 boolean micro = str22.startsWith("micro", 4);// true 187 // 23、subSequence() 方法返回一个新的字符序列,它是此序列的一个子序列。 188 /* 189 public CharSequence subSequence(int beginIndex(起始索引), int endIndex(结束索引)) 190 */ 191 CharSequence charSequence = str22.subSequence(4, 14); // micro-soft 192 // 24、substring() 方法返回字符串的子字符串。 193 String substring = str22.substring(4, 14);// micro-soft 194 // 25、toCharArray() 方法将字符串转换为字符数组。 195 char[] chars1 = str22.toCharArray(); // www.micro-soft.com 196 // 26、toLowerCase() 方法将字符串转换为小写。 197 // toUpperCase() 方法将字符串小写字符转换为大写。 198 // toString() 方法返回此对象本身(它已经是一个字符串)。 199 // 27、trim() 方法用于删除字符串的头尾空白符。 200 String str23 = " z y y "; 201 String trim = str23.trim();// z y y(中间的空白不动) 202 // 28、valueOf() 方法 返回 Object 参数的字符串表示形式。(是一个static方法) 203 char[] chars2 = {'z','y','y',}; 204 String s1 = String.valueOf(chars2); // zyy 205 // 29、contains() 方法用于判断字符串中是否包含指定的字符或字符串。 206 boolean z = s1.contains("z");// true 207 boolean x = s1.contains("x");// false 208 // 30、isEmpty() 方法用于判断字符串是否为空。 209 // 字符串通过 length() 方法计算字符串长度,如果返回 0,即为空字符串。 210 boolean empty = str23.isEmpty();// false 211 } 212 }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号