Systemd
https://www.ruanyifeng.com/blog/2016/03/systemd-tutorial-commands.html
https://www.freedesktop.org/software/systemd/man/systemd-analyze.html
#how to remove systemd service
systemctl stop [servicename] systemctl disable [servicename] rm /etc/systemd/system/[servicename] rm /etc/systemd/system/[servicename] # and symlinks that might be related rm /usr/lib/systemd/system/[servicename] rm /usr/lib/systemd/system/[servicename] # and symlinks that might be related systemctl daemon-reload systemctl reset-failed
#inside of enable/disable a service
- sudo systemctl enable application.service
This will create a symbolic link from the system’s copy of the service file (usually in /lib/systemd/system or /etc/systemd/system) into the location on disk where systemd looks for autostart files (usually /etc/systemd/system/some_target.target.wants. We will go over what a target is later in this guide).
To disable the service from starting automatically, you can type:
This will remove the symbolic link that indicated that the service should be started automatically.
(RT)
systemd is a new init system and system manager that has become so popular that it has been widely transformed into the new standard init system by most Linux distributions.
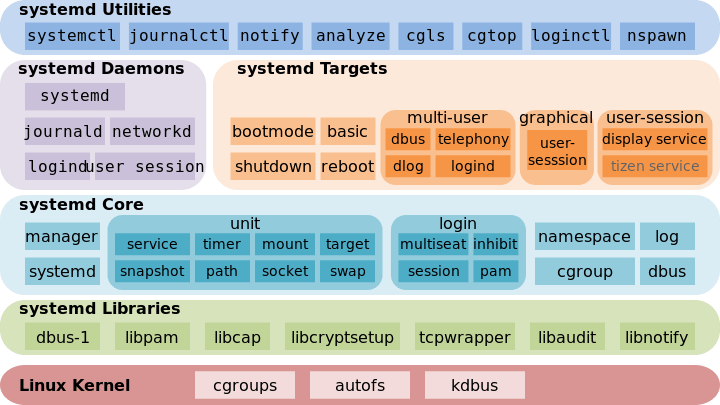
systemd Features:
- systemd provides aggressive parallelization capabilities
- Uses socket and D-Bus activation for starting services
- Offers on-demand starting of daemons
- Keeps track of processes using Linux cgroups
- Supports snapshotting and restoring of the system state
- Maintains mount and automount points
- Implements an elaborate transactional dependency-based service control logic
Service Commands:
These are the most commonly used service commands on a Linux system to manage services.
| Short Description | SysVinit Command | systemd Command |
| To Start a Service | service example start | systemctl start example |
| To Stop a Service | service example stop | systemctl stop example |
| Stop and then Start a Service (Restart a Service) | service example restart | systemctl restart example |
| Reload a Service (Reload the config file) | service example reload | systemctl reload example |
| Restarts if the service is already running | service example condrestart | systemctl condrestart example |
| How to check if a service is currently running | service example status | systemctl status example |
| How to enable a service on boot/startup | chkconfig example on | systemctl enable example |
| How to disable a service on boot/startup | chkconfig example off | systemctl disable example |
| How to check if a service is configured to start on boot or not | chkconfig example –list | systemctl is-enabled example |
| How to display a list of enabled or disabled services on boot with runlevels information | chkconfig | systemctl list-unit-files –type=service |
| Create a new service file or modify any configuration | chkconfig example –add | systemctl daemon-reload |
Runlevels/Targets:
The systemd has a concept of targets, which serves a similar purpose as runlevels, but operates slightly differently. Each target is named instead of numbers and is intended to serve a specific purpose.
| Short Description | SysVinit Command | systemd Command |
| To halt the system | 0, halt | runlevel0.target, poweroff.target, systemctl halt |
| Single user mode | 1, S, single | runlevel1.target, rescue.target |
| Multi User | 2 | runlevel2.target, multi-user.target |
| Multi User with Network | 3 | runlevel3.target, multi-user.target |
| Experimental (No User) | 4 | runlevel4.target, multi-user.target |
| Multi-user with Graphical & Network | 5 | runlevel5.target, graphical.target |
| To reboot a system | 6, reboot | runlevel6.target, reboot.target, systemctl reboot |
| Emergency shell | emergency | emergency.target |
Other systemd Commands:
There are other commands in systemd that are very useful.
| Short Description | systemd Command |
| Control the system hostname | hostnamectl |
| Team daemon control tool | teamdctl |
| Control the system time and date | timedatectl |
| Query the systemd journal | journalctl |
| How to check system boot time | systemd-analyze or systemd-analyze time |
| How to check each service time consumption at startup | systemd-analyze blame |
| Kill all processes associated with a service | systemctl kill example |
| List all running services | systemctl |
| Show system status | systemctl status |
| How to run the systemd command on a remote machine | systemctl status example -H user@remotehost |




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号