java学习02-变量
内存

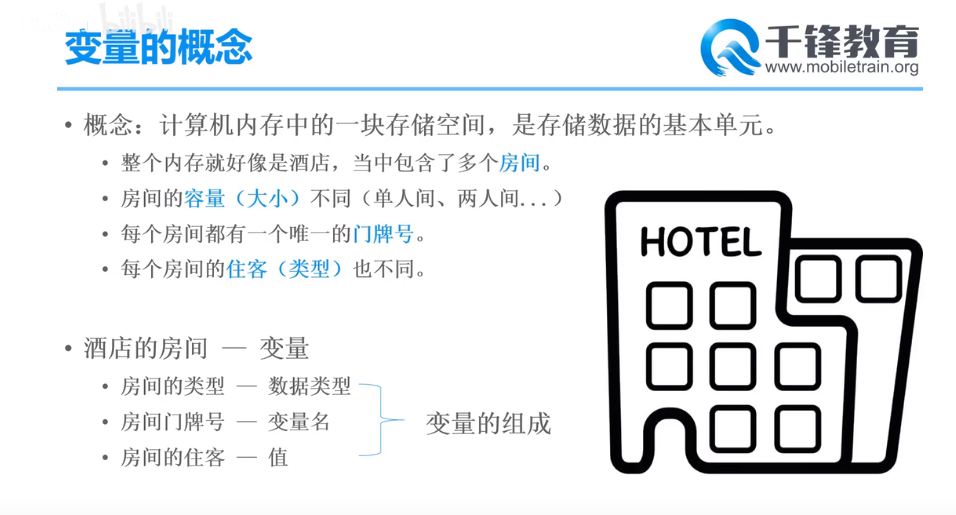
变量的概念

public class TestVariable{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//声明变量
int money;
money = 100;
// println() 输出后换行
System.out.println(money); //打印变量
System.out.print("money"); //打印文本
}
}
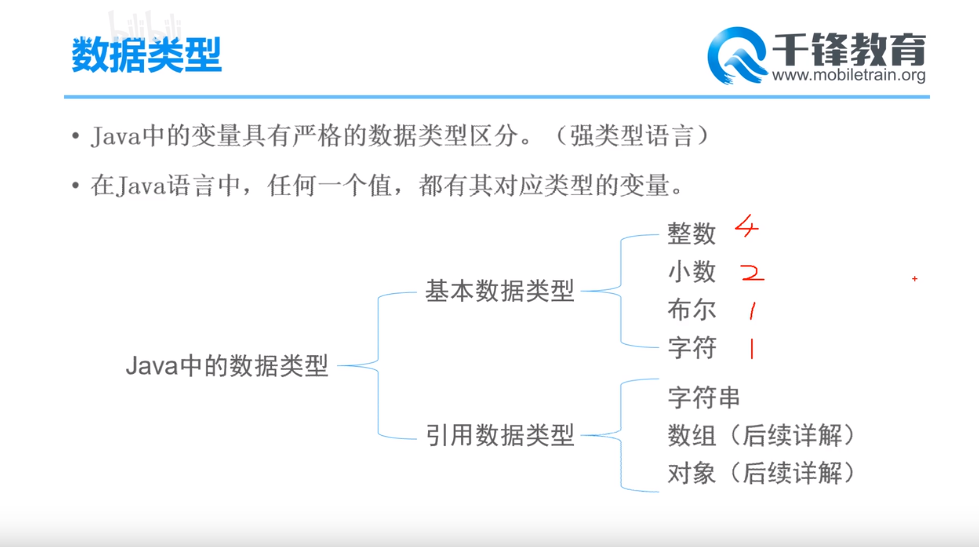
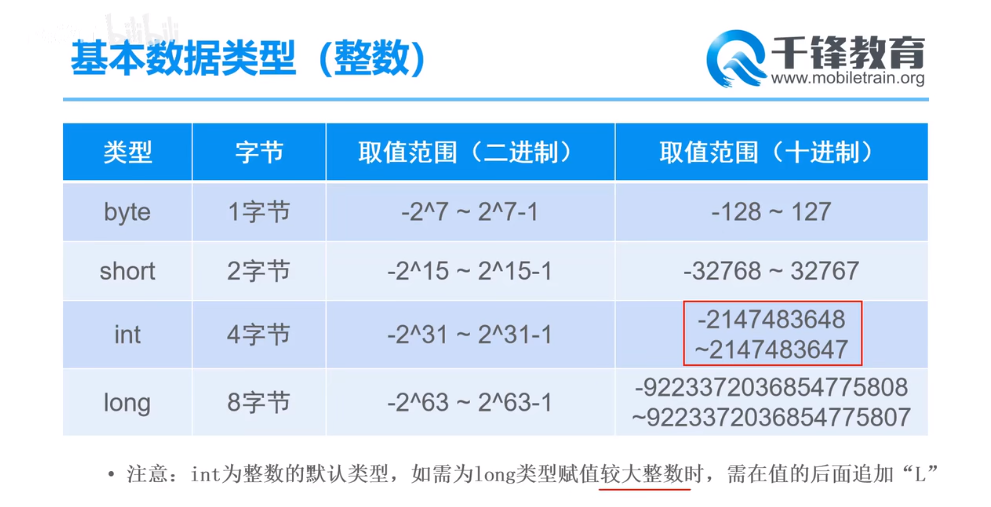
整数
public class TestType{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//数据类型
//整数
byte b = 127; // -128 ~ 127 (共计256个整数)
System.out.println(b);
short s = -32768; // -32768 ~ 32767 (共计65536个整数)
System.out.println(s);
int i = -2147483648; // -2147483648 ~ 2147483647(共计42亿个整数)
System.out.println(i);
// java中所有的“整数字面值”的默认类型时int,当证书字面值超过int的取值范围时,则提醒“过大的整数”
//在使用长整数时,当定义的值超过int的取值范围时,需要在定义的值后加上L
long l = 2147483648L;
System.out.println(l);
}
}
小数/浮点数:单精度、双精度
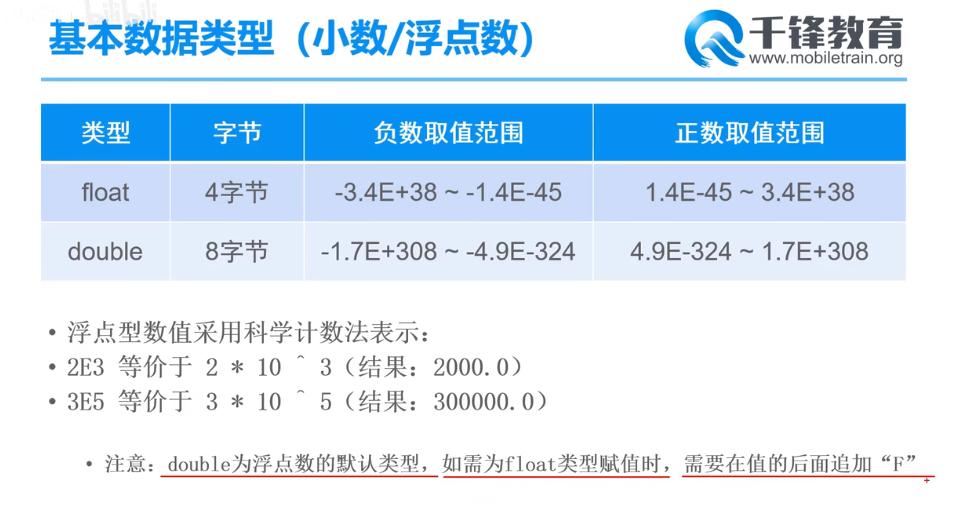
// 小数/浮点数 // float 单精度浮点型;double 双精度浮点型 double d = 1.2; System.out.println(d); // 1.2 double d2 = 1; System.out.println(d2); // 1.0 // java中所有的“小数字面值”的默认类型时double,当小数字面值超过double的取值范围时,则报错 // 当定义float单精度小数时,需要在小数后加 F float f = 1.5F; System.out.println(f); // 1.5 // 科学计数法 double d3 = 2E3; // 2.0 * 10 ^ 3 System.out.println(d3); // 2000.0 double d4 = 2E7; // 2.0 * 10 ^ 7 System.out.println(d4); // 2.0E7 float f2 = 5E4F; // 5.0 * 10^4 追加F代表float System.out.println(f2); // 50000.0 //取值范围 //float正数取值范围 float floatMin = 0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014F; // float的最小正数 System.out.println(floatMin); // 1.4E-45 float floatMax = 340000000000000000000000000000000000000.0F; // float的最大正数 System.out.println(floatMax); // 3.4E38 //float负数取值范围 float floatMin2 = -340000000000000000000000000000000000000.0F; // float的最小负数 System.out.println(floatMin2); // -3.4E38 float floatMax2 = -0.0000000000000000000000000000000000000000000014F; // float的最大fu数 System.out.println(floatMax2); // -1.4E-45 //double正数取值范围 double doubleMin = 4.9E-324; // 0.0000000000000000000000000(323个0)49 System.out.println(doubleMin); double doubleMax = 1.7E308; // 170000000000000000000000000(307个0).0 System.out.println(doubleMax); //double负数取值范围 double doubleMax2 = -4.9E-324; // -0.0000000000000000000000000(323个0)49 System.out.println(doubleMax2); double doubleMin2 = -1.7E308; // -170000000000000000000000000(307个0).0 System.out.println(doubleMin2);
布尔型boolearn
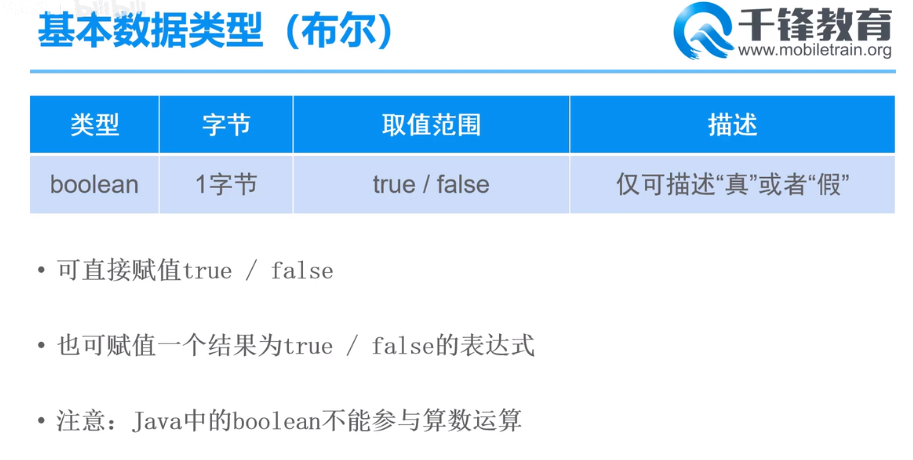
// 布尔型 boolean b1 = true; // true/false; System.out.println(b1); // true boolean b2 = 5 > 4; System.out.println(b2); // true
字符

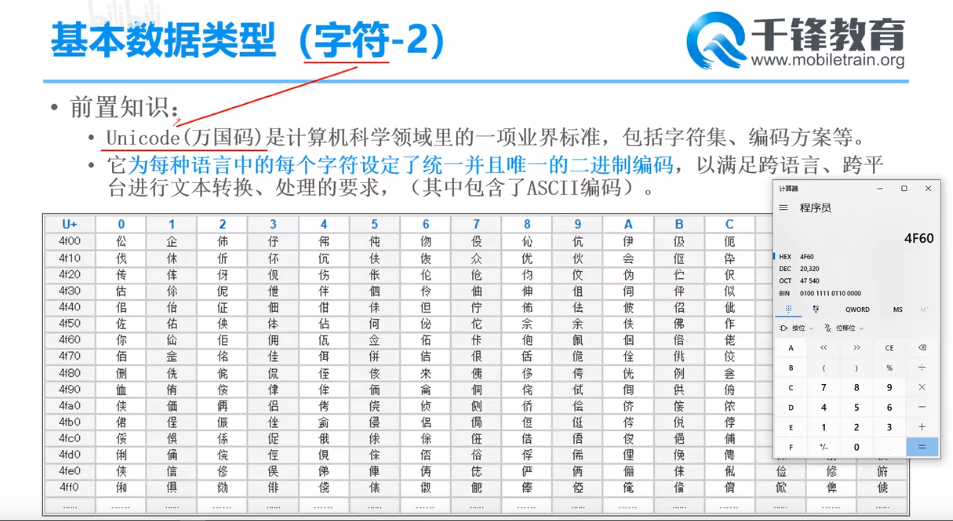
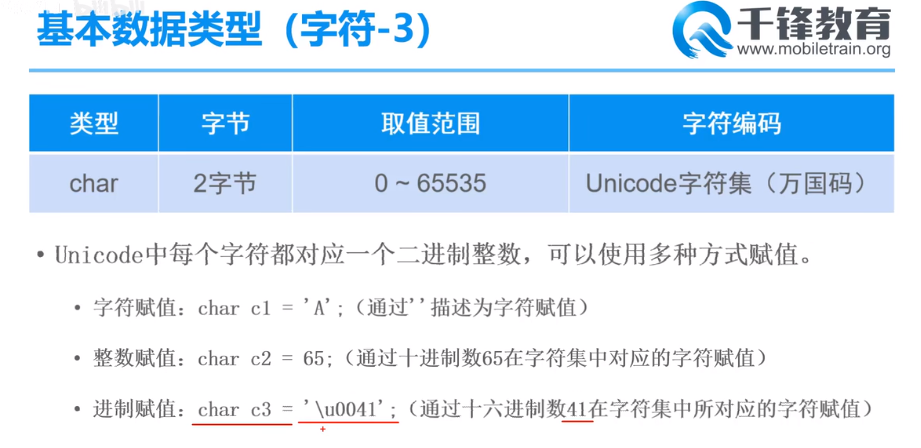
// 字符 char c1 = 'A'; // 字符赋值,原生、基本的赋值方式(常用) System.out.println(c1); // A char c2 = 65; // 整数赋值,通过十进制数65在ASCII和Unicode字符集中找到对应的字符赋值 System.out.println(c2); // A char c3 = '\u0041'; // 进制赋值,通过十六进制数41转换成十进制后在ASCII和Unicode字符集中找到对应的字符赋值 System.out.println(c3); // A
转义字符

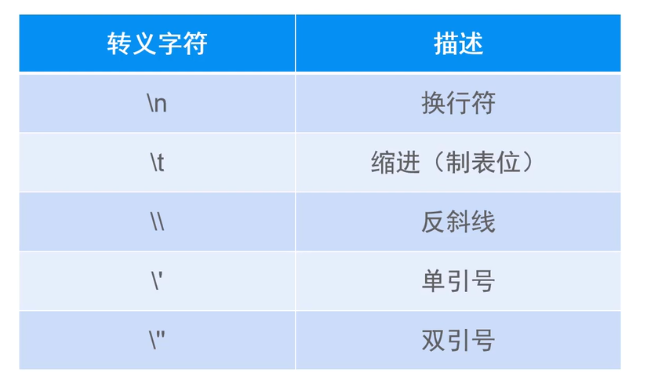
// \转义字符
char c4 = '\'';
System.out.println(c4); // '
char c5 = '\"';
System.out.println(c5); // "
// \t制表符
System.out.println("Hello\tWorld"); // Hellow World
// \n换行符
System.out.println("Hello\nWorld"); // Hellow
// World
// \u转义字符,表示后面跟一个十六进制数,通过这个十六进制数来指定一个字符
System.out.println("\u0041"); // A
字符串
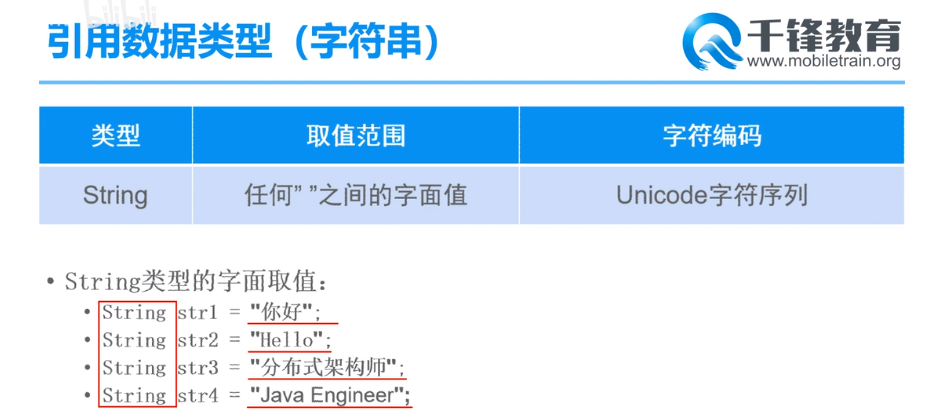
//字符串 任何“”之间的字面值都是 String str1 = "Hello World"; System.out.println(str1); // Hello World
类型转换
自动类型转换
1.两种类型相互兼容;2.目标类型的范围 大于 源类型 范围;
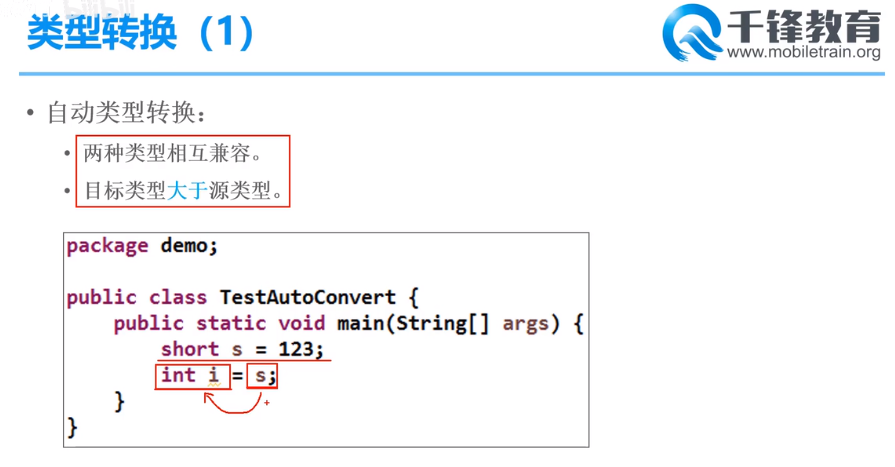
//自动类型转换 // 整数->整数 short s = 123; int i = s; System.out.println(i); // 123 // 小数->小数 float f = 100.0F; double d = f; System.out.println(d); // 100.0 // 整数-> 小数 int i2= 100; double d2 = i2; System.out.println(d2); // 100.0 //字符->整数 char c = 'A'; int i3 = c; System.out.println(i3); // 65 //字符->小数 char c2 = 'a'; double d3 = c2; System.out.println(d3); // 97 // boolean无法与其他类型进行转换
强制类型转换
1.两种类型相互兼容;2.目标类型的范围 小于 源类型 范围;
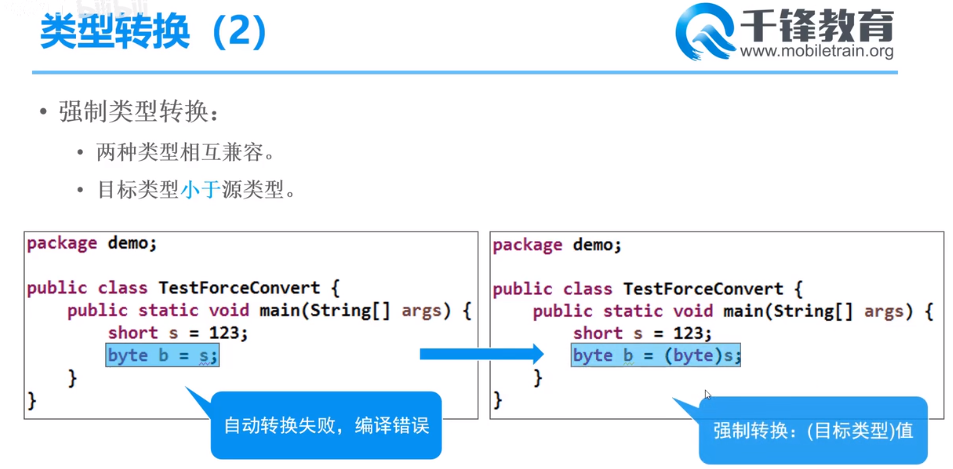
整数强转整数

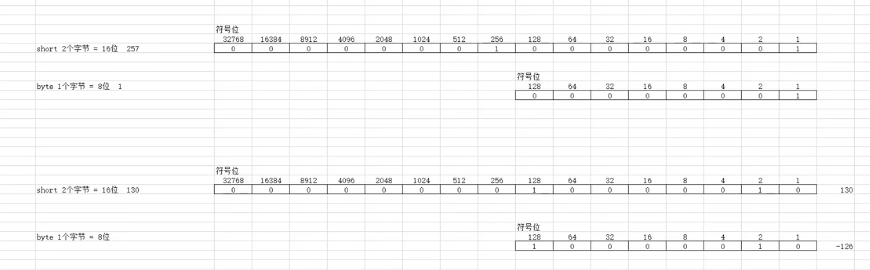
// 类型转换 //目标类型长足够,数据完整 short s = 123; byte b = (byte)s; //强制类型转换 成功 System.out.println(b); // 123 //目标类型长足不够,数据截取 short s2 = 257; byte b2 = (byte)s2; //强制类型转换 成功 System.out.println(b2); // 1
解释数据截断
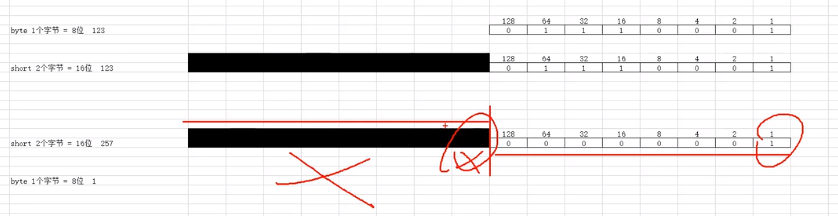
//目标类型长足不够,数据截取 符号位变化,变成负数 short s3 = 130; byte b3 = (byte)s3; //强制类型转换 数据截取 System.out.println(b3); // -126
小数强转整数,数据截断
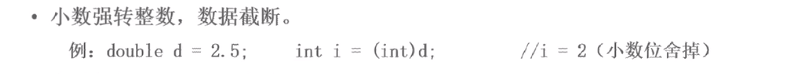
字符整数互转
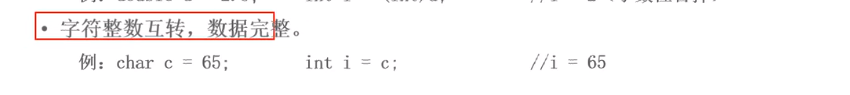
//字符 强转 整数 char c = 'A'; int i2 = c; System.out.println(i2); // 65 //整数 强转 字符 char c2 = (char)i2; System.out.println(c2); // A // 字符与整数转换的注意事项 short s4 = -1; // -32768~ 32767 char c3 = (char)s4; //因为在ascii编码字符集中没有负数,所以找不到相应的字符,就会显示为问号 System.out.println(c3); // ?





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号