Complex.hpp
#ifndef COMPLEX_HPP #define COMPLEX_HPP #include<iostream> #include<cmath> using namespace std; class Complex{ private: double real,imag; public: Complex (double real0=0,double imag0=0):real(real0),imag(imag0){} double get_real()const{return real;} double get_imag()const{return imag;} void show()const; Complex(const Complex &p); friend Complex add(Complex a,Complex b); void add(const Complex &p); friend bool is_equal(const Complex &a,const Complex &b); friend double abs(const Complex &p); }; void Complex::show()const{ if(imag!=0) cout<<real<<imag<<"i"; else cout<<real; } Complex::Complex(const Complex &p){ real=p.real; imag=p.imag; } void Complex::add(const Complex &p){ real=real+p.real; imag=imag+p.imag; } Complex add(Complex a,Complex b){ a.real=a.real+b.real; a.imag=a.imag+b.imag; return a; } bool is_equal(const Complex &a,const Complex &b){ if(a.real==b.real&&a.imag==b.imag) return true; else return false; } double abs(const Complex &p){ return sqrt (pow(p.real,2)+pow(p.imag,2)); } #endif
task3.cpp
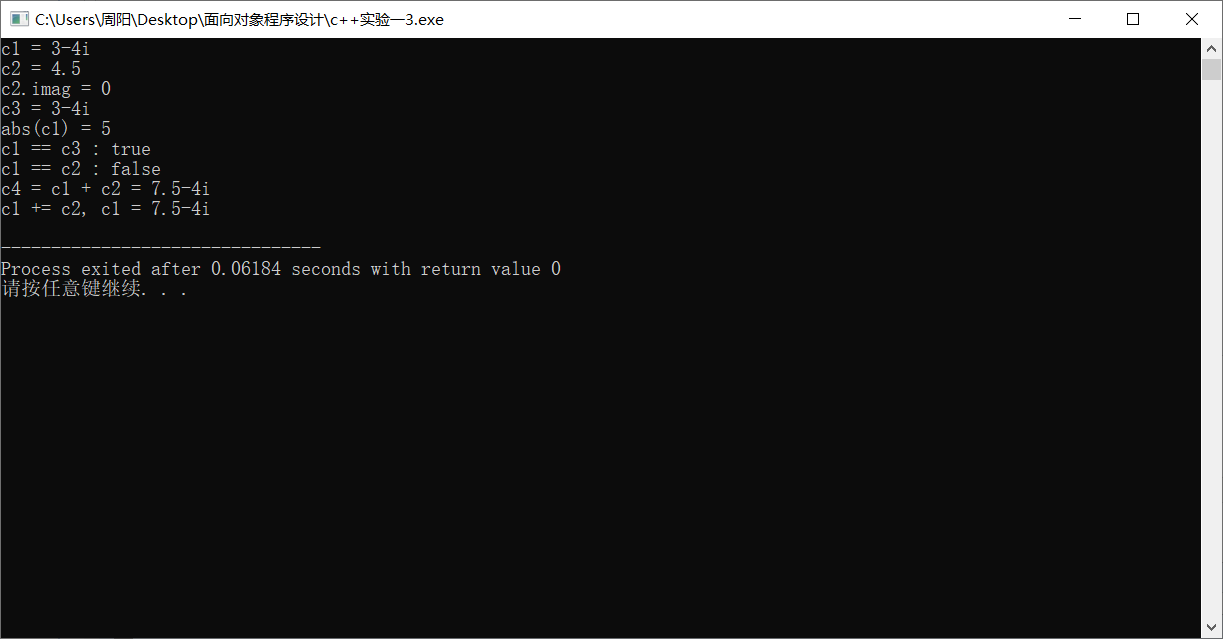
#include "Complex.hpp" #include <iostream> int main() { using namespace std; Complex c1(3, -4); const Complex c2(4.5); Complex c3(c1); cout << "c1 = "; c1.show(); cout << endl; cout << "c2 = "; c2.show(); cout << endl; cout << "c2.imag = " << c2.get_imag() << endl; cout << "c3 = "; c3.show(); cout << endl; cout << "abs(c1) = "; cout << abs(c1) << endl; cout << boolalpha; cout << "c1 == c3 : " << is_equal(c1, c3) << endl; cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl; Complex c4; c4 = add(c1, c2); cout << "c4 = c1 + c2 = "; c4.show(); cout << endl; c1.add(c2); cout << "c1 += c2, " << "c1 = "; c1.show(); cout << endl; }
task3运行截图
User.hpp
#ifndef USER_HPP #define USER_HPP #include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; class User{ private: string name; string passwd; string email; static int n; public: User(string name0); User(string name0,string passwd0,string email0); void set_email(); void change_passwd(); void print_info(); static void print_n(); }; int User::n=0; User::User(string name0):name(name0),passwd("111111"),email("\0"){ ++n; } User::User(string name0,string passwd0,string email0):name(name0),passwd(passwd0),email(email0){ ++n; } void User::print_info(){ cout<<name<<endl; cout<<"******"<<endl; cout<<email<<endl; } void User::change_passwd(){ cout<<"Enter old password:"; string pa; cin>>pa; for(int i=1;i<=3;i++) { if(i!=3&&pa!=passwd) { cout<<"password input error.Please re-enter again:"; cin>>pa; } if(i==3&&pa!=passwd) { cout<<"password input error.Please try after a while."<<endl; } } } void User::set_email(){ cout<<"Enter email adress:"; string a; cin>>a; email=a; cout<<"email is set successfully..."<<endl; } void User::print_n(){ cout<<"there are "<<n<<" users."; } #endif
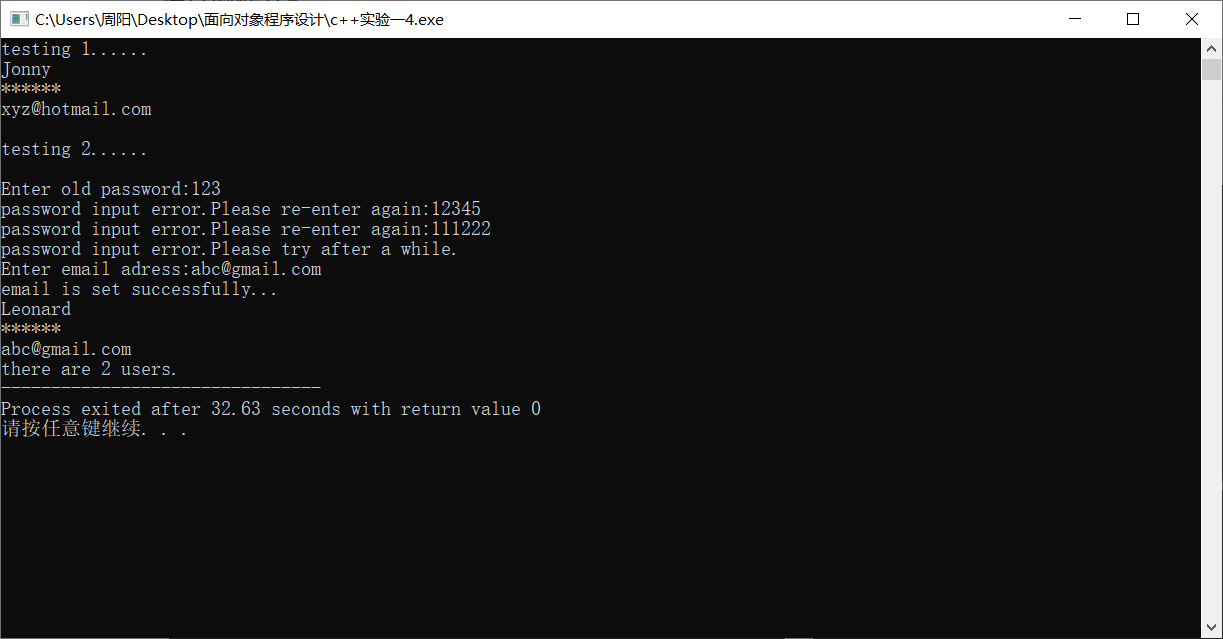
#include "User.hpp" #include <iostream> int main() { using namespace std; cout << "testing 1......" << endl; User user1("Jonny", "92197", "xyz@hotmail.com"); user1.print_info(); cout << endl << "testing 2......" << endl << endl; User user2("Leonard"); user2.change_passwd(); user2.set_email(); user2.print_info(); User::print_n(); }
task4运行截图
实验总结:
1、可以用setfill()和setw()来排版,其中setfill()为永久有效,直至下一个setfill(),而setw()为一次有效;
2、static修饰的可以直接用类名访问;
3、const的使用可以保护数据还能防止友元函数的无法识别。



