实验三
#include <stdio.h> char score_to_grade(int score); // 函数声明 int main() { int score; char grade; while(scanf("%d", &score) != EOF) { grade = score_to_grade(score); // 函数调用 printf("分数: %d, 等级: %c\n\n", score, grade); } return 0; } // 函数定义 char score_to_grade(int score) { char ans; switch(score/10) { case 10: case 9: ans = 'A'; break; case 8: ans = 'B'; break; case 7: ans = 'C'; break; case 6: ans = 'D'; break; default: ans = 'E'; } return ans; }

问题一:将得分按>=90为A,>=80为B,>=70为C,>=60为D,<60为E进行转化;形参类型为int, 返回值类型为char
问题二:每个case执行后没有break,会以此执行之下的所有语句。ans需用‘’接收

2
#include <stdio.h> int sum_digits(int n); // 函数声明 int main() { int n; int ans; while(printf("Enter n: "), scanf("%d", &n) != EOF) { ans = sum_digits(n); // 函数调用 printf("n = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, ans); } return 0; } // 函数定义 int sum_digits(int n) { int ans = 0; while(n != 0) { ans += n % 10; n /= 10; } return ans; }
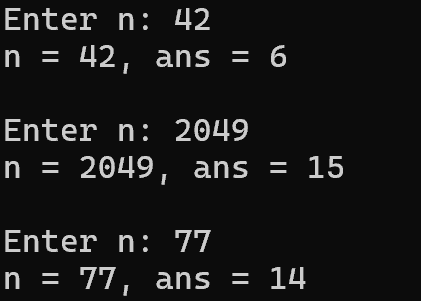
问题一:求正整数n各位数值之和
问题二:可以实现等同效果,
算法思维区别:前者使用了迭代的思维,即使用循环结构达成目标;后者则使用了递归的思维,即通过调用函数自身达成目标
3
#include <stdio.h> int power(int x, int n); // 函数声明 int main() { int x, n; int ans; while(printf("Enter x and n: "), scanf("%d%d", &x, &n) != EOF) { ans = power(x, n); // 函数调用 printf("n = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, ans); } return 0; } // 函数定义 int power(int x, int n) { int t; if(n == 0) return 1; else if(n % 2) return x * power(x, n-1); else { t = power(x, n/2); return t*t; } }
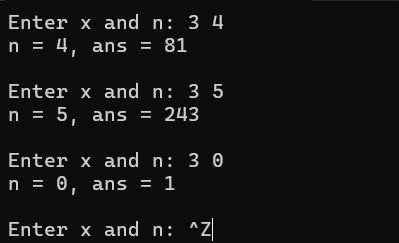
问题一:函数power的功能是计算出x的n次方
问题二:是递归模型函数
4
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> int is_prime(int n); int main(){ int i,count=0; printf("100以内的孪生素数:\n"); for(i=2;i<=100;i++){ if(is_prime(i)==1 && is_prime(i+2)==1){ printf("%d %d\n",i,i+2); count+=1; } } printf("100以内的孪生素数共有%d个\n",count); system("pause"); return 0; } int is_prime(int n){ int j; for(j=2;j<=n/2;j++){ if(n%j==0) return 0; } return 1; }

5
#include<stdio.h> #include<stdlib.h> void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to);//递归 void moveplate(unsigned int n,char from,char to);//移动 static int x=0; int main(){ unsigned int n; while(scanf("%u",&n)!=EOF){ hanoi(n,'A','B','C'); printf("一共移动了%d次\n",x); x=0; } system("pause"); return 0; } void hanoi(unsigned int n,char from,char temp,char to){ if(n==1) moveplate(n,from,to); else { hanoi(n-1,from,to,temp); moveplate(n,from,to); hanoi(n-1,temp,from,to); } x+=1; } void moveplate(unsigned int n,char from,char to){ printf("%u: %c-->%c\n",n,from,to); }
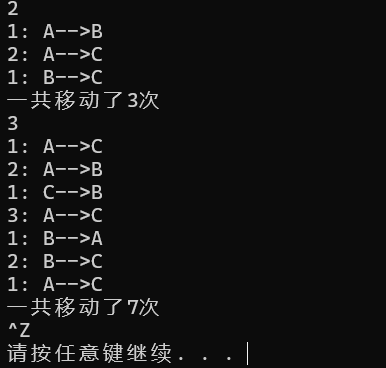
6
方法一
#include <stdio.h> int func(int n, int m); int main() { int n, m; int ans; while (scanf_s("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) { ans = func(n, m); printf("n = %d, m = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, m, ans); } return 0; } int func(int n, int m) { int up=n, down=m; int c=0; if (m == 0 || m == n) return 1; while ((m > 1)and (n > m - 1)) { --n, --m; up *= n; down *= m; } if(down>0) c = up / down; return c; }
方法二
#include <stdio.h> int func(int n, int m); int main() { int n, m; int ans; while (scanf_s("%d%d", &n, &m) != EOF) { ans = func(n, m); printf("n = %d, m = %d, ans = %d\n\n", n, m, ans); } return 0; } int func(int n, int m) { int c1, c2; int c=0; int up1 = n - 1 ,down1 = m; int up2 = n - 1, down2 = m-1; if (n < m) return 0; if (m == n or m == 0) return 1; if (m == 1) return n; else return func(n - 1, m) + func(n - 1, m - 1); while ( (n > m - 1) and (m > 1)) { --n, --m; up1 *= n,up2 *=n; down1 *= m,down2*=m; } c1 = up1 / down1; c2 = up2 / down2; c = c1 + c2; return c; }
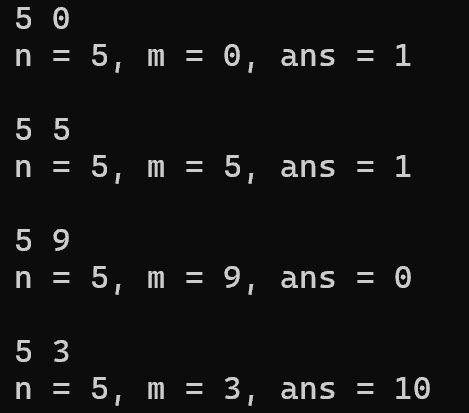
7
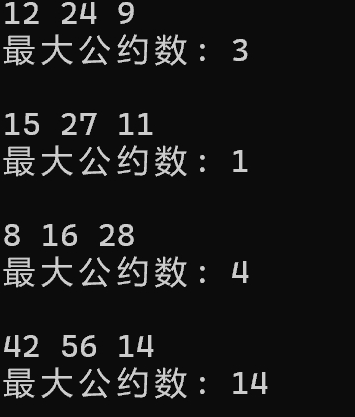
#include <stdio.h> int gcd(int a, int b, int c); int main() { int a, b, c; int ans; while (scanf_s("%d%d%d", &a, &b, &c) != EOF) { ans = gcd(a, b, c); printf("最大公约数: %d\n\n", ans); } return 0; } int gcd(int a,int b,int c) { while (a != b) { if (a > b) a = a - b; else b = b - a; } while (c != b) { if (c > b) c = c - b; else b = b - c; } while (a != c) { if (a > c) a = a - c; else c = c - a; } return a; }


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号