python-list、dict 基础知识
1. 列表操作
1.1 列表
list = [1,2,3,'James','Paul']
list = [i for i in range(10)]
列表的拆分
names=['1','2','3']
a,b,c=names
print(a,b,c)
1.2 列表创建,深浅拷贝
li = [1,3,2,4,5,6,7,8,9]
li2=li /浅拷贝,修改list2会对1产生影响
li3=li.copy() /浅拷贝 内存地址不一样,但是如果有嵌套LIST,会对LIST产生影响
# li4=copy.deepcopy(li)
li5=li [:] /深拷贝
print(li3,li5)
1.3 添加元素:
list.append() :尾部新增元素
>>>
list = [1,2,3]
>>> list.append(5)
>>> list
[1, 2, 3, 5]
list.insert():插入元素 list.insert(index, object) 参数一:index 位置, 参数二:object
>>>
list = [1,2,3,5]
>>> list.insert(3,4)
>>> list
[1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
list.extend():扩展列表 list.extend(tablelist),左右与 + 类似
>>>
list1 = [1,2,3]
>>> list2 = ['a','b']
>>> list1.extend(list2)
>>> list1
[1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b']
+ 号用于组合列表, list1+list2
>>> L1
= [1,2,3]
>>> L2 = ['a', 'b']
>>> L1+L2
[1, 2, 3, 'a', 'b']
* 号用于重复列表
>>> L1
= [1,2,3]
>>> L1*3
[1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3, 1, 2, 3]
1.4 访问列表元素
>>> a = ['a',5,'z']
>>> a[2]
'z'
元素重新赋值:=
>>>a[2] = 'LL'
>>>a
['a',5,‘LL’]
1.5 顺序遍历,迭代:
for循环
>>> list = [1,2,3,4,5]
>>> for i in list:
print(i)
使用for循环和enumerate()函数实现,同时输出索引值和元素内容:
list = ['中国', '美国', '英国', '俄罗斯']
for index, item in enumerate(list):
print(index+1, item)
1 中国
2 美国
3 英国
4 俄罗斯
1.6 删除元素:
list.remove(object):# 参数object 如有重复元素,只会删除最靠前的
>>> list = [1,2,'a','b','a']
>>> list.remove('a')
>>> list
[1, 2, 'b', 'a'] # 第一个‘a’被删除,后面的未被移除
list.pop(index): /默认为删除最后一个元素,index -- 可选参数,要移除列表元素的对应索引值
>>>
list = [1,2,3,4,5]
>>> list.pop() / 默认删除最后一个元素
5
>>> list
[1, 2, 3, 4]
>>> list.pop(1) / 删除指定索引(index=1)的元素
2
>>> list
[1, 3, 4]
del list[index] :/可以删除整个列表或指定元素或者列表切片,list删除后无法访问。
>>>
list
[1, 3, 4]
>>> del list[1]
>>> list
[1, 4]
>>> del list
>>> list
<class 'list'>
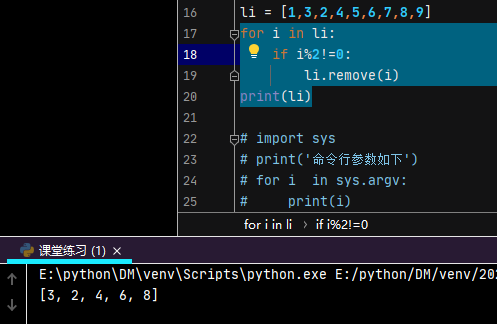
删除元素时不能使用循环删除,否则会导致下标错乱
li = [1,3,2,4,5,6,7,8,9]
# for i in li:
# if i%2!=0:
# li.remove(i)
# print(li)
以上代码可修改
for i in li:
if i%2==0:
list2.append(i)
print(list2)
1.7 排序和反转:
list.reverse() : /列表元素反转
>>> list = [1,2,3,4,5]
>>> list.reverse()
>>> list [5, 4, 3, 2, 1]
list.sort():排序,sort有三个默认参数 ,key=函数,reverse=False 因此可以制定排序参数
>>> a = [1,2,5,6,3]
>>> a.sort()
>>> a
[1, 2, 3, 5, 6]
python3X中,不能将数字和字符一起排序,会出现此报错
>>> a = [5,1,'z','h']
>>> a.sort()
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "<stdin>", line 1, in
<module>
TypeError: '<' not supported between instances of
'str' and 'int'
reverse=False,升序排序(默认);
reverse=True,降序排序
>>> a =
[1,5,9,10,3]
>>> a.sort()
>>> a
[1, 3, 5, 9, 10]
>>> a.sort(reverse=True)
>>> a
[10, 9, 5, 3, 1]
sorted():sorted(list)
>>> A =
[1,8,2,5]
>>> sorted(A)
[1, 2, 5, 8]
>>> sorted(A,reverse=True)
[8, 5, 2, 1]
>>> A
[1, 8, 2, 5]
>>>
注:sorted()函数与sort()方法有一点不同,sort()会在原list的上重新排列并保存,而sorted()不会改变原列表的顺序,只是生成新的排序列表
1.8 列表切片:
列表的位置,或索引,第一个索引是0,第二个索引是1,反向从-1开始
L = ['spam', 'Spam', 'SPAM!', 'Sam', 'Paul','Kate']
L[0], L[1], L[2], /正向访问
L[-1],L[-2] /正向访问
L[ :] /访问所有
1.9 列表操作常用函数和方法:
Join函数
“”.join(l) /#通过某个字符串,把list里面的每一个元素连接起来,返回一个新的字符串
Sctirp() /字符串去空格
- 列表操作包含以下函数:
cmp(list1, list2):比较两个列表的元素 (python3已丢弃)
import operator /比较函数在交互式模式下可以这样使用:
>>> a = [1, 2]
>>> b = [1, 3]
>>> import operator
>>> operator.eq(a, b)
False
len(list):列表中元素个数
max(list):返回列表元素最大值
min(list):返回列表元素最小值
list(seq):将元组转换为列表
tuple(seq):将列表转换为元祖
sorted(list):排序列表元素顺序 / 字符串排序
s='4567'
print(sorted(s,reverse=True))

- 列表操作常用操作包含以下方法:
list.append(obj):在列表末尾添加新的对象
list.count(obj):统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数
list.extend(seq):在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表)
list.index(obj):从列表中找出某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置
list.insert(index, obj):将对象插入列表
list.pop(obj=list[-1]):移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值
list.remove(obj):移除列表中某个值的第一个匹配项
list.reverse():反向列表中元素
list.sort([func]):对原列表进行排序
list.clear(): 清空列表 (python3.0)
list判断字段是否存在
list.count(i)>0 list.index >=0
list.stript() 去掉空格
"".join(list) / 链接字符串
l=['a','b','c']
r=''.join(l) //list转换成字符串
print(r)
2. dict
dict 新增,删除,查询 ,修改,可支持的函数和方法
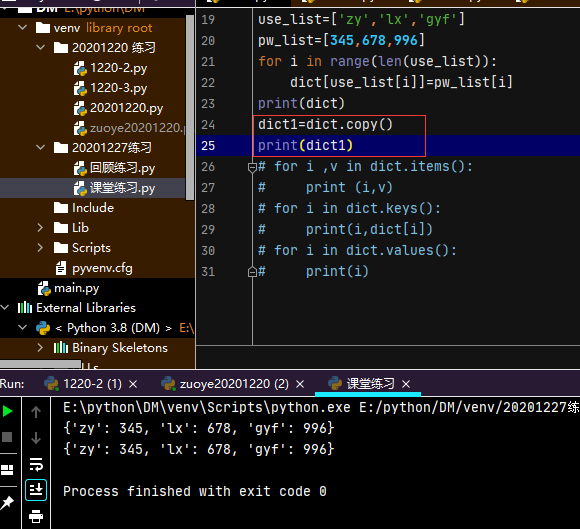
2.1 创建字典的方法
dict = {'Name': 'Zara', 'Age': 7,'adress':'2344opk'}
dict=[] /空字典
use_list=['zy1','gy','lili']
pw_list=[123,456,789]
for i in range(len(use_list):
dict[use[list[i]]=pw_list[i] /通过列表添加字典
print(dict)
复制创建
dict1=dict.copy()
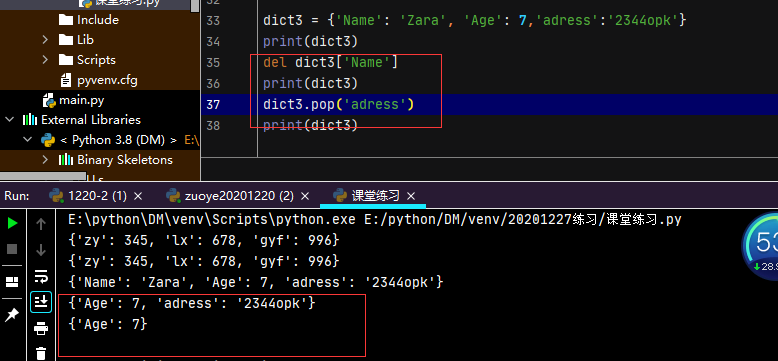
2.2 字典的删除
dict.pop['adress'] /返回键值
del dict['Name'] /删除键值
2.3 字典的查询
- 通过键值查询,
- 通过循环 items() ,values,keys;
dict['Name']
for i,v in dict.items():
print(i,v)
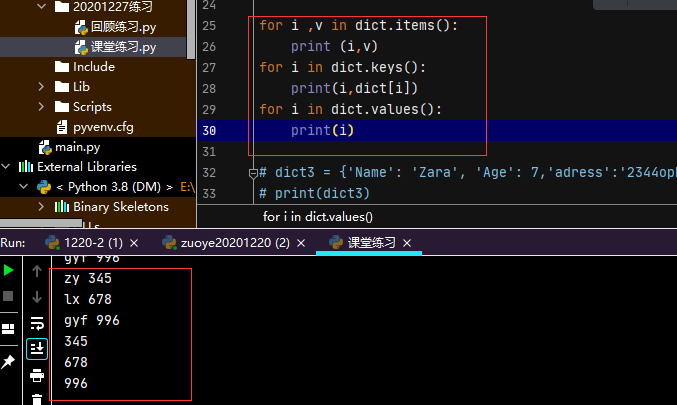
for i in dict.values():
print(i,dict.get(i)
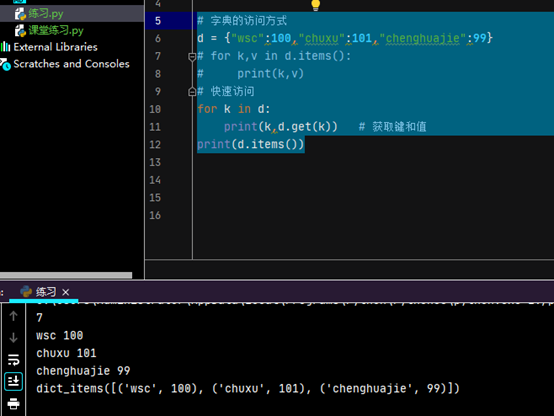
字典的实例
字典sorted函数实例;对list进行排序# 字典排序
d = {"wsc":100,"chuxu":101,"chenghuajie":99} print(d.items()) result=sorted(d.items(),key=lambda a:a[1]) print(result)
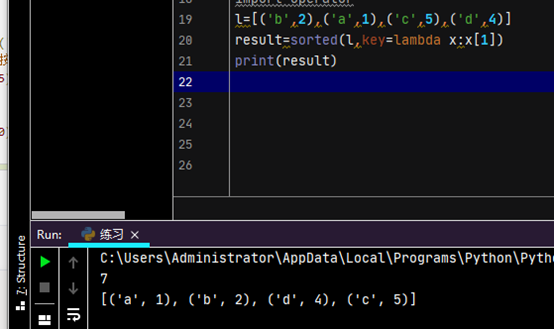
# print(x)
# 对list进行排序
# l=[('b',2),('a',1),('c',5),('d',4)]
# result=sorted(l,key=lambda x:x[1])
# print(result)
2.4 判断字典是否存在
dict.get(Name)

2.5 文件打印数据字典
可以转换成json
import json
dict={'a':1,'b':2,'c':3,'d':4}
js= json.dumps(dict)
file = open('open.xtx', 'w')
第2种方案
dict={'a':1,'b':2,'c':3,'d':4}
file = open('open.txt', 'w')
for i in dict:
file.write(i+''+str(dict[i])+'\n')
1.2 从文件总读取字典打印
with open('open.txt','r+') as fd:
dict2=eval(fd.read())
print(dict2)
把字典写入文件
with open('open.txt','w') as fd:
fd.write(str(dic))
字典写入文件



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号