剑指offer
题目列表:
本文旨在刷完剑指offer,并提供讲解,帮助大家顺利通过面试,文章有什么不足,还请各位大佬指出,我一定立马改正!谢谢各位大佬😊!
16. 替换空格
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
string replaceSpaces(string &str) {
string ans;
for(auto &&s : str){
if(s != ' ') ans.push_back(s);
else ans.append("%20");
}
return ans;
}
};
15. 二维数组中的查找
题解:
利用从左到右,从上到下的性质,从数组右上角开始寻找。
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
bool searchArray(vector<vector<int>> array, int target) {
if(array.empty() || array[0].empty()) return false;
int i = 0, j = array[0].size() - 1;
while(i < array.size() && j >= 0){
if(target > array[i][j]) i ++ ;
else if(target < array[i][j]) j -- ;
else return true;
}
return false;
}
};
17. 从尾到头打印链表
题解:
使用栈或者翻转链表都可以,这里使用递归调用。
AC代码,展开查看
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> res;
vector<int> printListReversingly(ListNode* head) {
dfs(head);
return res;
}
void dfs(ListNode* head){
if(!head) return;
dfs(head -> next);
res.push_back(head -> val);
}
};
20. 用两个栈实现队列
题解:
简单模拟即可。
AC代码,展开查看
class MyQueue {
public:
/** Initialize your data structure here. */
vector<int> a, b;
MyQueue() {
}
/** Push element x to the back of queue. */
void push(int x) {
while(b.size()) a.push_back(b.back()), b.pop_back();
a.push_back(x);
}
/** Removes the element from in front of queue and returns that element. */
int pop() {
while(a.size()) b.push_back(a.back()), a.pop_back();
int num = b.back(); b.pop_back();
return num;
}
/** Get the front element. */
int peek() {
while(a.size()) b.push_back(a.back()), a.pop_back();
return b.back();
}
/** Returns whether the queue is empty. */
bool empty() {
return a.empty() && b.empty();
}
};
/**
* Your MyQueue object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MyQueue obj = MyQueue();
* obj.push(x);
* int param_2 = obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.peek();
* bool param_4 = obj.empty();
*/
24. 机器人的运动范围
题解:
bfs
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
using PII = pair<int, int>;
const static int N = 51;
bool st[N][N];
int getNum(int x, int y){
return x / 10 + x % 10 + y / 10 + y % 10;
}
int movingCount(int threshold, int rows, int cols){
if(!rows || !cols) return 0;
int res = 0;
queue<PII> q;
q.push({0, 0});
int dx[4] = {-1, 0, 1, 0}, dy[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1};
while(q.size()){
auto [x, y] = q.front(); q.pop();
if(getNum(x, y) > threshold || st[x][y]) continue;
res ++ ;
st[x][y] = true;
for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++ ){
int a = x + dx[i], b = y + dy[i];
if(a < 0 || a >= rows || b < 0 || b >= cols) continue;
q.push({a, b});
}
}
return res;
}
};
25. 剪绳子
题解:
拆分尽可能多的三。
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
int maxProductAfterCutting(int n) {
if(n <= 3) return n - 1;
int res = 1;
while(n >= 5){
res *= 3;
n -= 3;
}
return n * res;
}
};
TOTO 重建二叉树
题解:
使用栈或者翻转链表都可以,这里使用递归调用。
AC代码,展开查看
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> res;
vector<int> printListReversingly(ListNode* head) {
dfs(head);
return res;
}
void dfs(ListNode* head){
if(!head) return;
dfs(head -> next);
res.push_back(head -> val);
}
};
40. 顺时针打印矩阵
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> printMatrix(vector<vector<int> > matrix) {
vector<int> res;
if(matrix.empty() || matrix[0].empty()) return res;
int n = matrix.size(), m = matrix[0].size();
vector<vector<bool>> st(n, vector<bool>(m, false));
int dx[4] = {0, 1, 0, -1}, dy[4] = {1, 0, -1, 0};
for(int i = 0, x = 0, y = 0, d = 0; i < n * m; i ++ ){
res.push_back(matrix[x][y]);
st[x][y] = true;
int a = x + dx[d], b = y + dy[d];
if(a < 0 || a >= n || b < 0 || b >= m || st[a][b]){
d = (d + 1) % 4;
a = x + dx[d], b = y + dy[d];
}
x = a, y = b;
}
return res;
}
};
41. 包含min函数的栈
题解:
使用使用一个栈存储最小值,每次那最小值的时候,则从这个栈中拿。
AC代码,展开查看
class MinStack {
public:
/** initialize your data structure here. */
vector<int> a, b;
MinStack() {
}
void push(int x) {
a.push_back(x);
if(b.empty() || b.back() >= x) b.push_back(x);
}
void pop() {
if(a.back() == b.back()) b.pop_back();
a.pop_back();
}
int top() {
return a.back();
}
int getMin() {
return b.back();
}
};
/**
* Your MinStack object will be instantiated and called as such:
* MinStack obj = new MinStack();
* obj.push(x);
* obj.pop();
* int param_3 = obj.top();
* int param_4 = obj.getMin();
*/
44. 分行从上往下打印二叉树
AC代码,展开查看
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> printFromTopToBottom(TreeNode* root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
if(!root) return res;
queue<TreeNode*> q;
q.push(root);
while(!q.empty()){
int n = q.size();
vector<int> v;
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++ ){
auto t = q.front(); q.pop();
v.push_back(t -> val);
if(t -> left) q.push(t -> left);
if(t -> right) q.push(t -> right);
}
res.push_back(v);
}
return res;
}
};
47. 二叉树中和为某一值的路径
题解:
使用使用一个栈存储最小值,每次那最小值的时候,则从这个栈中拿。
AC代码,展开查看
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
vector<vector<int>> findPath(TreeNode* root, int sum) {
if(!root) return res;
dfs(root, sum);
return res;
}
void dfs(TreeNode *root, int sum){
sum -= root -> val;
path.push_back(root -> val);
if(!root -> left && !root -> right && !sum) res.push_back(path);
if(root -> left) dfs(root -> left, sum);
if(root -> right) dfs(root -> right, sum);
path.pop_back();
}
};
51. 数字排列
样例:
输入:[1,2,3]
输出:
[
[1,2,3],
[1,3,2],
[2,1,3],
[2,3,1],
[3,1,2],
[3,2,1]
]
样例递归图示:
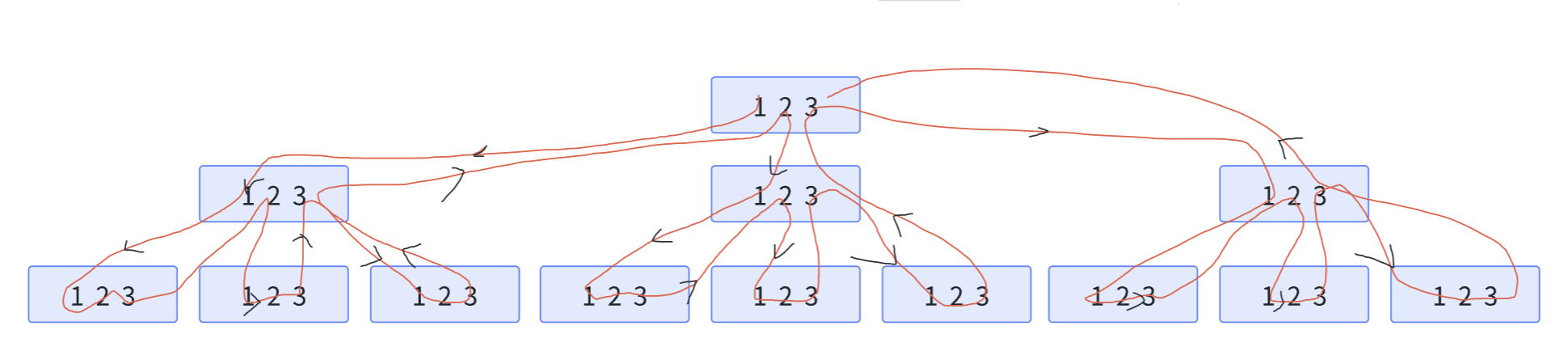
continue会去掉一部分枝叶。
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
const static int N = 10;
bool st[N];
vector<vector<int>> res;
vector<int> path;
vector<vector<int>> permutation(vector<int>& nums) {
sort(nums.begin(), nums.end());
dfs(nums, 0);
return res;
}
void dfs(vector<int> &nums, int u){
if(u == nums.size()){
res.push_back(path);
return;
}
for(int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i ++ ){
if(st[i] || i > 0 && nums[i - 1] == nums[i] && !st[i - 1]) continue; // 1
st[i] = true;
path.push_back(nums[i]);
dfs(nums, u + 1);
st[i] = false;
path.pop_back();
}
}
};
56. 从1到n整数中1出现的次数
思路:
从高位开始模拟,假设某一位为1,算有多少。最后将结果求和即是答案。
例如一个abcdef的一个数字:
假设c位置出现1
- 高位任意取: 0 ~ ab - 1, 0 ~ 999 -> ab * 1000
- 高位固定:
- 当c=0时,不存在c位置为1的数
- 当c=1时,0~def -> def + 1
- 当c>1时,0~999 -> 1000
点击查看代码
class Solution {
public:
int numberOf1Between1AndN_Solution(int n) {
if(n == 0) return 0;
vector<int> num;
while(n) num.push_back(n % 10), n /= 10;
int res = 0;
for(int i = num.size() - 1; i >= 0; i -- ){
int l = 0, r = 0, t = 1;
for(int j = num.size() - 1; j > i; j -- ) l = l * 10 + num[j];
for(int j = i - 1; j >= 0; j -- ) r = r * 10 + num[j], t *= 10;
res += l * t;
if(num[i] == 1) res += r + 1;
else if(num[i] > 1) res += t;
}
return res;
}
};
61. 最长不含重复字符的子字符串
题解:
双指针,确保i-j之间的字符串只出现以及即可。
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
// 1
int m[26];
int longestSubstringWithoutDuplication(string s) {
int res = 0;
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ ){
m[s[i] - 'a'] ++ ;
while(m[s[i] - 'a'] > 1) m[s[j ++ ] - 'a'] -- ;
res = max(res, i - j + 1);
}
return res;
}
// 2
int longestSubstringWithoutDuplication(string s) {
int res = 0;
unordered_map<char, int> m;
for(int i = 0, j = 0; i < s.size(); i ++ ){
m[s[i]] ++ ;
while(m[s[i]] > 1) m[s[j ++ ]] -- ;
res = max(res, i - j + 1);
}
return res;
}
};
65. 数组中的逆序对
题解:
归并排序
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
int merge_sort(vector<int> &a, vector<int> &b, int l, int r){
if(l >= r) return 0;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
int res = merge_sort(a, b, l, mid) + merge_sort(a, b, mid + 1, r);
int i = l, j = mid + 1, k = l;
while(i <= mid && j <= r){
if(a[i] <= a[j]) b[k ++ ] = a[i ++ ];
else b[k ++ ] = a[j ++ ], res += mid - i + 1;
}
while(i <= mid) b[k ++ ] = a[i ++ ];
while(j <= r) b[k ++ ] = a[j ++ ];
for(i = l; i <= r; i ++ ) a[i] = b[i];
return res;
}
int inversePairs(vector<int>& a) {
vector<int> b(a.size());
return merge_sort(a, b, 0, a.size() - 1);
}
};
69. 数组中数值和下标相等的元素
题解:
由于所给数组单调递增,并且寻找下标和数组元素相等的元素,可以使用二分查找。
不熟悉二分查找的可以看我的这篇文章. 二分查找图解
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
int getNumberSameAsIndex(vector<int>& a) {
int l = -1, r = a.size();
while(l + 1 < r){
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(a[mid] <= mid) l = mid;
else r = mid;
}
return l;
}
};
73. 数组中只出现一次的两个数字
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> findNumsAppearOnce(vector<int>& nums) {
int sum = 0;
for(auto &num : nums) sum ^= num;
int k = 0;
while((sum >> k & 1) == 0) k ++ ;
int x = 0;
for(auto &num : nums){
if((num >> k & 1) == 0) x ^= num;
}
return {x, sum ^ x};
}
};
80. 骰子的点数
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
const static int N = 12;
int f[N][N * 6];
vector<int> numberOfDice(int n) {
f[0][0] = 1;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ){
for(int j = 1; j <= n * 6; j ++ ){
for(int k = 1; k <= 6; k ++ ){
if(j >= k) f[i][j] += f[i - 1][j - k];
}
}
}
vector<int> res;
for(int i = n; i <= 6 * n; i ++ ){
res.push_back(f[n][i]);
}
return res;
}
};
83. 股票的最大利润
AC代码,展开查看
class Solution {
public:
const static int N = 510;
int f[N][2];
int maxDiff(vector<int>& nums) {
if(nums.empty()) return 0;
f[0][0] = 0;
f[0][1] = -nums[0];
for(int i = 1; i < nums.size(); i ++ ){
f[i][0] = max(f[i - 1][0], f[i - 1][1] + nums[i]);
f[i][1] = max(f[i - 1][1], -nums[i]);
}
return f[nums.size() - 1][0];
}
};
88. 树中两个结点的最低公共祖先
递归思路
AC代码,展开查看
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if(root == nullptr || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode *left = lowestCommonAncestor(root->left, p, q);
TreeNode *right = lowestCommonAncestor(root->right, p, q);
if(left == nullptr) return right;
if(right == nullptr) return left;
return root;
}
};
TODO 使用kotlin制作一个Gif制作工具,APK

 字符串、线性表、队列、栈、哈希表、dfs、bfs
字符串、线性表、队列、栈、哈希表、dfs、bfs

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号