jsp、el表达式
summarize
jsp有9个不需要定义直接用的对象,只有一个对象 异常 exception 只有在错误的页面才可以使用
jsp有4大域:① pageContext:当前jsp范围 ② request域:一次请求 ③ response域:一次会话 ④ application域:整个web应用
Servlet3大域:
① 请求作用域request域:一次请求,存放提示信息,属HTTPServletRequest
②会话作用域 response域:一次会话,存放用户信息,属HTTPSession
③全局作用域 application:应用程序作用域,从程序运行到程序停止,服务器不关,作用域一直有效,属ServletContext
1.jsp内置/隐式对象(9个)----- 笔试
jsp被翻译成servlet之后,service方法中有9个对象定义并初始化完毕
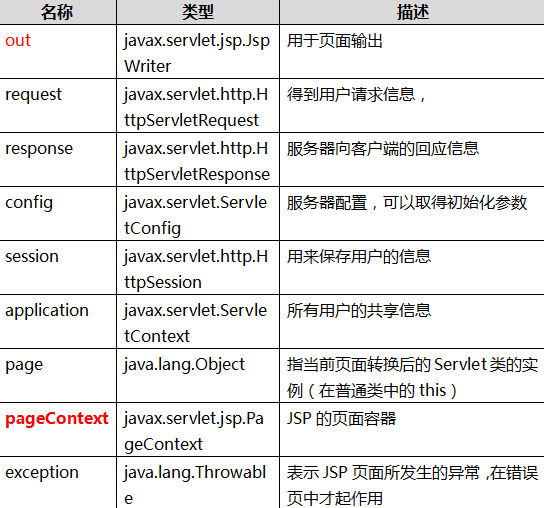 我们只学 out、和pageContext对象
我们只学 out、和pageContext对象
(1)out对象(out缓冲区4种输出方式)
out的类型:JspWriter
out作用:向客户端输出内容----out.write()
jsp 4种输出对象
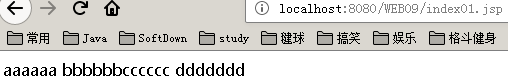
<body>
aaaaaa
<%
out.write("bbbbbb");
response.getWriter().write("cccccc");
%>
<%="ddddddd" %>
</body>
结果:
out缓冲区默认8kb 可设置成0 代表关闭out缓冲区 内容直接写到respons缓冲器
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" pageEncoding="UTF-8" buffer="0kb"%>
原理解释:
除了respones之外其他的输出方式都先在jsp.java文件中被翻译为out.write,然后被存进out缓冲区。
Tomcat内核直接从response缓冲区中取东西,而out缓冲区的东西必须先复制到respones缓冲区在被取出,所以可以解释为什么出现上述顺序,当设置buffer为0kb时,出现abcd顺序。
原理图

(1)pageContext对象
jsp页面的上下文对象,作用如下:
page对象与pageContext对象不是一回事
1)pageContext是一个域对象
setAttribute(String name,Object obj)
getAttribute(String name)
removeAttrbute(String name)
pageContext可以向指定的其他域中存取数据
setAttribute(String name,Object obj,int scope)
getAttribute(String name,int scope)
removeAttrbute(String name,int scope)
代码展示:向域中存值,在取值:
<body>
<%
String name=(String)pageContext.getAttribute("goods");
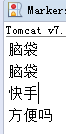
/*向request域中设置值 */
pageContext.setAttribute("goods","脑袋",pageContext.REQUEST_SCOPE);
/* 向session域中设置值 */
pageContext.setAttribute("goods","方便吗",pageContext.SESSION_SCOPE);
/*向application域中设置值 */
pageContext.setAttribute("goods","快手",pageContext.APPLICATION_SCOPE);
%>
<%
String name1=(String)pageContext.findAttribute("goods");
System.out.println(name1);
%>
<% //从request域中取值 System.out.println(pageContext.getAttribute("goods",pageContext.REQUEST_SCOPE)); //从application域中取值 System.out.println(pageContext.getAttribute("goods",pageContext.APPLICATION_SCOPE)); //从session域中取值 System.out.println(pageContext.getAttribute("goods",pageContext.SESSION_SCOPE)); %> </body>
findAttribute(String name)--依次从pageContext域,request域,session域,application域中获 取属性
在某个域中获取后将不在向后寻找
依次从小到大获取“goods”,只要从4个域中获取后就不会在去其他域寻找,因为4个域都是用的goods。
代码:
<% String name1=(String)pageContext.findAttribute("goods"); System.out.println(name1); %>
结果:
JSP有四大域的总结:
pageContext域:当前jsp页面范围
request域:一次请求
session域:一次会话
application域:整个web应用
4.jsp标签(动作)
1)页面包含(动态包含):<jsp:include page="被包含的页面"/>
静态包含:index.jsp文件中内容:
|
1
2
3
4
|
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="GB18030"%><%@ include file="/header.jsp" %><%@ include file="/content.jsp" %><%@ include file="/footer.jsp" %> |
页面显示结果:
被编译成的java文件:

动态包含 index.jsp文件中内容:
|
1
2
3
4
|
<%@ page language="java" import="java.util.*" pageEncoding="GB18030"%><jsp:include page="/header.jsp"></jsp:include><jsp:include page="/content.jsp"></jsp:include><jsp:include page="/footer.jsp"></jsp:include> |
页面显示结果:
被编译成的java文件:
总结
静态和动态包含执行结果相同,但过程不同,编译成的java文件数目不同。
静态和动态包含的区别与联系
注:下文将包含有其它文件的jsp文件称为主体文件,比如上文中的index.jsp文件。将被包含的文件称为包含文件,比如上文中的header.jsp文件。
-
<%@ include file=” ”%>是指令元素。<jsp:include page=” ”/>是行为元素
-
最终编译成java文件的数目不同。(从上面的例子可以看出)
-
静态包含在转换成为java文件时,将包含文件的内容“复制”到主体文件,然后作为一个整体编译。最终编译为一个java文件。
-
动态包含:各个jsp文件分别转换,分别编译。编程成多个java文件。
-
-
执行时间不同
静态包含发生在:JSP---->java文件阶段。
动态包含发生在:执行class文件阶段。动态加入。
-
静态包含在两个文件中不能有相同的变量,动态包含允许。
由于静态包含相当于将包含文件内容直接复制到主体文件中,如果出现相同的变量,就会出现覆盖等问题,导致文件出错。而动态包含相当于调用不同的jsp,变量所在的空间不同,自然不会出现覆盖等现象。
-
无论是动态包含还是静态包含,其request对象都是相同的。也就是同一个request对象。
静态包含最终编译成一个java文件,有一个request对象很好理解。而动态包含最终编译成多个jsp文件,为何会使用一个request对象呢?其实这些jsp组合的过程是一个请求转发的过程,自然也使用同一个request对象了
2)请求转发:<jsp:forward page="要转发的资源" /> (已过时,现在几乎不用)
pm
注意:建实体类,private时,包装尽量用大写Double,因为小写不包含null,大Double包含null,避免空指针
package com.oracle.domain; //创建一个实体类 并封装 public class Product { private String pid; private String pname; private Double market_price; private Double shop_price; private String pimage; private String pdate; private Integer is_hot; private String pdesc; private Integer pflag; private String cid; public String getPid() { return pid; } public void setPid(String pid) { this.pid = pid; } public String getPname() { return pname; } public void setPname(String pname) { this.pname = pname; } public Double getMarket_price() { return market_price; } public void setMarket_price(Double market_price) { this.market_price = market_price; } public Double getShop_price() { return shop_price; } public void setShop_price(Double shop_price) { this.shop_price = shop_price; } public String getPimage() { return pimage; } public void setPimage(String pimage) { this.pimage = pimage; } public String getPdate() { return pdate; } public void setPdate(String pdate) { this.pdate = pdate; } public Integer getIs_hot() { return is_hot; } public void setIs_hot(Integer is_hot) { this.is_hot = is_hot; } public String getPdesc() { return pdesc; } public void setPdesc(String pdesc) { this.pdesc = pdesc; } public Integer getPflag() { return pflag; } public void setPflag(Integer pflag) { this.pflag = pflag; } public String getCid() { return cid; } public void setCid(String cid) { this.cid = cid; } @Override public String toString() { return "Product [pid=" + pid + ", pname=" + pname + ", market_price=" + market_price + ", shop_price=" + shop_price + ", pimage=" + pimage + ", pdate=" + pdate + ", is_hot=" + is_hot + ", pdesc=" + pdesc + ", pflag=" + pflag + ", cid=" + cid + "]"; } } ----------------------------------------- package com.oracle.dao; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.PreparedStatement; import java.sql.ResultSet; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.QueryRunner; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanHandler; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.BeanListHandler; import org.apache.commons.dbutils.handlers.ScalarHandler; import com.oracle.domain.Condition; import com.oracle.domain.Product; import com.oracle.tools.JDBCUtils; import com.oracle.tools.MyDBUtils; public class ProductDao { // 查询所有商品 public List<Product> getALL() throws SQLException{ /*// 获得连接 Connection conn=JDBCUtils.getConn(); String sql="select * from product"; PreparedStatement pst=conn.prepareStatement(sql); ResultSet rs=pst.executeQuery(); // 处理结果集 ArrayList<Product> arr=new ArrayList<Product>(); while(rs.next()){ //rs.取行的值 Product pro=new Product(); pro.setPid(rs.getString("pid")); pro.setPname(rs.getString("pname")); pro.setMarket_price(rs.getDouble("market_price")); pro.setIs_hot(rs.getInt("is_hot")); pro.setPdate(rs.getString("pdate")); pro.setPimage(rs.getString("pimage")); pro.setPdesc(rs.getString("pdesc")); pro.setPflag(rs.getInt("pflag")); pro.setCid(rs.getString("cid")); arr.add(pro); } return arr;*/ // 创建QueryRunner对象 QueryRunner qr=new QueryRunner(MyDBUtils.getDataSource()); String sql="select * from product"; List<Product> arr=qr.query(sql,new BeanListHandler<Product>(Product.class)); return arr; } // 添加商品 public void add(Product product) throws SQLException{ // 创建Queryrunner对象 QueryRunner qr=new QueryRunner(MyDBUtils.getDataSource());//获得连接池对象 String sql="insert into product(pid,pname,market_price,shop_price,pdate,pdesc,is_hot,cid) values(?,?,?,?,?,?,?,?)"; // 下面获取一定注意要按上面的字符串顺序来 Object[] obj={product.getPid(),product.getPname(),product.getMarket_price(),product.getShop_price(),product.getPdate(),product.getPdesc(),product.getIs_hot(),product.getCid()}; // 执行SQL qr.update(sql,obj); } // 根据pid查询商品--就一条记录--用BeanHandler public Product getProductById(String pid) throws SQLException{ QueryRunner qr=new QueryRunner(MyDBUtils.getDataSource()); String sql="select *from product where pid=?"; Product product=qr.query(sql, new BeanHandler<Product>(Product.class),pid); return product; } // 根据pid修改商品 public void edit(Product product) throws SQLException{ QueryRunner qr=new QueryRunner(MyDBUtils.getDataSource()); String sql="update product set pname=?,market_price=?,shop_price=?,pdesc=?,is_hot=?,cid=? where pid=?"; Object[] obj={product.getPname(),product.getMarket_price(),product.getShop_price(),product.getPdesc(),product.getIs_hot(),product.getCid(),product.getPid()}; qr.update(sql,obj); } // 根据pid删除商品 public void delete(String pid) throws SQLException{ QueryRunner qr=new QueryRunner(MyDBUtils.getDataSource()); String sql="delete from product where pid=?"; qr.update(sql,pid); } // 根据Condition条件查询商品 public List<Product> getProductByCondition(Condition condition) throws SQLException{ // 创建QueryRunner对象 QueryRunner qr=new QueryRunner(MyDBUtils.getDataSource()); // 获取sql String sql="select * from product where 1=1";//where 1=1是一个恒等:不管下面对不对,上面语句永远没问题 // 定义个数组 ArrayList<Object> arr=new ArrayList<Object>(); // 两个条件:1.condition不等于空 2. condition.getname不等于空串 if(condition.getPname()!=null&&condition.getPname().trim()!=""){ sql+=" and pname like ?";//注意 and前面+空格 arr.add("%"+condition.getPname()+"%");//模糊查询需要加% 因为有like,下面就不用加了 } if(condition.getIs_hot()!=null&&condition.getIs_hot()!=""){ sql+=" and is_hot=?"; arr.add(condition.getIs_hot()); } if(condition.getCid()!=null&&condition.getCid().trim()!=""){ sql+=" and cid=?"; arr.add(condition.getCid()); } List<Product> list=qr.query(sql, new BeanListHandler<Product>(Product.class),arr.toArray()); return list; } // 查询商品总条数 public Integer getTotalCount() throws SQLException{ QueryRunner qr=new QueryRunner(MyDBUtils.getDataSource()); String sql="select count(*) from product"; Long count=qr.query(sql,new ScalarHandler<Long>()); return count.intValue(); } // 分页查询商品 public List<Product> getProductByPage(int index,Integer currentCount) throws SQLException{ QueryRunner qr=new QueryRunner(MyDBUtils.getDataSource()); String sql="select * from product limit ?,?"; List<Product> list=qr.query(sql, new BeanListHandler<Product>(Product.class),index,currentCount); return list; } } -------------------------------------------------- package com.oracle.service; import java.sql.SQLException; import java.util.List; import com.oracle.dao.ProductDao; import com.oracle.domain.Condition; import com.oracle.domain.PageBean; import com.oracle.domain.Product; public class ProductService { private ProductDao productDao = new ProductDao(); // 查询所有商品 public List<Product> getAll() { List<Product> arr = null; try { arr = productDao.getALL(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return arr; } // 添加商品 public void add(Product product) { try { productDao.add(product); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } // 根据pid查询商品 public Product getProductById(String pid) { Product product = null; try { product = productDao.getProductById(pid); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return product; } // 根据pid修改商品 public void edit(Product product) { try { productDao.edit(product); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } // 根据pid删除商品 public void delete(String pid) { try { productDao.delete(pid); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } } // 根据Condition查询商品 public List<Product> getProductByCondition(Condition condition) { List<Product> list = null; try { list = productDao.getProductByCondition(condition); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } return list; } // 分页查询商品 // 目的:封装PageBean返回给Servlet public PageBean<Product> getPageBean(Integer currentPage,Integer currentCount){ // 创建PageBean PageBean<Product> pageBean=new PageBean<Product>(); // 设置当前页 pageBean.setCuerrentCount(currentPage); // 设置每页显示条数 pageBean.setCurrentPage(currentCount); // 设置总条数 select count(*) from product int totalcount=0; try { totalcount=productDao.getTotalCount(); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } pageBean.setTotalCount(totalcount); // 计算总页数=总条数/每页显示条数 Integer totalPage=(int)Math.ceil(totalcount*1.0/currentCount);//注意:因为整数/整数,只能等于整数,所以,这里向上取整 // 设置总页数 pageBean.setTotalPage(totalPage); // 设置每页显示的数据 // select * from product limit 起始条数,每页显示条数 // 起始条数=(当前页-1)*每页显示条数 // 定义 int index=(currentPage-1)*currentCount; // 定义空 List<Product> list=null; try { list=productDao.getProductByPage(index, currentCount); } catch (SQLException e) { // TODO Auto-generated catch block e.printStackTrace(); } pageBean.setList(list); return pageBean; } } ------------------------------------------------------ package com.oracle.web; import java.io.IOException; import java.util.List; import javax.servlet.ServletException; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServlet; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest; import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse; import com.oracle.domain.Product; import com.oracle.service.ProductService; public class ProductListServlet extends HttpServlet { private ProductService productService=new ProductService(); public void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { // 获取所有商品 List<Product> list=productService.getAll(); request.setAttribute("ProductList",list); // 请求转发 request.getRequestDispatcher("/product_list.jsp").forward(request, response); } public void doPost(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) throws ServletException, IOException { doGet(request, response); } }
EL技术
1.EL 表达式概述
EL(Express Lanuage)表达式可以嵌入在jsp页面内部,减少jsp脚本的编写,EL 出现的目的是要替代jsp页面中脚本的编写。
2.EL从域中取出数据(EL最重要的作用)
jsp脚本:<%=request.getAttribute(name)%>
EL表达式替代上面的脚本:${requestScope.name}
EL最主要的作用是获得四大域中的数据,格式${EL表达式}
EL获得pageContext域中的值:${pageScope.key};
EL获得request域中的值:${requestScope.key};
EL获得session域中的值:${sessionScope.key};
EL获得application域中的值:${applicationScope.key};
EL从四个域中获得某个值${key}; 相当于findAttribute(String name)
---同样是依次从pageContext域,request域,session域,application域中 获取属性,在某个域中获取后将不在向后寻找
1 package com.oracle.domain; 2 //创建一个class 并私有 3 public class User { 4 private String name; 5 private int age; 6 public String getName() { 7 return name; 8 } 9 public void setName(String name) { 10 this.name = name; 11 } 12 public int getAge() { 13 return age; 14 } 15 public void setAge(int age) { 16 this.age = age; 17 } 18 @Override 19 public String toString() { 20 return "User [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]"; 21 } 23 } 25 ------------------------------------- 26 <%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" 27 pageEncoding="UTF-8"%> 28 <!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd"> 29 <html> 30 <head> 31 <meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=UTF-8"> 32 <title>Insert title here</title> 33 </head> 34 <body> 35 <% 36 pageContext.setAttribute("name","张三 "); 37 request.setAttribute("name1","李四"); 38 session.setAttribute("name2","王五"); 39 application.setAttribute("name3","赵六"); 40 %> 41 42 <%-- <%request.getAttribute("name") %> --%> 43 ${name} 44 ${name1} 45 ${name2} 46 ${name3} 47 48 </body> 49 </html>
运行结果:

用el表达式,尽量把名字不要存同样的,因为如果都一样,用${name} 只会一次从小到大 获取一个值就不会在其他域寻找
另一种方法取对象
<body> <% pageContext.setAttribute("name","张三 "); /* request.setAttribute("name1","李四"); session.setAttribute("name2","王五"); application.setAttribute("name3","赵六"); */ /*向域中存对象 */ User user=new User(); user.setName("张三"); user.setAge(2); request.setAttribute("user",user); %> <%-- <%request.getAttribute("name") %> --%> ${name} ${user.name}...${user.age} </body> </html>
向域中获取对象
<body>
<%
pageContext.setAttribute("name","张三 ");
User user=new User();
user.setName("张三");
user.setAge(2);
request.setAttribute("user",user);/* 向域中存集合 */
User user2=new User();
user2.setName("李四");
user2.setAge(3);
ArrayList<User> arr=new ArrayList<User>();
arr.add(user);
arr.add(user2);
application.setAttribute("list",arr);
%>
<%-- <%request.getAttribute("name") %> --%><!-- 从域里取值 -->
${list[0].name}
${list[1].age}
运行结果
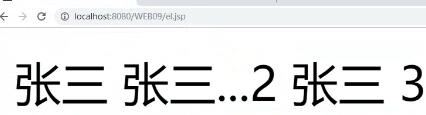
运行结果:

EL执行表达式
访问数据 ${userinfo.id} //1.访问userinfo的id属性。.和[]用于访问数据,二者等价。 ${userinfo[id]} ${userinfo.[user-name]} //当属性名含有特殊符号时,就只能使用[],而不能${userinfo.user-name} ${arrBook[0]} //2.(假定arrBook为数组对象)访问request范围中的数组arrBook中的第一个元素 ${goodsList[0]} //3.(假定goodsList为List对象)访问request范围中的goodsList的第一个元素 算术运算 ${5/2} 或者 ${5 div 2} //5除以2 ${17%3} 或者 %{17 mod 3} //17求余3 ${1+2} //注意+无法实现两个字符串的拼接,只能做算术运算。 判空 ${empty user1} //user1==null或者user1==""的话,都会返回true。 逻辑关系运算 ${10==10} 或者 ${10 eq 10} //返回true ${10!=10} 或者 ${10 ne 10} //返回false ${10<10} 或者 ${10 lt 10} //返回false ${10>=10} 或者 ${10 ge 10} //返回true ${ true && true } 等价 ${"true" && "true"} //可知,字符串会转为Boolean进行处理。 ${!true} 或者 ${not true} 条件运算 ${empty user1? "user1为null或空":user1} //判断user1是否为空,然后输出对应的值。
例如:
${1+1}
<!--第一种 -->
${1+2 }

${empty user}
<!--第二种 --> ${empty arr}<!-- 判断empty是否为空:如果域里没有arr:true,如果有:false--> ${!empty name}<!--判断域里面是否有name -->

${user==null?true:false}
<!-- 第三种 --> ${name==null?"用户名不存在":"用户名已存在 }<!--name是域里的key值 -->






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号