牛客周赛 Round 81 C、D
牛客周赛 Round 81 C、D
C-加法入门(二分、思维)
题意
- 在这一场麻将的背景下面,给一个区间[l,r],把里面的数字翻转,判断翻转之后麻将塔还平衡不平衡
思路
-
先判断l和r是否在同一层,如果同一层,那翻转没有问题,而如果l和r间隔了一层,翻转肯定不平衡
-
所以就仔细考虑l和r是相邻两层的情况
-
题面给的信息,其实给了每行的左端点和右端点,假设所在层数是n,那左端点就是n*(n-1)/2+1,右端点n*(n+1)/2,然后就可以根据这个,判断出来l和r分别在哪一层
-
第一层[左端点,l]的数量cnt_l是l-左端点+1,第二层[左端点,r]的数量cnt_r是r-左端点+1
如果cnt_l>cnt_r的话,那就仍然平衡
- 如果相等的话,也是不可以的
![]()
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
vector<int>ans;
ll leftNode(ll n) { // 左端点
return n * (n - 1) / 2 + 1;
}
ll rightNode(ll n) { // 右端点
return n * (n + 1) / 2;
}
ll getFloor(ll x) { // 用二分找l、r在哪一层
ll l = 1, r = 1e9;
ll m = 0, ans = 0;
while (l <= r) {
m = (l + r) >> 1;
if (leftNode(m) > x) { // 区间比x大
r = m - 1;
}
else if (rightNode(m) < x) { // 区间比x小
l = m + 1;
}
else {
ans = m;
break;
}
}
return ans;
}
void solve() {
ll n, l, r;
cin >> n >> l >> r;
ll floor_l = getFloor(l);
ll floor_r = getFloor(r);
if (floor_l == floor_r) {
ans.push_back(1);
}
else if (floor_l == floor_r - 1) {
ll cnt_l = l - leftNode(floor_l) + 1; // 第一层左边的数量
ll cnt_r = r - leftNode(floor_r) + 1; // 第二层左边的数量
if (cnt_l > cnt_r) {
ans.push_back(1);
}
else {
ans.push_back(0);
}
}
else {
ans.push_back(0);
}
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) {
solve();
}
for (auto x : ans) {
cout << (x ? "Yes" : "No") << endl;
}
return 0;
}
D-中场撸猫(排序、构造)
题意
- 给一个n*n的矩阵,然后计算最多可以构造出几层的麻将塔
思路
- 为了构造尽可能高的塔,每次都尽可能选小的数字,因为塔里面的数字是递增的
- 于是可以给矩阵的每一行排序,第i层,选i个数字,第i+1层,选i+1个数字......直到某一层没办法选足够的数字
- 对于第i层而言,前i-1个数字,比如第j个数字,要大于上一层的第j个数字,最后第i个数字,要大于上一层的最后一个数字,于是按照这样的规则构造就行
代码
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
#define endl '\n'
using namespace std;
vector<int>ans;
void solve() {
int n; cin >> n;
vector<vector<int>>map(n + 1, vector<int>(n + 1, 0));
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
cin >> map[i][j];
}
sort(map[i].begin() + 1, map[i].end());
}
int res = 1;
vector<int>last; // 上一层的数字
last = { map[1][1] };
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) { // 尝试搭建第i层
vector<int>cur; // 当前层的数字,最后覆盖last
// 选i-1个数字,然后看能不能选够i-1个数字,并且还有多余的数字填最后一个数字
int pos = 0;
for (int j = 1; j <= i-1; j++) {
bool found = false;;
for (int k = pos + 1; k <= n; k++) {
if (map[i][k] >= last[j-1]) {
cur.push_back(map[i][k]);
pos = k;
found = true; // 可以找到合适的数字,那就可以更新found
break;
}
}
if (!found) { // 没法找齐前i-1个数字,那第i层没法构造,答案是i-1
ans.push_back(i-1);
return;
}
}
// 找齐了前i-1个数字,看最后一个数字能不能也找到
if (pos != n) { // 矩阵第i行的数字还没用完,直接用上一次选的数字的下一个数
// 毕竟前一个数num1已经大于上一层的最后一个数了,选num1的下一个数字,num2是大于num1的
cur.push_back(map[i][pos + 1]);
res = i; // 更新一下最优解
}
else {
res = i - 1; // 矩阵第i行的数字已经用完了
break;
}
last = cur; // 让当前层,成为上一层,继续尝试
}
ans.push_back(res);
}
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(nullptr);
int _ = 1;
cin >> _;
while (_--) {
solve();
}
for (auto i : ans) {
cout << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}

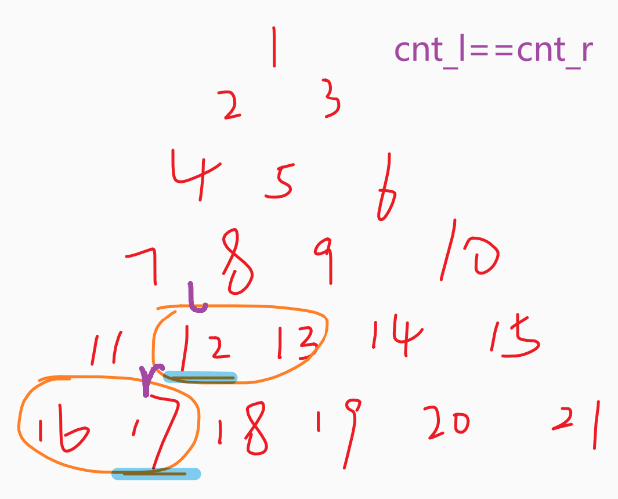

 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号