#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<set>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
/*
前置知识:
对于函数类型,非重写隐藏,重写(virtual)覆盖
对于变量,是隐藏
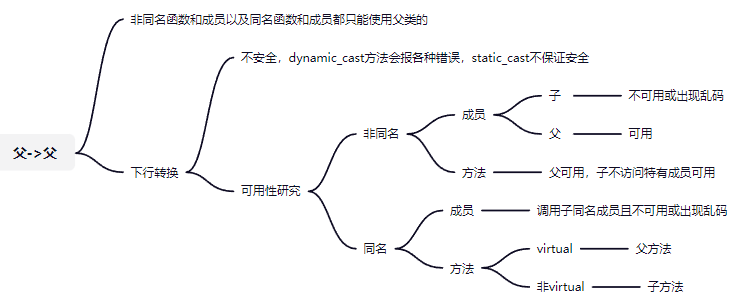
被隐藏的属性,在子类被强制转换成父类后,访问的是父类中的属性
被覆盖的方法,在子类被强制转换成父类后,调用的还是子类自身的方法
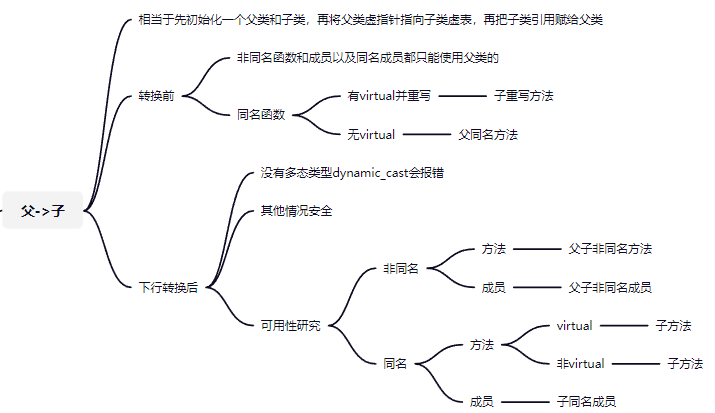
子类转父类后能访问的函数是其他父类所有函数,父类非虚函数(父无virtual)或子类重写函数(父有virtual),(隐藏被展开,重写被覆盖)
父类转子类后能访问到的是其他两类所有函数,父类虚函数(有virtual)或子类同名函数(无virtual)。子类的虚函数并没有隐藏父类的所以访问到的是父类虚函数。
*/
class parent
{
public:
parent(){cout<<"parent created"<<endl;}
void func() {cout<<"parent"<<endl;}
void parels(){cout<<"parent else\n"<<endl;}
};
class child : public parent
{
private:
int nums = 114514;
public:
child(){cout<<"child created"<<endl;}
void func()
{
cout<<"child"<<endl;
cout<<nums<<endl;
}
void sonels(){cout<<"child else\n"<<endl;}
};
//1.基本类型转换可行性
void pointer_change()
{
void* ptr;
int* ptr2=new int(1919);
try
{
static_cast<int*>(ptr);
reinterpret_cast<int*>(ptr);
//const_cast<int*>(ptr);失败
//dynamic_cast<int*>(ptr);失败
reinterpret_cast<void*>(ptr2);
static_cast<void*>(ptr2);
//const_cast<void*> (ptr2);失败
//dynamic_cast<void*>(ptr2);失败
const int* ptr_const_lim = const_cast<int*> (ptr2);
}
catch(...)
{
throw std::exception();
}
}
//2.基类转换精度
void static_base()
{
double lim_test_double = 1.259;
cout<<lim_test_double<<endl;
//static先int后double
int lim_test_int = static_cast<int> (lim_test_double);
double lim_test_double2 = static_cast<double>(lim_test_int);
cout<<lim_test_int<<endl;
cout<<lim_test_double2<<endl;
//结果:转换完成后精度丢失
}
void reinterpret_base()
{
double lim_test_double = 1.259;
cout<<lim_test_double<<endl;
//reinterpret先int后double,转换的是指针类
int* lim_test_int = reinterpret_cast<int*> (&lim_test_double);
double* lim_test_double2 = reinterpret_cast<double*>(lim_test_int);
cout<<*lim_test_int<<endl;
cout<<*lim_test_double2<<endl;
//结果:转换为int后结果混乱,再转为double完成后精度不丢失[1]
}
/*前置知识:
基类指针new子类,指针直接不能访问子类的方法,
但是同名函数写成一个虚函数,就能用来调用各种派生类方法,
这就是继承的优越性。
*/
//基类指针new子类
void parent_to_child()
{
parent* ptr = new child();
ptr->func();
/*
情况:
父无子任意:输出父方法
父virtual子任意:输出子方法
*/
}
//父子转换
//static下行转换
void satic_func_down()
{
//parent* ptr = new parent();
parent* ptr = new child();
ptr->func();
//static下行转换,不安全,如果Parent指针并没有实际指向一个Child对象,这个转换仍然会成功,但是结果是未定义的[2]。
child* ptrc = static_cast<child*>(ptr);
ptrc->parels();
ptrc->func();
/*情况:
父virtual子任意:父转子访问父,但是如果父类指针指子类,会调用子类方法(两次都调用子方法)
父无子无:父转子访问子,但是可能出现上述错误,但是如果父类指针指子类,会直接调用子类方法(第一次父方法,第二次子方法且不出现错误)
父无子virtual: 无继承无隐藏,段错误,但是如果父类指针指子类,会直接调用子类方法(第一次父方法,第二次子方法且不出现错误)
*/
}
//static上行转换
void satic_func_up()
{
child* ptr = new child();
//child* ptr = new parent(); 错误!禁止子类指针指向基类
ptr->func();
//static上行转换,安全
parent* ptrc = static_cast<parent*>(ptr);
//ptrc->parels();
ptrc->func();
/*情况:
父无子任意:子转父访问父,调用被隐藏父方法
父virtual自任意:子转父访问子,调用被重写方法
*/
}
//dynamic下行转换
void dynamic_func_down()
{
parent* ptr = new child();
//parent* ptr = new parent(); //错误! dynamic_cast会进行安全判定[3],如果非安全会返回0,此时父指针指向父类,不安全
ptr->func();
//dynamic下行转换,安全
//child* ptrc = dynamic_cast<child*>(ptr);
/*运行时 dynamic_cast 的操作数必须包含多态类类型*/
//ptrc->func();
//ptrc->parels();
/*情况:同上括号内*/
}
//const转换
void show_const()
{
int* const_show_int = new int(20);
const int* const_show_int2 = const_cast<const int*>(const_show_int); // 转换为常量指针
*const_show_int = 3;
//*const_show_int2 = 4; // 不能修改
std::cout<<*const_show_int<<std::endl;
std::cout<<*const_show_int2<<std::endl;
std::cout<<const_show_int<<std::endl;
std::cout<<const_show_int2<<std::endl; //但是两者指向的地址是一致的,也就是说可以用前者来修改后者的const
//将常量指针转为非常量
parent con_ptr;
const parent* con_p = &con_ptr;
parent* con_p1 = const_cast<parent*>(con_p);
//将指针常量转换为非指针常量
parent* const lim_con = &con_ptr;
parent* lim_con1 = const_cast<parent*>(lim_con);
//将常量指针常量转换为非常量指针常量或指针常量或者常量指针。
const parent* const concon_ptr = &con_ptr;
parent* concon_ptr1 = const_cast<parent*>(concon_ptr);
const parent* concon_ptr2 = const_cast<parent*>(concon_ptr);
parent* const concon_ptr3 = const_cast<parent*>(concon_ptr);
}
int main()
{
//pointer_change();
/*-------------------------------*/
//static_base();
//reinterpret_base();
/*-------------------------------*/
//parent_to_child();
/*-------------------------------*/
satic_func_down();
//satic_func_up();
//dynamic_func_down();
/*-------------------------------*/
//show_const();
return 0;
}
//拓展知识
/*
[1]reinterpret_cast原理:
reinterpret_cast编译不会产生任何CPU指令,它是一个编译时指令,
也就是说它的原理是在编译时将表达式的二进制段直接视为被强转的类型进行转换
所以不会对二进制段进行操作,因此不掉精度。
*/
/*
[2]强转的大致原理、virtual的大致原理:
本质来说,static_cast类似于隐式强转
对于基本类型来说,就是直接的取模舍弃高位,所以char(1byte)转int(4byte)总是成功,反过来则精度丢失
对于对象类,自己一个猜想:C的继承可以由结构体嵌套大概实现,从而子类的实例的内存大于基类,因此允许父类指针指向子类。
但是由于是父类指针,指向的空间只有父类的部分,因此一开始不允许调用子类方法(猜的,有机会汇编验证)
那么父函数写成virtual怎么就又能用了呢?
先贴个严鸽鸽的文章:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/563418849
类的函数自身是不占类空间的,但是虚函数会让类多出一个虚函数指针和虚表,
那么子类也会多出这个虚表,初始指向函数地址和父类一致,当重写之后,就会指向重写的地址,多出的指针就能够交给子类实现自身同名函数(为了固定形式)
因此new出来的指针可以直接调用子类方法。
*/
/*[4]---dynamic_cast<>禁止基类转换,是很严格的转换
执行安全检查,由RTTI(Run Time Type Identification运行时类型识别)实现:
RTTI简介:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_34489443/article/details/102470944
*/
/*
[5]多继承的情况:
在多继承情况下,有多少个基类就有多少个虚函数表指针,前提是基类要有虚函数才算上这个基类。
注意:
1.子类虚函数会覆盖每一个父类的每一个同名虚函数。
2.父类中没有的虚函数而子类有,填入第一个虚函数表中,且用父类指针是不能调用。
3.父类中有的虚函数而子类没有,则不覆盖。仅子类和该父类指针能调用。
使用某个父类指向子类,就不能调用另一个父类的实方法
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_36359022/article/details/81870219
虚函数表在代码的.rodata段(只读数据区)
*/








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号