Python数据分析第三周作业随笔
第一部分——飞机客户数据分析预测
代码一:数据探索
#代码7-1 数据探索 #对数据进行基本的探索 #返回缺失值个数以及最大、最小值 import pandas as pd datafile = "D:\\360MoveData\\Users\\86130\\Documents\\Tencent Files\\2268756693\\FileRecv\\air_data(1).csv"# 航空原始数据,第一行为属性标签 resultfile = "D:\\360MoveData\\Users\\86130\\Documents\\Tencent Files\\2268756693\\FileRecv\\explore.csv"# 数据探索结果表 # 读取原始数据,指定UTF-8编码(需要用文本编辑器将数据转换为UTF-8编码) data = pd.read_csv(datafile,encoding = 'utf-8') # 包括对数据的基本描述,percentiles参数是指定计算多少的分位数表(如¼分位数、中位数等) explore = data.describe(percentiles = [] ,include = 'all').T # describe()函数自动计算非空值数,需要手动计算空值数 explore['null'] = len(data)-explore['count'] explore = explore[['null','max','min']] #explore.columns = [u'空值数',u'最大值',u'最小值'] #表头重命名 ''' 这里只选取部分探索结果。 describe()函数自动计算的字段有count(非空值数)、unique(唯一值数)、top(频数最高者)、 freq(最高频数)、mean(平均值)、std(方差)、min(最小值)、50%(中位数)、max(最大值) ''' explore.to_csv(resultfile) #导出结果
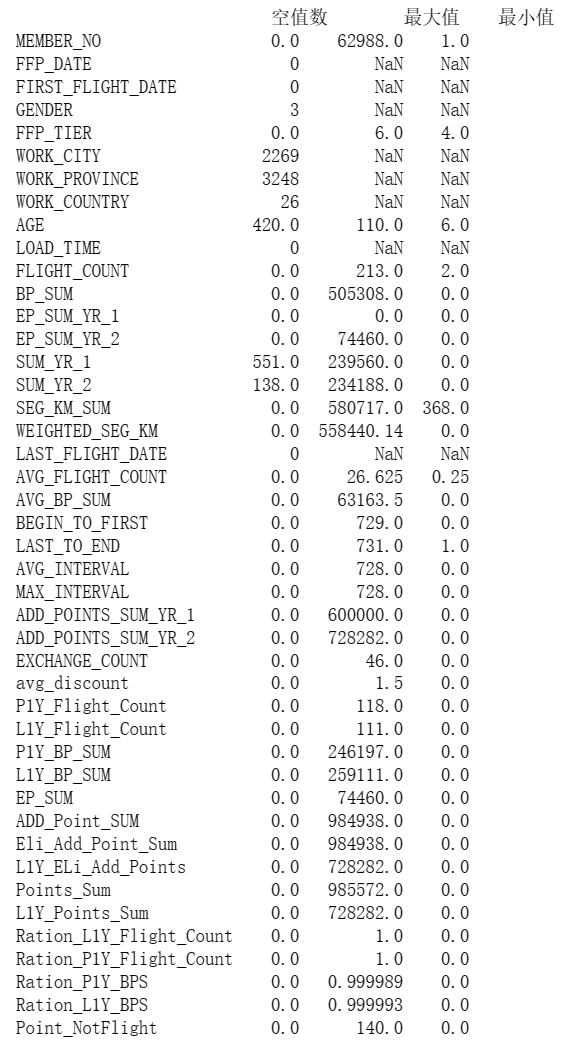
代码二:分析数据并绘制基本图像
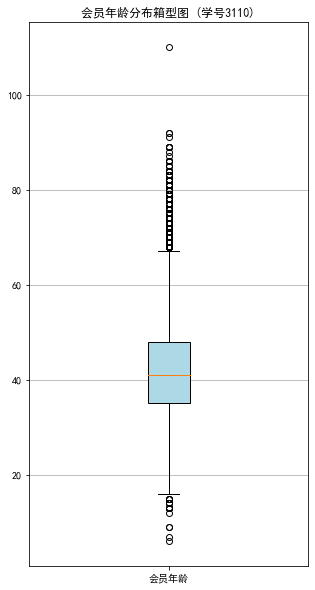
#代码7-2 探索客户的基本信息分布情况 #客户信息类别 #提取会员入会年份 import pandas as pd import matplotlib.pyplot as plt from datetime import datetime ffp = data['FFP_DATE'].apply(lambda x:datetime.strptime(x,'%Y/%m/%d')) ffp_year = ffp.map(lambda x : x.year) #绘制各年份会员入会人数直方图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,5)) # 设置画布大小 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei' #设置中文显示 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False plt.hist(ffp_year,bins='auto',color='#0504aa') plt.xlabel('年份') plt.ylabel('入会人数') plt.title('各年份会员入会人数(学号3110)') plt.show() plt.close #提取会员不同性别人数 male = pd.value_counts(data['GENDER'])['男'] female = pd.value_counts(data['GENDER'])['女'] #绘制会员性别比例饼图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(7,4)) #设置画布大小 plt.pie([male,female],labels=['男','女'],colors=['lightskyblue','lightcoral'],autopct='%1.1f%%') plt.title('会员性别比例(学号3110)') plt.show() plt.close #提取不同级别会员的人数 lv_four = pd.value_counts(data['FFP_TIER'])[4] lv_five = pd.value_counts(data['FFP_TIER'])[5] lv_six = pd.value_counts(data['FFP_TIER'])[6] #绘制会员各级别人数条形图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,5)) #设置画布大小 plt.bar(x=range(3),height=[lv_four,lv_five,lv_six],width=0.4,alpha=0.8,color='skyblue') plt.xticks([index for index in range(3)],['4','5','6']) plt.xlabel('会员等级') plt.ylabel('会员人数') plt.title('会员各级别人数 (学号3110)') plt.show() plt.close # 提取会员年龄 age = data['AGE'].dropna() age = age.astype('int64') # 绘图会员年龄分布箱型图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5, 10)) plt.boxplot(age, patch_artist=True, labels = ['会员年龄'], # 设置x轴标题 boxprops = {'facecolor':'lightblue'}) # 设置填充颜色 plt.title('会员年龄分布箱型图 (学号3110)') # 显示y坐标的底线 plt.grid(axis='y') plt.show() plt.close
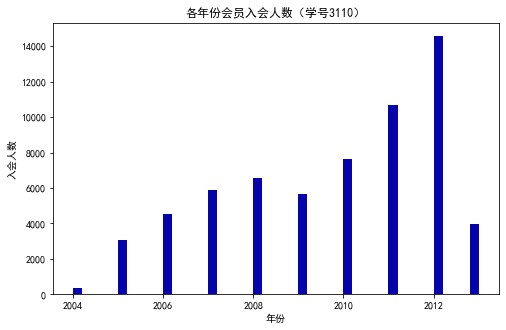
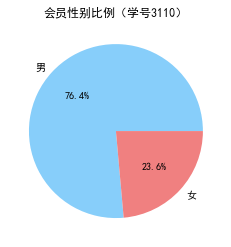
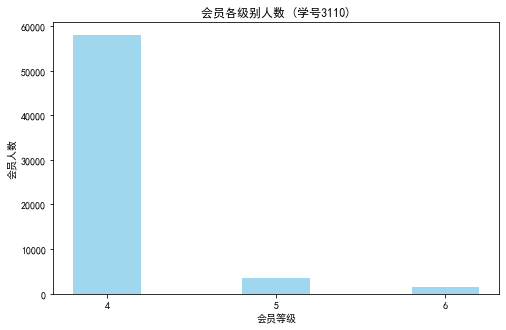
代码三:客户乘机数据分析箱型图
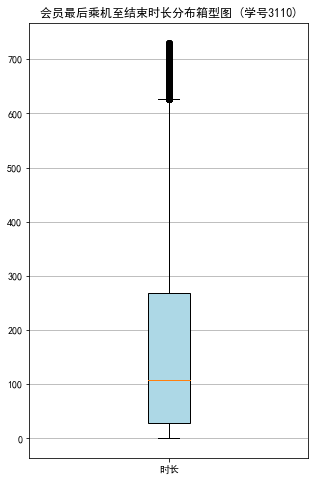
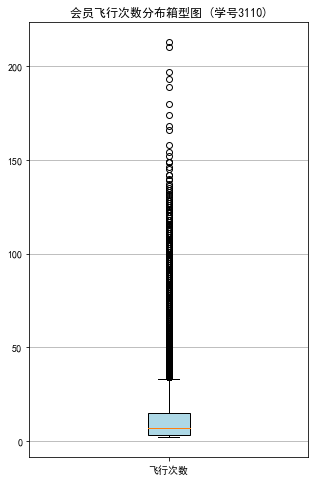
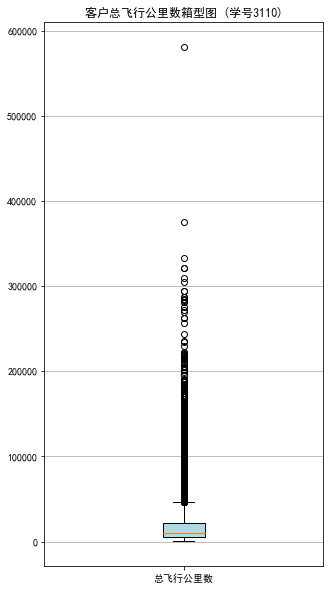
#代码7-3 探索客户乘机信息分布情况 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt lte =data['LAST_TO_END'] fc = data['FLIGHT_COUNT'] sks = data['SEG_KM_SUM'] #绘制最后乘机至结束时长箱型图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5,8)) plt.boxplot(lte, patch_artist=True, labels = ['时长'], #设置x轴标题 boxprops = {'facecolor':'lightblue'}) #设置填充颜色 plt.title('会员最后乘机至结束时长分布箱型图 (学号3110)') #显示y坐标轴的底线 plt.grid(axis='y') plt.show() plt.close #绘制客户飞行次数箱型图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5,8)) plt.boxplot(fc, patch_artist=True, labels = ['飞行次数'], #设置x轴标题 boxprops = {'facecolor':'lightblue'}) #设置填充颜色 plt.title('会员飞行次数分布箱型图 (学号3110)') # 显示y坐标的底线 plt.grid(axis='y') plt.show() plt.close # 绘制客户总飞行公里数箱型图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5,10)) plt.boxplot(sks, patch_artist=True, labels = ['总飞行公里数'], # 设置x轴标题 boxprops = {'facecolor':'lightblue'}) # 设置填充颜色 plt.title('客户总飞行公里数箱型图 (学号3110)') # 显示y坐标的底线 plt.grid(axis='y') plt.show() plt.close
代码四:会员积分数据分析直方图
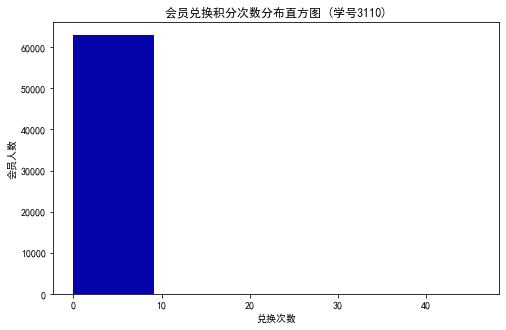
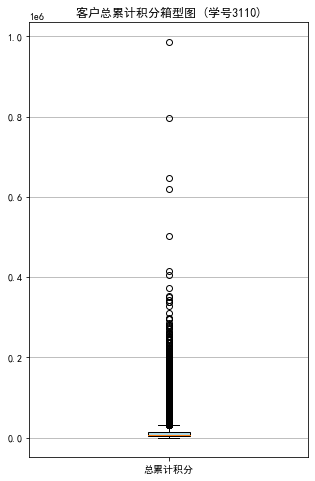
#代码7-4 探索客户积分信息分布情况 import matplotlib.pyplot as plt ec = data['EXCHANGE_COUNT'] #绘制会员兑换积分次数直方图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,5)) #设置画布大小 plt.hist(ec,bins=5,color='#0504aa') plt.xlabel('兑换次数') plt.ylabel('会员人数') plt.title('会员兑换积分次数分布直方图 (学号3110)') plt.show() plt.close #提取会员总累计积分 ps = data['Points_Sum'] #绘制会员总累计积分箱型图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(5,8)) plt.boxplot(ps, patch_artist=True, labels = ['总累计积分'], #设置x轴标题 boxprops = {'facecolor':'lightblue'}) #设置填充颜色 plt.title('客户总累计积分箱型图 (学号3110)') # 显示y坐标的底线 plt.grid(axis='y') plt.show() plt.close
代码五:相关矩阵及热力图
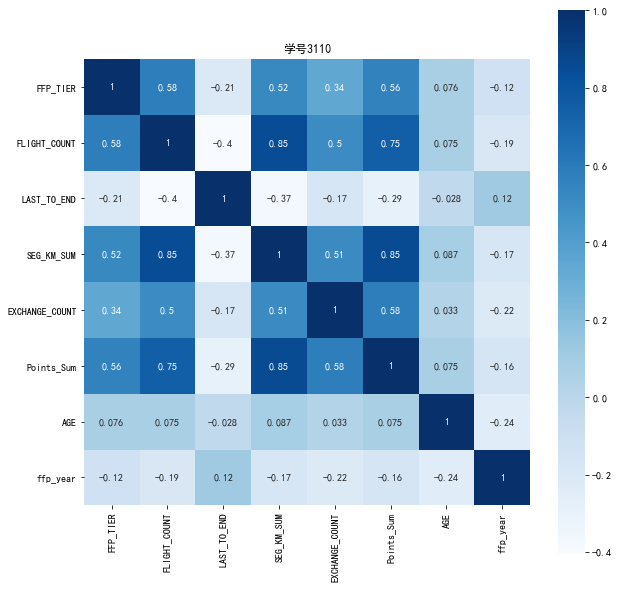
#代码7-5 相关系数矩阵与热力图 data_corr = data[['FFP_TIER','FLIGHT_COUNT','LAST_TO_END','SEG_KM_SUM','EXCHANGE_COUNT','Points_Sum']] age1 = data['AGE'].fillna(0) data_corr['AGE'] = age1.astype('int64') data_corr['ffp_year'] = ffp_year #计算相关性矩阵 dt_corr = data_corr.corr(method='pearson') print('相关性矩阵为:\n',dt_corr) #绘制热力图 import seaborn as sns plt.subplots(figsize=(10,10)) #设置画面大小 sns.heatmap(dt_corr,annot=True,vmax=1,square=True,cmap='Blues') plt.title('学号3110') plt.show() plt.close
相关性矩阵为:
FFP_TIER FLIGHT_COUNT LAST_TO_END SEG_KM_SUM \
FFP_TIER 1.000000 0.582447 -0.206313 0.522350
FLIGHT_COUNT 0.582447 1.000000 -0.404999 0.850411
LAST_TO_END -0.206313 -0.404999 1.000000 -0.369509
SEG_KM_SUM 0.522350 0.850411 -0.369509 1.000000
EXCHANGE_COUNT 0.342355 0.502501 -0.169717 0.507819
Points_Sum 0.559249 0.747092 -0.292027 0.853014
AGE 0.076245 0.075309 -0.027654 0.087285
ffp_year -0.116510 -0.188181 0.117913 -0.171508
EXCHANGE_COUNT Points_Sum AGE ffp_year
FFP_TIER 0.342355 0.559249 0.076245 -0.116510
FLIGHT_COUNT 0.502501 0.747092 0.075309 -0.188181
LAST_TO_END -0.169717 -0.292027 -0.027654 0.117913
SEG_KM_SUM 0.507819 0.853014 0.087285 -0.171508
EXCHANGE_COUNT 1.000000 0.578581 0.032760 -0.216610
Points_Sum 0.578581 1.000000 0.074887 -0.163431
AGE 0.032760 0.074887 1.000000 -0.242579
ffp_year -0.216610 -0.163431 -0.242579 1.000000
代码六:进行数据清洗
#代码7-6 清洗空值与异常值 import numpy as np import pandas as pd datafile = "D:\\360MoveData\\Users\\86130\\Documents\\Tencent Files\\2268756693\\FileRecv\\air_data(1).csv" cleanedfile = "D:\\360MoveData\\Users\\86130\\Documents\\Tencent Files\\2268756693\\FileRecv\\data_cleaned.csv" #读取数据 airline_data = pd.read_csv(datafile,encoding = 'utf-8') print('原始数据的形状为:',airline_data.shape) #去除票价为空的记录 airline_notnull = airline_data.loc[airline_data['SUM_YR_1'].notnull() & airline_data['SUM_YR_2'].notnull(),:] print('删除缺失记录后数据的形状为:',airline_notnull.shape) # 只保留票价非零的,或者平均折扣率不为0且总飞行公里数大于0的记录 index1 = airline_notnull['SUM_YR_1'] != 0 index2 = airline_notnull['SUM_YR_2'] != 0 index3 = (airline_notnull['SEG_KM_SUM']>0) & (airline_notnull['avg_discount'] != 0) index4 = airline_notnull['AGE'] >100 # 去除年龄大于100的记录 airline = airline_notnull[(index1 | index2) & index3 & ~index4] print('数据清洗后数据的形状为:', airline.shape) airline.to_csv(cleanedfile) # 保存清洗后的数据
原始数据的形状为: (62988, 44) 删除缺失记录后数据的形状为: (62299, 44) 数据清洗后数据的形状为: (62043, 44)
代码七:属性选择
# 代码7-7 属性选择 import pandas as pd import numpy as np # 读取数据清洗后的数据 cleanedfile = "D:\\360MoveData\\Users\\86130\\Documents\\Tencent Files\\2268756693\\FileRecv\\data_cleaned.csv" # 数据清洗后保存的文件路径 airline = pd.read_csv(cleanedfile, encoding='utf-8') # 选取需求属性 airline_selection = airline[['FFP_DATE', 'LOAD_TIME', 'LAST_TO_END', 'FLIGHT_COUNT', 'SEG_KM_SUM', 'avg_discount']] print('筛选的属性前5行为:\n', airline_selection.head())
筛选的属性前5行为:
FFP_DATE LOAD_TIME LAST_TO_END FLIGHT_COUNT SEG_KM_SUM avg_discount
0 2006/11/2 2014/3/31 1 210 580717 0.961639
1 2007/2/19 2014/3/31 7 140 293678 1.252314
2 2007/2/1 2014/3/31 11 135 283712 1.254676
3 2008/8/22 2014/3/31 97 23 281336 1.090870
4 2009/4/10 2014/3/31 5 152 309928 0.970658
代码八:属性构造与数据标准化
# 代码7-8 属性构造与数据标准化 # 构造属性L L = pd.to_datetime(airline_selection['LOAD_TIME']) - pd.to_datetime(airline_selection['FFP_DATE']) L = L.astype('str').str.split().str[0] L = L.astype('int')/30 # 合并属性 airline_features = pd.concat([L,airline_selection.iloc[:,2:]],axis=1) print('构建的LRFMC属性前5行为:\n', airline_features.head()) # 数据标准化 from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler data = StandardScaler().fit_transform(airline_features) np.savez("D:\\360MoveData\\Users\\86130\\Documents\\Tencent Files\\2268756693\\FileRecv\\airline_scale.npz", data) print('标准化后LRFMC 5个属性为:\n', data[:5,:])
构建的LRFMC属性前5行为:
0 LAST_TO_END FLIGHT_COUNT SEG_KM_SUM avg_discount
0 90.200000 1 210 580717 0.961639
1 86.566667 7 140 293678 1.252314
2 87.166667 11 135 283712 1.254676
3 68.233333 97 23 281336 1.090870
4 60.533333 5 152 309928 0.970658
标准化后LRFMC 5个属性为:
[[ 1.43579256 -0.94493902 14.03402401 26.76115699 1.29554188]
[ 1.30723219 -0.91188564 9.07321595 13.12686436 2.86817777]
[ 1.32846234 -0.88985006 8.71887252 12.65348144 2.88095186]
[ 0.65853304 -0.41608504 0.78157962 12.54062193 1.99471546]
[ 0.3860794 -0.92290343 9.92364019 13.89873597 1.34433641]]
代码九:K-Meas聚类标准化后的数据
#代码7-9 K-Meas聚类标准化后的数据 import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.cluster import KMeans #导入K-Mmeans算法 #读取标准化后的数据 airline_scale = np.load("D:\\360MoveData\\Users\\86130\\Documents\\Tencent Files\\2268756693\\FileRecv\\airline_scale.npz")['arr_0'] k = 5 #确定聚类中心数 #构建模型,随机种子设为123 kmeans_model = KMeans(n_clusters=k,random_state=123) fit_kmeans = kmeans_model.fit(airline_scale) #模型训练 #查看聚类结果 kmeans_cc = kmeans_model.cluster_centers_ #聚类中心 print('各聚类中心为:\n',kmeans_cc) kmeans_labels = kmeans_model.labels_ #样本的类别标签 print('各样本的类别标签为:\n',kmeans_labels) r1 = pd.Series(kmeans_model.labels_).value_counts() #统计不同类别样本的数目 print('最终每个类别的数目为:\n',r1) #输出聚类分群的结果 cluster_center = pd.DataFrame(kmeans_model.cluster_centers_,\ columns = ['ZL','ZR','ZF','ZM','ZC']) #将聚类中心放在数据中 cluster_center.index = pd.DataFrame(kmeans_model.labels_).\ drop_duplicates().iloc[:,0] #将样本类别作为数据框索引 print(cluster_center)
各聚类中心为:
[[-0.70030628 -0.41502288 -0.16081841 -0.16053724 -0.25728596]
[ 0.0444681 -0.00249102 -0.23046649 -0.23492871 2.17528742]
[ 0.48370858 -0.79939042 2.48317171 2.42445742 0.30923962]
[ 1.1608298 -0.37751261 -0.08668008 -0.09460809 -0.15678402]
[-0.31319365 1.68685465 -0.57392007 -0.5367502 -0.17484815]]
各样本的类别标签为:
[2 2 2 ... 0 4 4]
最终每个类别的数目为:
0 24630
3 15733
4 12117
2 5337
1 4226
dtype: int64
ZL ZR ZF ZM ZC
0
2 -0.700306 -0.415023 -0.160818 -0.160537 -0.257286
1 0.044468 -0.002491 -0.230466 -0.234929 2.175287
3 0.483709 -0.799390 2.483172 2.424457 0.309240
0 1.160830 -0.377513 -0.086680 -0.094608 -0.156784
4 -0.313194 1.686855 -0.573920 -0.536750 -0.174848
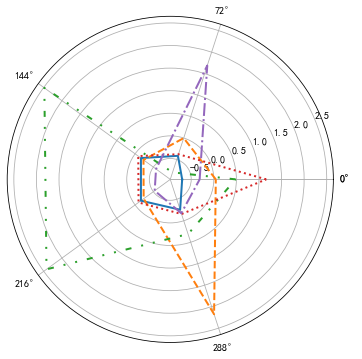
代码十:绘制客户分群雷达图
# 代码7-10 绘制客户分群雷达图 %matplotlib inline import matplotlib.pyplot as plt import pandas as pd import numpy as np from sklearn.cluster import KMeans #导入K-Mmeans算法 # 客户分群雷达图 labels = ['ZL','ZR','ZF','ZM','ZC'] legen = ['客户群' + str(i + 1) for i in cluster_center.index] # 客户群命名 lstype = ['-', '--', (0, (3,5,1,5,1,5)), ':', '-.'] kinds = list(cluster_center.iloc[:, 0]) # 由于雷达图要保证数据闭合,因此再添加L列,并转换为np.ndarray cluster_center = pd.concat([cluster_center, cluster_center[['ZL']]], axis=1) centers = np.array(cluster_center.iloc[:, 0:]) # 分割圆周长,并让其闭合 n = len(labels) angle = np.linspace(0, 2*np.pi, n, endpoint=False) angle = np.concatenate((angle, [angle[0]])) #绘图 fig = plt.figure(figsize=(8,6)) ax = fig.add_subplot(111,polar=True) #以极坐标的形式绘制图形 plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei' #设置中文显示 plt.rcParams['axes.unicode_minus'] = False #用来正常显示负号 #画线 for i in range(len(kinds)): ax.plot(angle,centers[i],linestyle=lstype[i],linewidth=2,label=kinds[i]) #添加属性标签 ax.set_thetagrids(angle * 180 / np.pi,labels) plt.title('客户特征分析雷达图(学号3110)') plt.legend(legen) plt.show() plt.close
![]()
第二部分:电信客户流失分析预测
代码1:读取并简单分析数据
import pandas as pd data=pd.read_csv('D:\大三下大数据分析\课堂练习第三周\客户流失数据\\WA_Fn-UseC_-Telco-Customer-Churn.csv')# 加载数据 data.shape # 查看数据大小
data.head()
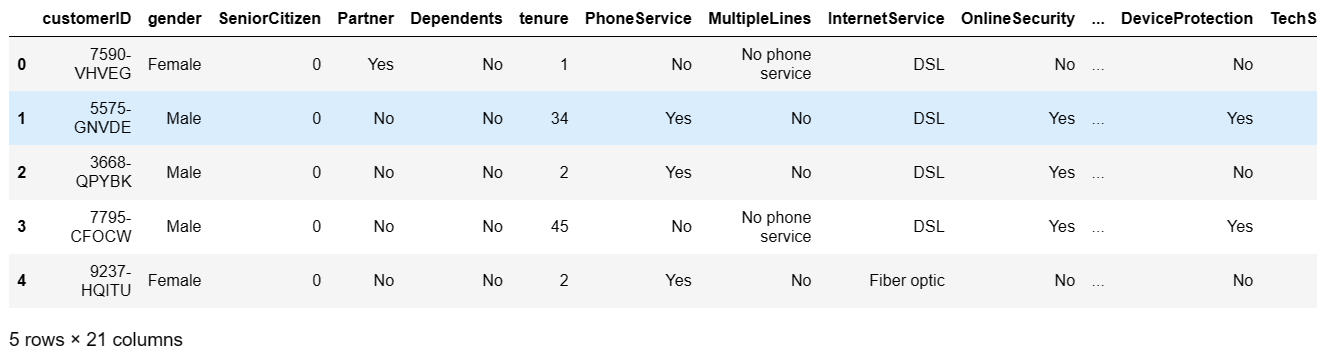
data.dtypes# 查看数据类型

data.info() # 打印摘要

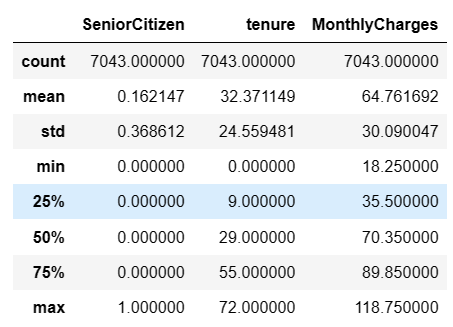
data.describe() # 描述性统计信息
代码2:客户流失数据分析
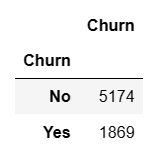
User_info=data.groupby(by="Churn")["Churn"].count() User_info=pd.DataFrame(User_info) User_info
代码3:查看数据类型
print(telcon.info()) #查看数据类型
<class 'pandas.core.frame.DataFrame'> RangeIndex: 7043 entries, 0 to 7042 Data columns (total 21 columns): # Column Non-Null Count Dtype --- ------ -------------- ----- 0 customerID 7043 non-null object 1 gender 7043 non-null object 2 SeniorCitizen 7043 non-null int64 3 Partner 7043 non-null object 4 Dependents 7043 non-null object 5 tenure 7043 non-null int64 6 PhoneService 7043 non-null object 7 MultipleLines 7043 non-null object 8 InternetService 7043 non-null object 9 OnlineSecurity 7043 non-null object 10 OnlineBackup 7043 non-null object 11 DeviceProtection 7043 non-null object 12 TechSupport 7043 non-null object 13 StreamingTV 7043 non-null object 14 StreamingMovies 7043 non-null object 15 Contract 7043 non-null object 16 PaperlessBilling 7043 non-null object 17 PaymentMethod 7043 non-null object 18 MonthlyCharges 7043 non-null float64 19 TotalCharges 7043 non-null object 20 Churn 7043 non-null object dtypes: float64(1), int64(2), object(18) memory usage: 1.1+ MB None
代码4:处理缺失值和归一化处理
#TotalCharges表示总费用,这里为对象类型,需要转换为float类型 ''' convert_numeric=True表示强制转换数字(包括字符串),不可转换为NaN---已被弃用 您可以根据需要替换所有非数字值,以NaN使用with函数中的apply列,然后替换为by 并将所有值最后替换为s by : df to_numeric 0 fillna int astype ''' data['TotalCharges']=data['TotalCharges'].apply(pd.to_numeric, errors='coerce').fillna(0).astype(int) print(data['TotalCharges'].dtypes) # print(pd.isnull(data['TotalCharges']).sum()) #再次查找是否存在缺失值

#处理缺失值 print(data.dropna(inplace=True)) #删除掉缺失值所在的行 print(data.shape)
#数据归一化处理 #对Churn列中的YES和No分别用1和0替换,方便后续处理 data['Churn'].replace(to_replace='Yes',value=1,inplace=True) data['Churn'].replace(to_replace='No',value=0,inplace=True) print(data['Churn'].head())

代码5:绘制客户流失情况饼图
#查看流失客户占比 churnvalue=telcon[ "Churn" ].value_counts() labels=telcon["Churn"].value_counts().index rcParams["figure.figsize"]=6,6 plt.pie(churnvalue,labels=labels,colors=["blue","yellow"],explode=(0.1,0),autopct='%1.1f', shadow=True) plt.title( '客户流失情况饼图(3110) ',fontsize=15) plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei' #设置中文显示 plt.show()
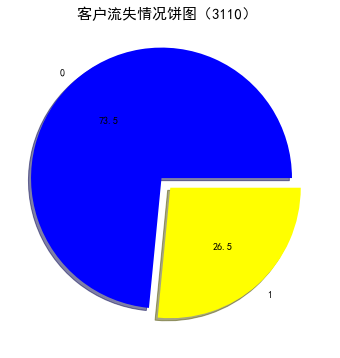
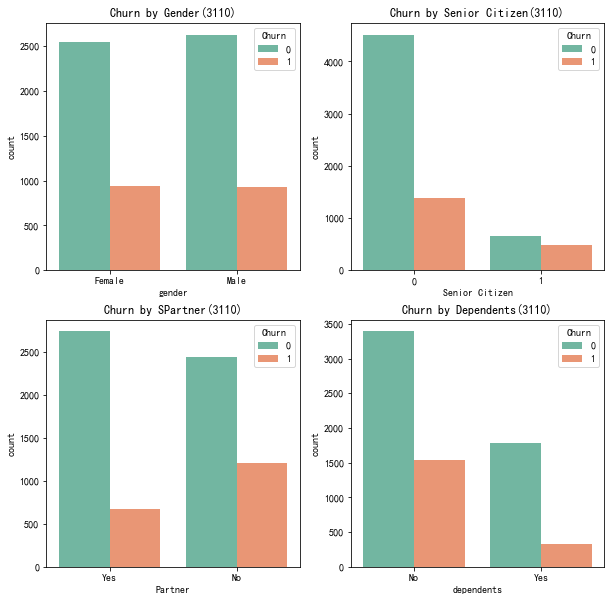
代码6:客户流失影响直方图
#性别、老年人、配偶、亲属对流客户流失率的影响 plt.figure(figsize=(10,10)) plt.subplot(2,2,1) gender=sns.countplot(x='gender',hue='Churn',data=telcon,palette='Set2') #palette参数表示设置颜色,设置为主颜色paste12 plt.xlabel('gender') plt.title('Churn by Gender(3110)') plt.subplot(2,2,2) seniorcitizen=sns.countplot(x='SeniorCitizen',hue='Churn',data=telcon,palette='Set2') plt.xlabel('Senior Citizen') plt.title('Churn by Senior Citizen(3110)') plt.subplot(2,2,3) partner=sns.countplot(x='Partner',hue='Churn',data=telcon,palette='Set2') plt.xlabel('Partner') plt.title('Churn by SPartner(3110)') plt.subplot(2,2,4) dependents=sns.countplot(x='Dependents',hue='Churn',data=telcon,palette='Set2') plt.xlabel('dependents') plt.title('Churn by Dependents(3110)') plt.show()
代码7:特征值
charges=telcon.iloc[:,1:20] # #对特征进行编码 # #离散特征的编码分为两种情况: # #1.离散特征的取值之间没有太大意义,比如color:[red,blue],那么就使用one-hot编码 # #2.离散特征的取值有大小意义,比如size:[X,XL,XXL],那么就使用数值的映射【X:1,XL:2,XXL:3】 corrdf=charges.apply(lambda x:pd.factorize(x)[0]) print(corrdf.head())

代码8:热力图
#使用热地图显示相关系数 charges=telcon.iloc[:,1:20] corrdf=charges.apply(lambda x:pd.factorize(x)[0]) corr=corrdf.corr() # ''' # heatmap 使用热力图展示系数矩阵情况 # linewidths 热力图矩阵之间的间隔大小 # annot 设定是否显示每个色块系数值 # ''' plt.figure(figsize=(30,20)) ax=sns.heatmap(corr,xticklabels=corr.columns,yticklabels=corr.columns,linewidths=0.2,cmap='YlGnBu',annot=True) plt.title('相关系数热力图(3110) ',fontsize=15) plt.rcParams['font.sans-serif'] = 'SimHei' #设置中文显示 plt.show()
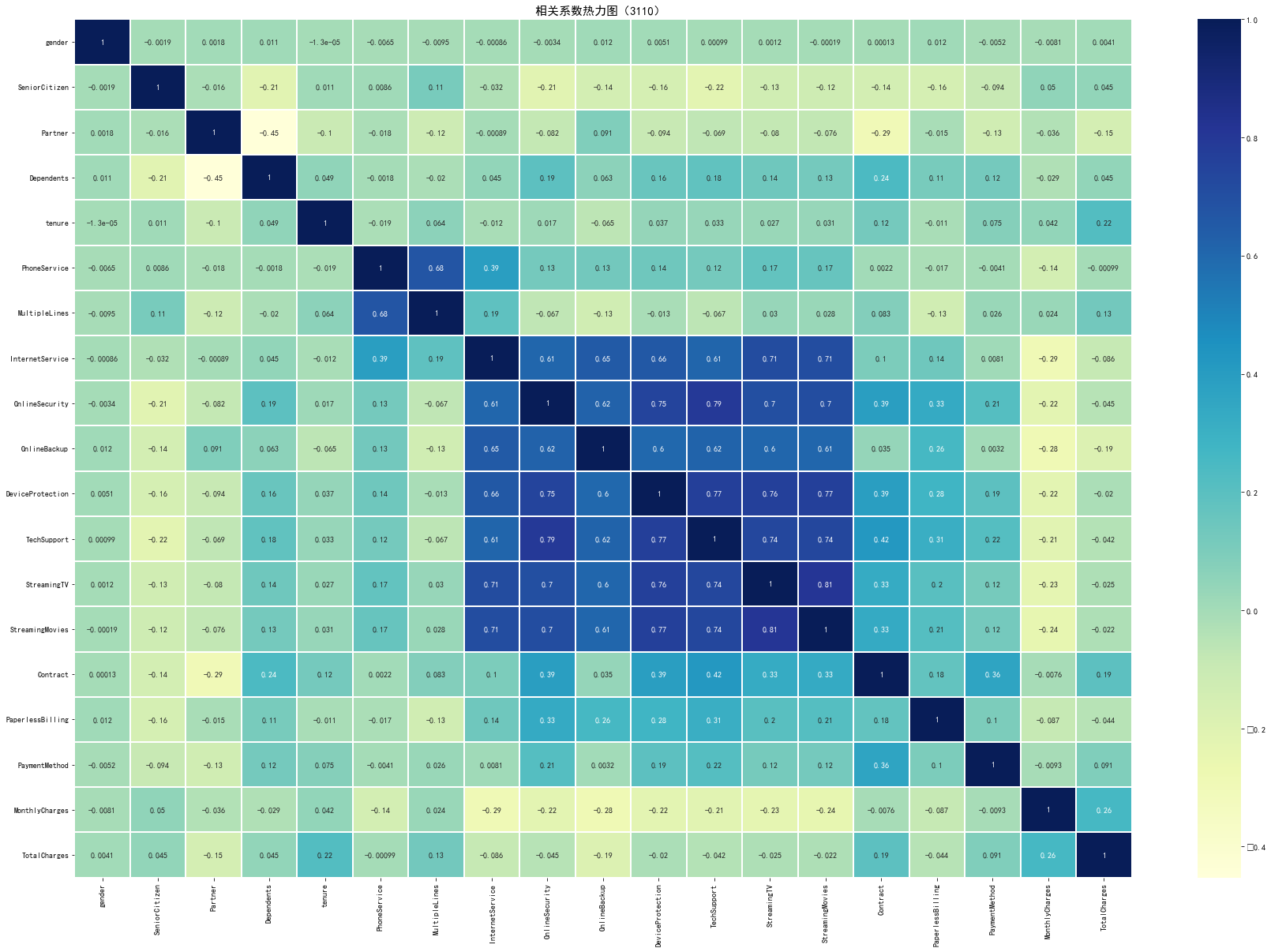
代码9:电信用户是否流失与各变量之间的相关性
#电信用户是否流失与各变量之间的相关性 plt.figure(figsize=(15,8)) tel_dummies.corr()['Churn'].sort_values(ascending=False).plot(kind='bar') plt.title('correlations between Churn and variables(3110)') plt.show()
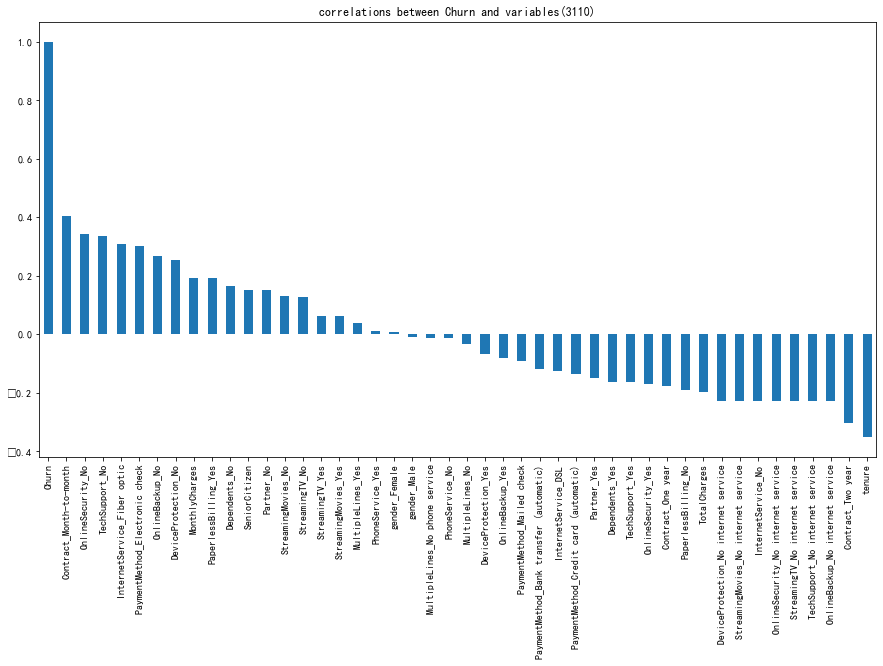
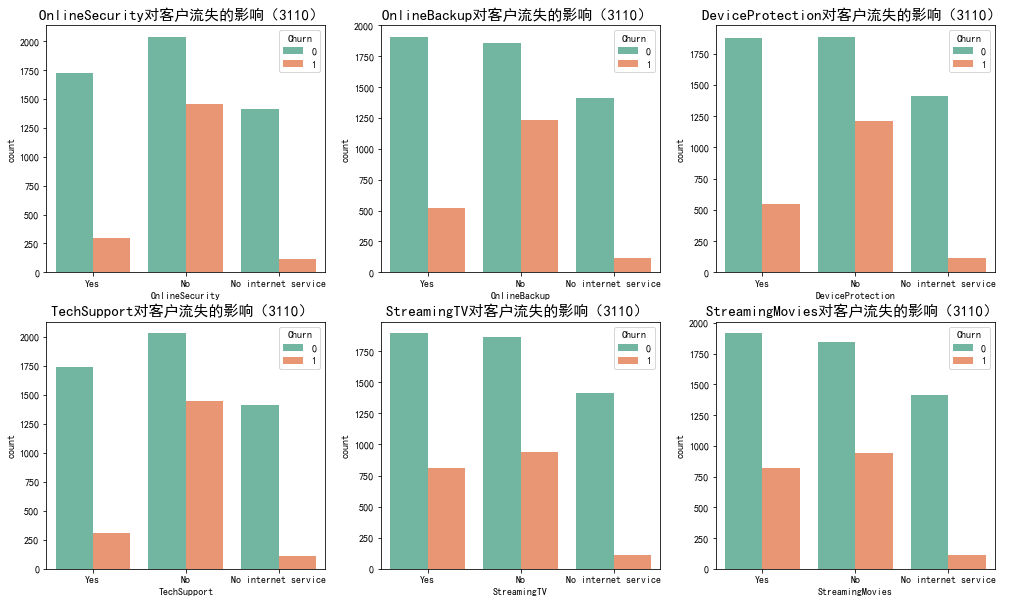
代码10:网络安全服务、在线备份业务、设备保护业务、技术支持服务、网络电视、网络电影和无互联网服务对客户流失率的影响
#网络安全服务、在线备份业务、设备保护业务、技术支持服务、网络电视、网络电影和无互联网服务对客户流失率的影响 covariable=['OnlineSecurity','OnlineBackup','DeviceProtection','TechSupport','StreamingTV','StreamingMovies'] plt.figure(figsize=(17,10)) for i,item in enumerate(covariable): plt.subplot(2,3,(i+1)) ax=sns.countplot(x=item,hue='Churn',data=telcon,palette='Set2',order=['Yes','No','No internet service']) plt.xlabel(str(item)) plt.title(str(item)+'对客户流失的影响(3110) ',fontsize=15) i=i+1 plt.show()
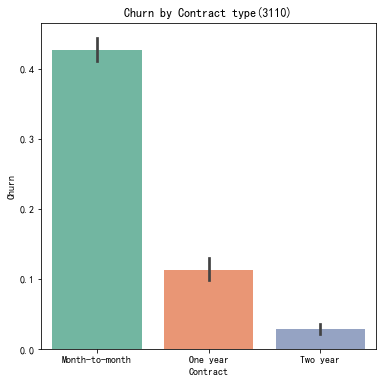
代码11:绘制签订合同方式对客户流失率的影响直方图
#签订合同方式对客户流失率的影响 ax=sns.barplot(x='Contract',y='Churn',data=telcon,palette='Set2',order=['Month-to-month','One year','Two year']) # seaborn 的 barplot() 利用矩阵条的高度反映数值变量的集中趋势,bar plot 展示的是某种变量分布的平均值, # 当需要精确观察每类变量的分布趋势,boxplot 与 violinplot 往往是更好的选择。 plt.title('Churn by Contract type(3110)') plt.show()
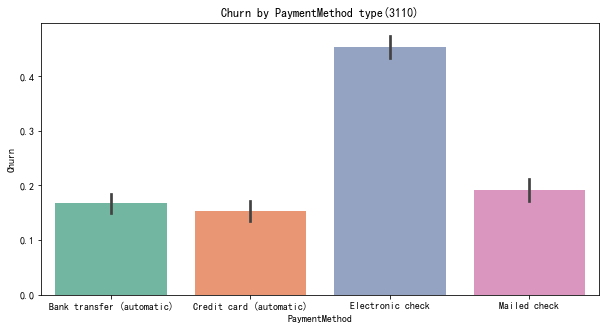
代码12:绘制付款方式对客户流失率的影响直方图
#付款方式对客户流失率的影响 plt.figure(figsize=(10,5)) ax=sns.barplot(x='PaymentMethod',y='Churn',data=telcon,palette='Set2',order=['Bank transfer (automatic)','Credit card (automatic)','Electronic check','Mailed check']) plt.title('Churn by PaymentMethod type(3110)') plt.show()




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号