CSRF攻击的原理:
①用户正常登录A银行网站,
②A网站返回cookie信息给用户,浏览器保存cookie信息
③在A网站没有退出登录的情况下(或者说cookie信息没过期), 登录了恶意网站B
④恶意网站B,提前准备好转账表单或者其它请求 ,将其隐藏. 把提交到A网站的按钮设置为一个"领取优惠券"的图片链接.用户 点击链接
⑤在用户主观未知的情况下,访问A网站,此时浏览器会自动携带cookie信息
⑥A网站识别到cookie信息,默认为是用户本人做出的请求,根据请求做出相应的操作.
⑦用户收到损失.
flask的处理方式:
1、简单Flask程序
from flask import Flask
app = Flask(__name__)
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello World!'
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
2、Flask运行流程
2.1、实例化Flask类生产app对象
from flask import Flask app = Flask(__name__)
2.2、注册url,路由,endpoint到内存中
@app.route('/')
def hello_world():
return 'Hello World!'
2.2.1、class Flask(_PackageBoundObject) 类中route()方法
def route(self, rule, **options):
def decorator(f):
endpoint = options.pop('endpoint', None)
self.add_url_rule(rule, endpoint, f, **options)
return f
return decorator
2.2.2、class Flask(_PackageBoundObject) 类中add_url_rule()方法
def add_url_rule(self, rule, endpoint=None, view_func=None, **options):
if endpoint is None:
endpoint = _endpoint_from_view_func(view_func)
options['endpoint'] = endpoint
methods = options.pop('methods', None)
# if the methods are not given and the view_func object knows its
# methods we can use that instead. If neither exists, we go with
# a tuple of only ``GET`` as default.
if methods is None:
methods = getattr(view_func, 'methods', None) or ('GET',)
if isinstance(methods, string_types):
raise TypeError('Allowed methods have to be iterables of strings, '
'for example: @app.route(..., methods=["POST"])')
methods = set(item.upper() for item in methods)
# Methods that should always be added
required_methods = set(getattr(view_func, 'required_methods', ()))
# starting with Flask 0.8 the view_func object can disable and
# force-enable the automatic options handling.
provide_automatic_options = getattr(view_func,
'provide_automatic_options', None)
if provide_automatic_options is None:
if 'OPTIONS' not in methods:
provide_automatic_options = True
required_methods.add('OPTIONS')
else:
provide_automatic_options = False
# Add the required methods now.
methods |= required_methods
rule = self.url_rule_class(rule, methods=methods, **options)
rule.provide_automatic_options = provide_automatic_options
self.url_map.add(rule)
if view_func is not None:
old_func = self.view_functions.get(endpoint)
if old_func is not None and old_func != view_func:
raise AssertionError('View function mapping is overwriting an '
'existing endpoint function: %s' % endpoint)
self.view_functions[endpoint] = view_func
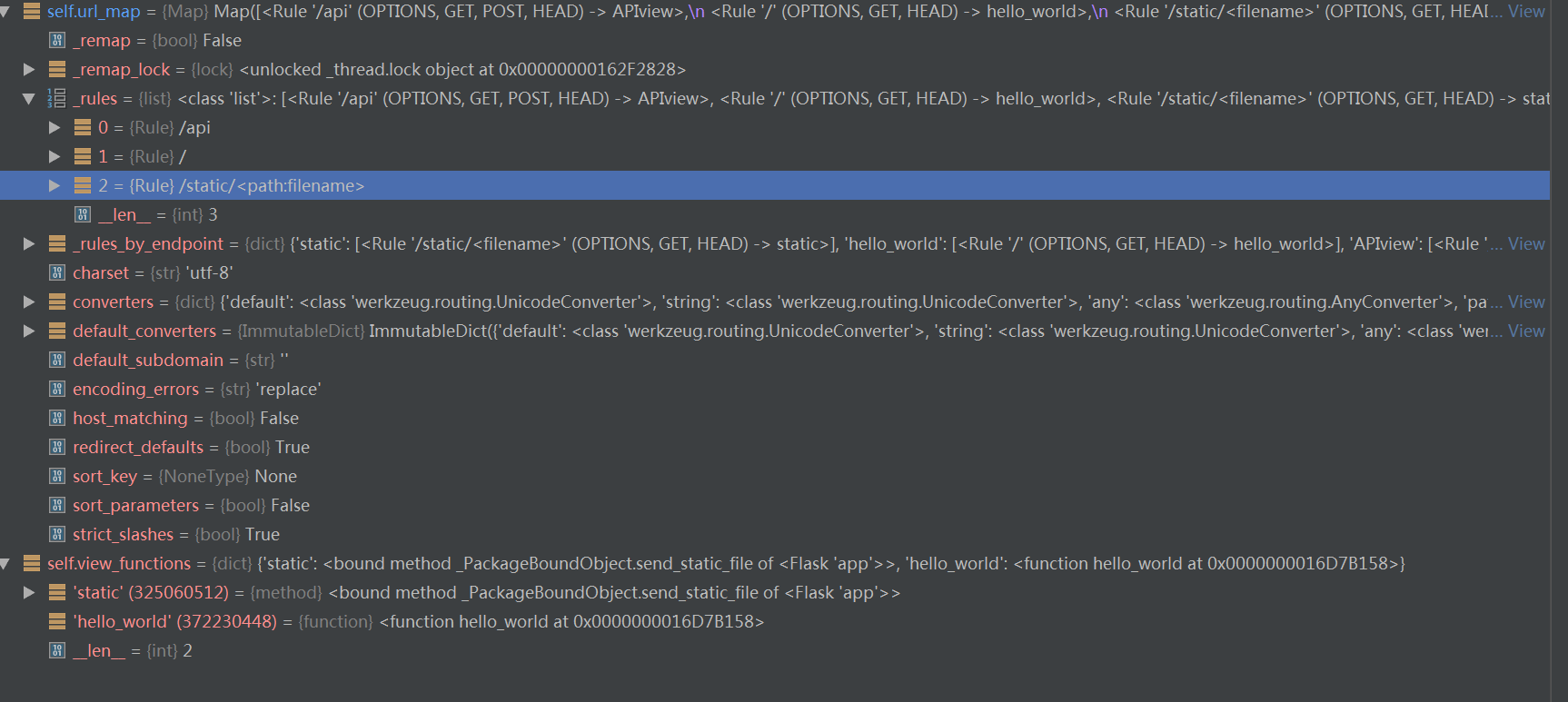
执行完之后,将url放入app.url_map中;将视图函数放入app.view_functions中:
2.3、运行app.run(),检测客户端请求,并作出响应
if __name__ == '__main__':
app.run()
2.3.1、执行Flask类中的run()方法
def run(self, host=None, port=None, debug=None, **options):
from werkzeug.serving import run_simple
if host is None:
host = '127.0.0.1'
if port is None:
server_name = self.config['SERVER_NAME']
if server_name and ':' in server_name:
port = int(server_name.rsplit(':', 1)[1])
else:
port = 5000
if debug is not None:
self.debug = bool(debug)
options.setdefault('use_reloader', self.debug)
options.setdefault('use_debugger', self.debug)
try:
run_simple(host, port, self, **options)
finally:
# reset the first request information if the development server
# reset normally. This makes it possible to restart the server
# without reloader and that stuff from an interactive shell.
self._got_first_request = False
try之前的代码都是配置host、port、debug等参数。try中调用wsgi工具包werkzeug中的runsimple函数,用来建立socket链接,监听客户端数据,并进行解析处理,然后通过路由匹配找到视图函数,将数据交给视图处理后,再进行打包发给客户端。最后一行代码是将app中的_got_first_request标志置为False。当第一次客户端请求到来时置位True,用来触发before_first_request装饰器(第一次请求来在视图函数前面执行的代码)的运行。
2.3.2、请求来的时候执行流程
请求来的时候执行run_simple(host, port, self, **options)中的第三个参数,即self(),self就是app,因此执行Flask类中__call__方法。
Flask类中__call__方法:
def __call__(self, environ, start_response):
"""Shortcut for :attr:`wsgi_app`."""
return self.wsgi_app(environ, start_response)
2.3.3、wsgi_app中的environ,start_response
from werkzeug.wrappers import Response
from werkzeug.serving import run_simple
def run_server(environ, start_response):
print("environ:",environ)
print("type environ:",type(environ))
print("start_response:", start_response)
print("type start_response:", type(start_response))
response = Response('hello')
return response(environ, start_response)
if __name__ == '__main__':
run_simple('127.0.0.1', 8000, run_server)
environ的类型是:<class 'dict'>,即字典类型
environ的内容如下:
environ: {
'wsgi.version': (1, 0),
'wsgi.url_scheme': 'http',
'wsgi.input': < _io.BufferedReader name = 736 > ,
'wsgi.errors': < _io.TextIOWrapper name = '<stderr>'
mode = 'w'
encoding = 'UTF-8' > ,
'wsgi.multithread': False,
'wsgi.multiprocess': False,
'wsgi.run_once': False,
'werkzeug.server.shutdown': < function WSGIRequestHandler.make_environ. < locals > .shutdown_server at 0x0000000012E1B510 > ,
'SERVER_SOFTWARE': 'Werkzeug/0.14.1',
'REQUEST_METHOD': 'POST',
'SCRIPT_NAME': '',
'PATH_INFO': '/',
'QUERY_STRING': '',
'REMOTE_ADDR': '127.0.0.1',
'REMOTE_PORT': 11556,
'SERVER_NAME': '127.0.0.1',
'SERVER_PORT': '8000',
'SERVER_PROTOCOL': 'HTTP/1.1',
'CONTENT_TYPE': 'application/json',
'HTTP_CACHE_CONTROL': 'no-cache',
'HTTP_POSTMAN_TOKEN': 'fc8d2fdf-23c6-4461-9177-9c3965f09932',
'HTTP_USER_AGENT': 'PostmanRuntime/7.3.0',
'HTTP_ACCEPT': '*/*',
'HTTP_HOST': '127.0.0.1:8000',
'HTTP_ACCEPT_ENCODING': 'gzip, deflate',
'CONTENT_LENGTH': '0',
'HTTP_CONNECTION': 'keep-alive'
}
start_response的类型是:<class 'function'>,即函数类型
start_response的内容:
start_response: <function WSGIRequestHandler.run_wsgi.<locals>.start_response at 0x0000000012E2C510>
2.4、Flask类中的wsgi_app()方法
def wsgi_app(self, environ, start_response):
ctx = self.request_context(environ)
ctx.push()
error = None
try:
try:
# 对请求进行处理
response = self.full_dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
error = e
# 处理异常
response = self.handle_exception(e)
except:
error = sys.exc_info()[1]
raise
# 将处理后的数据返回
return response(environ, start_response)
finally:
if self.should_ignore_error(error):
error = None
ctx.auto_pop(error)
2.5、Flask类中的full_dispatch_request()方法
def full_dispatch_request(self):
"""Dispatches the request and on top of that performs request
pre and postprocessing as well as HTTP exception catching and
error handling.
.. versionadded:: 0.7
"""
# 处理第一次请求前的装饰器before_first_requst函数
self.try_trigger_before_first_request_functions()
try:
request_started.send(self)
rv = self.preprocess_request()
# 如果before_request函数们处理返回的值为None,则进行正式处理
if rv is None:
rv = self.dispatch_request()
except Exception as e:
rv = self.handle_user_exception(e)
# 使用after_response装饰器函数对视图函数执行后的结果进行处理
return self.finalize_request(rv)
2.5.1、Flask类中的try_trigger_before_first_request_functions()方法
def try_trigger_before_first_request_functions(self):
"""Called before each request and will ensure that it triggers
the :attr:`before_first_request_funcs` and only exactly once per
application instance (which means process usually).
:internal:
"""
if self._got_first_request:
return
with self._before_request_lock:
if self._got_first_request:
return
# self.before_first_request_funcs = [],列表中存放函数
for func in self.before_first_request_funcs:
func()
self._got_first_request = True
2.5.2、Flask类中的preprocess_request()方法
def preprocess_request(self):
"""Called before the actual request dispatching and will
call each :meth:`before_request` decorated function, passing no
arguments.
If any of these functions returns a value, it's handled as
if it was the return value from the view and further
request handling is stopped.
This also triggers the :meth:`url_value_preprocessor` functions before
the actual :meth:`before_request` functions are called.
"""
bp = _request_ctx_stack.top.request.blueprint
funcs = self.url_value_preprocessors.get(None, ())
if bp is not None and bp in self.url_value_preprocessors:
funcs = chain(funcs, self.url_value_preprocessors[bp])
for func in funcs:
func(request.endpoint, request.view_args)
# 获取before_requesth装饰器函数并处理
funcs = self.before_request_funcs.get(None, ())
if bp is not None and bp in self.before_request_funcs:
funcs = chain(funcs, self.before_request_funcs[bp])
for func in funcs:
rv = func()
if rv is not None:
return rv
2.5.3、Flask类中的dispatch_request()方法
def dispatch_request(self):
"""Does the request dispatching. Matches the URL and returns the
return value of the view or error handler. This does not have to
be a response object. In order to convert the return value to a
proper response object, call :func:`make_response`.
.. versionchanged:: 0.7
This no longer does the exception handling, this code was
moved to the new :meth:`full_dispatch_request`.
"""
req = _request_ctx_stack.top.request
if req.routing_exception is not None:
self.raise_routing_exception(req)
rule = req.url_rule
# if we provide automatic options for this URL and the
# request came with the OPTIONS method, reply automatically
if getattr(rule, 'provide_automatic_options', False) \
and req.method == 'OPTIONS':
return self.make_default_options_response()
# otherwise dispatch to the handler for that endpoint
# 根据rule.endpoint找到app.view_functions中对应的处理函数,然后将req.view_args传入,
# 进行视图函数处理,最后将结果返回
return self.view_functions[rule.endpoint](**req.view_args)



