JavaIO流(二)
2.IO流
I:指input,称为输入流:负责把数据读到内存中去
O:指output ,称为输出流:负责写数据出去
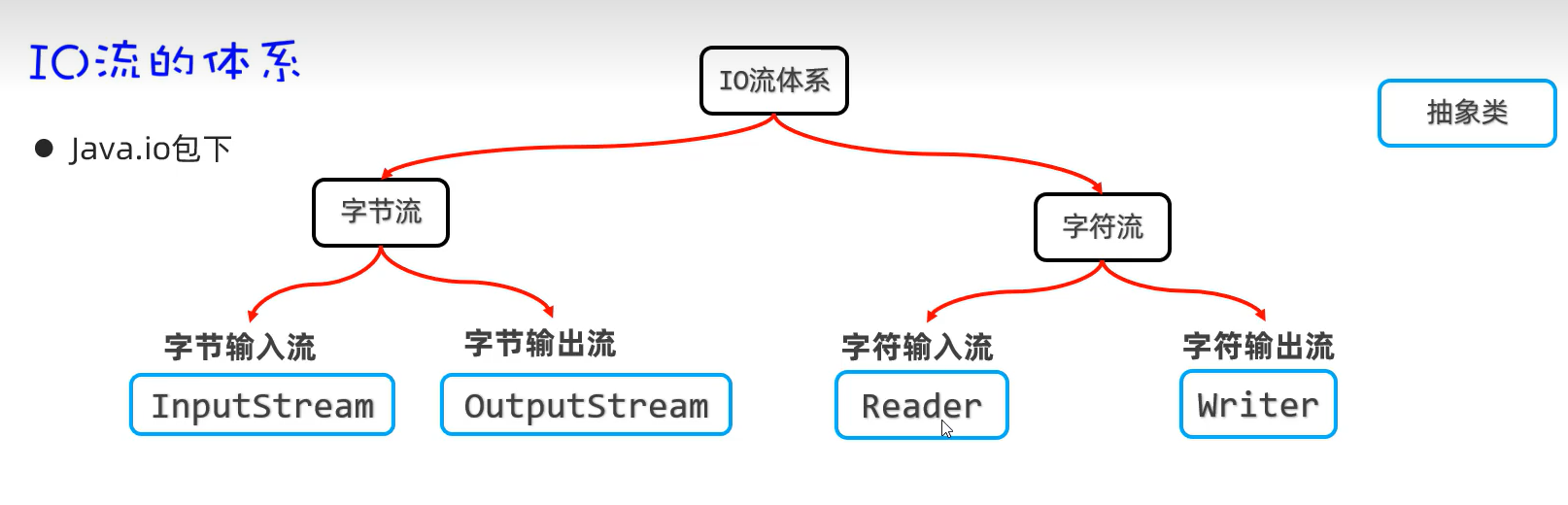
1.IO流的分类
按照流的方向分:
- 输入流
- 输出流
按照流中数据的最小单位分:
-
字节流
-
适合操作所有类型的文件
例如:音频、视频、图片、文本复制、转移等。
-
-
字符流
- 只适合操作纯文本文件
比如:读写TXT、java文件等
总体分为四大流
- 字节输入流:以内存为基准,来自磁盘文件/网络中的数据以字节的形式读入到内存中去的流。
- 字节输出流:以内存为基准,把内存中的数据以字节写出到磁盘文件或者网络中去的流。
- 字符输入流:以内存为基准,来自磁盘文件/网络中的数据以字符的形式读入到内存中去的流。
- 字符输出流:以内存为基准,把内存中的数据以字符写出到磁盘文件或者网络介质中去的流。
1.字节流
1.文件字节输入流(FileInputStream)
- public int read():每次读取一个字节返回,如果没有数据了,返回-1.
package com.IO.byte_stream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/*
目标:掌握文件字节输入流,每次读取一个字节
*/
public class FileInputStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.创建文件字节输入流管道,与源文件接通
//FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan01.txt"));
//简化写法
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan01.txt");//多态
//2.开始读取文件的字节数据
//public int read():每次读取一个字节返回,如果没有数据了,返回-1.
int b1 = is.read();
System.out.println((char)b1);
int b2 = is.read();
System.out.println((char)b2);
int b3 = is.read();
System.out.println(b3);
}
}
使用循环改造代码:
//3.使用循环改造上述代码
int b;//用于记住读取的字节
while ((b = is.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char)b);
}
// 读取数据性能很差
// 读取汉字输出会乱码!!无法避免的!!!
// 流使用完毕之后,必须关闭!释放系统资源!
is.close();
注意事项:
- 读取数据性能很差
- 读取汉字输出会乱码!!无法避免的!!!
- 流使用完毕之后,必须关闭!释放系统资源!(is.close();)
掌握使用FileInputStream每次读取多个字节:
- public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException
- 每次读取多个字节到字节数组中去,返回读取的字节数量,读取完毕会返回-1
package com.IO.byte_stream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
/*
目标:掌握使用FileInputStream每次读取多个字节
*/
public class FileInputStreamTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.创建一个字节输入流对象代表字节输入流管道与源文件接通
FileInputStream s1 = new FileInputStream("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan02.txt");
//2.开始读取文件中的字节数据,每次读取多个字节
//public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException
// 每次读取多个字节到字节数组中去,返回读取的字节数量,读取完毕会返回-1
byte[] buffer =new byte[3];
int len = s1.read(buffer);
String res = new String(buffer);
System.out.println(res);
System.out.println("每次读取的字节数量为:"+len);
int len2 = s1.read(buffer);
//注意:读取多少,倒出多少。
String res2 = new String(buffer,0,len2);
System.out.println(res2);
System.out.println("每次读取的字节数量为:"+len);
int len3 = s1.read(buffer);
System.out.println(len3);//-1
}
}
循环改造上述代码:
//3.使用循环改造
byte[] buffer = new byte[3];
int len;//记录每次读取了多少个字节
while((len = s1.read(buffer)) != -1 ){
String str = new String(buffer,0,len);
System.out.print(str);
}
// 性能得到了明显的提升!!
// 这种方案也不能避免读取汉字输出乱码的问题!!
s1.close();//关闭流
注意:
- 性能得到了明显的提升!!
- 这种方案也不能避免读取汉字输出乱码的问题!!
文件字节输入流:一次性读取完全部字节
- 方式一:自己定义一个字节数组与被读取的文件大小一样大,然后使用该字节数组,一次读完文件的全部字节
package com.IO.byte_stream;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
/*
目标:掌握使用FileInputStream一次性读取完文件的全部字节
*/
public class FileInputStreamTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileInputStream is = new FileInputStream("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan03.txt");
//准备数组
File file = new File("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan03.txt");
long size = file.length();
byte[] buffer = new byte[(int)size];
int len = is.read(buffer);
System.out.println(new String(buffer));
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(len);
}
}
注意:
- 直接把文件数据全部读取到一个字节数组可以避免乱码
- 如果文件过大,创建的字节数组也会过大,可能会引起内存溢出
- 读写文本内容更适合用字符流
2.文件字节输出流(FileOutputStream)
package com.IO.byte_stream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
public class FileOutputStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1.创建一个字节输出流管道与目标文件接通
// 覆盖管道:覆盖之前的数据
//FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("basic-grammar/src/yehuan04.txt");
// 追加数据管道
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("basic-grammar/src/yehuan04.txt",true);
//2.开始写字节数据
os.write('a');//‘a’也是一个字节
os.write(97);//97 就是一个字节,代表a
byte[] bytes = "我爱你中国abc".getBytes();
os.write(bytes);
os.write(bytes,0,15);
//换行符
os.write("\r\n".getBytes());
os.close();
}
}
案例:文件复制(可复制一切文件)
package com.IO.byte_stream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.InputStream;
//目标:使用字节流实现文件复制的操作
public class CopyTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//需求:复制文件
//1.创建一个字节输入流管道与源文件接通
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan04.txt");
//2.创建一个字节输出流管道与源文件接通
FileOutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan05.txt");
//3.创建一个字节数组,负责转移字节数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
os.close();
is.close();
System.out.println("复制完成");
}
}
释放资源的方式
- try-catch-finally
- finally代码区的特点:无论try中的程序是正常运行了还是出现异常,最后都一定执行finally区,除非JVM终止
- 作用:一般用于在程序执行完成后进行资源的释放操作(专业级做法)
package com.IO.resource;
import java.io.*;
public class Test02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
System.out.println(10 / 0);
//需求:复制文件
//1.创建一个字节输入流管道与源文件接通
is = new FileInputStream("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan04.txt");
//2.创建一个字节输出流管道与源文件接通
os = new FileOutputStream("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan05.txt");
System.out.println(10/0);
//3.创建一个字节数组,负责转移字节数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("复制完成");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
//释放资源的操作
try {
if(os != null) os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
try {
if(is != null) is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
}
- try-with-resource (该资源使用完毕后,会自动调用其close()方法,完成对资源的释放)
4.字符流
FileReader(文件字符输入流):和字节输入流的用法差不多
- 作用:以内存为基准,来自磁盘文件/网络中的数据以字符的形式读入到内存中去的流。
package com.IO.char_stream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.Reader;
/*
目标:掌握文件字符输入流每次读取一个字符
*/
public class FileReaderTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
Reader fr = new FileReader("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan05.txt");
){
//读取文本文件的内容
// int c;//记住每次读取的字符编号
// while ((c = fr.read()) != -1){
// System.out.print((char)c);
// }
//每次读取一个字符的形式,性能肯定是比较差的。
//每次读取多个字符
char[] buffer = new char[3];
int len;//记录每次读取多少个字符
while ((len = fr.read(buffer)) != -1) {
System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, len));
}
//性能是比较不错的
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
FileWriter(文件字符输出流):和字节输出流的用法差不多
- 作用:以内存为基准,把内存中的数据以字符写出到磁盘文件或者网络介质中去的流。
package com.IO.char_stream;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
public class FileWriterTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//0.创建一个文件字符输出流管道与目标文件接通。
try (
//覆盖管道
//Writer fw = new FileWriter("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan06out.txt");
//追加数据的管道
Writer fw = new FileWriter("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan06out.txt",true);
){
//1.public void writer(int c):写一个字符出去
fw.write(97);
fw.write('b');
fw.write('欢');
fw.write("\r\n");
//2.public void writer(String c):写一个字符串出去
fw.write("我爱你中国");
fw.write("\r\n");
//3.public void writer(String c,int pos,int len):写字符串的一部分出去
fw.write("我爱你中国",0,5);
fw.write("\r\n");
//4.public void writer(char[] buffer):写一个字符数组出去
char[] buffer = {'夜','冷','昼','欢'};
fw.write(buffer);
fw.write("\r\n");
//5.public void writer(char[],int pos,int len):写字符数组的一部分出去
fw.write(buffer,0,2);
fw.write("\r\n");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
字符输出流的注意事项:
- 字符输出流写出数据后,必须刷新流(fw.flush(),刷新了后面还可以继续使用),或者关闭流(fw.close() 包含了刷新流,关闭了就不能继续使用了),写出去的数据才能生效。
字节流、字符流的使用场景:
- 字节流适合做一切文件数据的拷贝(音视频,文本);字节流不适合读取中文内容输出
- 字符流适合做文本文件的操作(读、写)。
5.缓冲流
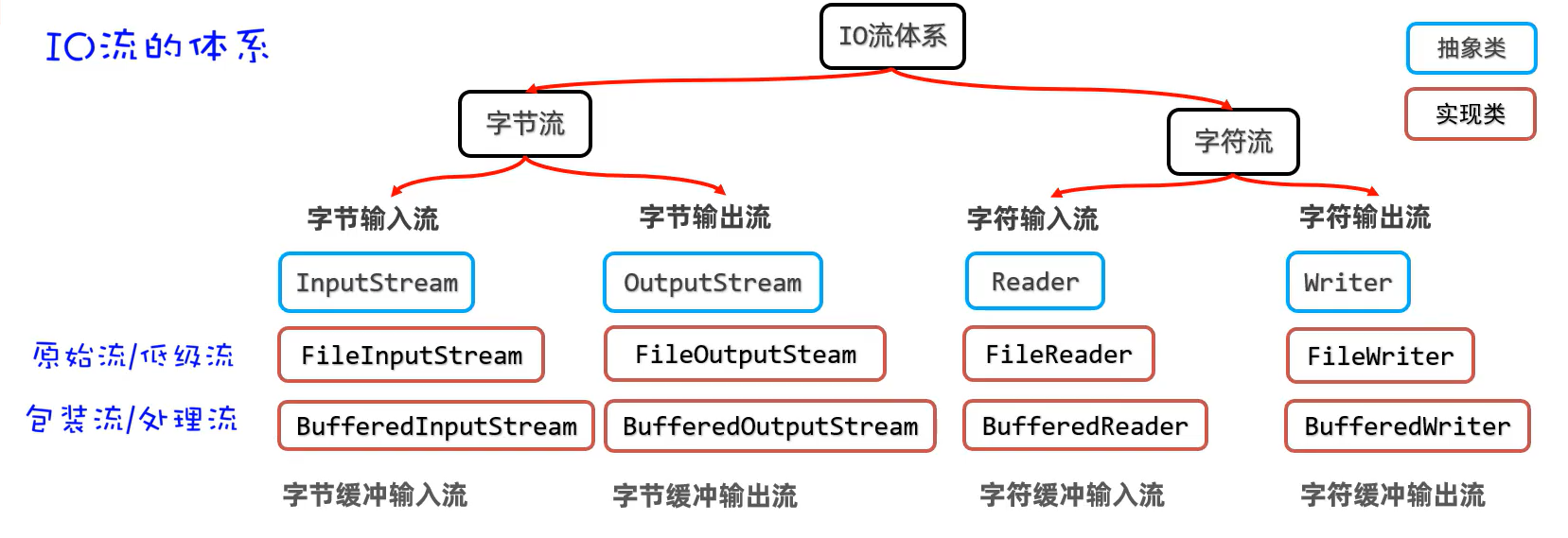
- 作用:对原始流进行包装,以提高原始流读写数据的性能
字节缓冲流
- 作用:提高字节流读写数据的性能
- 原理:字节缓冲输入流(BufferedInputStream)自带了8KB缓冲池;字节缓冲输出流(BufferedOutputStream)也自带了8KB缓冲池。
package com.IO.buffered_stream;
import java.io.*;
public class BufferedInputStreamTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan04.txt");
//1.定义一个字节缓冲输入流包装原始流的字节输入流
InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is,8192*2);//可以声明缓冲池的大小
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan05bak.txt");
//2.定义一个字节缓冲输出流包装原始流的字节输出流
OutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os,8192*2);
){
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
bos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("复制完成");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
字符缓冲流
BufferedReader(字符缓冲输入流)
- 作用:自带8k的字符缓冲池,可以提高字符输入流读取数据的性能
package com.IO.buffered_stream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.Reader;
public class BufferedReaderTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
Reader fr = new FileReader("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan07.txt");
//创建一个字符缓冲输入流包装原始的字符输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
){
// char[] buffer = new char[3];
// int len;
// while ((len = br.read(buffer)) != -1) {
// System.out.print(new String(buffer,0,len));
// }
//新增功能 readLine() 读取一行数据
// System.out.println(br.readLine());
// System.out.println(br.readLine());
// System.out.println(br.readLine());
// System.out.println(br.readLine());
String line;//记录每次读取一行的数据
while((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}
BufferedWriter(字符缓冲输出流)
- 作用:自带8k的字符缓冲池,可以提高字符输入流读取数据的性能
package com.IO.buffered_stream;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.Writer;
public class BufferedWriterTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
Writer fw = new FileWriter("basic-grammar\\src\\yehuan08out.txt", true);
//创建一个字符缓冲输出流管道包装原始的字符输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
){
bw.write('a');
bw.write(97);
bw.write('夜');
bw.newLine();//换行
bw.write("我爱你中国abc");
bw.newLine();//换行
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号