集合
什么是集合
-
概念
对象的容器,实现了对对象常用的操作
-
和数组的区别
-
数组长度固定,集合长度不固定
-
数组可以存储基本类型和引用类型,集合只能存储引用类型
-
Collection体系
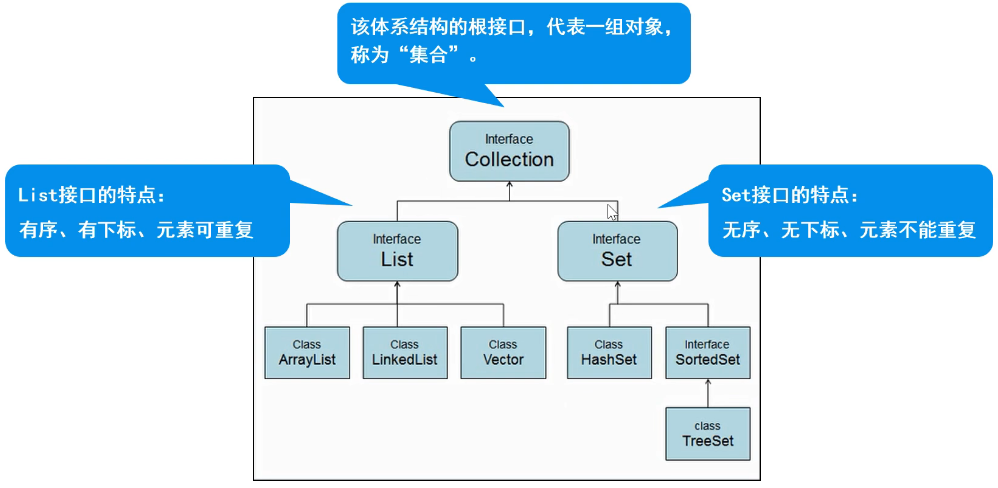
Collection父接口
创建集合 Collection collection = new ArrayList();//注意Collection不提供任何具体实现,故此处new一个ArrayList
-
常用方法
-
添加元素
collection.add(); -
删除元素
collection.remove();collection.clear(); -
遍历元素(重点)
-
使用增强for(因为无下标)
for(Object object : collection){ } -
使用迭代器
//hasNext(); 有没有下一个元素
//next(); 获取下一个元素
//remove(); 删除当前元素
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String object = (String)it.next(); //强转
// 可以使用it.remove(); 进行移除元素
// collection.remove(); 不能用collection其他方法 会报并发修改异常
}
-
-
判断
collection.contains();collection.isEmpty();
-
代码参考
package com.pc.zjs;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* Collection接口的使用
*(1)添加元素
*(2)删除元素
*(3)遍历元素
*(4)判断
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Collection collection=new ArrayList();
//(1)添加元素
collection.add("苹果");
collection.add("西瓜");
collection.add("榴莲");
System.out.println("元素个数"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection);
//删除元素
//collection.remove("榴莲");
//collection.clear();删除全部
//System.out.println("删除之后"+collection.size());
//(3)遍历元素
//3.1增强for
System.out.println("------使用增强for-------");
for(Object object:collection){
System.out.println(object);
}
//3.2使用迭代器
/*
hasNext();有没有下一个元素
next();获取下一个元素
remove();删除当前元素
*/
System.out.println("------使用迭代器--------");
Iterator it=collection.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
String s = (String)it.next();
System.out.println(s);
//collection.remove(s);此处迭代器正在使用collection不允许对collection 进行操作
it.remove();
}
System.out.println("元素个数"+collection.size());
/*
(4)判断
*/
System.out.println(collection.contains("西瓜"));
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
}
}
package com.pc.zjs;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.Iterator;
/**
* Collection的使用:保存学生信息
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//新建Collection对象
Collection collection = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1=new Student("张三",20);
Student s2=new Student("张无忌",18);
Student s3=new Student("王二",22);
//1.添加数据
collection.add(s1);
collection.add(s2);
collection.add(s3);
System.out.println("元素个数"+collection.size());
System.out.println(collection.toString());
//2.删除
//collection.remove(s1);
//collection.clear();
//System.out.println("删除之后"+collection.size());
//3.遍历
/*
3.1增强for
*/
System.out.println("----使用增强for----");
for(Object object:collection){
Student s=(Student)object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//3.2迭代器
System.out.println("---使用迭代器---");
Iterator it = collection.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student)it.next();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//4.判断
System.out.println(collection.contains(s1));
System.out.println(collection.isEmpty());
}
}
package com.pc.zjs;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
//super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
List子接口
特点:有序、有下标、元素可重复
创建集合对象 List list = new ArrayList<>( );
-
常用方法
-
添加元素
list.add( );会对基本类型进行自动装箱 -
删除元素 可以用索引
list.remove(0)当删除数字与索引矛盾时 对数字强转
list.remove((Object) 10)或list.remove(new Integer(10)) -
遍历
-
使用for遍历
for(int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++){System.out.println(list.get(i));
} -
使用增强for
for(Object object: list){ } -
使用迭代器
Iterator it = list.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
String object = (String)it.next(); //强转
// 可以使用it.remove(); 进行移除元素
// collection.remove(); 不能用collection其他方法 会报并发修改异常
} -
使用列表迭代器 💡(注意和迭代器区别)
ListIterator li = list.listIterator();
while(li.hasNext()){
System.out.println(li.nextIndex() + ":" + li.next()); //从前往后遍历
}
while(li.hasPrevious()){
System.out.println(li.previousIndex() + ":" + li.previous()); //从后往前遍历
}
-
-
获取
list.indexOf( ); -
返回子集合
sublist(x, y);左闭右开List subList = list.subList(1, 3);返回索引 1、2
-
List实现类
-
ArrayList 【重点】
-
数组结构实现,必须要连续空间,查询快、增删慢
-
jdk1.2版本,运行效率块、线程不安全
-
-
Vector
-
数组结构实现,查询快、增删慢
-
jdk1.0版本,运行
-
-
LinkedList
-
双向链表结构实现,无需连续空间,增删快,查询慢
-
ArrayList
创建集合 ArrayList arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
-
添加元素
arrayList.add(); -
删除元素
arrayList.remove(new Student("name", 10));
这里重写了 equals(this == obj) 方法
public boolean equals(Object obj){
//1 判断是不是同一个对象
if(this == obj){
return true;
}
//2 判断是否为空
if(obj == null){
return false;
}
//3 判断是否是Student类型
if(obj instanceof Student){
Student == (Student)obj;
//4 比较属性
if(this.name.equals(s.getName()) && this.age == s.getAge()){
return true;
}
}
//5 不满足条件返回false
return false;
}
-
遍历元素【重点】
-
使用迭代器
Iterator it = arrayList.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student)it.next(); //强转
} -
列表迭代器
ListIterator li = arrayList.listIterator();
while(li.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student)li.next(); //从前往后遍历
}
while(li.hasPrevious()){
Student s = (Student)li.previous();//从后往前遍历
}
-
-
判断
arrayList.contains();和arrayList.isEmpty(); -
查找
arrayList.indexof();
参考代码
package com.pc.zjs;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
public class Demo04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
List list=new ArrayList();
//1.添加数字数据(自动装箱)
list.add(20);
list.add(30);
list.add(40);
list.add(50);
list.add(60);
System.out.println("元素个数"+list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
//2删除操作
//list.remove(0);
list.remove((Object)20);
//list.remove(new Integer(20));
System.out.println("删除元素"+list.size());
System.out.println(list.toString());
//3补充方法sublist,返回子集和,含头不含尾
List sublist=list.subList(1, 3);
System.out.println(sublist.toString());
}
}
package com.pc.zjs;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.ListIterator;
/**
* ArrayList的使用
*/
public class Demo05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList arrayList=new ArrayList<>();
//1.添加元素
Student s1=new Student("刘德华",20);
Student s2=new Student("郭富城",22);
Student s3=new Student("梁朝伟",18);
arrayList.add(s1);
arrayList.add(s2);
arrayList.add(s3);
System.out.println("元素个数"+arrayList.size());
System.out.println(arrayList.toString());
//2.删除元素
//arrayList.remove(s1);
arrayList.remove(new Student("刘德华",20));
System.out.println("删除之后"+arrayList.size());
//3.遍历元素【重点】
//3.1使用迭代器
System.out.println("---使用迭代器---");
Iterator it = arrayList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student)it.next();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//3.2使用列表迭代器
System.out.println("---使用列表迭代器---");
ListIterator lit = arrayList.listIterator();
while (lit.hasNext()){
Student s = (Student)lit.next();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
System.out.println("---使用列表迭代器逆序---");
while (lit.hasPrevious()){
Student s=(Student)lit.previous();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//4.判断
System.out.println(arrayList.contains(new Student("梁朝伟",18)));
System.out.println(arrayList.isEmpty());
//5.查找
System.out.println(arrayList.indexOf(new Student("梁朝伟",18)));
}
}
package com.pc.zjs;
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
//super();
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
ArrayList源码分析
DEFAULT_CAPACITY = 10; //默认容量
//注意:如果没有向集合中添加任何元素时,容量0,添加一个后,容量为10
//每次扩容是原来的1.5倍
elementData存放元素的数组
size 实际元素个数
Vector
创建集合 Vector vector = new Vector<>();
增加、删除、判断同上
遍历中枚举器遍历
Enumeration en = vector.elements();
while(en.hasMoreElements()){
String o = (String)en.nextElement();
System.out.println(o);
}
package com.pc.zjs01;
import java.util.Enumeration;
import java.util.Vector;
/**
* 演示Vector的使用
*/
public class Demo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
Vector vector=new Vector<>();
//1.添加元素
vector.add("草莓");
vector.add("芒果");
vector.add("西瓜");
System.out.println("元素个数"+vector.size());
//2.删除
// vector.remove(0);
// vector.remove("西瓜");
// vector.clear();
//3.遍历
//使用枚举器
Enumeration en=vector.elements();
while (en.hasMoreElements()){
String o=(String)en.nextElement();
System.out.println(o);
}
//判断
System.out.println(vector.contains("西瓜"));
System.out.println(vector.isEmpty());
//vector其他方法
//firstElement,lastElement,elementAt();
}
}
LinkedList
创建链表集合LinkedList li = new LinkedList<>();
常用方法与List一致
package com.pc.zjs01;
import com.pc.zjs.Student;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
/**
* LinkedList的使用
*
*/
public class Demo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//创建集合
LinkedList linkedList=new LinkedList<>();
//1.添加元素
Student s1=new Student("刘德华",20);
Student s2=new Student("郭富城",22);
Student s3=new Student("梁朝伟",18);
linkedList.add(s1);
linkedList.add(s2);
linkedList.add(s3);
System.out.println("元素个数"+linkedList.size());
System.out.println(linkedList.toString());
//2.删除
// linkedList.remove(new Student("刘德华",20));
// System.out.println("删除之后"+linkedList.size());
// linkedList.clear();
//3.遍历
//3.1for遍历
System.out.println("---for遍历---");
for (int i = 0; i < linkedList.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(linkedList.get(i));
}
//3.2增强for
System.out.println("---增强for---");
for(Object object:linkedList){
Student s=(Student)object;
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//3.3使用迭代器
System.out.println("---使用迭代器---");
Iterator it = linkedList.iterator();
while (it.hasNext()){
Student s= (Student) it.next();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//3.4使用列表迭代器
System.out.println("---使用列表迭代器---");
Iterator lit = linkedList.listIterator();
while (lit.hasNext()){
Student s= (Student) lit.next();
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
//4判断
System.out.println(linkedList.contains(s1));
System.out.println(
