笨办法学python习题31-40
习题31:作出决定
代码展示
print("""You enter a dark room with two doors.Do you go through door #1 or door #2?""")
door = input("> ")
if door == "1":
print("There's a giant bear here eating a cheese cake.")
print("What do you do?")
print("1.Take the cake.")
print("2.Scream at the bear.")
bear = input("> ")
if bear == "1":
print("The bear eats your face off.Good job!")
elif bear == "2":
print("The bear eats your lege off.Good job!")
else:
print(f"Well,doing {bear} is probably better.")
print("Bear runs away.")
elif door == "2":
print("You stare into the endless abyss at Cthulhu;s retina.")
print("1.Blueberries.")
print("2.Yellow jacket clothespins.")
print("3.Understanding revolvers yelling melodies.")
insanity = input("> ")
if insanity == "1" or insanity == "2":
print("Your body survives powered by a mind of jello.")
print("Good job!")
else:
print("The insanity rots your eyes into a pool of muck.")
print("Good job!")
else:
print("You stumble around and fall on a knife and die.Good job!")
运行截图

定义一个变量,用来记录用户的输入结果,依据变量值来判断if语句的分支选择:bear = input("> ")(注:》只是用户来提示用户输入,非必要存在)
习题32:循环和列表
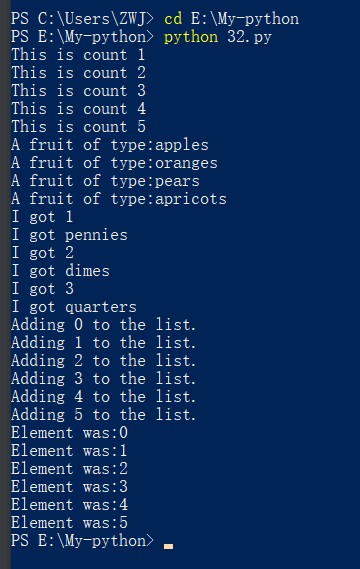
代码展示
the_count = [1,2,3,4,5]
fruits = ['apples','oranges','pears','apricots']
change = [1,'pennies',2,'dimes',3,'quarters']
#this first kind of for-loop goes through a list
for number in the_count:
print(f"This is count {number}")
#same as above
for fruit in fruits:
print(f"A fruit of type:{fruit}")
#also we can go through mixed lists too
#notice we have to use {} since we don't know what's in it
for i in change:
print(f"I got {i}")
#we can also build lists,first start with an empty one
elements = []
#then use the range function to do 0 to 5 counts
for i in range(0,6):
print(f"Adding {i} to the list.")
#append is a function that lists understand
elements.append(i)
#now we can print them out too
for i in elements:
print(f"Element was:{i}")
运行截图
菜鸟教程for循环
菜鸟教程range函数
range()函数能够创建一整个函数列表,一般用在for循环当中。
函数语法:range(start,stop[,step])
start:计数是从start开始,一般默认为0。eg:range(5)等价于range(0,5)
stop:计数到stop结束,但不包括stop。eg:range(0,5)创建列表为[1,2,3,4]
step:步长,默认为1,eg:range(0,5)= range(0,5,1)
- range函数为创建一个列表,直接将range函数创建的列表赋值给elements[]而不通过for循环赋值是否可行?,修改代码为
elements = range(0,6),重新运行此函数得到了与之前相同的输出
菜鸟教程-列表
列表的数据项不需要具有相同的类型,访问列表中的值通过索引实现,列表索引从0开始
for循环开始时循环变量就被定义了,每次循环到它的时候,它都被重新初始化为当前循环中的元素值
elements.append()函数的功能时在列表尾部追加元素
习题33:while循环
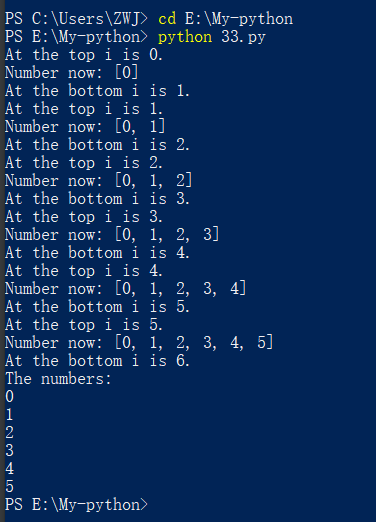
代码展示
i = 0
numbers = []
while i < 6:
print(f"At the top i is {i}.")
numbers.append(i)
i = i+1
print("Number now:",numbers)
print(f"At the bottom i is {i}.")
print("The numbers:")
for num in numbers:
print(num)
运行截图
用for循环改写while循环
i = 0
numbers = []
elements = range(0,6)
for j in elements:
print(f"At the top i is {i}.")
numbers.append(i)
i = i+1
print("Numbers now = ",numbers)
print(f"At the bottom i is {i}.")
print("The numberd")
for m in numbers:
print(m)
习题35:分支和函数
from sys import exit
def gold_room():
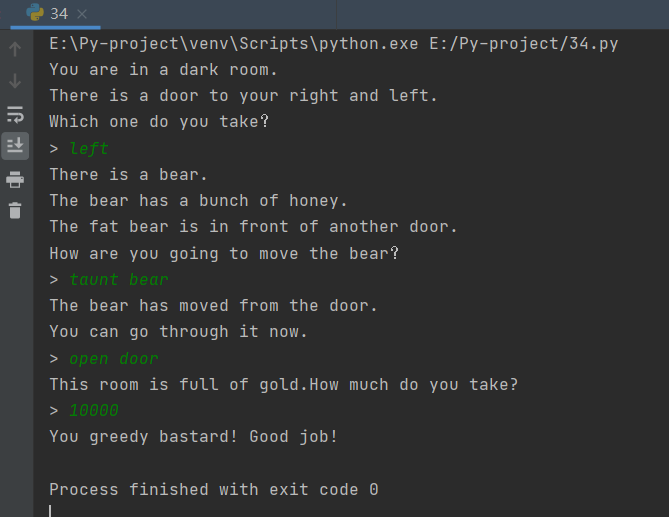
print("This room is full of gold.How much do you take?")
choice = input("> ")
if "0" in choice or "1" in choice:
how_much = int(choice)
else:
dead("Man,learn to type your number!")
if how_much<50:
print("Nicec,you're not greedy,ypu win!")
exit(0)
else:
dead("You greedy bastard!")
def bear_room():
print("There is a bear.")
print("The bear has a bunch of honey.")
print("The fat bear is in front of another door.")
print("How are you going to move the bear?")
bear_moved = False
while True:
choice = input("> ")
if choice == "take honey":
dead("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.")
elif choice == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved:
print("The bear has moved from the door.")
print("You can go through it now.")
bear_moved = True
elif choice == "taunt bear" and bear_moved:
dead("The bear gets pissed off and chews your leg off.")
elif choice == "open door" and bear_moved:
gold_room()
else:
print("I got no idea what that means.")
def cthulhu_room():
print("Here you see the great evil cthulhu.")
print("He,it,whatever stars at you and you go insane.")
print("Do you flee for you life or eat your head?")
choice = input("> ")
if "flee" in choice:
start()
elif "head" in choice:
dead("Well that was tasty!")
else:
cthulhu_room()
def dead(why):
print(why,"Good job!")
exit(0)
def start():
print("You are in a dark room.")
print("There is a door to your right and left.")
print("Which one do you take?")
choice = input("> ")
if choice == "right":
cthulhu_room()
elif choice == "left":
bear_room()
else:
dead("You stumble around the room until you starve.")
start()
运行截图:
input函数的参数是一个将被打印出来的字符,通常用来提示用户输入
exit(0)可以用来终止某个程序,而其中的数字则用来表示是否是遇到错误而终止的,exit(1)通常表示程序发生了错误,而exit(0)则表示程序是正常退出的
习题38:列表的操作
代码展示
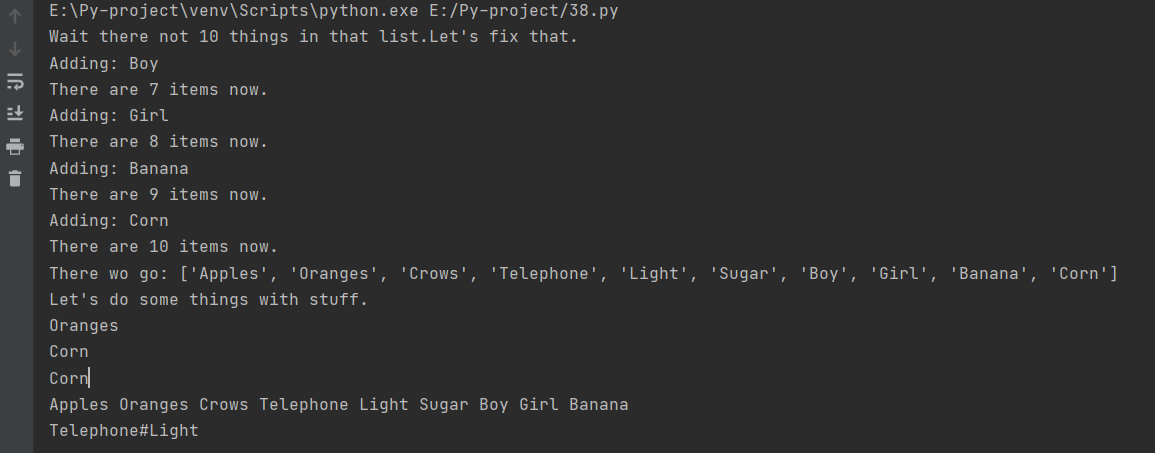
ten_things = "Apples Oranges Crows Telephone Light Sugar"
print("Wait there not 10 things in that list.Let's fix that.")
stuff = ten_things.split(' ')#字符串切割函数,并且返回切割后的字符串列表
more_stuff = ["Day","Night","Song","Frisbee","Corn","Banana","Girl","Boy"]#最后入栈最先出栈
while len(stuff) != 10:
next_one = more_stuff.pop() #将more_stuff列表中的首个元素出栈,并赋值给next_one变量
print("Adding:",next_one) #打印出next_one变量
stuff.append(next_one) #追加元素
print(f"There are {len(stuff)} items now.")
print("There wo go:",stuff)
print("Let's do some things with stuff.")
print(stuff[1])
print(stuff[-1])
print(stuff.pop())#将列表中的第一个元素出栈并且直接打印
print(' '.join(stuff))#
print('#'.join(stuff[3:5]))#
运行截图
*Python split() 通过指定分隔符对字符串进行切片,如果参数 num 有指定值,则分隔 num+1 个子字符串,返回分割后的字符串列表。
*python join()函数详解:,用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符生成一个新的字符串
*stuff[3:5]实现的功能为:这是一个列表的切片动作,它会从列表索引为3的位置开始取值,直至索引为4的元素,注意:这里并不包括索引为5的元素,跟range(3,5)的例子是一样的
*join函数的参数是你要连接的多个字符串构成的数组,是在你要插入的字符串上调用的一个方法函数
习题39:字典
代码展示
stuff = {'name':'zwj','age':22,'weight':106,23:'lky'}
print(stuff['name'])
print(stuff['age'])
print(stuff['weight'])
print(stuff[23])
stuff['city'] = 'beijing'
print(stuff['city'])
stuff[1] = 1998#此时的1不再代表索引位置
print(stuff)
del stuff['name']
print(stuff)
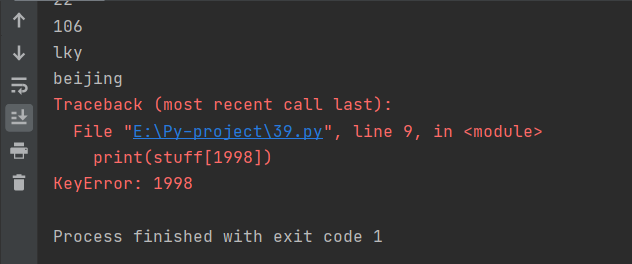
运行截图
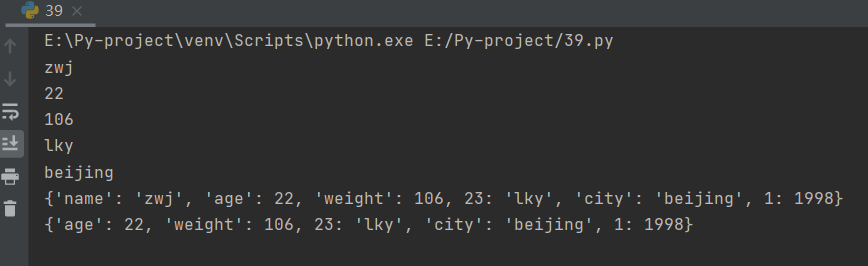
*尝试输出print(stuff[1998]),系统提示错误,表示字典中的对应值一般为根据前面的索引后面的
代码展示
#create a mapping of state to abbreviation缩写
states = {
'Oregon':'OR',
'Florida':'FL',
'California':'CA',
'New York':'NY',
'Michigan':'MI'
}
#create a basic set of states and some cities in them
cities = {
'CA':'San Francisco',
'MI':'Detroit',
'FL':'Jacksonville'
}
#add some more cities
cities['NY'] = 'New York'
cities['OR'] = 'Portland'
#print out some cities
print('-'*20)
print("NY State has:",cities['NY'])
print("OR State has:",cities['OR'])
#print some states
print('-'*20)
print("Michigan's abbreviation is:",states['Michigan'])
print("Florida's abbreviation is:",states['Florida'])
#print every state abbreviation
print('-'*20)
for state,abbrev in list(states.items()):
print(f"{state} is abbreviated {abbrev}")
#print every city in state
print('-'*20)
for abbrev,city in list(cities.items()):
print(f"{abbrev} has the city {city}")
#now do both at the same time
print('-'*20)
for state,abbrev in list(states.items()):
print(f"{state} is abbreviated {abbrev},and it has city {cities[abbrev]}")
#safely get a abbreviation by state that might be there
print('-'*20)
state = states.get('Taxes')
if not state:
print("Sorry,no Taxes")
else:
print("Yes!")
#get a city with a default value
city = cities.get('TX','Does Not Exist')
print(f"The city for the state 'TX' is:{city}")
city = cities.get('MI','Does Not Exist')
print(f"The city for the state 'TX' is:{city}")
运行截图
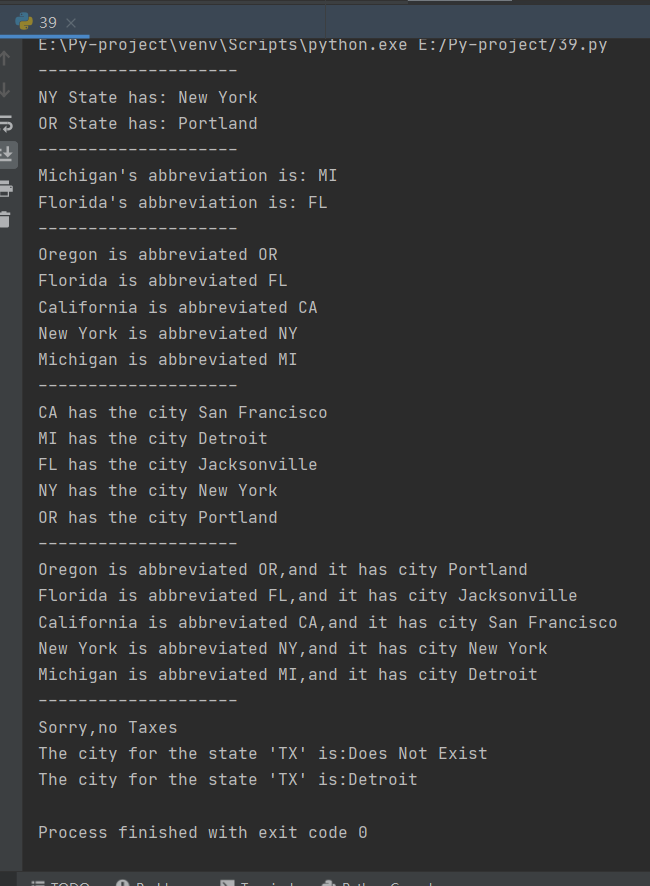
*Python 字典(Dictionary) items() 函数以列表返回可遍历的(键, 值) 元组数组。
*Python 字典(Dictionary) get() 函数返回指定键的值




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号