明码(2018蓝桥杯)
题目详情页面:https://www.lanqiao.cn/courses/2786/learning/?id=67808
题目描述:
汉字的字形存在于字库中,即便在今天,16点阵的字库也仍然使用广泛. 16点阵的字库把每个汉字看成是16x16个像素信息.并把这些信息记录在字节中. 一个字节可以存储8位信息,用32个字节就可以存一个汉字的字形了. 把每个字节转为2进制表示,1表示墨迹,О表示底色.每行2个字节,一共16行,布局是: 第1字节,第2字节 第3字节,第4字节 .… .… 第31字节,第32字节 这道题目是给你一段多个汉字组成的信息,每个汉字用32个字节表示,这里给出了字节作为有符号整数的值. 题目的要求隐藏在这些信息中.你的任务是复原这些汉字的字形,从中看出题目的要求,并根据要求填写答案. 这段信息是(一共10个汉字): 4 0 4 0 4 0 4 32 -1 -16 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 8 32 8 32 16 34 16 34 32 30 -64 0 16 64 16 64 34 68 127 126 66 -124 67 4 66 4 66 -124 126 100 66 36 66 4 66 4 66 4 126 4 66 40 0 16 4 0 4 0 4 0 4 32 -1 -16 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 4 32 8 32 8 32 16 34 16 34 32 30 -64 0 0 -128 64 -128 48 -128 17 8 1 -4 2 8 8 80 16 64 32 64 -32 64 32 -96 32 -96 33 16 34 8 36 14 40 4 4 0 3 0 1 0 0 4 -1 -2 4 0 4 16 7 -8 4 16 4 16 4 16 8 16 8 16 16 16 32 -96 64 64 16 64 20 72 62 -4 73 32 5 16 1 0 63 -8 1 0 -1 -2 0 64 0 80 63 -8 8 64 4 64 1 64 0 -128 0 16 63 -8 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 4 -1 -2 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 5 0 2 0 2 0 2 0 7 -16 8 32 24 64 37 -128 2 -128 12 -128 113 -4 2 8 12 16 18 32 33 -64 1 0 14 0 112 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 9 32 9 16 17 12 17 4 33 16 65 16 1 32 1 64 0 -128 1 0 2 0 12 0 112 0 0 0 0 0 7 -16 24 24 48 12 56 12 0 56 0 -32 0 -64 0 -128 0 0 0 0 1 -128 3 -64 1 -128 0 0
题目分析:
此题的本质为进制的转换,本质上没有什么难点(水),值得注意的是数字在计算机中是以补码的方式存放的,此题仅仅要求以8位原码方式打印,
所以在求负数源码的时候会遇到按位取反末尾加一的操作。此时不能使用 num = ~num 的方式取反,
计算机中存放0的是以补码的方式,此时取反会 得到 num = -1。
取1的反则会得到 -2。
运行结果:
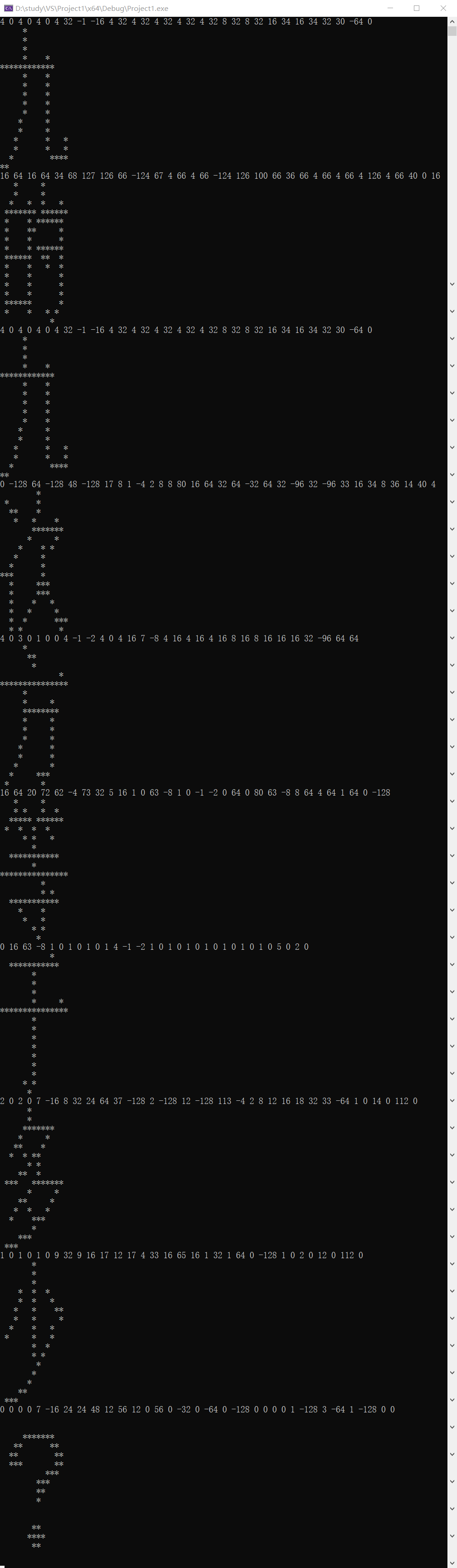
所以答案是 9的9次方 = 387420489
代码:
C:
#pragma warning(disable:4996) #include<bits/stdc++.h> int main() { int num[2]; int a[8];//用于存放8位二进制位 while (~scanf("%d %d", &num[0], &num[1])) { for (int z = 0;z < 2;z++) { bool flag = true; memset(a, 0, sizeof(a)); if (num[z] < 0) { flag = false; num[z] = abs(num[z]); } int index = 7; while (num[z] >= 1) { a[index] = num[z] % 2; num[z] /= 2; index--; } if (!flag) { int x = 7; while (a[x] == 0) x--; while (x >= 0) { if (a[x] == 1)a[x] = 0; if (a[x] == 0)a[x] = 1; x--; } } for (int z = 0;z < 8;z++) if (a[z] == 1) printf("*"); else printf(" "); } printf("\n"); } }
python3.9:
import sys def binary(n): s = bin(n) start = s.index('b') + 1 str1 = s[start:] str1 = list(str1) y = 8 - len(str1) str3 = ['0'] * y str3 += str1 if n < 0: str3 = str3[::-1] x = str3.index('1') x += 1 while x < len(str3): if str3[x] == '1': str3[x] = '0' else: if str3[x] == '0': str3[x] = '1' x += 1 str3 = str3[::-1] x = 0 while x < 8: if str3[x] == '1': str3[x] = '*' if str3[x] == '0': str3[x] = ' ' x += 1 str2 = ''.join(str3) return str2 while True: str = sys.stdin.readline() if not str: break i = 0 '''存放10个数''' binar = [] while i < 32: binar.append(int(str.split(' ')[i])) i += 1 x = 0 while x < 32: flag = True num1 = binary(binar[x]) num2 = binary(binar[x + 1]) x += 2 print(num1 + num2)





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号