JAVA内存划分
java的内存划分为5个部分:
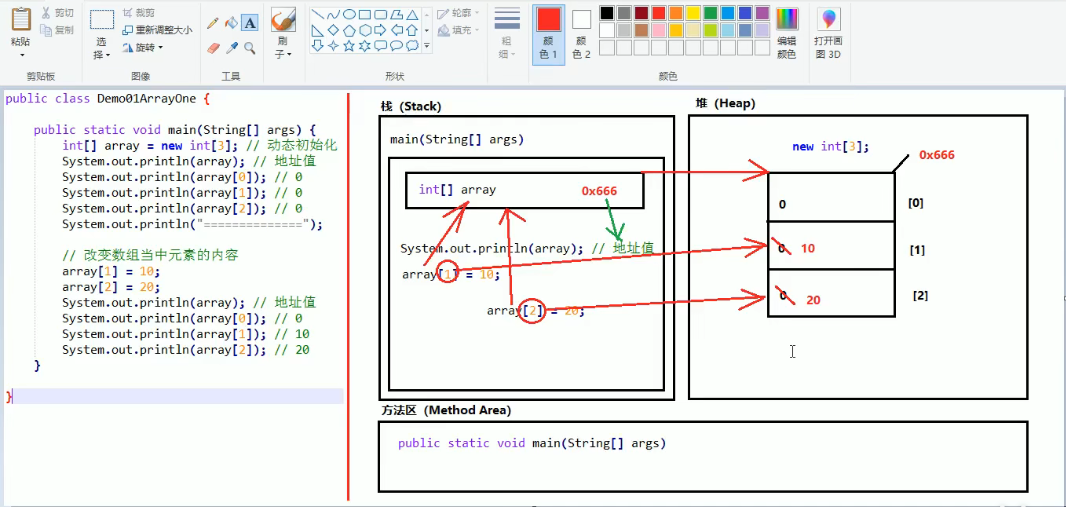
1、栈(stack):存放的都是方法中的局部变量。方法的运行一定要在栈当中
局部变量:方法的参数,或者是方法体{}中内部的变量
作用域:一旦超出作用域,立刻从栈内存中消失
2、堆(Heap):凡是new出来的东西,都在堆当中
堆内存里面的东西都有一个地址值:16进制
堆内存里面的数据,都有一个默认值。规则:
基本数据:整型,默认0;
浮点型,默认为0.0;
字符型,默认为‘\u0000’
布尔型,默认为false
引用类型数据:字符串、数组、对象,默认为null
3、方法区(Method Area):储存.class相关信息,包含方法的信息;
4、本地方法栈(Native Method Stack):与操作系统相关。
5、寄存器(pc Register):与CPU相关
一、数组:
1、一个数组的情况
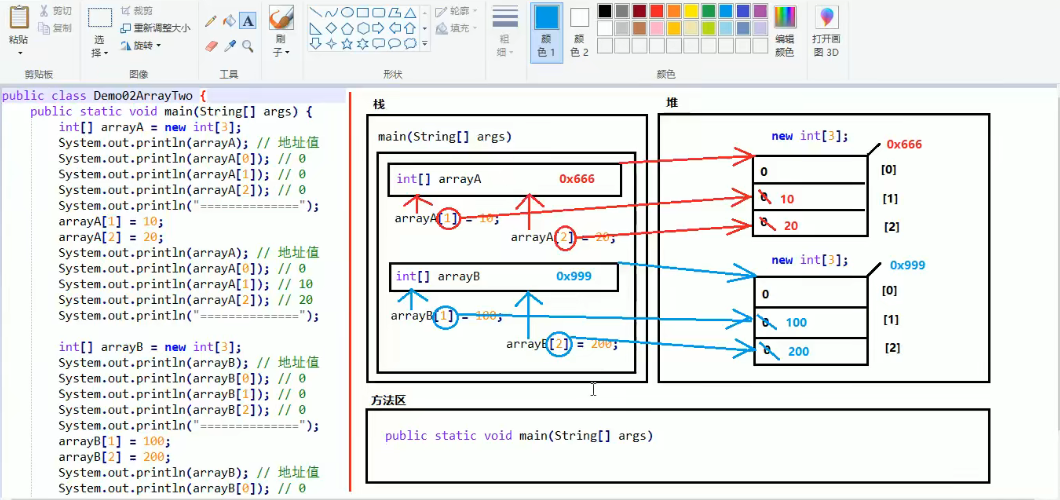
2、两个数组的情况
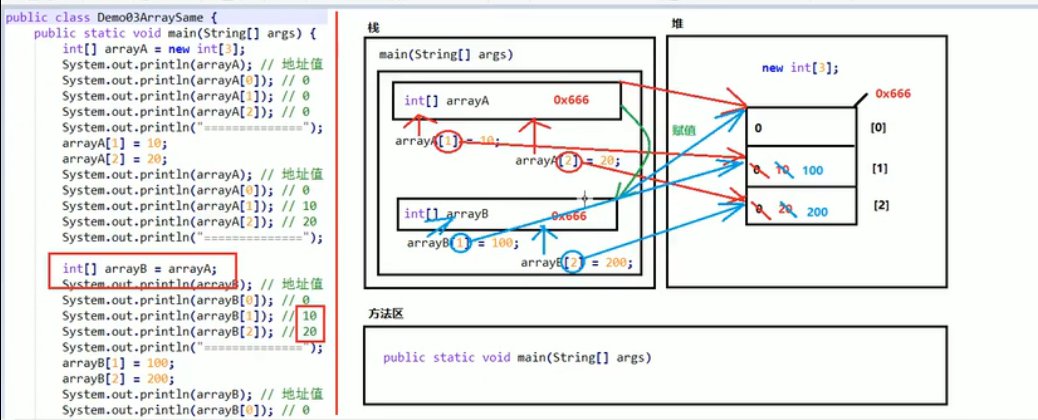
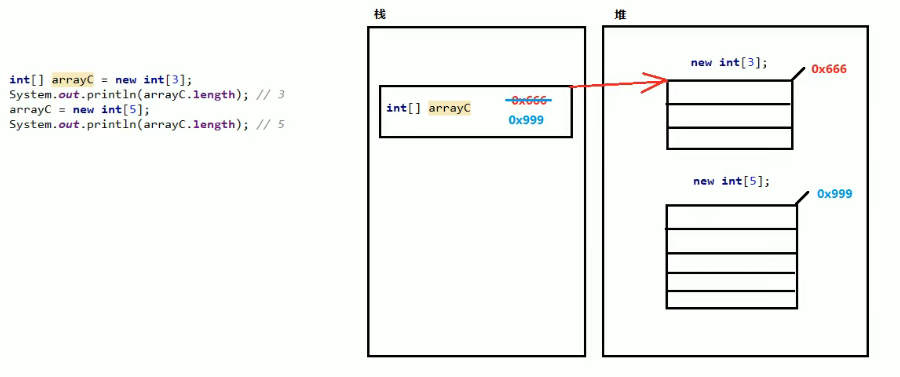
二、两个引用指向同一个数组的内存图
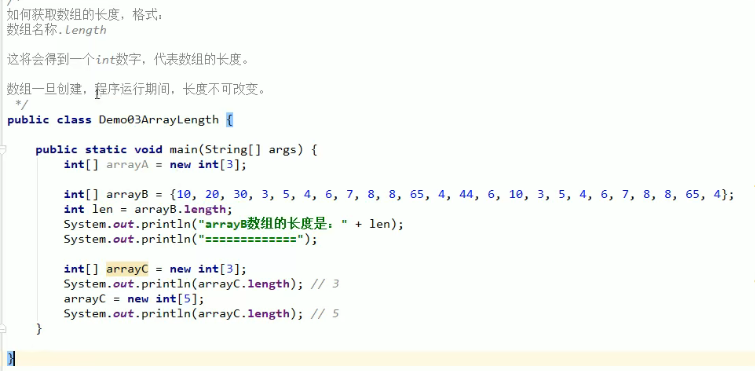
数组一旦new创建,在程序运行期间,长度不可改变
三、对象
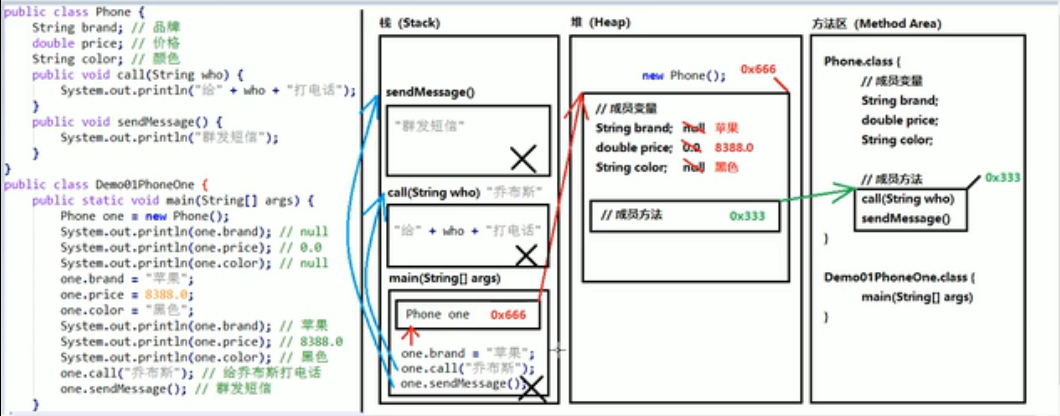
1、一个对象的内存图
public class Phone {
// 成员变量
String brand; // 品牌
double prince; // 价格
String color; // 颜色
// 成员方法
public void call(String who) {
System.out.println("给打" + who + "电话");
}
public void sendMessage() {
System.out.println("群发短信");
}
}
public class Demo01PhoneOne {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone one = new Phone();
System.out.println(one.brand); // null
System.out.println(one.prince); // 0.0
System.out.println(one.color); // null
System.out.println("=============");
one.brand = "苹果";
one.prince = 8388.0;
one.color = "黑色";
System.out.println(one.brand); // 苹果
System.out.println(one.prince); // 8388.0
System.out.println(one.color); // 黑色
System.out.println("=============");
one.call("乔布斯");
one.sendMessage();
}
}
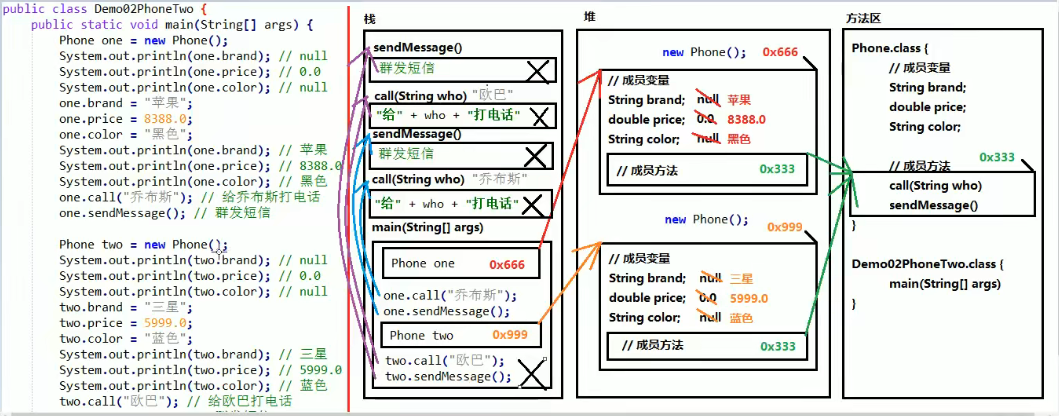
2、两个对象使用同一个方法区内存
public class Phone {
// 成员变量
String brand; // 品牌
double prince; // 价格
String color; // 颜色
// 成员方法
public void call(String who) {
System.out.println("给打" + who + "电话");
}
public void sendMessage() {
System.out.println("群发短信");
}
}
public class Demo02PhoneTwo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone one = new Phone();
System.out.println(one.brand); // null
System.out.println(one.prince); // 0.0
System.out.println(one.color); // null
System.out.println("=============");
one.brand = "苹果";
one.prince = 8388.0;
one.color = "黑色";
System.out.println(one.brand); // 苹果
System.out.println(one.prince); // 8388.0
System.out.println(one.color); // 黑色
System.out.println("=============");
one.call("乔布斯");
one.sendMessage();
System.out.println("============================");
Phone two = new Phone();
System.out.println(two.brand); // null
System.out.println(two.prince); // 0.0
System.out.println(two.color); // null
System.out.println("=============");
two.brand = "三星";
two.prince = 5999.0;
two.color = "蓝色";
System.out.println(two.brand); // 三星
System.out.println(two.prince); // 5999.0
System.out.println(two.color); // 蓝色
System.out.println("=============");
two.call("欧巴");
two.sendMessage();
System.out.println("============================");
}
}
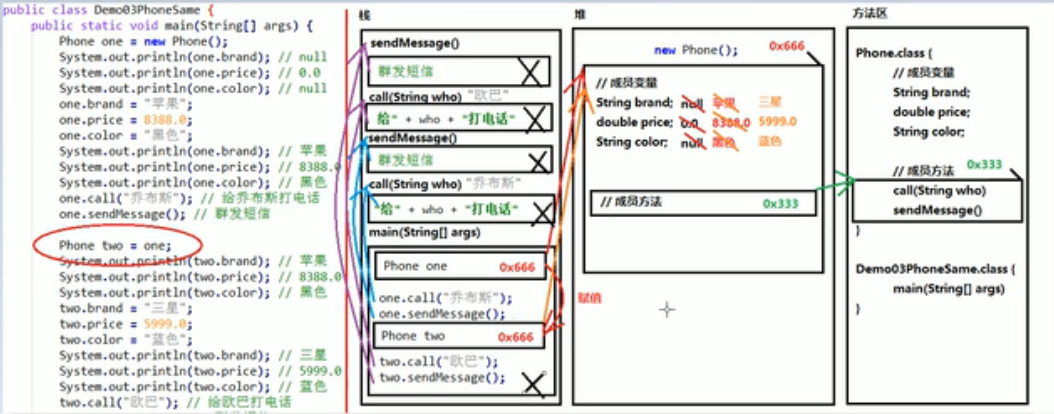
3、两个引用变量指向同一个对象
public class Demo03PhoneThree {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone one = new Phone();
System.out.println(one.brand); // null
System.out.println(one.prince); // 0.0
System.out.println(one.color); // null
System.out.println("=============");
one.brand = "苹果";
one.prince = 8388.0;
one.color = "黑色";
System.out.println(one.brand); // 苹果
System.out.println(one.prince); // 8388.0
System.out.println(one.color); // 黑色
System.out.println("=============");
one.call("乔布斯");
one.sendMessage();
System.out.println("============================");
Phone two = one;
System.out.println(two.brand); // 苹果
System.out.println(two.prince); // 8388.0
System.out.println(two.color); // 黑色
System.out.println("=============");
two.brand = "三星";
two.prince = 5999.0;
two.color = "蓝色";
System.out.println(two.brand); // 三星
System.out.println(two.prince); // 5999.0
System.out.println(two.color); // 蓝色
System.out.println("=============");
two.call("欧巴");
two.sendMessage();
System.out.println("============================");
}
}
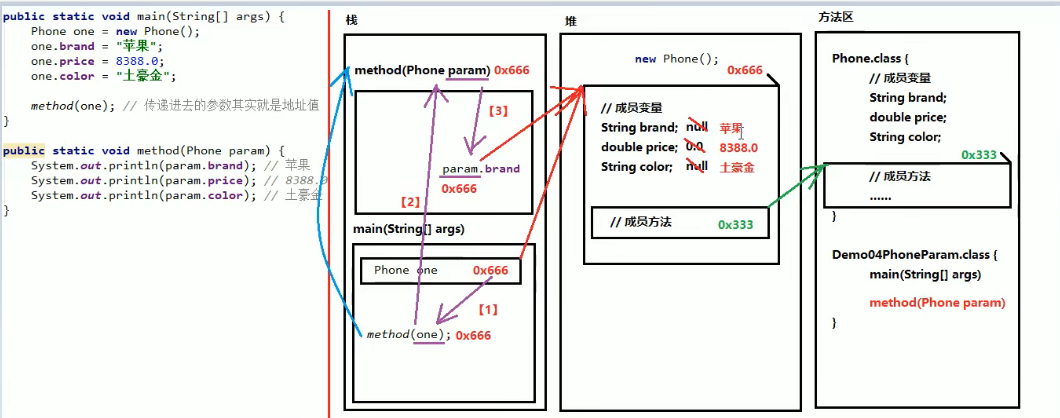
四、使用对象类型,作为方法的参数
当一个对象作为参数,传递到方法中去,实际上传递过去的是对象的地址值
public class Demo04PhoneFour {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone one = new Phone();
System.out.println(one.brand); // null
System.out.println(one.prince); // 0.0
System.out.println(one.color); // null
System.out.println("=============");
one.brand = "苹果";
one.prince = 8388.0;
one.color = "土豪金";
method(one);
}
public static void method(Phone param) {
System.out.println(param.brand); // 苹果
System.out.println(param.prince); // 8388.0
System.out.println(param.color); // 土豪金
}
}
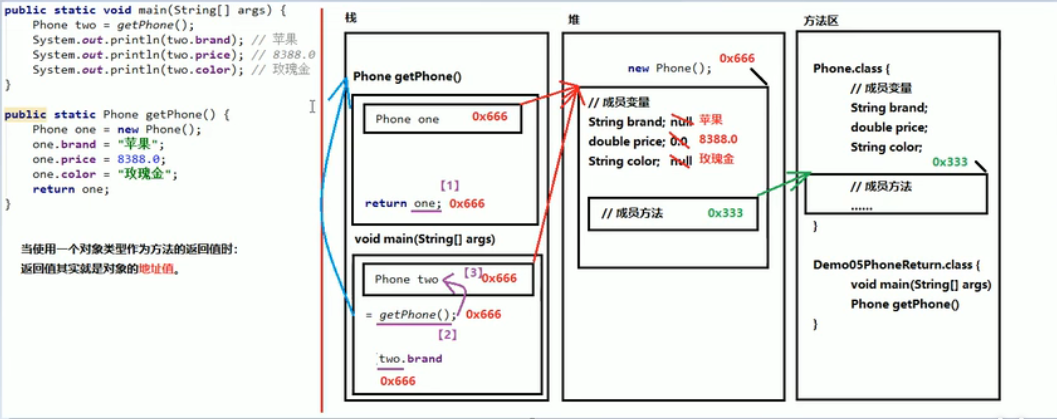
五、使用对象类型,作为方法的返回值
当使用对象作为方法的返回值时,返回值其实是对象的地址值
public class Demo05PhoneFive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Phone two = getPhone();
System.out.println(two.brand); // 苹果
System.out.println(two.prince); // 8388.0
System.out.println(two.color); // 玫瑰金
}
public static Phone getPhone() {
Phone one = new Phone();
one.brand = "苹果";
one.prince = 8388.0;
one.color = "玫瑰金";
return one;
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号