springmvc学习指南 之---第40篇 好久不见我的tomcat 现在想起你,能告诉我<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>秘密吗
事情是这样子的,看到一个关于springmvc源码解读的文章,他说tomcat是如何初始化ApplicationContext容器的,
springMVC源码分析--容器初始化(一)ContextLoaderListener
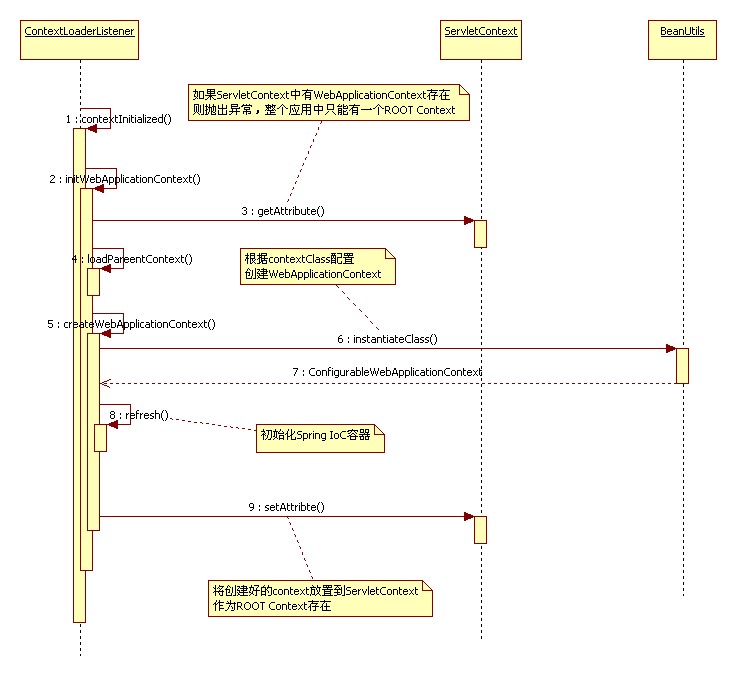
这个图,写的非常好
<web-app xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd"
version="3.0">
<!-- The definition of the Root Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<context-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/root-context.xml</param-value>
</context-param>
<!-- Creates the Spring Container shared by all Servlets and Filters -->
<listener>
<listener-class>org.springframework.web.context.ContextLoaderListener</listener-class>
</listener>
<filter>
<filter-name>csrfFilter</filter-name>
<filter-class>org.springframework.web.filter.DelegatingFilterProxy</filter-class>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
</filter>
<filter-mapping>
<filter-name>csrfFilter</filter-name>
<url-pattern>/*</url-pattern>
</filter-mapping>
<!-- Processes application requests -->
<servlet>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<init-param>
<param-name>contextConfigLocation</param-name>
<param-value>/WEB-INF/spring/appServlet/servlet-context.xml</param-value>
</init-param>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
<async-supported>true</async-supported>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>appServlet</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
<!-- Disables Servlet Container welcome file handling. Needed for compatibility with Servlet 3.0 and Tomcat 7.0 -->
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file></welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
</web-app>
这里主要表达的是添加了这个listener,那么这个listenter是tomcat加载的流程中加载的,
以前我是tomcat源码专家呢,那么在哪里加载的这个listner呢?那么就捋捋
这个是<listener>标签,那么那查看 WebRuleSet 类
在
digester.addCallMethod(prefix + "web-app/listener/listener-class", "addApplicationListener", 0);
看到.这个是对于StanderContext对象进行添加, addApplicationListener
那么就要定位到StanderContext .addApplicationListener方法
类名 public class StandardContext public void addApplicationListener(String listener) { synchronized (applicationListeners) { String results[] =new String[applicationListeners.length + 1]; for (int i = 0; i < applicationListeners.length; i++) { if (listener.equals(applicationListeners[i])) return; results[i] = applicationListeners[i]; } results[applicationListeners.length] = listener; applicationListeners = results; } fireContainerEvent("addApplicationListener", listener); // FIXME - add instance if already started? }
接着看调用在哪里 StandandContext 3211 行
// Send application start events if (debug >= 1) log("Sending application start events"); setApplicationListeners(results); Object instances[] = getApplicationListeners(); if (instances == null) return (ok); ServletContextEvent event = new ServletContextEvent(getServletContext()); for (int i = 0; i < instances.length; i++) { if (instances[i] == null) continue; if (!(instances[i] instanceof ServletContextListener)) continue; ServletContextListener listener = (ServletContextListener) instances[i]; try { fireContainerEvent("beforeContextInitialized", listener); listener.contextInitialized(event); fireContainerEvent("afterContextInitialized", listener); } catch (Throwable t) { fireContainerEvent("afterContextInitialized", listener); log(sm.getString("standardContext.listenerStart", instances[i].getClass().getName()), t); ok = false; } } return (ok);
这就连上了,调用了listener.contextInitailized(event)方法
@Override public void contextInitialized(ServletContextEvent event) { initWebApplicationContext(event.getServletContext()); }
initWebApplicationContext 方法在他的父类
ContextLoader 上面
public WebApplicationContext initWebApplicationContext(ServletContext servletContext) { if (servletContext.getAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE) != null) { throw new IllegalStateException( "Cannot initialize context because there is already a root application context present - " + "check whether you have multiple ContextLoader* definitions in your web.xml!"); } Log logger = LogFactory.getLog(ContextLoader.class); servletContext.log("Initializing Spring root WebApplicationContext"); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization started"); } long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis(); try { // Store context in local instance variable, to guarantee that // it is available on ServletContext shutdown. if (this.context == null) { this.context = createWebApplicationContext(servletContext); } if (this.context instanceof ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) { ConfigurableWebApplicationContext cwac = (ConfigurableWebApplicationContext) this.context; if (!cwac.isActive()) { // The context has not yet been refreshed -> provide services such as // setting the parent context, setting the application context id, etc if (cwac.getParent() == null) { // The context instance was injected without an explicit parent -> // determine parent for root web application context, if any. ApplicationContext parent = loadParentContext(servletContext); cwac.setParent(parent); } configureAndRefreshWebApplicationContext(cwac, servletContext); } } servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, this.context); ClassLoader ccl = Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader(); if (ccl == ContextLoader.class.getClassLoader()) { currentContext = this.context; } else if (ccl != null) { currentContextPerThread.put(ccl, this.context); } if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) { logger.debug("Published root WebApplicationContext as ServletContext attribute with name [" + WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE + "]"); } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { long elapsedTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime; logger.info("Root WebApplicationContext: initialization completed in " + elapsedTime + " ms"); } return this.context; } catch (RuntimeException ex) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", ex); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, ex); throw ex; } catch (Error err) { logger.error("Context initialization failed", err); servletContext.setAttribute(WebApplicationContext.ROOT_WEB_APPLICATION_CONTEXT_ATTRIBUTE, err); throw err; } }
以上标记为黄色的行就对应了,我张贴的逻辑图的过程,
看了的东西,真是记不住, 看到别人的分析,确实比我强呢,所以最近就加强看springmvc的东西吧



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号