Java的常见类学习
一、Scanner
1、使用next()方法:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// 从键盘接收数据
// next方式接收字符串
System.out.println("next方式接收:");
// 判断是否还有输入
if (scan.hasNext()) {
String str1 = scan.next();
System.out.println("输入的数据为:" + str1);
}
scan.close();
}
}
next方式接收:
runoob com
输入的数据为:runoob
2、使用nextLine()方法:
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ScannerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);
// 从键盘接收数据
// nextLine方式接收字符串
System.out.println("nextLine方式接收:");
// 判断是否还有输入
if (scan.hasNextLine()) {
String str2 = scan.nextLine();
System.out.println("输入的数据为:" + str2);
}
scan.close();
}
}
输出结果:
nextLine方式接收:
runoob com
输入的数据为:runoob com
next() 与 nextLine() 区别
next():
-
1、一定要读取到有效字符后才可以结束输入。
-
2、对输入有效字符之前遇到的空白,next() 方法会自动将其去掉。
-
3、只有输入有效字符后才将其后面输入的空白作为分隔符或者结束符。
-
next() 不能得到带有空格的字符串。
nextLine():
-
1、以Enter为结束符,也就是说 nextLine()方法返回的是输入回车之前的所有字符。
-
2、可以获得空白。
3、其他输出:
同理有nextLong()、nextDouble()、nextInt()等方法
其中:nextInt()和nextInt(int Radix)方法的区别:
ava的Scanner类中的nextInt()默认读入的是十进制,nextInt(int radix)中的radix指定的是读入数字的进制。 例如nextInt(8)表示读入的数据是8进制,如果你输入9就会报错。nextInt(16)就表示读入的数据是16进制,你输入a得到的就是10
二、Number&&Math
1、Number类
一般地,当需要使用数字的时候,我们通常使用内置数据类型,如:byte、int、long、double 等。然而,在实际开发过程中,我们经常会遇到需要使用对象,而不是内置数据类型的情形。为了解决这个问题,Java 语言为每一个内置数据类型提供了对应的包装类。所有的包装类(Integer、Long、Byte、Double、Float、Short)都是抽象类 Number 的子类。
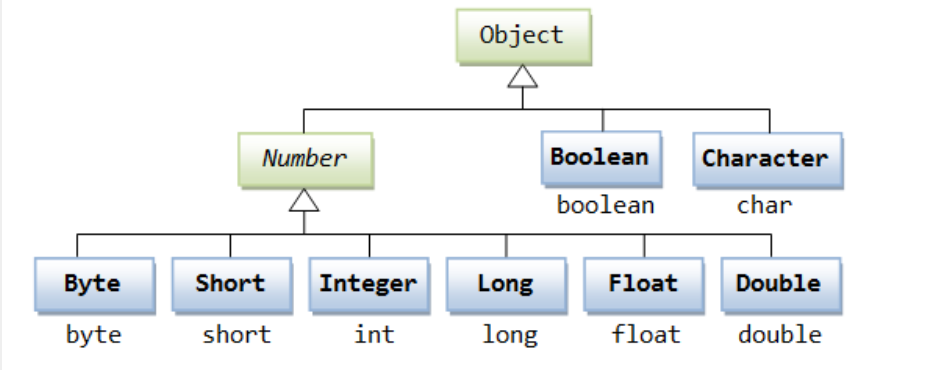
一个装箱和拆箱的例子
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Integer x = 5;
x = x + 10;
System.out.println(x);
}
}
输出结果:15
理解:
装箱即装成一个对象,对象就可以点方法了,而普通的x是没有办法点方法的!当需要运算时,就自动拆箱。
当 x 被赋为整型值时,由于x是一个对象,所以编译器要对x进行装箱。然后,为了使x能进行加运算,所以要对x进行拆箱。
2、Math类
public class Test {
public static void main (String []args)
{
System.out.println("90 度的正弦值:" + Math.sin(Math.PI/2));
System.out.println("0度的余弦值:" + Math.cos(0));
System.out.println("60度的正切值:" + Math.tan(Math.PI/3));
System.out.println("1的反正切值: " + Math.atan(1));
System.out.println("π/2的角度值:" + Math.toDegrees(Math.PI/2));
System.out.println(Math.PI);
}
}
输出结果:
90 度的正弦值:1.0
0度的余弦值:1.0
60度的正切值:1.7320508075688767
1的反正切值: 0.7853981633974483
π/2的角度值:90.0
3.141592653589793
启示:
Math 的方法都被定义为 static 形式,通过 Math 类可以在主函数中直接调用。
所以,在开发中如果定义一个工具类,那个方法可以设置为public static,这样就可以直接类调用,不用再new一个实例了!
3、Number&Math的常见方法
| 序号 | 方法与描述 |
|---|---|
| 1 | |
| 2 | |
| 3 | |
| 4 | |
| 5 | |
| 6 | |
| 7 | |
| 8 | |
| 9 | |
| 10 | |
| 11 | |
| 12 | |
| 13 | |
| 14 | |
| 15 | |
| 16 | |
| 17 | |
| 18 | |
| 19 | |
| 20 | |
| 21 | |
| 22 | |
| 23 | |
| 24 | |
| 25 | |
| 26 | |
| 27 |
三、Random
public class Random
extends Object
implements Serializable
Direct Known Subclasses:
// 两个子类
SecureRandom`, `ThreadLocalRandom
构造函数
Random() | Creates a new random number generator. |
|---|---|
Random(long seed) |
Creates a new random number generator using a single long seed. |
seed种子,涉及到随机数生成算法,如果不给种子默认为时间戳。
常见方法
double | nextDouble() | Returns the next pseudorandom, uniformly distributed double value between 0.0 and 1.0 from this random number generator's sequence. |
|---|---|---|
float |
nextFloat() |
Returns the next pseudorandom, uniformly distributed float value between 0.0 and 1.0 from this random number generator's sequence. |
double |
nextGaussian() |
Returns the next pseudorandom, Gaussian ("normally") distributed double value with mean 0.0 and standard deviation 1.0 from this random number generator's sequence. |
int |
nextInt() |
Returns the next pseudorandom, uniformly distributed int value from this random number generator's sequence. |
int |
nextInt(int bound) |
Returns a pseudorandom, uniformly distributed int value between 0 (inclusive) and the specified value (exclusive), drawn from this random number generator's sequence. |
long |
nextLong() |
Returns the next pseudorandom, uniformly distributed long value from this random number generator's sequence. |
注意:
在Random类中int随机数可以设置边界bound,而double和flood等没有限制,默认为0.0到1.0,如果要设置边界可以使用Random的子类ThreadLocalRandom类。
启示:要学会看JavaAPI文档(即jdk文档)
四、ThreadLocalRandom
用法:
// 因为涉及到多线程,直接使用类点current()当前时间戳再点方法
double aDouble = ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextDouble(1.5, 2.5);
System.out.println("aDouble = " + aDouble);
其他方法:
double | nextDouble() | Returns a pseudorandom double value between zero (inclusive) and one (exclusive). |
|---|---|---|
double |
nextDouble(double bound) |
Returns a pseudorandom double value between 0.0 (inclusive) and the specified bound (exclusive). |
double |
nextDouble(double origin, double bound) |
Returns a pseudorandom double value between the specified origin (inclusive) and bound (exclusive). |
float |
nextFloat() |
Returns a pseudorandom float value between zero (inclusive) and one (exclusive). |
double |
nextGaussian() |
Returns the next pseudorandom, Gaussian ("normally") distributed double value with mean 0.0 and standard deviation 1.0 from this random number generator's sequence. |
int |
nextInt() |
Returns a pseudorandom int value. |
int |
nextInt(int bound) |
Returns a pseudorandom int value between zero (inclusive) and the specified bound (exclusive). |
int |
nextInt(int origin, int bound) |
Returns a pseudorandom int value between the specified origin (inclusive) and the specified bound (exclusive). |
long |
nextLong() |
Returns a pseudorandom long value. |
long |
nextLong(long bound) |
Returns a pseudorandom long value between zero (inclusive) and the specified bound (exclusive). |
long |
nextLong(long origin, long bound) |
Returns a pseudorandom long value between the specified origin (inclusive) and the specified bound (exclusive). |
五、Date
构造器
其他的都过时了
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
Date() |
Allocates a Date object and initializes it so that it represents the time at which it was allocated, measured to the nearest millisecond. |
Date(long date) |
Allocates a Date object and initializes it to represent the specified number of milliseconds since the standard base time known as "the epoch", namely January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 GMT. |
例子
System.out.println(new Date()); // 注意时间戳的单位是秒,Date接受的单位是毫秒,所以乘以1000 System.out.println(new Date(1611672503L * 1000));
输出:
Tue Jan 26 22:48:53 GMT+08:00 2021 Tue Jan 26 22:48:23 GMT+08:00 2021
一些方法
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
boolean |
after(Date when) |
Tests if this date is after the specified date. |
boolean |
before(Date when) |
Tests if this date is before the specified date. |
Object |
clone() |
Return a copy of this object. |
int |
compareTo(Date anotherDate) |
Compares two Dates for ordering. |
boolean |
equals(Object obj) |
Compares two dates for equality. |
static Date |
from(Instant instant) |
Obtains an instance of Date from an Instant object. |
long |
getTime() |
Returns the number of milliseconds since January 1, 1970, 00:00:00 GMT represented by this Date object. |
void |
setTime(long time) |
Sets this Date object to represent a point in time that is time milliseconds after January 1, 1970 00:00:00 GMT. |
int |
hashCode() |
Returns a hash code value for this object. |
使用:
// 返回时间戳 1611672851170 System.out.println(new Date().getTime()); // 1060289198 System.out.println(new Date().hashCode());
注意:Date类很多东西都淘汰了,所以项目开发中经常使用其他类代替
六、SimpleDateFormat
结构
-
java.lang.Object 最大的类
-
-
java.text.Format 格式化的总类
-
-
java.text.DateFormat 日期格式化的类,是抽象的,所以一般使用其子类
-
-
java.text.SimpleDateFormat 用于日期格式转换
-
-
-
构造器
| Constructor | Description |
|---|---|
SimpleDateFormat() |
Constructs a SimpleDateFormat using the default pattern and date format symbols for the default |
SimpleDateFormat(String pattern) |
Constructs a SimpleDateFormat using the given pattern and the default date format symbols for the default |
SimpleDateFormat(String pattern, DateFormatSymbols formatSymbols) |
Constructs a SimpleDateFormat using the given pattern and date format symbols. |
SimpleDateFormat(String pattern, Locale locale) |
Constructs a SimpleDateFormat using the given pattern and the default date format symbols for the given locale. |
注意:
pattern的意思是形式,可以自己定义输出的日期格式!
yyyy : 年
MM : 月
dd : 日
HH : 小时
mm : 分钟
ss : 秒
方法
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
void |
applyLocalizedPattern(String pattern) |
Applies the given localized pattern string to this date format. |
void |
applyPattern(String pattern) |
Applies the given pattern string to this date format. |
Object |
clone() |
Creates a copy of this SimpleDateFormat. |
boolean |
equals(Object obj) |
Compares the given object with this SimpleDateFormat for equality. |
StringBuffer |
format(Date date, StringBuffer toAppendTo, FieldPosition pos) |
Formats the given Date into a date/time string and appends the result to the given StringBuffer. |
Date |
parse(String text, ParsePosition pos) |
Parses text from a string to produce a Date. |
例子
// format()方法按照指定格式输出
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(simpleDateFormat.format(date));
结果:
2021-01-27 12:03:37
// 把自定义的格式解析为标准格式
Date date = new Date();
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String format = simpleDateFormat.format(date);
System.out.println(simpleDateFormat.parse(format));
结果:
Wed Jan 27 12:19:19 GMT+08:00 2021
那么Date类中的淘汰方法被谁代替了呢?下面引入Calendar类!玩日期还是用这个日历类!
七、Calendar
注意
-
构造函器没有公开,使用了单例设计模式,所以实例化的方法要Calendar.getInstance();
-
这个类像Math一样也是个工具类,所以他的表示日期的参数大多是static,使用get()和set()方法对日期进行操作。
方法
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
abstract void |
add(int field, int amount) |
Adds or subtracts the specified amount of time to the given calendar field, based on the calendar's rules. |
boolean |
after(Object when) |
Returns whether this Calendar represents a time after the time represented by the specified Object. |
boolean |
before(Object when) |
Returns whether this Calendar represents a time before the time represented by the specified Object. |
int |
get(int field) |
Returns the value of the given calendar field. |
static Calendar |
getInstance() |
Gets a calendar using the default time zone and locale. |
abstract int |
getMinimum(int field) |
Returns the minimum value for the given calendar field of this Calendar instance. |
void |
set(int year, int month, int date, int hourOfDay, int minute, int second) |
Sets the values for the fields YEAR, MONTH, DAY_OF_MONTH, HOUR_OF_DAY, MINUTE, and SECOND. |
void |
setTime(Date date) |
Sets this Calendar's time with the given Date. |
其他方法见jdk9文档
例子
// 单例模式获取对象
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance(); System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH)); // 注意,西方的月份从0开始! System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH)); // 注意,西方的星期从星期天开始! System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK)); calendar.set(2022, 9,10); System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH));
运行结果:
Wed Jan 27 14:18:32 GMT+08:00 2021
2021 27 0 4 9
八、System
结构
public final class System
extends Object
final:没有类继承他了
Field Summary
| Modifier and Type | Field | Description |
|---|---|---|
static PrintStream |
err |
The "standard" error output stream. |
static InputStream |
in |
The "standard" input stream. |
static PrintStream |
out |
The "standard" output stream. |
这里有System.in和System.out方法
一些方法
| Modifier and Type | Method | Description |
|---|---|---|
static void |
arraycopy(Object src, int srcPos, Object dest, int destPos, int length) |
Copies an array from the specified source array, beginning at the specified position, to the specified position of the destination array. |
static String |
clearProperty(String key) |
Removes the system property indicated by the specified key. |
static Console |
console() |
Returns the unique |
static long |
currentTimeMillis() |
Returns the current time in milliseconds. |
static void |
exit(int status) |
Terminates the currently running Java Virtual Machine. |
static String |
getProperty(String key) |
Gets the system property indicated by the specified key. |
举例
// 获取当前时间戳 System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号