第二阶段Blog作业
一:前言
题目集4:知识点涉及了正则表达式的运用,对继承的运用,对重写的运用,实现类的继承,并定义相应类对象并进行测试。
共三题,题量相对较少,难度对我个人来说较大,前两题难度较大。
题目集5:知识点主要涉及了正则表达式的运用,使用List、Set或Map接口。
共五题,题量中等,难度主要在于后两题。
题目集6:知识点主要为正则表达式的运用,继承和多态的运用。
共六题,题量中等,难度主要在于后面两题。
二:设计与分析
1.题目集4(7-2)、题目集5(7-4)两种日期类聚合设计的优劣比较
聚合一类图
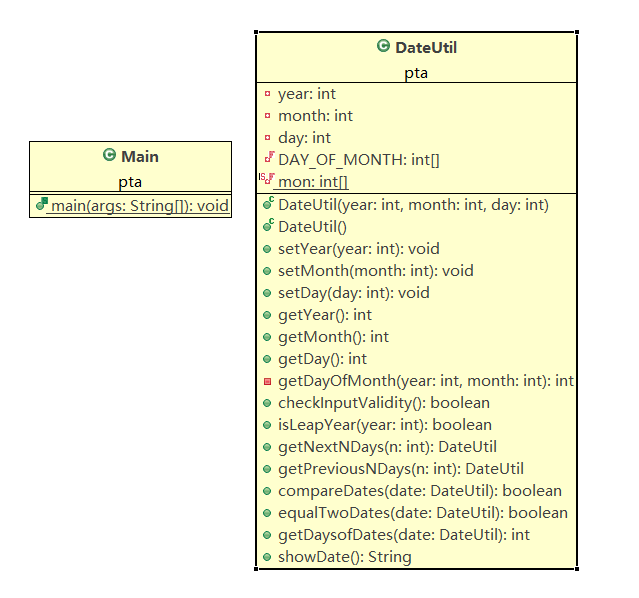
聚合二类图
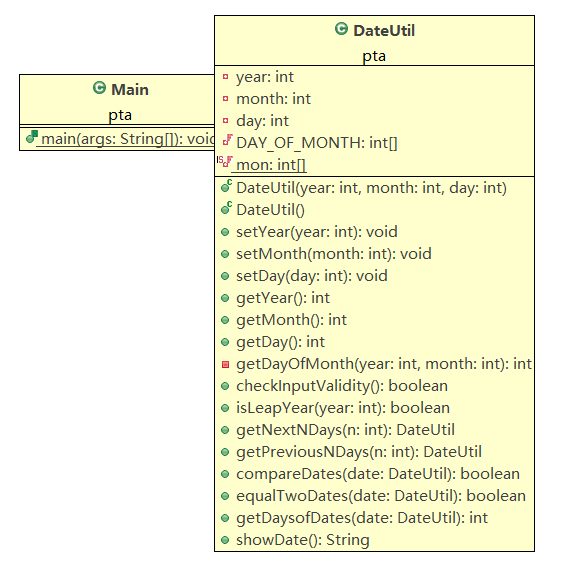
相差不是很大
聚合一代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
int year = 0;
int month = 0;
int day = 0;
int choice = input.nextInt();
if (choice == 1) { // test getNextNDays method
int m = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
m = input.nextInt();
if (m < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " next " + m + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getNextNDays(m).showDate());
} else if (choice == 2) { // test getPreviousNDays method
int n = 0;
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil date = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
if (!date.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
n = input.nextInt();
if (n < 0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
System.out.print(
date.getYear() + "-" + date.getMonth() + "-" + date.getDay() + " previous " + n + " days is:");
System.out.println(date.getPreviousNDays(n).showDate());
} else if (choice == 3) { //test getDaysofDates method
year = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
month = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
day = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherYear = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherMonth = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
int anotherDay = Integer.parseInt(input.next());
DateUtil fromDate = new DateUtil(year, month, day);
DateUtil toDate = new DateUtil(anotherYear, anotherMonth, anotherDay);
if (fromDate.checkInputValidity() && toDate.checkInputValidity()) {
System.out.println("The days between " + fromDate.showDate() +
" and " + toDate.showDate() + " are:"
+ fromDate.getDaysofDates(toDate));
} else {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
else{
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
}
}
class DateUtil {
private int year;
private int month;
private int day;
public DateUtil(int year, int month, int day) {
this.year = year;
this.month = month;
this.day = day;
}
public DateUtil(){}
public void setYear(int year) {
this.year = year;
}
public void setMonth(int month) {
this.month = month;
}
public void setDay(int day) {
this.day = day;
}
public int getYear() {
return year;
}
public int getMonth() {
return month;
}
public int getDay() {
return day;
}
private final int[] DAY_OF_MONTH = {31, 28, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31, 31, 30, 31, 30, 31};
private int getDayOfMonth(int year, int month) {
int days = DAY_OF_MONTH[month - 1];
if (month == 2 && isLeapYear(year)) {
days = 29;
}
return days;
}
public boolean checkInputValidity()//检测输入的年、月、日是否合法
{
if (year < 1820 || year > 2020) return false;
if (month < 1 || month > 12) return false;
// int _day = this.getDayOfMonth(year, month);
// return day <= _day;
return day >= 1 && day <= 31;
}
public boolean isLeapYear(int year)//判断year是否为闰年
{
return (year % 4 == 0 && year % 100 != 0) || year % 400 == 0;
}
public DateUtil getNextNDays(int n)//取得year-month-day的下n天日期
{
int year = this.year;
int month = this.month;
int day = this.day;
// day = Math.min(day, this.getDayOfMonth(year, month));
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
day++;
if (day > getDayOfMonth(year, month)) {
day = 1;
month++;
if (month > 12) {
month = 1;
year++;
}
}
}
return new DateUtil(year, month, day);
}
public DateUtil getPreviousNDays(int n)//取得year-month-day的前n天日期
{
int year = this.year;
int month = this.month;
int day = this.day;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
day--;
while (day < 1) {
month--;
if (month < 1) {
month = 12;
year--;
}
day += getDayOfMonth(year, month);
}
}
return new DateUtil(year, month, day);
}
public boolean compareDates(DateUtil date)//比较当前日期与date的大小(先后)
{
if (this.year > date.year) return true;
if (this.year == date.year) {
if (this.month > date.month) return true;
if (this.month == date.month) {
if (this.day >= date.day) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
public boolean equalTwoDates(DateUtil date)//判断两个日期是否相等
{
if (date != null) {
if (year == date.year && month == date.month && day == date.day) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
private static final int[] mon = {0, 31, 59, 90, 120, 151, 181, 212, 243, 273, 304, 334};
public int getDaysofDates(DateUtil date)//求当前日期与date之间相差的天数
{
DateUtil dateUtil1 = this; // 小
DateUtil dateUtil2 = date; // 大
if (this.compareDates(date)) {
dateUtil1 = date;
dateUtil2 = this;
}
int days;
int leapYearNum = 0;
for (int i = dateUtil1.getYear(); i < dateUtil2.getYear(); i++) {
if (isLeapYear(i)) {
leapYearNum++;
}
}
days = 365 * (dateUtil2.getYear() - dateUtil1.getYear()) + leapYearNum;
int d1 = mon[dateUtil1.getMonth() - 1] + dateUtil1.getDay() + (dateUtil1.getMonth() > 2 && isLeapYear(dateUtil1.getYear()) ? 1 : 0);
int d2 = mon[dateUtil2.getMonth() - 1] + dateUtil2.getDay() + (dateUtil2.getMonth() > 2 && isLeapYear(dateUtil2.getYear()) ? 1 : 0);
return days - d1 + d2;
}
public String showDate()//以“year-month-day”格式返回日期值
{
return year + "-" + month + "-" + day;
}
}
聚合二代码
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean key = true;
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int c = in.nextInt();
if(a < 0 || b < 0 || c<0) {
key = false;
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[a + b + c];
double[] areas = new double[a + b + c];
double sumArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
double cirRadius = in.nextDouble();
Circle circle = new Circle(cirRadius);
if (circle.validate()) {
shapes[i] = circle;
areas[i] = circle.getArea();
sumArea += areas[i];
} else {
key = false;
}
}
for (int i = a; i < a + b; i++) {
double recWidth = in.nextDouble();
double recLength = in.nextDouble();
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(recWidth, recLength);
if (rectangle.validate()) {
shapes[i] = rectangle;
areas[i] = rectangle.getArea();
sumArea += areas[i];
} else {
key = false;
}
}
for (int i = a + b; i < a + b + c; i++) {
double triLength1 = in.nextDouble();
double triLength2 = in.nextDouble();
double triLength3 = in.nextDouble();
Triangle triangle = new Triangle(triLength1,triLength2,triLength3);
if(triangle.validate()){
shapes[i] = triangle;
areas[i] = triangle.getArea();
sumArea += areas[i];
} else {
key = false;
}
}
if (!key) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
//1
System.out.println("Original area:");
for (int i = 0; i < a+b+c; i++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", areas[i]));
if(i == a+b+c)
break;
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
//2
System.out.println("Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f",sumArea));
//3
System.out.println("Sorted area:");
Arrays.sort(areas);
for (int i = 0; i < a+b+c; i++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", areas[i]));
if(i == a+b+c)
break;
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
//4
System.out.println("Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f",sumArea));
}
}
}
}
abstract class Shape {
public abstract double getArea();
public abstract boolean validate();
public abstract String toString();
}
class Circle extends Shape{
double radius;
Circle(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
@Override
public boolean validate() {
if(radius > 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return null;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
double width;
double length;
Rectangle(double width,double length){
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return width * length;
}
@Override
public boolean validate() {
if(width > 0 && length >0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return null;
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape {
double side1;
double side2;
double side3;
Triangle(double side1,double side2,double side3){
this.side1 = side1;
this.side2 = side2;
this.side3 = side3;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
double p = (side1 + side2 + side3) / 2;
return Math.sqrt(p * (p - side1) * (p - side2) * (p - side3));
}
@Override
public boolean validate() {
if(side1 > 0 && side2 >0 && side3 >0 && (side1 + side2) > side3 && (side1 + side3) > side2 && (side2 + side3) > side1 && Math.abs(side1 - side2) < side3 && Math.abs(side1 - side2) < side3 && Math.abs(side2 - side3) < side1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return null;
}
}
聚合二明显更加简洁,对代码的利用率也更加高,更加方便
2.题目集4(7-3)、题目集6(7-5、7-6)三种渐进式图形继承设计的思路与技术运用
题目集4(7-3)源码:
import java.util.Scanner;
class Shape {
public Shape(){
System.out.println("Constructing Shape");
}
public double getArea(){//求图形面积
return 0.0;
}
}
class Circle extends Shape {
public Circle(){
System.out.println("Constructing Circle");
}
private double radius;
public void setRadius(double radius) {
this.radius=radius;
}
public double getRadius(){
return radius;
}
@Override
public double getArea(){
return Math.PI*radius*radius;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
private double width;
private double length;
public Rectangle(){
System.out.println("Constructing Rectangle");
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width=width;
}
public double getWidth(){
return width;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length=length;
}
public double getLength(){
return length;
}
@Override
public double getArea(){
return length*width;
}
}
class Ball extends Circle {
public Ball(){
System.out.println("Constructing Ball");
}
@Override
public double getArea(){
return 4*super.getArea();
}
public double getVolume(){//求球体积
double Volume=getRadius();
return (4.0/3.0)*Math.PI*Volume*Volume*Volume;
}
}
class Box extends Rectangle {
public Box(){
System.out.println("Constructing Box");
}
private double height;
public double getHeight(){
return height;
}
public void setHeight(double height){
this.height=height;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
double width=getWidth();
double length=getLength();
return 2*(width*length+width*height+length*height);
}
public double getVolume()
{
return height*super.getArea();
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n;
Scanner scanner=new Scanner(System.in);
n=scanner.nextInt();
switch(n) {
case 1:
double r=scanner.nextDouble();
if(r<0.0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Circle circle=new Circle();
circle.setRadius(r);
System.out.println(String.format("Circle's area:%.2f",circle.getArea()));
}
break;
case 2:
double width=scanner.nextDouble();
double length=scanner.nextDouble();
if(width<0.0||length<0.0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Rectangle rectangle=new Rectangle();
rectangle.setLength(length);
rectangle.setWidth(width);
System.out.printf("Rectangle's area:%.2f%n",rectangle.getArea());
}
break;
case 3:
double r2=scanner.nextDouble();
if(r2<0.0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Ball ball=new Ball();
ball.setRadius(r2);
System.out.printf("Ball's surface area:%.2f%n",ball.getArea());
System.out.printf("Ball's volume:%.2f%n",ball.getVolume());
}
break;
case 4:
double width1=scanner.nextDouble();
double length1=scanner.nextDouble();
double height=scanner.nextDouble();
if(width1<0.0||length1<0.0||height<0.0) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
else {
Box box=new Box();
box.setHeight(height);
box.setWidth(width1);
box.setLength(length1);
System.out.printf("Box's surface area:%.2f%n",box.getArea());
System.out.printf("Box's volume:%.2f%n",box.getVolume());
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
}
}
}
题目集6(7-5、7-6)源码
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
boolean key = true;
int a = in.nextInt();
int b = in.nextInt();
int c = in.nextInt();
if(a < 0 || b < 0 || c<0) {
key = false;
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
Shape[] shapes = new Shape[a + b + c];
double[] areas = new double[a + b + c];
double sumArea = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < a; i++) {
double cirRadius = in.nextDouble();
Circle circle = new Circle(cirRadius);
if (circle.validate()) {
shapes[i] = circle;
areas[i] = circle.getArea();
sumArea += areas[i];
} else {
key = false;
}
}
for (int i = a; i < a + b; i++) {
double recWidth = in.nextDouble();
double recLength = in.nextDouble();
Rectangle rectangle = new Rectangle(recWidth, recLength);
if (rectangle.validate()) {
shapes[i] = rectangle;
areas[i] = rectangle.getArea();
sumArea += areas[i];
} else {
key = false;
}
}
for (int i = a + b; i < a + b + c; i++) {
double triLength1 = in.nextDouble();
double triLength2 = in.nextDouble();
double triLength3 = in.nextDouble();
Triangle triangle = new Triangle(triLength1,triLength2,triLength3);
if(triangle.validate()){
shapes[i] = triangle;
areas[i] = triangle.getArea();
sumArea += areas[i];
} else {
key = false;
}
}
if (!key) {
System.out.println("Wrong Format");
} else {
//1
System.out.println("Original area:");
for (int i = 0; i < a+b+c; i++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", areas[i]));
if(i == a+b+c)
break;
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
//2
System.out.println("Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f",sumArea));
//3
System.out.println("Sorted area:");
Arrays.sort(areas);
for (int i = 0; i < a+b+c; i++) {
System.out.print(String.format("%.2f", areas[i]));
if(i == a+b+c)
break;
System.out.print(" ");
}
System.out.println();
//4
System.out.println("Sum of area:" + String.format("%.2f",sumArea));
}
}
}
}
abstract class Shape {
public abstract double getArea();
public abstract boolean validate();
public abstract String toString();
}
class Circle extends Shape{
double radius;
Circle(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return Math.PI * radius * radius;
}
@Override
public boolean validate() {
if(radius > 0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return null;
}
}
class Rectangle extends Shape {
double width;
double length;
Rectangle(double width,double length){
this.width = width;
this.length = length;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
return width * length;
}
@Override
public boolean validate() {
if(width > 0 && length >0) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return null;
}
}
class Triangle extends Shape {
double side1;
double side2;
double side3;
Triangle(double side1,double side2,double side3){
this.side1 = side1;
this.side2 = side2;
this.side3 = side3;
}
@Override
public double getArea() {
double p = (side1 + side2 + side3) / 2;
return Math.sqrt(p * (p - side1) * (p - side2) * (p - side3));
}
@Override
public boolean validate() {
if(side1 > 0 && side2 >0 && side3 >0 && (side1 + side2) > side3 && (side1 + side3) > side2 && (side2 + side3) > side1 && Math.abs(side1 - side2) < side3 && Math.abs(side1 - side2) < side3 && Math.abs(side2 - side3) < side1) {
return true;
}
return false;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return null;
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double yuan;
double fang1,fang2;
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
yuan = in.nextDouble();
fang1 = in.nextDouble();
fang2 = in.nextDouble();
if(yuan>0&&fang1>0&&fang2>0)
{
Area a1 = new MyCircle(yuan);
double d1 = a1.calculateArea();
System.out.printf("%.2f\n",d1);
Area a2 = new MyRectangle(fang1,fang2);
double d2 = a2.calculateArea();
System.out.printf("%.2f",d2);
}
else
System.out.printf("Wrong Format");
}
}
interface Area {
double calculateArea();
}
class MyCircle implements Area {
private double r;
public MyCircle() {
super();
}
public MyCircle(double r) {
super();
this.r = r;
}
public double getR() {
return r;
}
public void setR(double r) {
this.r = r;
}
@Override
public double calculateArea() {
return Math.PI*Math.pow(r, 2);
}
}
class MyRectangle implements Area {
private double length;
private double width;
public MyRectangle() {
super();
}
public MyRectangle(double length, double width) {
super();
this.length = length;
this.width = width;
}
public double getLength() {
return length;
}
public void setLength(double length) {
this.length = length;
}
public double getWidth() {
return width;
}
public void setWidth(double width) {
this.width = width;
}
@Override
public double calculateArea() {
return length*width;
}
}
前面题目形状中我们看到,为了输出所有形状的周长与面积,需要建立多个数组进行多次循环。这次试验使用继承与多态来改进我们的设计。
定义抽象类Shape
属性:不可变静态常量double PI,值为3.14,
抽象方法:public double getPerimeter(),public double getArea()
Rectangle与Circle类均继承自Shape类。
Rectangle类(属性:int width,length)、Circle类(属性:int radius)。
带参构造函数为Rectangle(int width,int length),Circle(int radius)。
toString方法(Eclipse自动生成)
编写double sumAllArea方法计算并返回传入的形状数组中所有对象的面积和与、double sumAllPerimeter方法计算并返回传入的形状数组中所有对象的周长和。
main方法
1 输入整型值n,然后建立n个不同的形状。如果输入rect,则依次输入宽、长。如果输入cir,则输入半径。
2 然后输出所有的形状的周长之和,面积之和。并将所有的形状信息以样例的格式输出。 提示:使用Arrays.toString。
3 最后输出每个形状的类型与父类型.使用类似shape.getClass() //获得类型, shape.getClass().getSuperclass() //获得父类型;
心得:1、set()方法设置属性,this关键字的使用(区分同名的实例变量和局部变量如:this.name = name);get()获取属性,return返回值。2、继承extends,方法的重载,super关键字(调用父类的方法和属性如:super.getArea())。3、一种输出格式:String.format(“字符 参数的格式控制”,参数);
3.对三次题目集中用到的正则表达式技术的分析总结
正则表达式在题目集4第一题,题目集5第一题,第四题,题目集6前四题中有使用。
正则表达式描述了一种字符串匹配的模式,可以用来检查一个串是否含有某种子串、将匹配的子串替换或者从某个串中取出符合某个条件的子串等。
构造正则表达式的方法和创建数学表达式的方法一样。也就是用多种元字符与运算符可以将小的表达式结合在一起来创建更大的表达式。正则表达式的组件可以是单个的字符、字符集合、字符范围、字符间的选择或者所有这些组件的任意组合。
正则表达式是由普通字符(例如字符 a 到 z)以及特殊字符(称为"元字符")组成的文字模式。模式描述在搜索文本时要匹配的一个或多个字符串。正则表达式作为一个模板,将某个字符模式与所搜索的字符串进行匹配。
数字:^[0-9]*$
n位的数字:^\d{n}$
至少n位的数字:^\d{n,}$
m-n位的数字:^\d{m,n}$
零和非零开头的数字:^(0|[1-9][0-9]*)$
非零开头的最多带两位小数的数字:^([1-9][0-9]*)+(\.[0-9]{1,2})?$
带1-2位小数的正数或负数:^(\-)?\d+(\.\d{1,2})$
正数、负数、和小数:^(\-|\+)?\d+(\.\d+)?$
有两位小数的正实数:^[0-9]+(\.[0-9]{2})?$
有1~3位小数的正实数:^[0-9]+(\.[0-9]{1,3})?$
非零的正整数:^[1-9]\d*$ 或 ^([1-9][0-9]*){1,3}$ 或 ^\+?[1-9][0-9]*$
非零的负整数:^\-[1-9][]0-9"*$ 或 ^-[1-9]\d*$
非负整数:^\d+$ 或 ^[1-9]\d*|0$
非正整数:^-[1-9]\d*|0$ 或 ^((-\d+)|(0+))$
非负浮点数:^\d+(\.\d+)?$ 或 ^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0$
非正浮点数:^((-\d+(\.\d+)?)|(0+(\.0+)?))$ 或 ^(-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*))|0?\.0+|0$
正浮点数:^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*$ 或 ^(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*))$
负浮点数:^-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*)$ 或 ^(-(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)))$
浮点数:^(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?$ 或 ^-?([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0)$
汉字:^[\u4e00-\u9fa5]{0,}$
英文和数字:^[A-Za-z0-9]+$ 或 ^[A-Za-z0-9]{4,40}$
长度为3-20的所有字符:^.{3,20}$
由26个英文字母组成的字符串:^[A-Za-z]+$
由26个大写英文字母组成的字符串:^[A-Z]+$
由26个小写英文字母组成的字符串:^[a-z]+$
由数字和26个英文字母组成的字符串:^[A-Za-z0-9]+$
由数字、26个英文字母或者下划线组成的字符串:^\w+$ 或 ^\w{3,20}$
中文、英文、数字包括下划线:^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9_]+$
中文、英文、数字但不包括下划线等符号:^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]+$ 或 ^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]{2,20}$
可以输入含有^%&',;=?$\"等字符:[^%&',;=?$\x22]+
禁止输入含有~的字符:[^~\x22]+
4.题目集5(7-4)中Java集合框架应用的分析总结
题目集5(7-4)源码
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Set;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
String a;
StringBuilder ss=new StringBuilder();
Map<String, Integer> map=new HashMap<String, Integer>();
String []key= { "abstract","assert","boolean","break","byte","case","catch",
"char","class","const","continue","default","do","double","else",
"enum","extends","false","final","finally","float",
"for","goto","if","implements","import","instanceof",
"int","interface","long","native","new","null","package",
"private","protected","public","return","short","static",
"strictfp","super","switch","synchronized","this","throw",
"throws","transient","true","try","void","volatile","while"
};
int j=0;
for(int i=0;;i++) {
a=input.nextLine();
if(a.equals("exit"))
break;
if(a.matches("(.*)//(.*)"))
{String b[]=a.split("//");
ss.append(b[0]+" ");
}
else
{ss.append(a+" ");
}
}
int count=0;
String s=ss.toString();
Pattern p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\"");
Matcher m=p.matcher(s);
while(m.find()){
s=s.replace(m.group()," ");
p=Pattern.compile("\"(.*?)\"");
m=p.matcher(s);
}
p=Pattern.compile("/\\**(.*?)/");
m=p.matcher(s);
while(m.find()){
s=s.replace(m.group()," ");
m=p.matcher(s);
}
if(s.isEmpty())
{System.out.println("Wrong Format");
System.exit(0);
}
s=s.replace("["," ");
s=s.replace("]"," ");
s=s.replace("-","a");
s=s.replace("*","a");
s=s.replace("/","a");
s=s.replace("+","a");
s=s.replace(">","a");
s=s.replace("=","a");
s=s.replace("!","a");
s=s.replace(":","a");
s=s.replace("\\","a");
s= s.replaceAll("[^a-zA-Z]", " ");
String []s1=s.split("[ ' ']");
for(int i=0;i<s1.length;i++)
{
for( j=0;j<key.length;j++)
if(s1[i].equals(key[j]))
{
map.put(key[j], 0);
}
}
for( int i = 0;i<s1.length;i++)
{
for( j=0;j<key.length;j++)
if(s1[i].equals(key[j]))
{ count=map.get(key[j]);
map.put(key[j], count+1);
}
}
Set set=map.keySet();
Object[] arr=set.toArray();
Arrays.sort(arr);
for(Object k:arr){
System.out.println(map.get(k)+"\t"+k);
}
}
}
Set和List对比:
Set:检索元素效率低下,删除和插入效率高,插入和删除不会引起元素位置改变。
List:和数组类似,List可以动态增长,查找元素效率高,插入删除元素效率低,因为会引起其他元素位置改变。
集合框架之外的Map接口
Map将键映射到值的对象。一个映射不能包含重复的键;每个键最多只能映射一个值。
Map接口是Dictionary(字典)抽象类的替代品。
Map 接口提供三种collection 视图,允许以键集、值集合或键-值映射关系集的形式查看某个映射的内容。映射的顺序 定义为迭代器在映射的 collection 视图中返回其元素的顺序。某些映射实现可明确保证其顺序,如 TreeMap 类;某些映射实现则不保证顺序,如 HashMap 类。
有两个常见的已实现的子类:
HashMap:基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现。此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用 null 值和 null 键。(除了不同步和允许使用 null 之外,HashMap 类与 Hashtable 大致相同。)此类不保证映射的顺序,特别是它不保证该顺序恒久不变。
TreeMap:它实现SortedMap 接口的基于红黑树的实现。此类保证了映射按照升序顺序排列关键字,根据使用的构造方法不同,可能会按照键的类的自然顺序 进行排序(参见 Comparable),或者按照创建时所提供的比较器进行排序。
三:踩坑心得
1)第一道日期题目对于月份最大值的处理一开始用了switch和case,列举了12个月,到最后发现了mon_maxnum这个数组都没有用上,用case的时候不仅容易错,而且非常复杂,在第二个代码中就把返回月份最大值,直接用一个简单的方法返回了,下次做题的时候应该考虑清楚类图中的一些属性都有什么用,该怎么使用,然后再进行写代码的工作,这样可能会节省很多时间。
2)日期类的第二题和第一题有很多不同,因为年月日的类很简单,所以在日期处理的类中,包括了一些核心算法,而这个核心算法的一些顺序很重要,还是逻辑的问题,month.monthReduction();setDayMax();就比如这两个代码的先后顺序就很重要,如果按照自己的逻辑,它们两个谁先谁后都无所谓,但是如果把这两个代码位置换了的话,就会导致闰年2月到三月或者二月到1月出现问题,日期就会提前引用二月的日期,比如一月31日,但是运行后成了1月29日,就有一些逻辑错误,这个也改了一些时间。
4)题目集06(7-5),图形继承的题,检测输入数据合法性,一开始不管输入什么数据,输出都是wrong format,但是自己去看自己的代码觉得没有问题,然后到最后最后还是发现了一些逻辑错误,就是检验输入数据合法性,虽然都是判断,但是先正常进行,再输出wrong format 和先输wrong format 也是不一样的,所以要多注意这方面的逻辑,看看什么样的代码适合那种逻辑。
四:改进建议
有很多地方应当可以更加简洁,下次注意,使得自己的代码可以更加的简单,更加的有用
对于题目集04第三题,继承类题目,我认为可以写一个操作类,然后把求面积的方法都放在这一个类中,然后让这个类继承这个操作类,以后还可以加求体积等方法,很方便。
五:总结
学到了一些正则表达式的知识点以及应用 还需要多加练习,更熟悉的掌握正则表达式的知识点以及用法。学习到了类与类之间的关系,我认为这次最重要的就是明白了很多类与类之间的关系,比如关联,聚合,继承。这次的题目集让我对于继承有了更深的理解,因为理解了继承的好处,明白了它有什么用处,所以更好了理解了为什么要用继承,继承怎样使用。对于老师讲课的话没有很多意见,希望可以课上带我们多了解一些代码,多讲讲代码的具体作用。Java的路还很长,学无止境,希望自己可以认认真真,好好努力,学会学好它。加油加油加油!


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号