算法基础(3)
双指针算法 O(n)采用双指针算法的前提是具有单调性
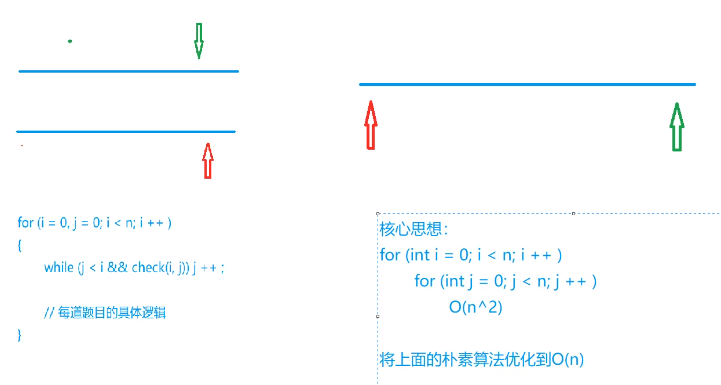
题目:提取单词
#include <iostream> #include <string.h> using namespace std ; const int N = 1e3+10; int main(){ char str[1000]; gets(str); int n = strlen(str); for(int i=0; i<n ; i++) { int j = i; while(j<n && str[j] !=' ') j++ ; for(int k=i; k<j ; k++) cout<<str[k]; cout<<endl; i=j; } return 0; }
最长连续不重复子序列(不是特别理解)
#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int N = 1e6+10; int n; int a[N],s[N]; int main(){ cin>>n ; for(int i=0; i<n;i++ ) cin>>a[i]; int res = 0; for( int i=0,j=0; i<n ; i++ ) { s[a[i]]++ ; while( s[a[i]] > 1 && j<i ) { s[a[j]]--; j++; } res = max(res, i-j+1); } cout<<res<<endl; return 0; }
提取目标和:
请你求出满足 A[i]+B[j]=xA[i]+B[j]=x 的数对 (i,j)(i,j)。
#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int N = 1e6+10; int a[N],b[N]; int main(){ int n,m,x; cin>>n>>m>>x; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i]; for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cin>>b[j]; for(int i=0,j=m-1; i<n || j>=0 ; ) { while( a[i]+b[j]>x ) j-- ; while( a[i]+b[j]<x ) i++ ; if(a[i]+b[j] == x ) { cout<<i<<' '<<j ; break; } } return 0; }
判断子序列:
#include <iostream> using namespace std; const int N = 1e6+10; int a[N],b[N]; int main(){ int n,m; cin>>n>>m; for(int i=0;i<n;i++) cin>>a[i]; for(int j=0;j<m;j++) cin>>b[j]; for(int i=0,j=0; i<n && j<m ; ) { while(a[i]==b[j] && i<n) { i++ ; j++; } while(a[i]!=b[j] && j<m ) j++; if(i==n) { cout<<"Yes"; return 0; } } cout<<"No"; return 0; }
位运算
n的二进制表示中第k位:
(1)先把第k位移到最后一位, x>>k ;
(2)看个位是什么 ; n>>k & 1;
lowbit(x): 返回x的最后一位1,例如10,即1010,返回10;
x & -x = x&(~x + 1)
例题:统计二进制数中的1的个数
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int lowbit(int x ) { return x&-x ; } int main() { int n; cin>>n ; while(n--) { int x; cin>>x ; int cnt = 0; while(x) { x -= lowbit(x) ; cnt++ ; } cout<<cnt<<' ' ; } }
离散化
基本概念:

例题:区间和,难度较大
#include <iostream> #include <vector> #include <algorithm> using namespace std; const int N = 1e6+10; int a[N],s[N]; int n,m; typedef pair<int,int> PII; vector<int> alls; vector<PII> add,query ; int find(int x ) //求离散化的结果 ,二分 { int l =0, r = alls.size()-1 ; while(l<r){ int mid =(l+r)/2; if(alls[mid]>=x) r=mid ; else l = mid+1; } return r+1 ; } int main(){ cin>>n>>m; for(int i=0; i<n;i++) { int x,c; cin>>x>>c; add.push_back({x,c}) ; alls.push_back(x); } for(int i=0;i<m;i++) { int l,r; cin>>l>>r; query.push_back({l,r}); alls.push_back(l); alls.push_back(r); } //去重 sort(alls.begin(), alls.end()) ; alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end()); //处理插入 for( auto item:add) { int x = find(item.first) ; a[x] += item.second ; } //预处理前缀和 for(int i=1; i<=alls.size(); i++) s[i] = s[i-1]+a[i] ; // 处理询问 for( auto item:query) { int l=find(item.first),r=find(item.second) ; cout<<s[r]-s[l-1]<<endl; } return 0; }
PS: 本文来自博客园,作者:尊滴菜,转载请注明原文链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/zundicai/p/17253627.html




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号