Miller Rabin 和 Pollard Rho
为什么我要把他俩放一起写呢?俩随机化算法常常一起用,简直是天生一对儿。
Miller Rabin 算法
定义
Miller-Rabin 素性测试[1]是进阶的素数判定方法。
实现
二次探测定理
如果 \(p\) 是奇素数,则 \(x^2 \equiv 1 \pmod p\) 的解为 \(x \equiv1 \pmod p\) 或 \(x\equiv p-1 \pmod p\)。
若要证明,只需要将上面的方程移项,再平方差公式,得到 \((x+1)(x-1)\equiv 0 \pmod p\),即可得出上面的结论。
假设需要判断的数是 \(p\),我们把 \(p-1\) 分解成 \(2^k \times t\) 的形式。
由费马小定理[2],当 \(p\) 是素数时,有 \(a^{2^k \times t}\equiv 1 \pmod p\)。
然后随机选择一个数 \(a\),计算出 \(a^t \bmod p\)。
让其不断的自乘,同时结合二次探测定理进行判断。如果我们自乘后的数 \(\bmod p =1\),但是之前的数 \(\bmod p \ne \pm 1\),那么这个数就是合数(违背了二次探测定理)。
这样乘 \(k\) 次,最后得到的数就是 \(a^{p-1}\)。那么最后计算出的数不为 \(1\),这个数也是合数(费马小定理)。
代码
int Test[20] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
int test_time = 12;
bool millerRabin(int p) {
if (p < 2) return 0;
int t = p - 1, k = 0;
while (!(t & 1)) { // 求出 k 和 t
t >>= 1;
k++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < test_time; i++) {
// 一般可以用前 12 个质数作为底数,当然也可以用随机数
if (p == Test[i]) return 1;
int a = fpow(Test[i], t, p);
for (int j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
if (a * a % p == 1 && a != 1 && a != p - 1) {
return 0; // 二次探测定理
}
a = a * a % p;
}
if (a != 1) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
Pollard Rho 算法
难评,看OI-WIKI吧。
引入
Pollard Rho 算法用于求快速找到一个正整数 \(n\) 的一个非平凡因数[3]。
生日悖论
不考虑出生年份(假设每年都是365天),问:一个房间中至少多少人,才能使其中两个人生日相通的概率达到 \(50\%\)?
解:假设一年有 \(n\) 天,房间中有 \(k\) 人,用 \(1\) 到 \(k\) 给这些人编号。假定每个人的生日均与分布于 \(n\) 天之中,且两个人的生日相互独立。设 \(k\) 个人生日互不相同的时间为 \(A\),则 \(P(A)=\prod_{i=0}^{k-1}\frac{n-i}{n}\)。然后烂糟推一堆得出:
将 \(n=365\) 代入,解得 \(k \ge 23\)。所以一个房间中至少有 \(23\) 人,使其两人生日相同的概率达到 \(50\%\),但这个数学事实非常反直觉,故称之为一个悖论。当 \(k>56,n=365\) 时,出现两个人同一天生日的概率将大于 \(99\%\)!
利用最大公约数求出一个约数
首先明确 \(n\) 和某个数的最大公约数一定是 \(n\) 的约数。我们可以通过 \(f(x)=(x^2+c)\bmod n\) 来生成一个序列 \({x_i}\):随机选取一个 \(x_i\),令 \(x_2=f(x_1),x_3=f(x_2),\dots,x_i=f(x_{i-1})\)。其中 \(c\) 是一个随机选取的常熟。
举个例子,设 \(n=50,c=6,x_1=1\),\(f(x)\) 生成的数据为 \(1,7,5,31,17,45,31,17,45,31,\dots\) 可以发现数据在 \(x_4\) 以后都在 \(31,17,45\) 循环。如果将这些数如下图一样排列起来,就发现他是一个这个玩意儿,长得像一个 \(\rho\),所以这个算法得名 rho。
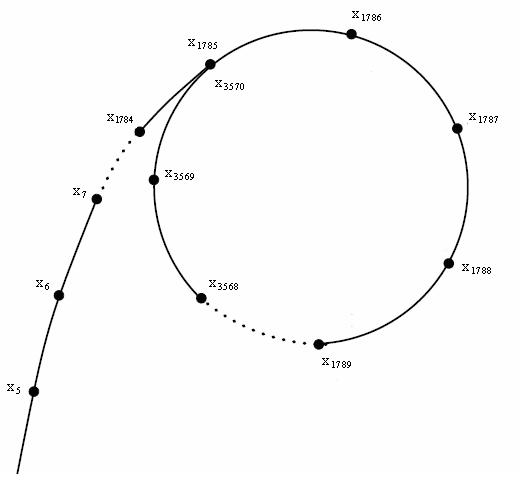
选择 \(f(x)=(x^2+c)\bmod n\) 作为这个生成函数序列,是因为它有一个性质:\(\forall x \equiv y \pmod p,f(x)\equiv f(y)\pmod p\),其中 \(p \mid n\)。
证明
若 \(x=y \pmod p\),则可以将它们表示为 \(x=k_1p+a,y=k_2p+a\),满足 \(k_1,k_2,a \in \mathbb{Z},a \in [0,p)\)。
\(f(x)=(x^2+c)\bmod n\),因此 \(f(x)=x^2+c-kn\),其中 \(k\in\mathbb{Z}\)。
\[\begin{align*} f(x) & = x^2+c-kn\\ & = (k_1p+a)^2+c-kn\\ & = k_1^2p^2+2k_1pa+a^2+c-kn\\\ & \equiv a^2+c \end{align*} \]同理, \(f(y)\equiv a^2+c \pmod p\),因此 \(f(x) \equiv f(y) \pmod p\)。
根据生日悖论,生成的序列中不同值的数量约为 \(\sqrt{n}\) 个。设 \(m\) 为 \(n\) 的最小非平凡因子,显然有 \(m \le \sqrt{n}\)。将 \({x_i}\) 中每一项对 \(m\) 取模,我们得到了一个新序列 \({y_i}\),并且根据生日悖论可以得知新序列中不同值的个数约为 \(O(\sqrt m) \le O(n^{\frac{1}{4}})\)。因此,我们可以在期望 \(O(n^{\frac{1}{4}})\) 的时间内找到两个位置 \(i,j\),使得 \(x_i\ne x_j \&\& y_i=y_j\),这意味着 \(n \nmid |x_i-x_j| \&\& m\mid |x_i-x_j|\),我们可以通过 \(\gcd(n,|x_i-x_j|)\) 获得 \(n\) 的一个非平凡因子。
代码实现
这是一个带了倍增优化的代码。
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
mt19937 wdz(time(0)); // 随机数
int N;
int gcd(int n, int m) {
return m == 0 ? n : gcd(m, n % m);
}
int pollard(int n, int c) {
int x, y, d, i = 1, k = 2;
x = wdz() * wdz() % (n - 1) + 1; // 此处的 wdz() 是随机数
y = x;
while (1) {
x = (x * x % n + c) % n;
d = gcd((x - y + n) % n, n);
if (1 < d && d < n) return d;
if (x == y) return n;
// x = y 说明构成了一个环,说明选定的 c 不好,那么重新来一遍
if (++i == k) {
k <<= 1;
y = x;
// 由于 y 不一定在环内,所以随时更新 y 的值,不然会死循
}
}
return 23333333; // 返回一个值,无实际意义
}
signed main() {
scanf("%lld", &N);
int p = N;
while (p >= N) {
p = pollard(N, wdz() * wdz() % (N - 1) + 1);
}
// p 为 N 的一个因子
printf("%lld\n", p);
return 0;
}
你别急,再给一个再加上 127 优化的代码。
int pollard(int n, int c) { // 127 优化的 pollard rho
int x, y, d, i = 1, k = 2, v = 1;
x = y = 0;
while (1) {
x = (x * x % n + c) % n;
v = v * abs(x - y) % n;
if (i % 127 == 0) {
d = gcd(v, n);
if (1 < d) return d;
}
if (x == y) return n;
if (++i == k) {
k <<= 1;
y = x;
d = gcd(v, n);
if (1 < d) return d;
}
}
return 23333333;
}
结合应用
例题
P4718 【模板】Pollard-Rho - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
对于每一个询问,给出一个整数。如果这个数是质数就输出
Prime;如果不是质数,输出它最大的质因子是哪个
代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
mt19937 wdz(time(0));
long long read() {
long long x = 0; char ch = getchar();
while (ch < '0' || ch > '9') ch = getchar();
while (ch >= '0' && ch <= '9') {
x = (x << 1) + (x << 3) + (ch ^ 48);
ch = getchar();
}
return x;
}
void write(long long x) {
if (x > 9) write(x / 10);
putchar(x % 10 + '0');
}
long long gcd(long long n, long long m) {
return m == 0 ? n : gcd(m, n % m);
}
long long fpow(long long a, long long x, long long MOD) {
a %= MOD;
long long ans = 1;
while (x) {
if (x & 1) ans = (__int128)ans * a % MOD;
a = (__int128)a * a % MOD;
x >>= 1;
}
return ans;
}
int Test[15] = {2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13, 17, 19, 23, 29, 31, 37};
int test_time = 12;
bool millerRabin(long long p) {
if (p < 2) return 0;
long long t = p - 1, k = 0;
while (!(t & 1)) {
t >>= 1;
k++;
}
for (long long i = 0; i < test_time; i++) {
if (p == Test[i]) return 1;
long long a = fpow(Test[i], t, p);
for (long long j = 1; j <= k; j++) {
if ((__int128)a * a % p == 1 && a != 1 && a != p - 1) {
return 0;
}
a = (__int128)a * a % p;
}
if (a != 1) return 0;
}
return 1;
}
long long pollard(long long n, long long c) { // 127 优化的 pollard rho
long long x, y, d, i = 1, k = 2, v = 1;
x = y = 0;
while (1) {
x = ((__int128)x * x % n + c) % n;
v = (__int128)v * abs(x - y) % n;
if (i % 127 == 0) {
d = gcd(v, n);
if (1 < d) return d;
}
if (x == y) return n;
if (++i == k) {
k <<= 1;
y = x;
d = gcd(v, n);
if (1 < d) return d;
}
}
return 23333333;
}
long long n, ans;
void resolve(long long x) { // 找到 x 的最大质因子,记录在 ans 中
if (x == 1 || x <= ans) return;
// 一个剪枝,如果 x 已经小于等于当前最大质因子,则绝对不可能产生比当前答案更大的解
if (millerRabin(x)) {
ans = max(ans, x);
return;
}
long long p = x;
while (p >= x) {
p = pollard(x, wdz() % (x - 1) + 1);
}
while (x % p == 0) x /= p;
resolve(x);
resolve(p);
}
int main() {
int qq = read();
while (qq--) {
n = read(), ans = 0;
resolve(n);
if (ans == n) {
printf("Prime\n");
} else {
write(ans);
putchar('\n');
}
}
return 0;
}


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号