Javascript基础1
javascript的数据类型

Null & Undefined类型
Null类型:
null 则用于表示尚未存在的对象)。如果函数或方法要返回的是对象,那么找不到该对象时,返回的通常是 null。
<script>
var x; // 声明的变量未初始化时,默认值是undefined
function f() {} //当函数无明确返回值时,返回值是undefined/
console.log(x); // undefined
console.log(f()); // undefined
</script>
运算符
算术运算符:
+ - * / % ++ --
比较运算符:
> >= < <= != == === !==
逻辑运算符:
&& || !
赋值运算符:
= += -= *= /=
字符串运算符:
+ 连接,两边操作数有一个或两个是字符串就做连接运算
- i++先引用,再计算
- ++i先计算,再引用
i=10;
res = i++;
console.log(res); // 10
console.log(i); // 11
Javascript的对象
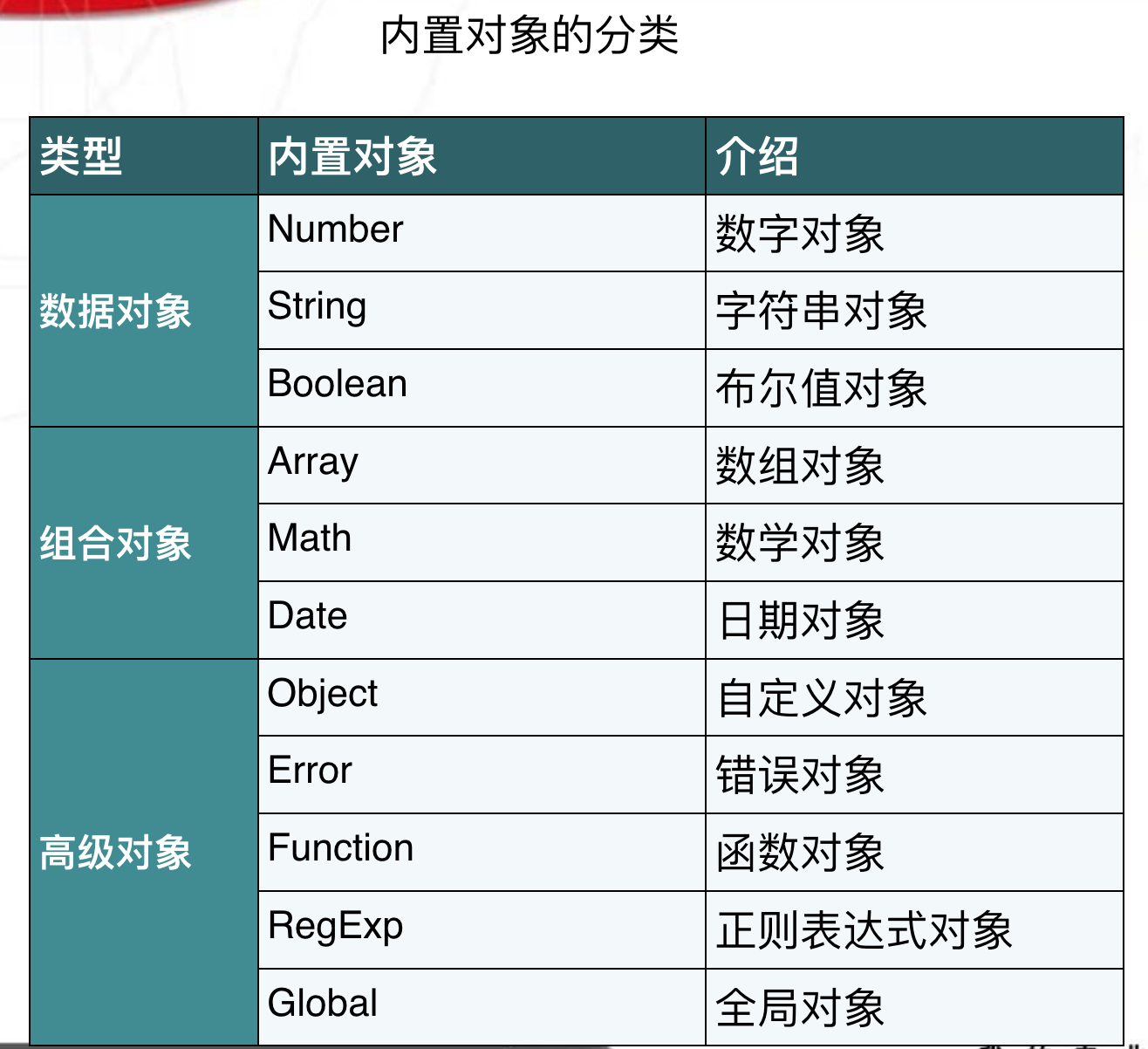
在JavaScript中除了null和undefined以外其他的数据类型都被定义成了对象,也可以用创建对象的方法定义变量,String、Math、Array、Date、RegExp都是JavaScript中重要的内置对象,在JavaScript程序大多数功能都是基于对象实现的。
函数对象
函数的定义
function 函数名 (参数){
函数体;
return 返回值;
}
函数对象的属性
<script>
function foo(a,b,c) {
return a+b+c;
}
console.log(foo(1,2,3));
// arguments的用处
function add() {
sum=0;
for(i=0;i<arguments.length;i++){
sum += arguments[i];
}
return sum
}
console.log(add(1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9)); // 45
// 匿名函数
(function(arg){console.log(arg);})("zou");
</script>
String对象
var s1 =" hello|world ";
var s2 = new String("hello world");
字符串对象的属性和函数
<script>
var s1 =" hello|world ";
var s2 = new String("hello world");
console.log(s1);
console.log(typeof s1); // string
console.log(s2);
console.log(typeof s2); //object
// 字符串对象的属性和函数
var s1 =" Hello|World ";
console.log(s1.length) //获取字符串的长度
console.log(s1.toLowerCase()); // 转为小写
console.log(s1.toUpperCase()); // 转为大写
console.log(s1.trim()); // 去除字符串两边浮动
console.log(s1.trim().length);
console.log(s1.charAt(1)); // 索引拿字符
console.log(s1.indexOf("|")); //字符拿索引
console.log(s1.match("ello")); // ["ello", index: 2, input: " Hello|World "]
// match返回匹配字符串的数组,如果没有匹配则返回null
console.log(s1.search("Hello")); // 1 search返回匹配字符串的首字符位置索引
console.log(s1.substr(1,10)); // Hello|Worl 字符串截断(顾尾)
console.log(s1.substring(1,10)); // Hello|Wor 字符串截断(不顾尾)
// 字符串切片操作 等价于python的[]
console.log(s1.slice(1,5)); // Hell
console.log(s1.slice(0,-2)); // Hello|Worl
console.log(s1.replace("H","h")); // hello|World 字符串替换
console.log(s1.split("|")) // [" Hello", "World "] 字符串切割
console.log(s1.concat("zouruncheng")); // Hello|World zouruncheng 字符串拼接
</script>
Array数组对象
三种创建方式
<script>
var l1 = [1,"zou",2,"run"];
var l2 = new Array([1,"zou",2,"run"]);
var l3 = new Array(4);
l3[0]=1;
l3[1]="zou";
l3[2]=2;
l3[3]="run";
</script>
数组对象的属性和方法
<script>
//数组对象的属性和方法
var l1 = [1,"zou",2,"run"];
// join方法
console.log(l1.join("-")); // 1-zou-2-run 将数组拼接成字符串
// concat拼接数组
console.log(l1.concat(3,"cheng")); // [1, "zou", 2, "run", 3, "cheng"]
console.log(typeof l1.concat([3,"cheng"])); // object
console.log(l1.concat(3,"cheng").toString()); // "1,zou,2,run,3,cheng"
console.log(typeof l1.concat(3,"cheng").toString()); // string
// 数组排序
var l2 = [12, 23 ,44, 100];
console.log(l2.reverse()); // [100, 44, 23, 12] 颠倒数组元素
console.log(l2.sort()); // [100, 12, 23, 44] 默认按第一个字符asc码大小比较
function foo(a,b) {
return a-b;
}
console.log(l2.sort(foo)); //[12, 23, 44, 100]
// 数组切片操作
var l2 = [12, 23 ,44, 100];
console.log(l2.slice(1,3)); // [23, 44]
console.log(l2.slice(1,-1)); // [23, 44]
// 删除子数组和替换
var a = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] ;
console.log(a.splice(1,2)); // [1, 2]
console.log(a); // [0, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
console.log(a.splice(10,0,11,12,13,13)); // [] 插入时返回空
console.log(a); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 12, 13, 13]
console.log();
// 数组的push和pop:
var a = [0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9] ;
a.push(10);
console.log(a); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10]
a.pop();
console.log(a); // [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
a.unshift(4,5);
console.log(a); // [4, 5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
a.shift();
console.log(a); // [5, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
</script>
Date对象
创建Date对象
//方法1:不指定参数
var nowd1=new Date();
alert(nowd1.toLocaleString( ));
//方法2:参数为日期字符串
var nowd2=new Date("2004/3/20 11:12");
alert(nowd2.toLocaleString( ));
var nowd3=new Date("04/03/20 11:12");
alert(nowd3.toLocaleString( ));
//方法3:参数为毫秒数
var nowd3=new Date(5000);
alert(nowd3.toLocaleString( ));
alert(nowd3.toUTCString());
//方法4:参数为年月日小时分钟秒毫秒
var nowd4=new Date(2004,2,20,11,12,0,300);
alert(nowd4.toLocaleString( ));//毫秒并不直接显示
Date对象的方法
获取日期和时间
getDate() 获取日
getDay () 获取星期
getMonth () 获取月(0-11)
getFullYear () 获取完整年份
getYear () 获取年
getHours () 获取小时
getMinutes () 获取分钟
getSeconds () 获取秒
getMilliseconds () 获取毫秒
getTime () 返回累计毫秒数(从1970/1/1午夜)
输出年月日星期
function getCurrentDate(){
//1. 创建Date对象
var date = new Date(); //没有填入任何参数那么就是当前时间
//2. 获得当前年份
var year = date.getFullYear();
//3. 获得当前月份 js中月份是从0到11.
var month = date.getMonth()+1;
//4. 获得当前日
var day = date.getDate();
//5. 获得当前小时
var hour = date.getHours();
//6. 获得当前分钟
var min = date.getMinutes();
//7. 获得当前秒
var sec = date.getSeconds();
//8. 获得当前星期
var week = date.getDay(); //没有getWeek
// 2014年06月18日 15:40:30 星期三
return year+"年"+changeNum(month)+"月"+day+"日 "+hour+":"+min+":"+sec+" "+parseWeek(week);
}
alert(getCurrentDate());
//解决 自动补齐成两位数字的方法
function changeNum(num){
if(num < 10){
return "0"+num;
}else{
return num;
}
}
//将数字 0~6 转换成 星期日到星期六
function parseWeek(week){
var arr = ["星期日","星期一","星期二","星期三","星期四","星期五","星期六"];
// 0 1 2 3 .............
return arr[week];
}
Math对象
//该对象中的属性方法 和数学有关.
abs(x) 返回数的绝对值。
exp(x) 返回 e 的指数。
floor(x)对数进行下舍入。
log(x) 返回数的自然对数(底为e)。
max(x,y) 返回 x 和 y 中的最高值。
min(x,y) 返回 x 和 y 中的最低值。
pow(x,y) 返回 x 的 y 次幂。
random() 返回 0 ~ 1 之间的随机数。
round(x) 把数四舍五入为最接近的整数。
sin(x) 返回数的正弦。
sqrt(x) 返回数的平方根。
tan(x) 返回角的正切。
//方法练习:
//alert(Math.random()); // 获得随机数 0~1 不包括1.
//alert(Math.round(1.5)); // 四舍五入
//练习:获取1-100的随机整数,包括1和100
//var num=Math.random();
//num=num*10;
//num=Math.round(num);
//alert(num)
//============max min=========================
/* alert(Math.max(1,2));// 2
alert(Math.min(1,2));// 1 */
//-------------pow--------------------------------
alert(Math.pow(2,4));// pow 计算参数1 的参数2 次方.




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号