地铁路线规划系统
个人项目—地铁路线规划系统设计及实现
问题综述:
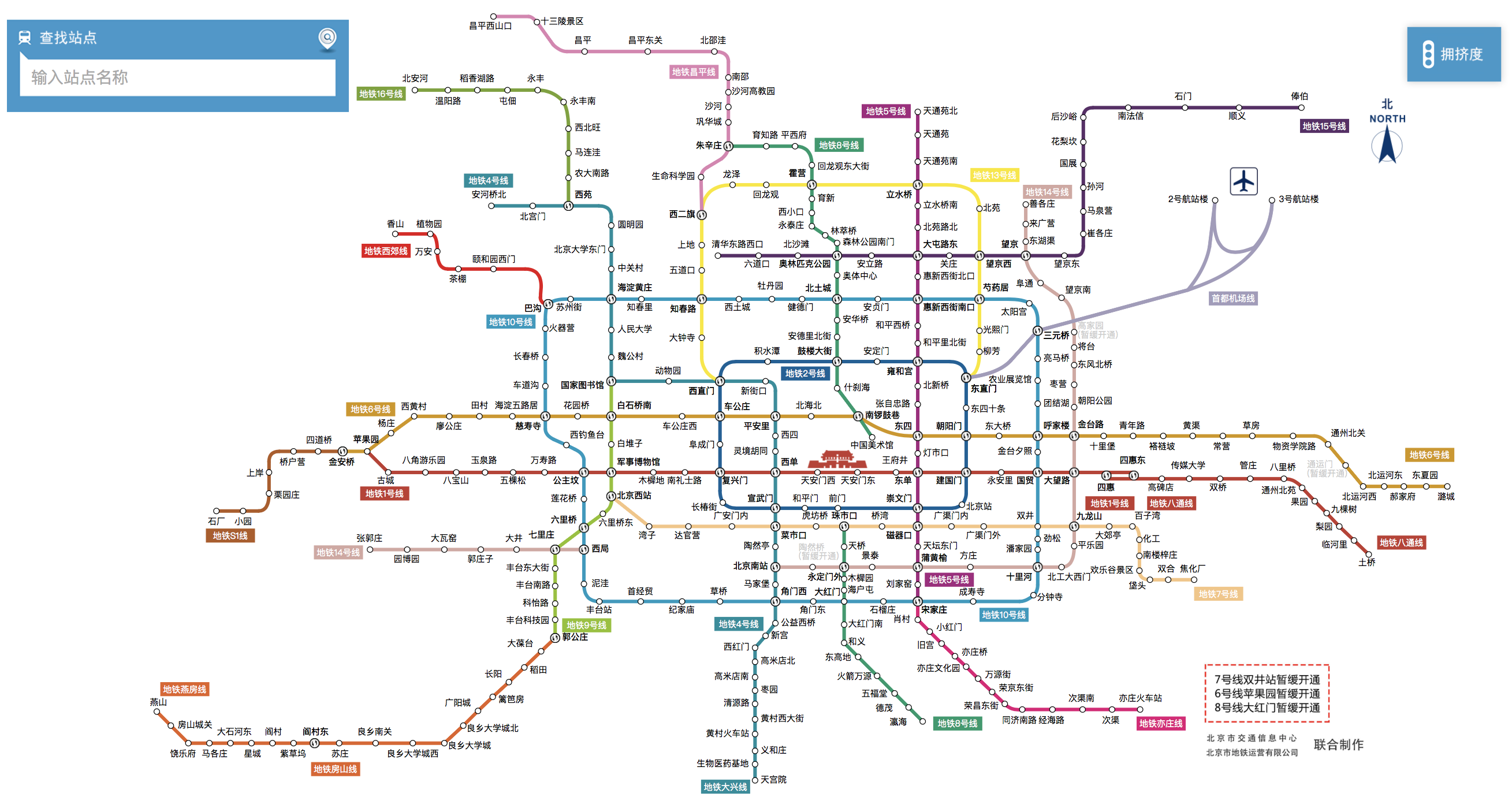
提供一个城市(以北京市为例,如上图地铁线路图所示)的地铁线路图及其相关信息,通过程序计算指定两站之间最短(最少经过站数)乘车路线,输出指定地铁线路的所有站点。首先,将地铁线路信息保存在data.txt中便于理解与使用,具体格式如下:
线路名1 站名1 站名2 站名3 ...
线路名2 站名1 站名2 站名3 ...
线路名3 站名1 站名2 站名3 ...
......
将所有线路名以及站点名都存储在data文件中后,继续之后的功能实现。
需求分析:
- 输入地铁线路名称,显示整条地铁线路站点
- 输入两个地铁站名称,并为其规划最短线路并输出
- 输入某条地铁线路,显示该条线路上的所有站点
- 若输入的线路或站点不存在,显示错误提示
解决思路:
- 实现语言:JAVA
- 收集数据并设计数据存储方式读入数据并构建地铁图的数据结构
- 设计并确定寻找最短路径算法,以广度优先遍历(BFS)算法为核心算法
- 使用测试案例对程序进行debug测试
具体实现:
1 数据存储格式及读取
Json格式是一种轻量级的数据交换格式,相对于xml格式比较简洁且易读,因此本项目采用Json格式存储数据(同时,由此本项目在编程是需要使用额外jar包),具体形式如下:
1 { 2 "lines": [ 3 { 4 "lineNo": 1, 5 "lineName": "1号线", 6 "stations": [ 7 { 8 "stationName": "苹果园" 9 }, 10 { 11 "stationName": "古城" 12 }, 13 ...... 14 ] 15 }, 16 { 17 "lineNo": 2, 18 "lineName": "2号线", 19 "stations": [ 20 { 21 "stationName": "积水潭" 22 }, 23 { 24 "stationName": "鼓楼大街" 25 }, 26 ...... 27 ] 28 }, 29 ...... 30 { 31 "lineNo": 23, 32 "lineName": "西郊线", 33 "stations": [ 34 { 35 "stationName": "香山" 36 }, 37 ...... 38 ] 39 } 40 ] 41 }
将地铁站点数据存放在json文件中,并可利用自建函数readJsonFile读取,其中,readJsonFile函数如下:
1 import java.io.*; 2 3 public class ReadUtil { 4 // 读取json文件 5 public static String readJsonFile(String fileName) { 6 String jsonStr = ""; 7 try { 8 // 打开文件 9 File jsonFile = new File(fileName); 10 FileReader fileReader = new FileReader(jsonFile); 11 Reader reader = new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(jsonFile),"utf-8");// 一般采用utf-8编码规则 12 int ch = 0; 13 StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); 14 while ((ch = reader.read()) != -1) { 15 sb.append((char) ch); 16 } 17 fileReader.close(); 18 reader.close(); 19 jsonStr = sb.toString(); 20 return jsonStr; 21 } catch (IOException e) { 22 e.printStackTrace(); 23 return null; 24 } 25 } 26 }
2 数据结构方法的确定及应用
将地铁线路图中的每个地铁站点看成一个节点,各个节点之间由地铁线路相连,类似于数据结构“图”中边的存在。因此,本项目将地铁各站点与线路之间的关联类比于“图”的关系,并使用数据结构“图”对地铁线路图进行重建,具体实现代码如下:
SubwayGraph类
1 import java.io.File; 2 import java.util.ArrayList; 3 import java.util.HashSet; 4 5 6 public class SubwayGraph { 7 public ArrayList<Station> stations=new ArrayList<>();// 建立站点List 8 public HashSet<Edge> edges=new HashSet<>(); 9 10 public ArrayList<Station> getStation() {// 获取站点并存入List 11 return stations; 12 } 13 14 public int findStation(String stationName){ 15 for(int i=0;i<stations.size();i++){ 16 if (stations.get(i).getStationName().equals(stationName)) 17 return i; 18 } 19 return 0; 20 } 21 22 public int isInV(Station station){ 23 for (int i=0;i<stations.size();i++){ 24 if (stations.get(i).getStationName().equals(station.getStationName())) 25 return i; 26 } 27 stations.add(station); 28 return 0; 29 } 30 31 public void addAdge(int a,int b,int c){ 32 this.edges.add(new Edge(a,b)); 33 } 34 35 public void addStation(String stationName, int lineNo, int change){ 36 // change的值为0表示不可换乘,1表示可换乘 37 int flag=0; 38 if (change == 1) 39 flag=findStation(stationName); 40 if (flag == 0) 41 stations.add(new Station(stationName)); 42 } 43 44 public int hashCode() { 45 final int prime = 31; 46 int result = 1; 47 long temp; 48 temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(x); 49 result = prime * result + (int) (temp ^ (temp >>> 32)); 50 temp = Double.doubleToLongBits(y); 51 result = prime * result + (int) (temp ^ (temp >>> 32)); 52 return result; 53 } 54 55 public void addEdge(int u,int v){ 56 this.edges.add(new Edge(u,v)); 57 } 58 59 public boolean equals(Object obj) { 60 if (this == obj) 61 return true; 62 if (obj == null) 63 return false; 64 if (getClass() != obj.getClass()) 65 return false; 66 MapNode other = (MapNode) obj; 67 if (Double.doubleToLongBits(x) != Double.doubleToLongBits(other.x)) 68 return false; 69 if (Double.doubleToLongBits(y) != Double.doubleToLongBits(other.y)) 70 return false; 71 return true; 72 } 73 public HashSet<Edge> getEdges(){ 74 return edges; 75 } 76 }
Edge类
1 public class Edge { 2 private int u; 3 private int station; 4 public Edge(int u,int station){ 5 this.u=u; 6 this.station=station; 7 } 8 public int getU() { 9 return u; 10 } 11 12 public void setU(int u) { 13 this.u = u; 14 } 15 16 public int getStation() { 17 return station; 18 } 19 20 public void setStation(int station) { 21 this.station = station; 22 } 23 }
Station类
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 import java.util.HashSet; 3 4 public class Station { 5 private String stationName; 6 private HashSet<Integer> line; 7 public Station(String stationName){ 8 this.stationName=stationName; 9 line=new HashSet<>(); 10 } 11 12 public String getStationName() { 13 return stationName; 14 } 15 16 public void setStationName(String stationName) { 17 this.stationName = stationName; 18 } 19 20 public HashSet<Integer> getLine() { 21 return line; 22 } 23 24 public void addLine(int no) { 25 this.line.add(no); 26 } 27 }
Line类
1 import java.util.ArrayList; 2 3 public class Line { 4 private int lineNo; 5 private String lineName; 6 private ArrayList<Station> stations=new ArrayList<>(); 7 8 public int getLineNo() { 9 return lineNo; 10 } 11 12 public void setLineNo(int lineNo) { 13 this.lineNo = lineNo; 14 } 15 16 public String getLineName() { 17 return lineName; 18 } 19 20 public void setLineName(String lineName) { 21 this.lineName = lineName; 22 } 23 24 public ArrayList<Station> getStations() { 25 return stations; 26 } 27 28 public void addStations(Station station) { 29 this.stations.add(station); 30 } 31 }
3 类职责分析
| 类名 | 方法名 | 功能职责分析 |
| SubwayGraph | findStation(String stationName) | 通过站点名寻找已存储的站点 |
| addStation(String stationName, int lineNo, int change) | 添加站点信息,站点信息包括站点名,所属线路编号和是否可以换乘 | |
| addEdge(int u,int v) | 在图中添加对应于站点的节点 | |
| Edge | Edge(int u,int station) | 在图中对应站点 |
| getU() | 通过输入获取线路信息并先存着 | |
| setU(int u) | 使用线路信息 | |
| getStation() | 通过输入获取站点信息并先存着 | |
| setStation(int station) | 使用站点信息 | |
| Station | Station(String stationName) | 站点名 |
| getStationName() | 获取站点名 | |
| setStationName(String stationName) | 将站点名压入数组 | |
| addLine(int no) | 通过json文件读取将站点添加到对应的线路中 | |
| Line | getLineNo() | 通过输入获取线路编号并先存着 |
| setLineNo(int lineNo) | 将线路压入数组 | |
| getLineName() | 获取线路编号 | |
| setLineName(String lineName) | 将线路名压入数组 | |
| addStations(Station station) | 通过json文件读取添加站点 |
4 最短路径算法的设计与实现
在本项目中,使用使用广度优先遍历(BFS)来寻找最短路径。BFS算法虽然没有dijkstra算法那么完善,但是足以满足寻找两点之间的最短路径值。并将两站点之间的距离换乘不在考虑范围之内,简化了题目的难度。BFS算法的具体实现如下。
1)主函数
1 public class subway { 2 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 3 ArrayList<Line> lines=new ArrayList<>(); 4 SubwayGraph graph=new SubwayGraph(); 5 String outputFileName=null; 6 String startStation=null; 7 String endStation=null; 8 String line=null; 9 SubwayManager a=new SubwayManager(); 10 System.out.println(args.length); 11 for (int i=0;i<args.length;i++){ 12 if (args[i].equals("-map")){ 13 String fileName=args[i+1]; 14 15 lines=a.getLines(fileName); 16 graph=a.createGraph(lines); 17 i++; 18 } 19 else if (args[i].equals("-a")){ 20 line=args[i+1]; 21 i++; 22 } 23 else if (args[i].equals("-b")){ 24 startStation=args[i+1]; 25 i++; 26 endStation=args[i+1]; 27 i++; 28 } 29 else if (args[i].equals("-o")){ 30 outputFileName=args[i+1]; 31 i++; 32 } 33 else throw new Exception("输入无效参数"); 34 } 35 if (line!=null){ 36 ArrayList<String> list = new ArrayList<>(); 37 for (Line i:lines){ 38 if (i.getLineName().equals(line)){ 39 list.add(i.getLineName()); 40 for (Station station:i.getStations()){ 41 list.add(station.getStationName()); 42 } 43 } 44 } 45 a.outputFile(list, outputFileName); 46 }else if (startStation!=null&&endStation!=null){ 47 ArrayList<Station> plan= a.Plan(graph,startStation,endStation); 48 ArrayList<String> list = a.getChange(plan, lines); 49 a.outputFile(list, outputFileName); 50 } 51 } 52 }
2)读取Json文件
1 public ArrayList<Line> getLines(String fileName) { 2 ArrayList<Line> lines = new ArrayList<>(); 3 String path = this.getClass().getResource("/" + fileName).getPath(); 4 JSONObject jobj = JSON.parseObject(ReadUtil.readJsonFile(path)); 5 JSONArray Jlines = jobj.getJSONArray("lines"); 6 for (int i = 0; i < Jlines.size(); i++) { 7 JSONObject Jline = (JSONObject) Jlines.get(i); 8 int lineNo = Jline.getInteger("lineNo"); 9 String lineName = Jline.getString("lineName"); 10 JSONArray Jstations = Jline.getJSONArray("stations"); 11 Line line = new Line(); 12 line.setLineName(lineName); 13 line.setLineNo(lineNo); 14 for (int j = 0; j < Jstations.size(); j++) { 15 JSONObject station = Jstations.getJSONObject(j); 16 line.addStations(new Station(station.getString("stationName"))); 17 } 18 lines.add(line); 19 } 20 return lines; 21 }
3)BFS核心代码
1 public static boolean bfs(Epax start, Epax end) { 2 LinkedList<Epax> queue = new LinkedList<>(); 3 queue.addLast(start); 4 while (!queue.isEmpty()) { 5 Epax vertex = queue.pollFirst(); // 从队首取出一个元素 6 if (vertex.isSerched()) {// 如果这个顶点已经完成过检索,则continue跳过 7 continue; 8 } 9 if (vertex == end) {// 如果到了终点,则可以返回了 10 return true; 11 } 12 else {// 如果取出的元素还不是终点,则把该顶点可以到达的邻居顶点全部添加到队尾 13 for (Epax next : vertex.getNext()) { 14 if (next.getPredecessor() == null && next != start) { 15 next.setPredecessor(vertex); 16 } 17 queue.addLast(next); 18 } 19 } 20 vertex.setSerched(true); 21 } 22 return false; 23 }
4)出行方案制定
1 public ArrayList<Station> Plan( SubwayGraph graph,String startSation,String endSation) { 2 ArrayList<Station> plan=null; 3 int a=graph.findStation(startSation); 4 int b=graph.findStation(endSation); 5 if (a==-1||b==-1){ 6 System.out.println("no Station"); 7 }else { 8 plan=DIJ(graph,a,b); 9 } 10 return plan; 11 }
5)保存结果
1 public void outputFile(ArrayList<String> list, String ouputfile) { 2 try { 3 // 相对路径,如果没有则要建立一个新的output.txt文件 4 File writeName = new File(ouputfile); 5 // 创建新文件,有同名的文件的话直接覆盖 6 writeName.createNewFile(); 7 try (FileWriter writer = new FileWriter(writeName); 8 BufferedWriter out = new BufferedWriter(writer) 9 ) { 10 int lineNo = -1; 11 for (String i : list) { 12 out.write(i + "\r\n"); 13 } 14 out.flush(); // 把缓存区内容压入文件 15 } 16 } catch (IOException e) { 17 e.printStackTrace(); 18 } 19 }
5 对项目程序进行debug测试
使用测试案例对程序进行检验,其中,输出结果输入结果第一行统计一共需要乘坐几个站点,如7(则需要经过7个站点),之后输出经过的站点。若需要换乘,则输出换乘信息。
(无换乘)测试案例
古城 复兴门
结果
11
古城
八角游乐园
八宝山
玉泉路
五棵松
万寿路
公主坟
军事博物馆
木樨地
南礼士路
复兴门
(有换乘)测试案例
万寿路 北京西站
结果
6
万寿路
公主坟
地铁10号线
莲花桥
六里桥
地铁9号线
六里桥东
北京西站
6 个人总结
本项目简要复习了数据结构和java项目设计的基本流程。





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号