反射
1.什么是反射?
-
反射它是框架设计的灵魂。
-
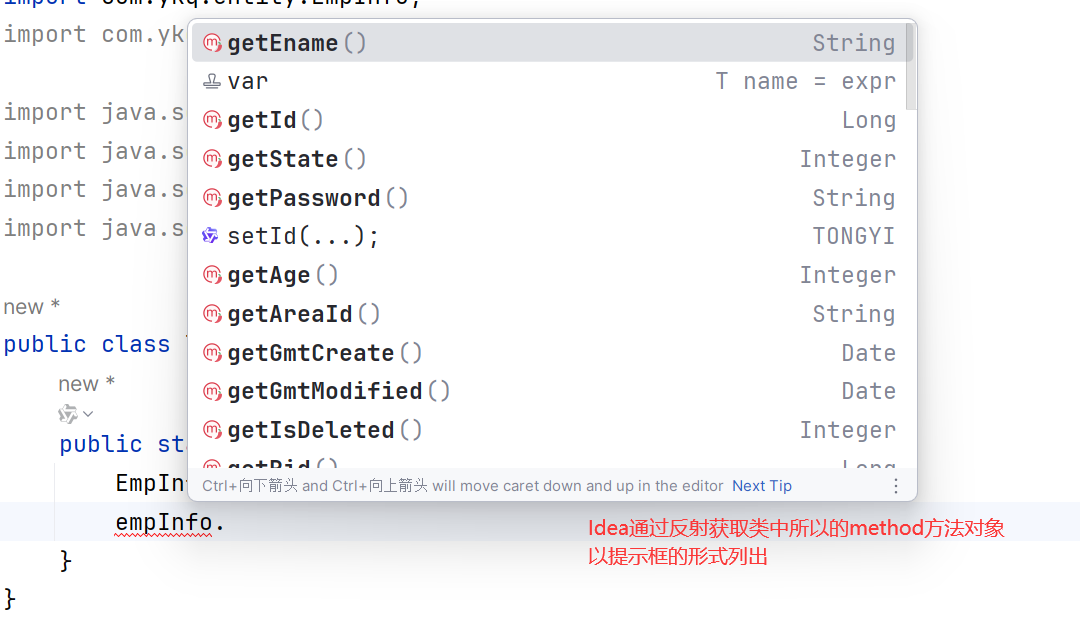
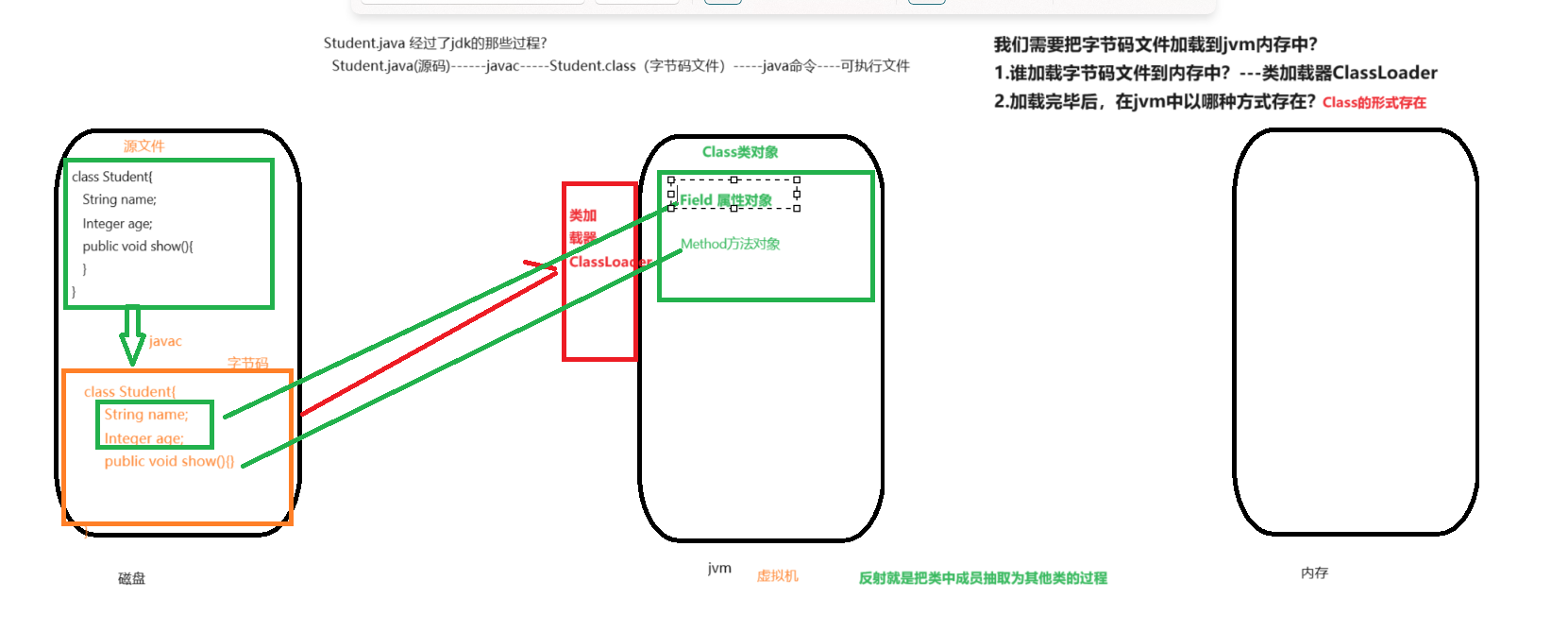
反射就是类在运行期间,把类中成员抽取为其他类的过程就是反射。
![]()
-
反射是为了解决在运行期,对某个实例一无所知的情况下,如何调用其方法或属性。
-
例子: spring框架中只需要传入类的路径----spring框架就会帮你创建类的对象。
2.获取Class反射类的方式
- 第一种: 通过类名.class属性
Class<Student> aClass = Student.class;
- 第二种: 通过类路径获取
Class aClass1 = Class.forName("com.ykq.test.Student");
- 第三种: 通过对象名获取反射类型
Student student = new Student();
Class aClass2 = student.getClass();
3. Class类中常用的方法
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class<Student> aClass = Student.class;
//通过反射类创建类对象--思考: mybatis SqlSession.getMapper(StudentDao.class)
//bean class= "com.ykq.Student"
Student student = aClass.newInstance();
System.out.println(student);
//获取反射类上的注解对象---反射是在运行时得到
MyAnnotation annotation = aClass.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
System.out.println(annotation.value());
}
-
根据反射类得到实例对象 newInstance()
-
得到反射类上的注解对象 getAnnotation()
4. 获取Method方法类对象
public static void main(String[] args) throws Throwable{
Class<Student> aClass = Student.class;
//得到本类中定义的所有Method类对象
Method[] declaredMethods = aClass.getDeclaredMethods();
for (Method m :declaredMethods){
System.out.println(m);
}
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
//获取本类中指定的方法对象
Method fun = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("fun",Integer.class);
System.out.println(fun);
//获取本类以及父类中所以public方法对象
Method[] methods = aClass.getMethods();
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
for (Method m :methods){
System.out.println(m);
}
//获取本类以及父类中指定的public方法对象
Method method = aClass.getMethod("equals", Object.class);
System.out.println(method);
}
-
getDeclaredMethods(): 得到本类中所有的方法。
-
getDeclaredMethod("方法名",参数类型):获取本类中指定的方法对象
-
getMethods():获取本类以及父辈类中public修饰的方法。
-
getMethod("方法名",参数类型):获取本类以及父辈类中指定public修饰的方法。
5. Method类对象中常用的方法
package com.ykq.test;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
public class Test04 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//泛型通配符
Class<?> aClass = Class.forName("com.ykq.test.People");
Object o = aClass.newInstance();
Method method = aClass.getMethod("print");
//执行该方法 返回该方法执行的结果.
//第一个参数表示执行方法的对象
Object result = method.invoke(o);
System.out.println(result);
System.out.println("~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~~");
Method method1 = aClass.getMethod("hehe", int.class);
Object result1 = method1.invoke(o, 25);
System.out.println(result1);
Method print02 = aClass.getDeclaredMethod("print02");
//IllegalAccessException: private私有方法不能被反射调用-->强力反射
print02.setAccessible(true);//设置允许访问私有成员
Object ressult2 = print02.invoke(o);
System.out.println(ressult2);
}
}
-
Object r=invoke(Object对象,参数值)
-
setAccessible()设置允许访问私有成员
6. 获取Field属性对象的方式
public static void main(String[] args) throws InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchFieldException {
Class<Student> aClass = Student.class;
Student student = aClass.newInstance();
Field name = aClass.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(name);
}
7. Field类中常用的方法
Class<Student> aClass = Student.class;
Student student = aClass.newInstance(); //new Student()
// System.out.println(student);
// Field name = aClass.getDeclaredField("name");
// name.set(student,"刘德华"); //student.setName("刘德华");
// System.out.println(student);
//
// Field age = aClass.getDeclaredField("age");
// age.setAccessible(true);
// age.set(student,18);
// System.out.println(student);
//获取属性名
Field[] declaredFields = aClass.getDeclaredFields();
for (Field declaredField : declaredFields) {
System.out.println(declaredField.getName());
//获取每个属性对象上的注解对象
MyAnnotation annotation = declaredField.getAnnotation(MyAnnotation.class);
String value = annotation.value();
System.out.println(value);
}
-
set(Object对象,值):为属性赋值
-
getName():获取属性名
-
getAnnotation():获取属性上的注解对象




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号