python基本数据类型的使用、转换----字符串(有待完善)
实例1:
capitalize(self)#首字母大写
str1 = "hello,world"
v = str1.capitalize()
print(v)====>Hello,world
实例2
casefold(self)#将所有都变小写,可变英文字符以及其他语言的小写
lower(self) #将所有都变小写,但只能对英文字符进行变更
upper(self) #将所有都变大写
islower(self) #判断字符串中是否全部为小写
isupper(self) #判断字符串中是否全部为大写,实例见实例18
str1 = "HELLO,World"
v1 = str1.casefold()
v2 = str1.lower()
v3 = v2.islower()
print(v1)=====>hello,world
print(v2)=====>hello,world
print(v3)=====>True
实例3
center(self, width, fillchar=None)#设置宽度,字符串居中,不足默认使用空格填充,可更改填充所用字符
ljust(self, width, fillchar=None)#设置宽度,字符串居左,不足默认使用空格填充,可更改填充所用字符
rjust(self, width, fillchar=None)#设置宽度,字符串居右,不足默认使用空格填充,可更改填充所用字符
zfill(self, width)#设置宽度,字符串居右,不足只能使用0进行填充,不推荐使用
str1 = "Hello"
v1 = str1.center(10, "*")
v2 = str1.center(10)
v3 = str1.ljust(10,"*")
v4 = str1.rjust(10,"*")
v5 = str1.zfill(10)
print(v1)=====>**Hello***
print(v2)=====> Hello
print(v3)=====>Hello*****
print(v4)=====>*****Hello
print(v5)=====>00000Hello
实例4
count(self, sub, start=None, end=None)#计算指定字符在字符串中出现的次数
str1 = "hello world"
v1 = str1.count("l", 0,5)#计算从字符串第0个字符到第5个字符(不包括第5个字符)之间字符“l”出现的次数
v2 = str1.count("l") #计算字符“l”在字符串str1中出现的次数
v3 = str1.count("l", 5) #计算从第5个字符开始到结束,字符“l”出现的次数
v4 = str1.count("l",None, 3)#计算从第0个字符到第3个字符(不包括第3个字符),字符“l”出现的次数
print(v1)=====>2
print(v2)=====>3
print(v3)=====>1
print(v4)=====>1
实例5
endswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None)#判断字符串是否以某个字符结束,可设置由哪个字符开始和由哪个字符结束
startswith(self, suffix, start=None, end=None)#判断字符串是否以某个字符开始,可设置由哪个字符开始和由哪个字符开始
str1 = "hello world"
v1 = str1.endswith("o")
v2 = str1.endswith("d")
v3 = str1.endswith("ld")
v4 = str1.endswith("o",0,5)
v5 = str1.startswith("e")
print(v1)=====>False
print(v2)=====>True
print(v3)=====>True
print(v4)=====>True
print(v5)=====>False
实例6
find(self, sub, start=None, end=None)#输出指定字符或字符串在整个字符串中的索引,找不到字符返回-1
index(self, sub, start=None, end=None)#功能和使用方式同上,区别:若找不到字符会报错“substring not found”,不推荐使用
str1 = "hello world"
v1 = str1.find("lo")
v2 = str1.find("w",3,7)
v3 = str1.find("m")
print(v1)=====>3
print(v2)=====>6
print(v3)=====>-1#未找到相应字符
实例7
format(self, *args, **kwargs)# 格式化,将一个字符串中的占位符替换为指定的值
str1 = "name : {name}, age : {age}"
v1 = str1.format(name = "Lily", age = "19")
str2 = "name : {0}, age : {1}, job : {2}"
v2 = str2.format("Bob", "29", "teacher")
print(v1)=====>name : Lily, age : 19
print(v2)=====>name : Bob, age : 29, job : teacher
实例8
format_map(self, mapping)# 格式化,传入的值 {"name": 'alex', "a": 19}
str1 = "name : {name}, age : {age}"
v1 = str1.format_map({"name" : "Lily", "age" : "19"})
print(v1)=====>name : Lily, age : 19
实例9
isalnum(self)#判断字符串中是否只包含数字和字母,返回值为布尔类型
str1 = "name : {name}, age : {age}"
str2 = "name90"
v1 = str1.isalnum()
v2 = str2.isalnum()
print(v1)=====>False
print(v2)=====>True
实例10
isalpha(self)#判断字符串中是否只包含字母、汉字,返回值为布尔类型
str1 = "we495966"
str2 = "name"
v1 = str1.isalpha()
v2 = str2.isalpha()
print(v1)=====>False
print(v2)=====>True
实例11
isdecimal(self)#判断字符串中是否只包含十进制字符(123)
isdigit(self)#判断字符串中是否只包含数字(123、②)
isnumeric(self)#判断字符串中是否只包含数字(例如:123,②,二,贰)
str1 = "7"
str2 = "a"
v1 = str1.isdecimal()
v2 = str2.isdecimal()
print(v1)=====>True
print(v2)=====>False
实例12
expandtabs(self, tabsize=8)#字符每8个(可自己设定,默认为8)一组,如遇到制表符\t则以空格补齐后输出,继续检索后面的字符
str1 = "dfaj\t0384358\t"
str2 = "name\tage\tjob\nLilei\t12\tstudent\nLily\t11\tstudent\n"
v1 = str1.expandtabs(6)
v2 = str2.expandtabs(10)
print(v1)=====>dfaj 0384358 #用户设定为以6个一组,dfaj四个字符后面遇到\t,补齐2个空格之后输出,继续检索后面的字符,038435无\t,输出,8后面有\t,输出8加5个空格
print(v2)=====>
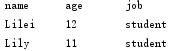
实例13
isidentifier(self)#判断字符串是否为标识符(标识符定义:由数字、字母、下划线组成,且数字不能开头)
str1 = "er"
str2 = "1jdk"
v1 = str1.isidentifier()
v2 = str2.isidentifier()
print(v1)=====>True
print(v2)=====>False
实例14
isprintable(self)#判断字符串中字符中是否包含不可显示的字符(例如\n\t)
str1 = "er"
str2 = "er\t"
v1 = str1.isprintable()
v2 = str2.isprintable()
print(v1)=====>True
print(v2)=====>False
实例15
isspace(self)#判断字符串中是否全部为空格
str1 = "ds dk"
str2 = " "
str3 = ""
v1 = str1.isspace()
v2 = str2.isspace()
v3 = str3.isspace()
print(v1)=====>False
print(v2)=====>True
print(v3)=====>False
实例16
istitle(self)#判断字符串是否为title格式(即每个字母首字母均为大写)
title(self)#将字符串中字母转换为title格式
str1 = "This is a python project"
v1 = str1.istitle()
str2 = str1.title()
v2 = str2.istitle()
print(v1)====>False
print(str1)==>This is a python project
print(v2)====>True
print(str2)==>This Is A Python Project
实例17
join(self, *args, **kwargs)#将字符串中字符按照指定分隔符分隔,适用中文、英文以及其他字符
str1 = "python"
t = " "
v1 = t.join(str1)
v2 = "_".join(str1)
print(v1)====>p y t h o n
print(v2)====>p_y_t_h_o_n
实例18
isupper(self)#判断字符串中字符是否全部为大写
str1 = "da"
str2 = "JKS"
v1 = str1.isupper()
v2 = str2.isupper()
print(v1)=====>False
print(v2)=====>True
实例19
strip(self, chars=None)#默认移除字符串中头部和尾部的空格、换行、制表,若chars有值(该值可为1到多个),则移除指定字符
rstrip(self, *args, **kwargs)#从右侧开始匹配移除
lstrip(self, *args, **kwargs)#从左侧开始匹配移除
str1 = "123hello world321"
v1 = str1.strip("123")
v2 = str1.rstrip("123")
v3 = str1.lstrip("123")
print(v1)=====>hello world
print(v2)=====>123hello world
print(v3)=====>hello world321
实例20
maketrans(*args, **kwargs)#方法用于创建字符映射的转换表,用于对应替换指定字符,与translate配合使用【注意,两个字符串长度需一致】
translate(self, table, deletechars=None)#将maketains创建的字符映射转换表转换成对应字符
s = "hello world"
m = s.maketrans("how", "123")
print(m)=====>{104: 49, 119: 51, 111: 50}
n = s.translate(m)
print(n)=====>1ell2 32rld
实例21
replace(self, old, new, count=None)#字符串中指定的旧子字符串替换成指定的新子字符串【注意:两个字符串长度不做要求】,默认全部替换,可指定替换次数
s = "hello world hello hello"
m = s.replace("hello", "123")#默认替换全部
n = s.replace("hello", "123", 1)#指定只做1次替换
print(m)=====>123 world 123 123
print(n)=====>123 world hello hello
实例22
partition(self, *args, **kwargs)#将字符串通过指定字符或字符串分割为3个部分(从左至右进行分割),必须指定字符或字符串
rpartition(self, *args, **kwargs)#将字符串通过指定字符或字符串分割为3个部分(从右至左分割),必须指定字符或字符串
s = "hello world hello hello"
m = s.partition("ll")
n = s.rpartition(" ")
print(m)=====>('he', 'll', 'o world hello hello')
print(n)=====>('hello world hello', ' ', 'hello')
实例23
split(self, *args, **kwargs)#将字符串通过指定分割符进行分割,返回结果为列表(从左至右分割)
rsplit(self, *args, **kwargs)#将字符串通过指定分割符进行分割,返回结果为列表(从右至左分割)
s = "hello world test python"
v1 = s.split("ll")#将字符串通过字符“ll”进行分割
v2 = s.rsplit(" ")#将字符串通过“ ”进行分割
v3 = s.split(" ", 2)#将字符串通过“ ”进行分割,分割2次
v4 = s.split(" ",2)[2]#将字符串通过“ ”进行分割,分割2次,并获取索引为2的项
u1,u2,u3 = s.split(" ", 2)#将字符串分割为3部分并把分割后的3部分保存到3个文件中
print(v1)=====>['he', 'o world test python']
print(v2)=====>['hello', 'world', 'test', 'python']
print(v3)=====>['hello', 'world', 'test python']
print(v4)=====>test python
print(u1)=====>hello
print(u2)=====>world
print(u3)=====>test python
实例24
swapcase(self)#大小写转换
s = "PythoN"
v1 = s.swapcase()
print(v1)=====>pYTHOn
实例25
splitlines(self, *args, **kwargs)#根据True、False判断是否保留\n,\r
s = "hello\tpython\nworld\rHI"
v1 = s.splitlines()
v2 = s.splitlines(True)
v3 = s.splitlines(False)
print(s)
print(v1)
print(v2)
print(v3)
============================

说明:关于字符\r:把光标移动到该行的开始位置,经常与换行符一起开始新的一行。
本例子中print(s)时未输出字符world,执行过程是这样的:输出world后遇到\r,光标被移动到行首,之后继续输出HI,world被覆盖了




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号