个人项目作业
1、项目地址:
https://github.com/ztyh30/wordCount
2、Word Count项目要求:
wc.exe 是一个常见的工具,它能统计文本文件的字符数、单词数和行数。这个项目要求写一个命令行程序,模仿已有wc.exe 的功能,并加以扩充,给出某程序设计语言源文件的字符数、单词数和行数。
实现一个统计程序,它能正确统计程序文件中的字符数、单词数、行数,以及还具备其他扩展功能,并能够快速地处理多个文件。
具体功能要求:
程序处理用户需求的模式为:
wc.exe [parameter] [file_name]
基本功能列表:
wc.exe -c file.c //返回文件 file.c 的字符数
wc.exe -w file.c //返回文件 file.c 的词的数目
wc.exe -l file.c //返回文件 file.c 的行数
扩展功能:
-s 递归处理目录下符合条件的文件。
-a 返回更复杂的数据(代码行 / 空行 / 注释行)。
空行:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符,例如“{”。
代码行:本行包括多于一个字符的代码。
注释行:本行不是代码行,并且本行包括注释。一个有趣的例子是有些程序员会在单字符后面加注释:
} //注释
在这种情况下,这一行属于注释行。
[file_name]: 文件或目录名,可以处理一般通配符。
高级功能:
-x 参数。这个参数单独使用。如果命令行有这个参数,则程序会显示图形界面,用户可以通过界面选取单个文件,程序就会显示文件的字符数、行数等全部统计信息。
3、实现功能:
-c:返回文件的字符数
-w: 返回文件的单词数
-l:返回文件的行数
-a:返回文件的代码行,注释行,空行
-s:递归处理目录下符合条件的文件,并输出每个文件所有结果
4、预计开发时间psp
|
PSP2.1 |
Personal Software Process Stages |
预估耗时(分钟) |
实际耗时(分钟) |
|
Planning |
计划 |
|
|
|
· Estimate |
· 估计这个任务需要多少时间 |
30 |
30 |
|
Development |
开发 |
|
|
|
· Analysis |
· 需求分析 (包括学习新技术) |
120 |
180 |
|
· Design Spec |
· 生成设计文档 |
20 |
10 |
|
· Design Review |
· 设计复审 (和同事审核设计文档) |
10 |
5 |
|
· Coding Standard |
· 代码规范 (为目前的开发制定合适的规范) |
30 |
20 |
|
· Design |
· 具体设计 |
30 |
20 |
|
· Coding |
· 具体编码 |
480 |
630 |
|
· Code Review |
· 代码复审 |
60 |
90 |
|
· Test |
· 测试(自我测试,修改代码,提交修改) |
60 |
40 |
|
Reporting |
报告 |
|
|
|
· Test Report |
· 测试报告 |
30 |
45 |
|
· Size Measurement |
· 计算工作量 |
20 |
20 |
|
· Postmortem & Process Improvement Plan |
· 事后总结, 并提出过程改进计划 |
30 |
20 |
|
合计 |
|
920 |
1110 |
5、思路:
通过Java的输入流读取文件,使用String类的各种api来实现各种功能。由于对Java不是很了解,故在菜鸟教程上学习了Java的用法等。
6、设计实现过程:
wc有两个类组成,一个是wc实现类,一个是测试类。实现类中一个函数对应一个功能,由主函数通过输入来调用各个函数。测试类通过junit实现单元测试。
函数:
characterCount(String file) : 统计字符数
lineCount(String file) :统计行数
wordCount(String file) :统计单词数
otherCount(String file) :统计代码行,注释行,空行
searchFileList(String path) :实现文件递归查询
traverseList(String fileName) : 实现对一个文件夹里所有文件执行以上所有函数
7、代码说明:
1.统计字符数
注意要去掉空格的影响
public static int characterCount(String file){ int character = 0; //字符数 String s = ""; BufferedReader br = null; try { br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(new File(file)))); while((s = br.readLine())!=null){ s = s.replaceAll(" ",""); character += s.length(); } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(br != null){ try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return character; }
2.统计单词数
对单词的定义:一个或连续的英文字母
通过正则表达式判断,我的判断标准: sdas/sdsad 算是两个单词,而不是一个
public static int wordCount(String file){ int word = 0; //单词 String s = ""; BufferedReader br = null; try { br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(new File(file)))); Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile("[a-zA-Z]+");//连续字母即为单词 while((s = br.readLine()) != null){ Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(s); while(matcher.find()){ word++; } } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(br != null){ try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return word;
}
3.统计行数
如果readLine()方法实现
public static int lineCount(String file){ int line = 0; //行数 String s = ""; BufferedReader br = null; try { br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(new File(file)))); while((s = br.readLine()) != null){ line++; } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(br != null){ try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } return line; }
4.统计代码行,注释行,空行
注释行:// }// /* */ 注意,必须以*/结尾在标记着注释行结束
空行:本行全部是空格或格式控制字符,如果包括代码,则只有不超过一个可显示的字符,例如“{”
通过String类的各种api,来实现判断
特别注意/* */这种注释行,通过flag标记,来判断/*的开始与*/结束,我的判断方式中,只有以*/结尾才使flag为false,其它不在末尾的*/不认为是注释结束
public static String otherCount(String file){ int spaceline = 0; //空行 int codeline = 0; //代码行 int noteline = 0; //注释行 boolean flag = false; //标记 String s = ""; BufferedReader br = null; try { br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(new FileInputStream(new File(file)))); while((s = br.readLine()) != null){ if(flag == false){ if(s.contains("/*") && !s.contains("*/")){ flag = true; } if(s.trim().indexOf("//") == 0 || s.trim().indexOf("}//") == 0 || s.trim().indexOf("/*") == 0){ noteline++; } else if(s.trim().length() > 1){ codeline++; } else{ spaceline++; } }else{ if(s.indexOf("*/") == s.length()-2){ flag = false; } noteline++; } } } catch (FileNotFoundException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } finally { if(br != null){ try { br.close(); } catch (IOException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } } } String result = spaceline+","+noteline+","+codeline; return result; }
5.递归处理文件夹,把文件加入到集合中
通过file.isDirectory() 判断是否是文件夹,如果是,则递归处理
如果是可读文件,则加入集合
public static List<String> searchFileList(String s){ File file = new File(s); File[] files = file.listFiles(); if(files == null || files.length == 0){ System.out.println("ERROR"); return null; }else{ for(File f : files){ if(f.isDirectory()){ searchFileList(f.getAbsolutePath());//递归处理 }else if(f.canRead() && f.isFile()){ fileList.add(f.getAbsolutePath());//如果是文件,则加入集合 }else{ continue; } } } return fileList; }
6.对文件集合进行处理
通过 searchFileList() 获得文件集合,并调用以上函数
public static void traverseList(String filename) { List<String> fileList = new ArrayList<>(); fileList = searchFileList(filename); if(fileList == null){ System.out.println("ERROR"); return; } for (String s : fileList) { int characters = 0; int wordCount = 0; int lineCount = 0; characters = characterCount(s); wordCount = wordCount(s); lineCount = lineCount(s); String str = otherCount(s); String[] arr = str.split(","); System.out.println("文件" + s + "的信息如下:"); System.out.println("字符总数:" + characters); System.out.println("单词总数:" + wordCount); System.out.println("总行数:" + lineCount); System.out.println("空行数:" + arr[0]); System.out.println("代码行数:" + arr[2]); System.out.println("注释总行数:" + arr[1]); } }
8、测试运行:
-c
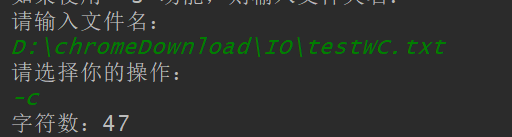
-l
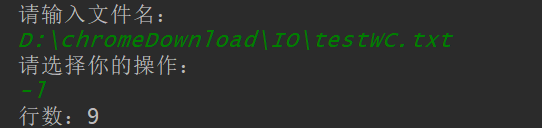
-w
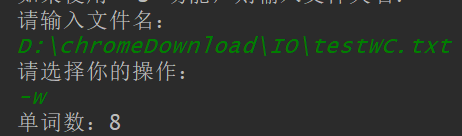
-a
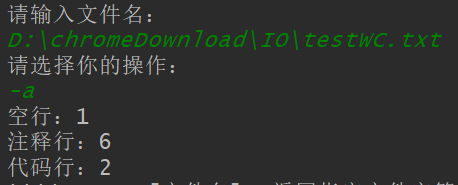
测试文件:

测试递归处理文件夹:
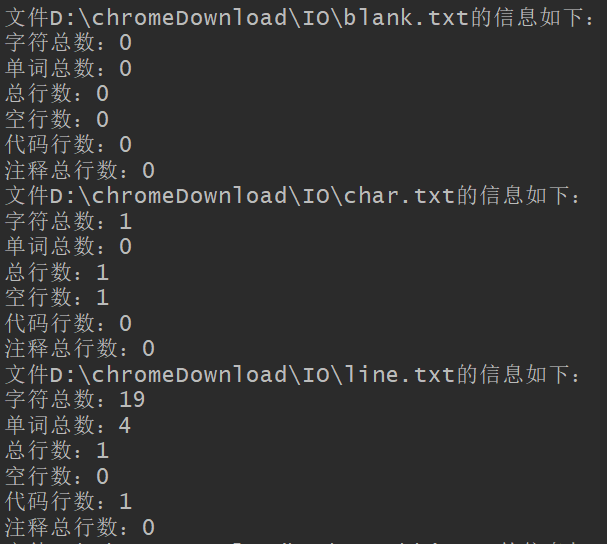
覆盖率:
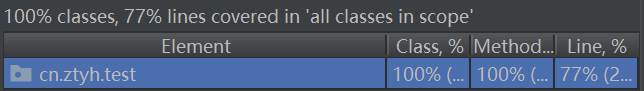
测试文件:
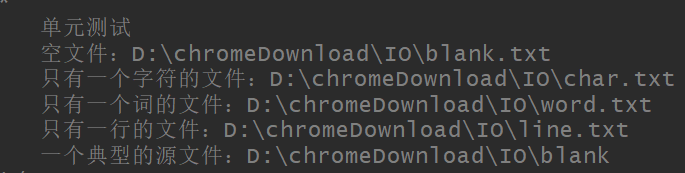
9、总结:
遇到问题:对Java语言的不熟练,如输入流,String类的api,单元测试等,需要花费大量时间去学习。由于缺少开发经验,项目的代码结构很混乱,并且代码冗余。
没有很好地计划,从而开发过程中没有一个好的指导,感觉很杂乱无章。同时,项目的各种功能并没有很好地进行测试。
这次给我的感受就是要做好计划,没有计划,一切都很混乱,开发前的构思比开发重要。要预留多余的时间,实际开发花费的时间比预想的要多许多。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号