CMU 15-445 2021 Project3 上
首先学习了解一下数据库的目录(catalog)、表、元组(tuple)、索引(index)的结构实现。
(以下代码都是官方已经实现好的,虽然不用我们自己做,但是还是值得学习的)
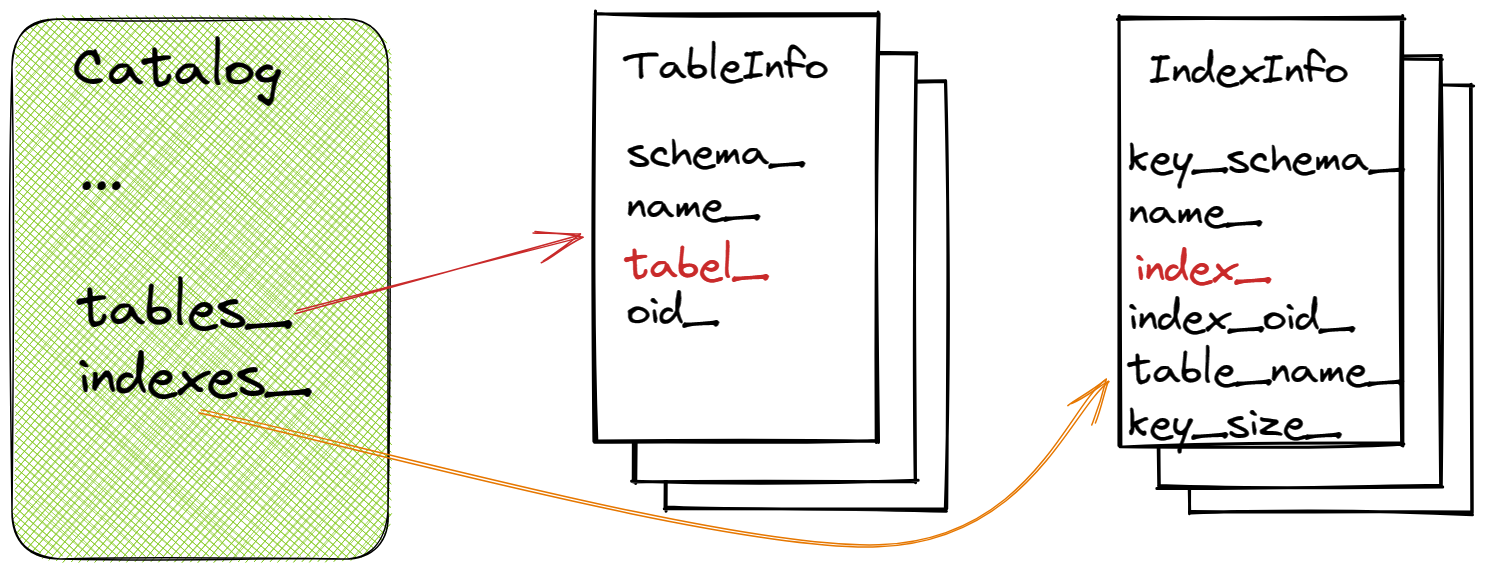
Catalog
Catalog是一种非持久性目录,设计用于由DBMS执行引擎中的执行者使用。它处理创建表、查找表、创建索引和查找索引。
成员变量
[[maybe_unused]] BufferPoolManager *bpm_;
[[maybe_unused]] LockManager *lock_manager_;
[[maybe_unused]] LogManager *log_manager_;
/**
* 映射 表信息结构体标识符 -> 表信息结构体(一个结构体对应一个真实的表)
*/
std::unordered_map<table_oid_t, std::unique_ptr<TableInfo>> tables_;
/** 映射 表名 -> 表信息结构体标识符 */
std::unordered_map<std::string, table_oid_t> table_names_;
/** 下一个被分配的表信息结构体标识符. */
std::atomic<table_oid_t> next_table_oid_{0};
/**
* 映射 索引信息结构体标识符 -> 索引信息结构体(一个结构体对应一个索引)
*/
std::unordered_map<index_oid_t, std::unique_ptr<IndexInfo>> indexes_;
/** 映射 索引名 -> 索引信息结构体标识符 */
std::unordered_map<std::string, std::unordered_map<std::string, index_oid_t>> index_names_;
/** 下一个被分配的索引信息结构体标识符. */
std::atomic<index_oid_t> next_index_oid_{0};
Schema
Schema可以看作属性集合(列 Column 集合),一般用于设置确定的表和索引的属性(列)
TableInfo
TableInfo类维护一个表的元数据
struct TableInfo {
TableInfo(Schema schema, std::string name, std::unique_ptr<TableHeap> &&table, table_oid_t oid)
: schema_{std::move(schema)}, name_{std::move(name)}, table_{std::move(table)}, oid_{oid} {}
/** The table schema */
Schema schema_;
/** The table name */
const std::string name_;
/** An owning pointer to the table heap */
std::unique_ptr<TableHeap> table_;
/** The table OID */
const table_oid_t oid_;
};
TableHeap 是对 TablePage 列表封装后的结构,提供对表页增删改查的功能。
其中 TablePage 是真实存放表中元组数据的结构,它继承自 Page 类,所以可以由缓冲池管理器和磁盘管理器读和存。
当当前表页存放不下一个元组数据,TableHeap 就会在列表尾添加一个表页用于插入数据。
后面会详细分析表页的精彩实现。
IndexInfo
struct IndexInfo {
IndexInfo(Schema key_schema, std::string name, std::unique_ptr<Index> &&index, index_oid_t index_oid,
std::string table_name, size_t key_size)
: key_schema_{std::move(key_schema)},
name_{std::move(name)},
index_{std::move(index)},
index_oid_{index_oid},
table_name_{std::move(table_name)},
key_size_{key_size} {}
/** The schema for the index key */
Schema key_schema_;
/** The name of the index */
std::string name_;
/** An owning pointer to the index */
std::unique_ptr<Index> index_;
/** The unique OID for the index */
index_oid_t index_oid_;
/** The name of the table on which the index is created */
std::string table_name_;
/** The size of the index key, in bytes */
const size_t key_size_;
};
结构图
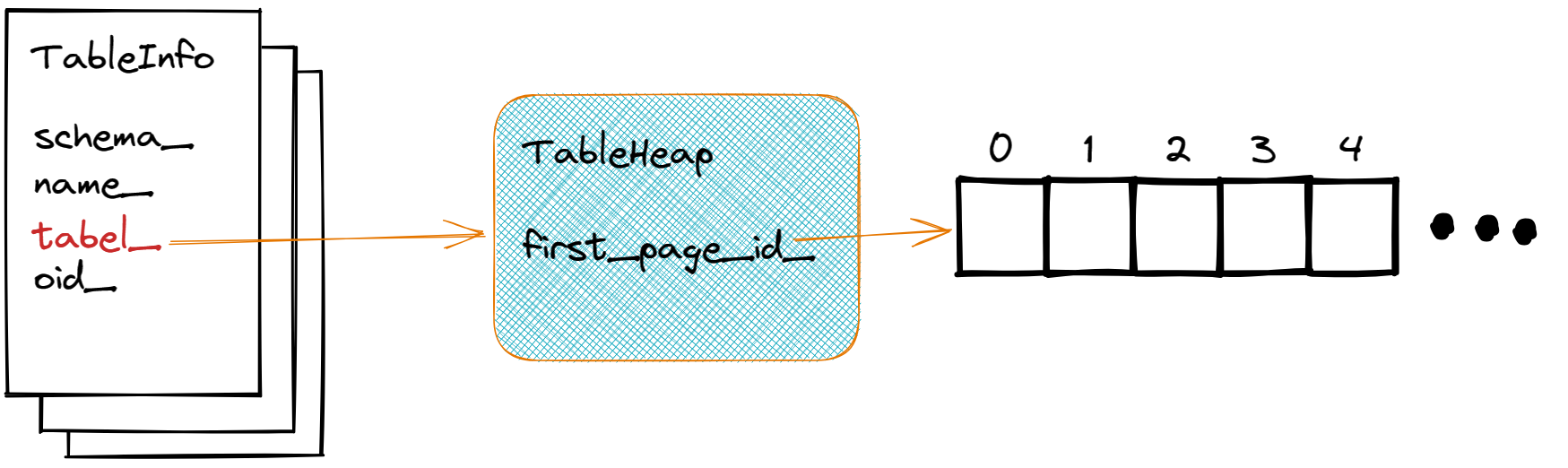
TableHeap
表堆表示磁盘上的物理表。是一个双向链接的页面列表。
class TableHeap {
friend class TableIterator;
...
private:
BufferPoolManager *buffer_pool_manager_;
LockManager *lock_manager_;
LogManager *log_manager_;
page_id_t first_page_id_{};
}
可以看到,它的结构其实非常简单,只有 first_page_id_ 一个关键属性。实际上,因为 TablePage 本质上是 Page,所以每次操作时,只需要获取列表头的 TablePage 对象然后按顺序往后遍历就可以完成各种各样的操作。这需要缓冲管理器的帮助,所以可以看到这里有 BufferPoolManager 对象。
结构图
TablePage
我们直到 Page 有两个关键的属性 page_id 和 data_。TablePage 继承自 Page,在其基础上设计了很多细节用于存储数据。
class TablePage : public Page {
...
private:
static_assert(sizeof(page_id_t) == 4);
static constexpr size_t SIZE_TABLE_PAGE_HEADER = 24;
static constexpr size_t SIZE_TUPLE = 8;
static constexpr size_t OFFSET_PREV_PAGE_ID = 8;
static constexpr size_t OFFSET_NEXT_PAGE_ID = 12;
static constexpr size_t OFFSET_FREE_SPACE = 16;
static constexpr size_t OFFSET_TUPLE_COUNT = 20;
static constexpr size_t OFFSET_TUPLE_OFFSET = 24;
static constexpr size_t OFFSET_TUPLE_SIZE = 28;
}
data_ 的大小是4096个字节,我们借助这块空间存储元组,但是很显然我们不能随便放进去就可以,放进去后还需要确保能知道当前的状态(存放的元组数量、剩余空间大小、每一个元组的开始存放位置...)
TablePage 的解决方法是将 data_ 的头部一部分字节用于存放上述的状态信息。
上面这么多变量就是记录在 data_ 中存放状态的位置:
- SIZE_TABLE_PAGE_HEADER,页面头信息的终止位置,即前24个字节会存放和页面本身有关的信息,如列表中前一个页面的id,后一个页面的id,可用空间大小...;
- OFFSET_PREV_PAGE_ID,即列表中前一个页面的id会存放在 data_ 的第8个字节开始的位置,占有4个字节(8-11);
- OFFSET_NEXT_PAGE_ID,即列表中后一个页面的id会存放在 data_ 的第12个字节开始的位置,占有4个字节(12-15);
- OFFSET_FREE_SPACE,空闲空间指针的位置,(16-19)
- OFFSET_TUPLE_COUNT,列表中已经存放的元组数量会记录在此位置(20-23)
- OFFSET_TUPLE_OFFSET,第一个插入元组的偏移:PAGE_SIZE(4096) - size
- OFFSET_TUPLE_SIZE,第一个元组数据的的大小:size。
OFFSET_TUPLE_OFFSET 和 OFFSET_TUPLE_SIZE 记录第一个元组位置信息的变量,一共占8个字节,所以 SIZE_TUPLE 设置为8。
因为有很多个元组,所以当有新的元组插入后,会从第32个字节位置开始添加新的元组位置信息,占用8个字节。
因为状态信息是从 data_ 头部往后延申的,所以元组数据要从后往前添加。直到需要添加的元组数据会与状态信息重叠,此时就不能添加元组了,需要新建 TablePage 放此元组数据。
结构图
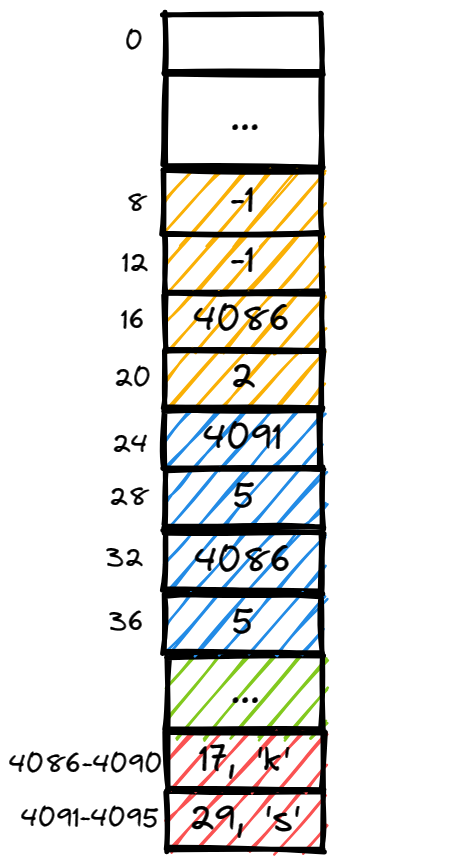
可以看到,这page存放了两个元组 { {29, 's'}, {17, 'k'} } ,每个元组大小都是5。
增删改查
InserTuple
bool TablePage::InsertTuple(const Tuple &tuple, RID *rid, Transaction *txn, LockManager *lock_manager,
LogManager *log_manager) {
BUSTUB_ASSERT(tuple.size_ > 0, "Cannot have empty tuples.");
// If there is not enough space, then return false.
if (GetFreeSpaceRemaining() < tuple.size_ + SIZE_TUPLE) {
return false;
}
// Try to find a free slot to reuse.
uint32_t i; // NOLINT
for (i = 0; i < GetTupleCount(); i++) {
// If the slot is empty, i.e. its tuple has size 0,
if (GetTupleSize(i) == 0) {
// Then we break out of the loop at index i.
break;
}
}
// If there was no free slot left, and we cannot claim it from the free space, then we give up.
if (i == GetTupleCount() && GetFreeSpaceRemaining() < tuple.size_ + SIZE_TUPLE) {
return false;
}
// Otherwise we claim available free space..
SetFreeSpacePointer(GetFreeSpacePointer() - tuple.size_);
memcpy(GetData() + GetFreeSpacePointer(), tuple.data_, tuple.size_);
// Set the tuple.
SetTupleOffsetAtSlot(i, GetFreeSpacePointer());
SetTupleSize(i, tuple.size_);
rid->Set(GetTablePageId(), i);
if (i == GetTupleCount()) {
SetTupleCount(GetTupleCount() + 1);
}
// Write the log record.
if (enable_logging) {
...
}
return true;
}
大致逻辑就是先验证是否有足够的空间来放这个元组,如果可以放,就获取写入数据的指针,然后写入元组,同时更新和添加内部的状态信息,最后记录日志(用于事件管理)。
MarkDelete
bool TablePage::MarkDelete(const RID &rid, Transaction *txn, LockManager *lock_manager, LogManager *log_manager) {
uint32_t slot_num = rid.GetSlotNum();
// If the slot number is invalid, abort the transaction.
if (slot_num >= GetTupleCount()) {
if (enable_logging) {
txn->SetState(TransactionState::ABORTED);
}
return false;
}
uint32_t tuple_size = GetTupleSize(slot_num);
// If the tuple is already deleted, abort the transaction.
if ((tuple_size & DELETE_MASK) == 0 || tuple_size == 0) {
if (enable_logging) {
txn->SetState(TransactionState::ABORTED);
}
return false;
}
if (enable_logging) {
...
}
// Mark the tuple as deleted.
if (tuple_size > 0) {
SetTupleSize(slot_num, tuple_size | DELETE_MASK);
}
return true;
}
DELETE_MASK = 0x80000000
核心就是将 tuple_size 的最高位置(32位)为1,标志这个元组会被标记删除,如果 tuple_size 位0,则说明被正式删除。
ApplyDelete
void TablePage::ApplyDelete(const RID &rid, Transaction *txn, LogManager *log_manager) {
uint32_t slot_num = rid.GetSlotNum();
BUSTUB_ASSERT(slot_num < GetTupleCount(), "Cannot have more slots than tuples.");
uint32_t tuple_offset = GetTupleOffsetAtSlot(slot_num);
uint32_t tuple_size = GetTupleSize(slot_num);
// Check if this is a delete operation, i.e. commit a delete.
if (IsDeleted(tuple_size)) {
tuple_size = UnsetDeletedFlag(tuple_size);
}
// Otherwise we are rolling back an insert.
// We need to copy out the deleted tuple for undo purposes.
Tuple delete_tuple;
delete_tuple.size_ = tuple_size;
delete_tuple.data_ = new char[delete_tuple.size_];
memcpy(delete_tuple.data_, GetData() + tuple_offset, delete_tuple.size_);
delete_tuple.rid_ = rid;
delete_tuple.allocated_ = true;
if (enable_logging) {
...
}
uint32_t free_space_pointer = GetFreeSpacePointer();
BUSTUB_ASSERT(tuple_offset >= free_space_pointer, "Free space appears before tuples.");
memmove(GetData() + free_space_pointer + tuple_size, GetData() + free_space_pointer, tuple_offset - free_space_pointer);
SetFreeSpacePointer(free_space_pointer + tuple_size);
SetTupleSize(slot_num, 0);
SetTupleOffsetAtSlot(slot_num, 0);
// Update all tuple offsets.
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < GetTupleCount(); ++i) {
uint32_t tuple_offset_i = GetTupleOffsetAtSlot(i);
if (GetTupleSize(i) != 0 && tuple_offset_i < tuple_offset) {
SetTupleOffsetAtSlot(i, tuple_offset_i + tuple_size);
}
}
}
这个函数就是正式删除,整个page会重新调整,在此tuple后面的数据会平移到被删元组的位置。
两个删除的区别:MarkDelete 方便简单,耗时少;ApplyDelete 能节约空间,但是全局调整会比较耗时。
GetTuple
bool TablePage::GetTuple(const RID &rid, Tuple *tuple, Transaction *txn, LockManager *lock_manager) {
// Get the current slot number.
uint32_t slot_num = rid.GetSlotNum();
// If somehow we have more slots than tuples, abort the transaction.
if (slot_num >= GetTupleCount()) {
if (enable_logging) {
txn->SetState(TransactionState::ABORTED);
}
return false;
}
// Otherwise get the current tuple size too.
uint32_t tuple_size = GetTupleSize(slot_num);
// If the tuple is deleted, abort the transaction.
if (IsDeleted(tuple_size)) {
if (enable_logging) {
txn->SetState(TransactionState::ABORTED);
}
return false;
}
// Otherwise we have a valid tuple, try to acquire at least a shared lock.
if (enable_logging) {
...
}
// At this point, we have at least a shared lock on the RID. Copy the tuple data into our result.
uint32_t tuple_offset = GetTupleOffsetAtSlot(slot_num);
tuple->size_ = tuple_size;
if (tuple->allocated_) {
delete[] tuple->data_;
}
tuple->data_ = new char[tuple->size_];
memcpy(tuple->data_, GetData() + tuple_offset, tuple->size_);
tuple->rid_ = rid;
tuple->allocated_ = true;
return true;
}
RID
class RID {
...
private:
page_id_t page_id_{INVALID_PAGE_ID};
uint32_t slot_num_{0}; // logical offset from 0, 1...
};
可以看出这是一个用于记录元组位置的数据结构,page_id_ 对应此元组存放的 TablePage,slot_num_ 对应此元组存放在此Page中的位次。这个类可以快速定位元组数据。
Index
Index 主要维护底层表的模式信息以及索引键和元组键之间的映射关系,并为外部世界提供一种抽象的方式来与底层索引实现交互,而不暴露实际实现的接口(实际的使用类是)。
class Index {
public:
...
virtual void InsertEntry(const Tuple &key, RID rid, Transaction *transaction) = 0;
virtual void DeleteEntry(const Tuple &key, RID rid, Transaction *transaction) = 0;
virtual void ScanKey(const Tuple &key, std::vector<RID> *result, Transaction *transaction) = 0;
private:
/** The Index structure owns its metadata */
std::unique_ptr<IndexMetadata> metadata_;
};
}
IndexMetadata 对象维护索引的元组模式和键属性,因为外部调用者不知道索引键的实际结构,所以维护这种映射关系并在元组键和索引键之间进行转换是索引的责任。
class IndexMetadata {
...
private:
/** The name of the index */
std::string name_;
/** The name of the table on which the index is created */
std::string table_name_;
/** key_schema_中的所有列在原表中所有列中的下标 */
const std::vector<uint32_t> key_attrs_;
/** The schema of the indexed key */
Schema *key_schema_;
};
ExtendibleHashTableIndex
template <typename KeyType, typename ValueType, typename KeyComparator>
class ExtendibleHashTableIndex : public Index {
...
protected:
// comparator for key
KeyComparator comparator_;
// container
ExtendibleHashTable<KeyType, ValueType, KeyComparator> container_;
}
ExtendibleHashTable 就是Poj2中实现的hash表,不记得的可以回顾上一篇文章(暂时未发布)
这个 container_ 用于存储元组的对应索引下所有值的hash值到此元组对应 RID 的映射。
InsertEntry
template <typename KeyType, typename ValueType, typename KeyComparator>
void HASH_TABLE_INDEX_TYPE::InsertEntry(const Tuple &key, RID rid, Transaction *transaction) {
// construct insert index key
KeyType index_key;
index_key.SetFromKey(key);
container_.Insert(transaction, index_key, rid);
}
index_key.SetFromKey(key); 就是通过传入元组使用给定的hash函数计算hash值赋给 index_key。
DeleteEntry
template <typename KeyType, typename ValueType, typename KeyComparator>
void HASH_TABLE_INDEX_TYPE::DeleteEntry(const Tuple &key, RID rid, Transaction *transaction) {
// construct delete index key
KeyType index_key;
index_key.SetFromKey(key);
container_.Remove(transaction, index_key, rid);
}
测试
官方给出的一个测试样例:
TEST(CatalogTest, IndexInteraction3) {
auto disk_manager = std::make_unique<DiskManager>("catalog_test.db");
auto bpm = std::make_unique<BufferPoolManagerInstance>(32, disk_manager.get());
auto catalog = std::make_unique<Catalog>(bpm.get(), nullptr, nullptr);
auto txn = std::make_unique<Transaction>(0);
const std::string table_name{"foobar"};
const std::string index_name{"index1"};
// Construct a new table and add it to the catalog
std::vector<Column> columns{
{"A", TypeId::SMALLINT}, {"B", TypeId::SMALLINT}, {"C", TypeId::SMALLINT}, {"D", TypeId::SMALLINT}};
Schema table_schema{columns};
auto *table_info = catalog->CreateTable(nullptr, table_name, table_schema);
EXPECT_NE(Catalog::NULL_TABLE_INFO, table_info);
// Construct an index for the table
std::vector<Column> key_columns{
{"A", TypeId::SMALLINT}, {"B", TypeId::SMALLINT}, {"C", TypeId::SMALLINT}, {"D", TypeId::SMALLINT}};
std::vector<uint32_t> key_attrs{0, 1, 2, 3};
Schema key_schema{key_columns};
// Index construction should succeed
auto *index_info = catalog->CreateIndex<GenericKey<8>, RID, GenericComparator<8>>(
txn.get(), index_name, table_name, table_schema, key_schema, key_attrs, 8, HashFunction<GenericKey<8>>{});
EXPECT_NE(Catalog::NULL_INDEX_INFO, index_info);
auto *index = index_info->index_.get();
// We should now be able to interect with the index
Tuple tuple{std::vector<Value>{ValueFactory::GetSmallIntValue(100), ValueFactory::GetSmallIntValue(101),
ValueFactory::GetSmallIntValue(102), ValueFactory::GetSmallIntValue(103)},
&table_schema};
// Insert an entry
RID rid{};
const Tuple index_key = tuple.KeyFromTuple(table_info->schema_, *index->GetKeySchema(), index->GetKeyAttrs());
index->InsertEntry(index_key, rid, txn.get());
// Scan should provide 1 result
std::vector<RID> results{};
index->ScanKey(index_key, &results, txn.get());
ASSERT_EQ(1, results.size());
// Delete the entry
index->DeleteEntry(index_key, rid, txn.get());
// Scan should now provide 0 results
results.clear();
index->ScanKey(index_key, &results, txn.get());
ASSERT_TRUE(results.empty());
remove("catalog_test.db");
remove("catalog_test.log");
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号