剑指offer刷题记录
剑指offer题解
题1 两个栈表示一个队列
思路:就是一个栈专门增加,一个栈专门删除队列
图解:
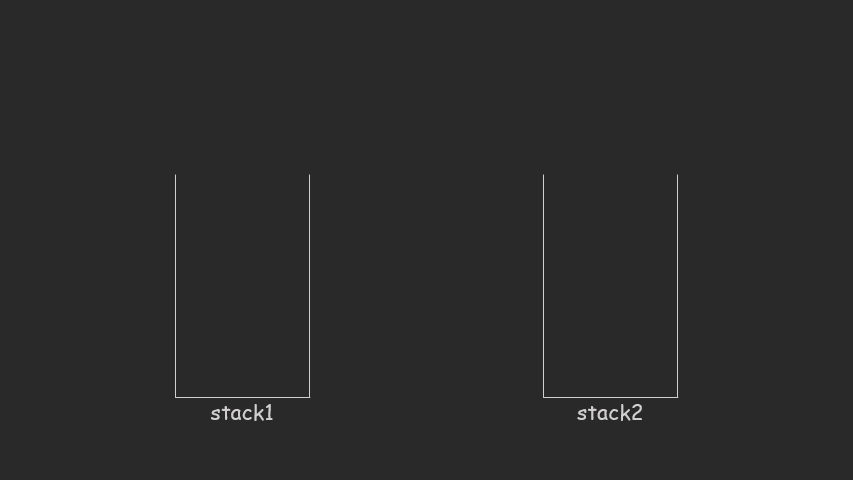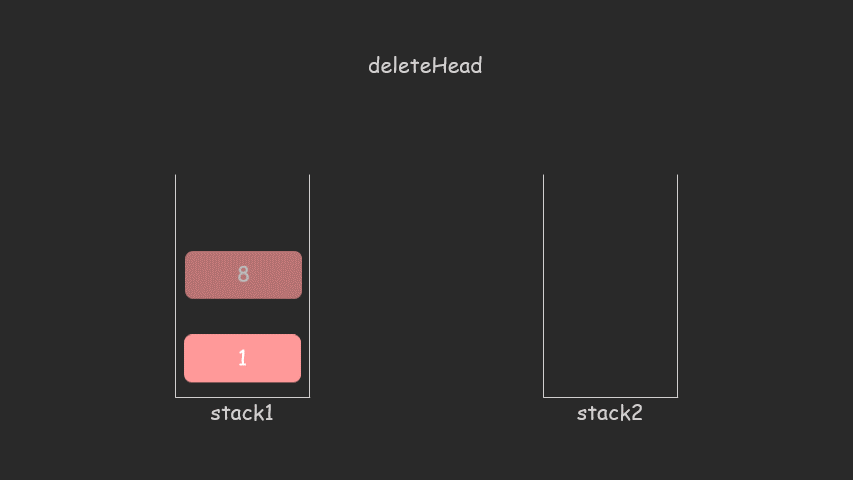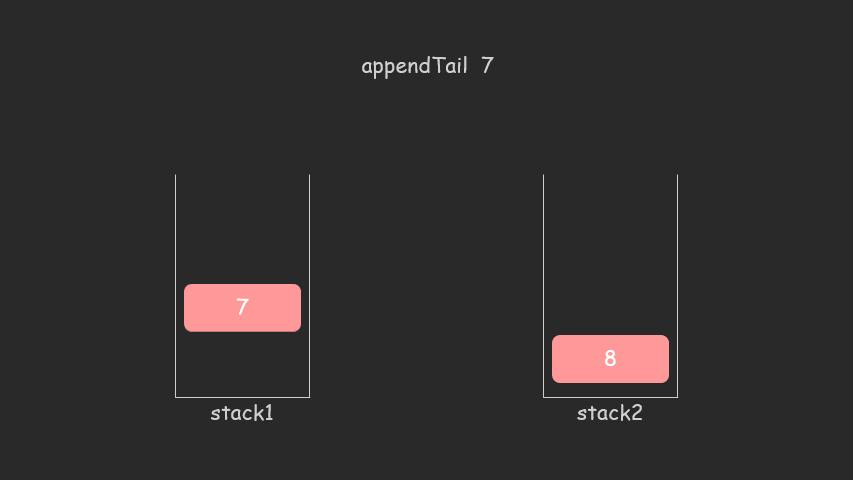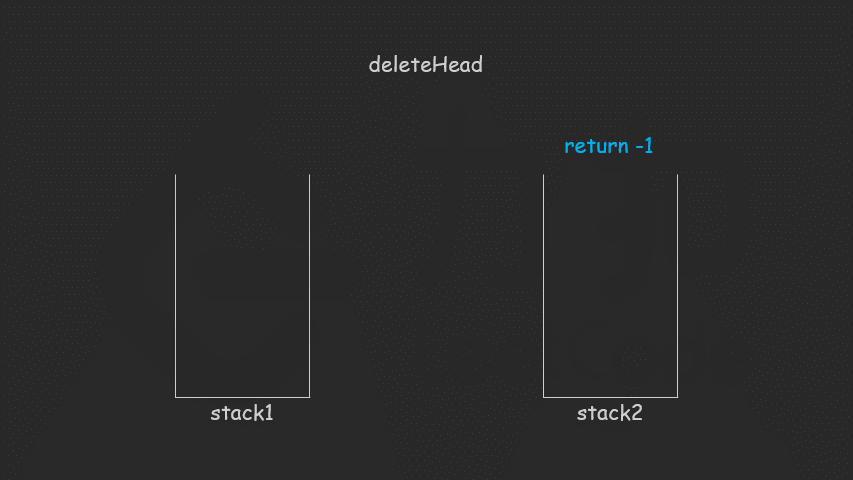
class CQueue {
Stack<Integer> stack1;
Stack<Integer> stack2;
public CQueue() {
stack1 = new Stack<Integer>();
stack2 = new Stack<Integer>();
}
public void appendTail(int value) {
stack1.push(value);
}
public int deleteHead() {
if(stack2.empty()){
while(!stack1.empty()){
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
if(stack2.empty()){
return -1;
}else{
return stack2.pop();
}
}
}
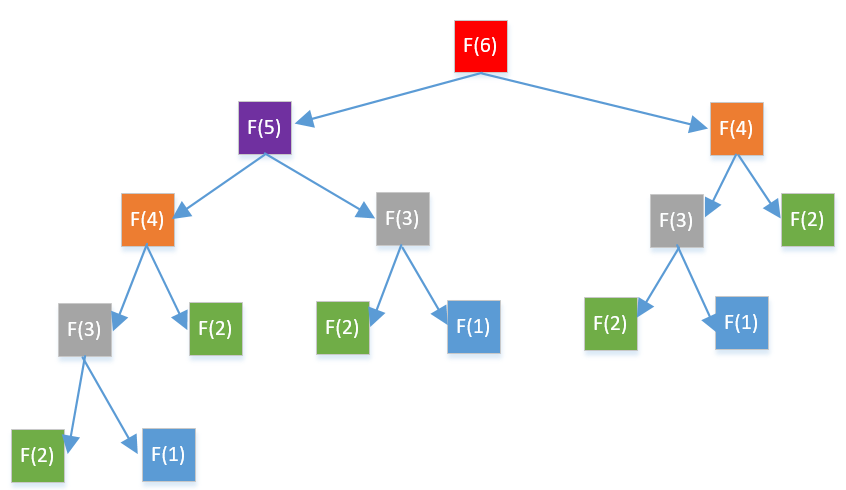
题2 斐波那契数列
思路: 动态规划
我们看到下面相同颜色的都是重复计算,当n越大,重复的越多,所以我们可以使用一个map把计算过的值存起来,每次计算的时候先看map中有没有,如果有就表示计算过,直接从map中取,如果没有就先计算,计算完之后再把结果存到map中
/*
递归调用,采用hashmap
*/
int constant = 1000000007;
public int fib(int n) {
return fib(n, new HashMap());
}
public int fib(int n, Map<Integer, Integer> map) {
if (n < 2)
return n;
if (map.containsKey(n))
return map.get(n);
int first = fib(n - 1, map) % constant;
map.put(n - 1, first);
int second = fib(n - 2, map) % constant;
map.put(n - 2, second);
int res = (first + second) % constant;
map.put(n, res);
return res;
}
//非递归调用
class Solution {
public int fib(int n) {
int a = 0;
int b = 1;
int sum;
for(int i = 0; i<n; i++){
sum = (a+b) % 1000000007;
a=b;
b = sum;
}
return a;
}
}
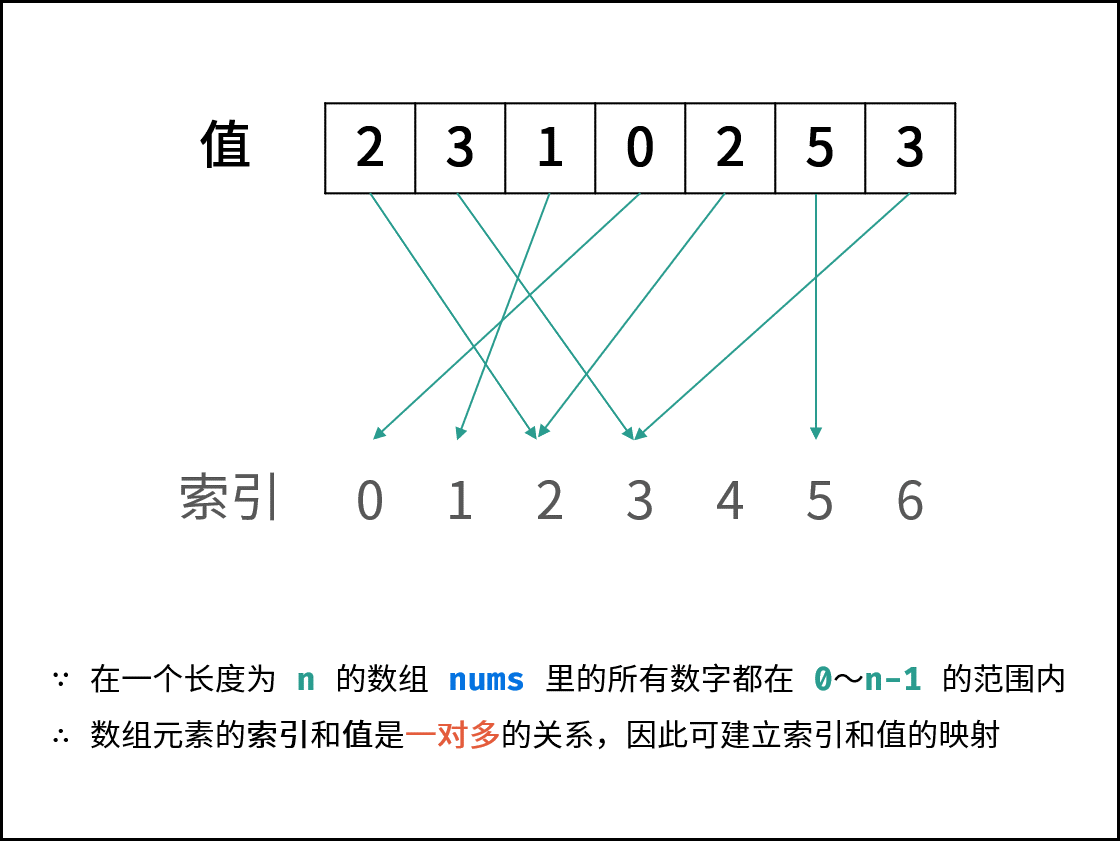
题3 03 数组中重复的数字
在一个长度为 n 的数组 nums 里的所有数字都在 0~n-1 的范围内。数组中某些数字是重复的,但不知道有几个数字重复了,也不知道每个数字重复了几次。请找出数组中任意一个重复的数字。
方法一:暴力枚举法
//暴力搜索
//时间复杂度为O(n^2)
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
for(int i = 0; i < nums.length;i++){
for(int j = i+1; j<nums.length;j++){
if(nums[j]==nums[i]){
return nums[i];
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}
方法二:哈希表
思路:哈希表(set)特点就是没有重复的数字,当查到重复数字后就返回。
//hashset
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
HashSet<Integer> hashset = new HashSet<Integer>();
int k = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<nums.length;i++){
hashset.add(nums[i]);
k++;
if(k !=hashset.size())
return nums[i];
}
return -1;
}
}
方法三:原地置换
图解
//原地置换
class Solution {
public int findRepeatNumber(int[] nums) {
int i = 0;
while(i < nums.length) {
if(nums[i] == i) {
i++;
continue;
}
if(nums[nums[i]] == nums[i]) return nums[i];
int tmp = nums[i];
nums[i] = nums[tmp];
nums[tmp] = tmp;
}
return -1;
}
}
题目4 剑指 Offer 04. 二维数组中的查找
在一个 n * m 的二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个高效的函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
示例:
现有矩阵 matrix 如下:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
给定 target = 5,返回 true。
给定 target = 20,返回 false。
方法一:暴力枚举(省略)
方法二:线性查找
由于给定的二维数组具备每行从左到右递增以及每列从上到下递增的特点,当访问到一个元素时,可以排除数组中的部分元素。从二维数组的右上角(或者左下角, 左上角和右上角不能排除)开始查找。如果当前元素等于目标值,则返回 true。如果当前元素大于目标值,则移到左边一列。如果当前元素小于目标值,则移到下边一行。可以证明这种方法不会错过目标值。如果当前元素大于目标值,说明当前元素的下边的所有元素都一定大于目标值,因此往下查找不可能找到目标值,往左查找可能找到目标值。如果当前元素小于目标值,说明当前元素的左边的所有元素都一定小于目标值,因此往左查找不可能找到目标值,往下查找可能找到目标值。
注: 相当于矩阵倒转45°变成了二叉搜索树
class Solution {
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
int rows = matrix.length, columns = matrix[0].length;
int row = 0, column = columns-1;
while(row < rows && column >=0){
if(matrix[row][column] == target){
return true;
}else if(matrix[row][column] > target){
column --;
}else{
row ++;
}
}
return false;
}
}
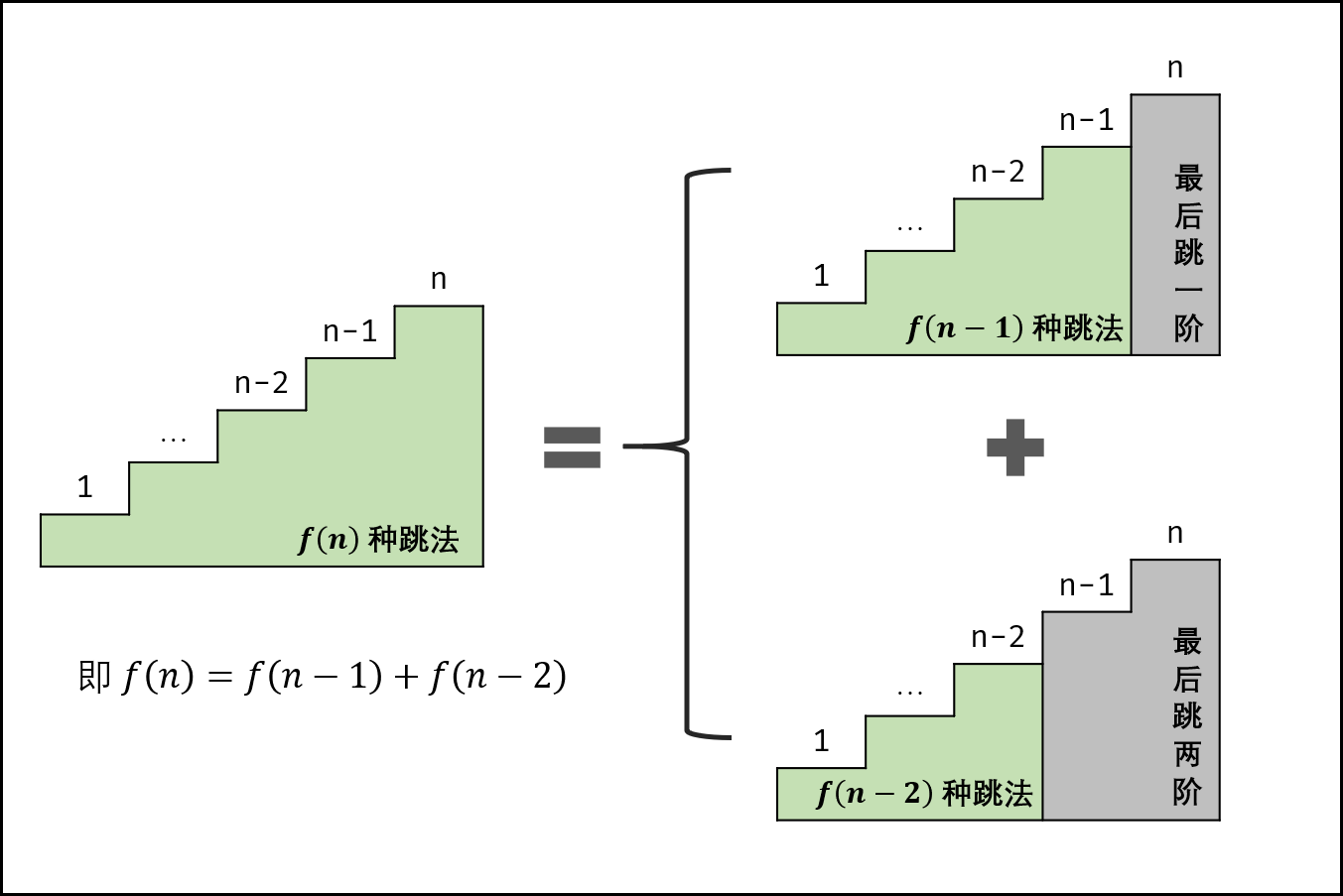
题目5 青蛙跳阶问题
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级台阶。求该青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
答案需要取模 1e9+7(1000000007),如计算初始结果为:1000000008,请返回 1。
思路: 青蛙跳一个台阶后,还剩下f(n-1)中跳法,跳两个台阶后,还剩下f(n-2)中方法,所以n个台阶总共有f(n) = f(n-1) +f(n-2)种跳法;
转化成了斐波那契数列,同题目二,可以用动态规划,或者是记忆规划做。
图解:
class Solution {
int constant = 1000000007;
public int numWays(int n) {
//斐波那契数列
return numWays(n, new HashMap());
}
public int numWays(int n, HashMap<Integer, Integer> map){
if(n < 2){
return 1;
}
if(map.containsKey(n)){
return map.get(n);
}
int first = numWays(n-1, map)%constant;
map.put(n-1,first);
int second = numWays(n-2,map)%constant;
map.put(n-2,second);
int res = (first + second)%constant;
map.put(n, res);
return res;
}
}
//动态规划
题6 剑指 Offer 05. 替换空格
请实现一个函数,把字符串 s 中的每个空格替换成"%20"。
eg:
输入:s = "We are happy."
输出:"We%20are%20happy."
思路:因为String类型是不可变字符串,所以需要将其放入StringBuffer中或者StringBuilder中然后遍历字符串;
class Solution {
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
StringBuffer res = new StringBuffer();
for(Character c: s.toCharArray()){
if(c == ' '){
res.append("%20");
}else{
res.append(c);
}
}
return res.toString();
}
}
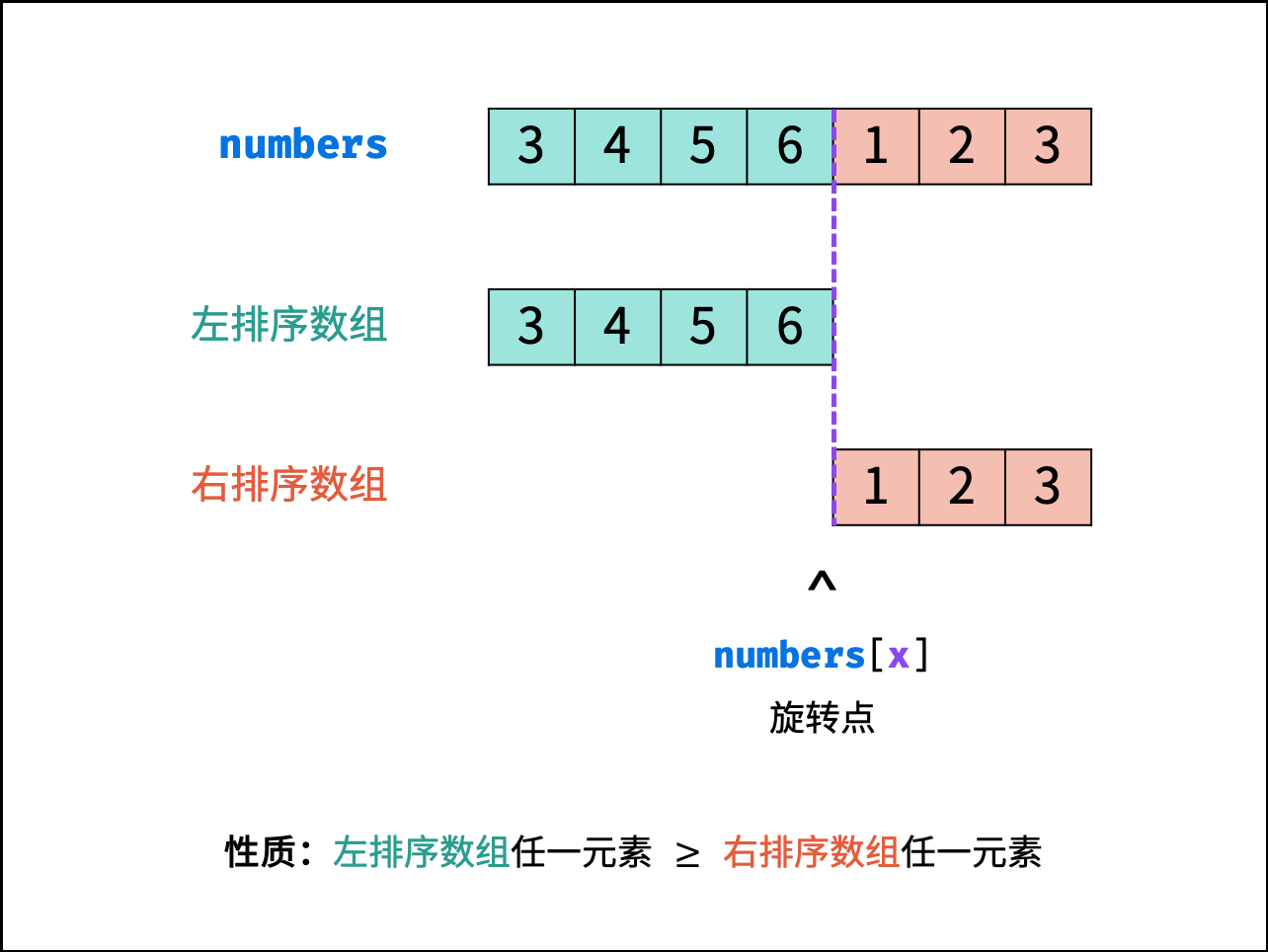
题7 旋转数组的最小数字(二分法)
class Solution {
public int minArray(int[] numbers) {
int i=0, j=numbers.length-1;
while(i<j){
int m =(i+j)/2;
if(numbers[m]>numbers[j]){
i=m+1;
}else if(numbers[m]<numbers[j]){
j=m;
}else{
int x=i;
for(int k = i+1; k<j;k++){
if(numbers[k]<numbers[x])
x = k;
}
return numbers[x];
}
}
return numbers[i];
}
}
题8 从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<Integer>();
ListNode tmp = head;
while(tmp != null){
stack.push(tmp.val);
tmp = tmp.next;
}
int []arr = new int[stack.size()];
for(int i = 0; i<arr.length;i++){
arr[i]=stack.pop();
}
return arr;
}
}
//不用栈分配空间
//倒着输出数组;
//执行用时:0 ms, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了100.00%的用户
//内存消耗:38.6 MB, 在所有 Java 提交中击败了94.42%的用户
class Solution {
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
ListNode tmp = head;
int k = 0;
while(tmp != null){
tmp = tmp.next;
k++;
}
int []arr = new int[k];
tmp = head;
for(int i = k -1 ; i>=0;i--){
arr[i] = tmp.val;
tmp = tmp.next;
}
return arr;
}
}
题9 矩阵中的路径
给定一个 m x n 二维字符网格 board 和一个字符串单词 word 。如果 word 存在于网格中,返回 true ;否则,返回 false 。
单词必须按照字母顺序,通过相邻的单元格内的字母构成,其中“相邻”单元格是那些水平相邻或垂直相邻的单元格。同一个单元格内的字母不允许被重复使用。
考点:DFS,深度优先搜索
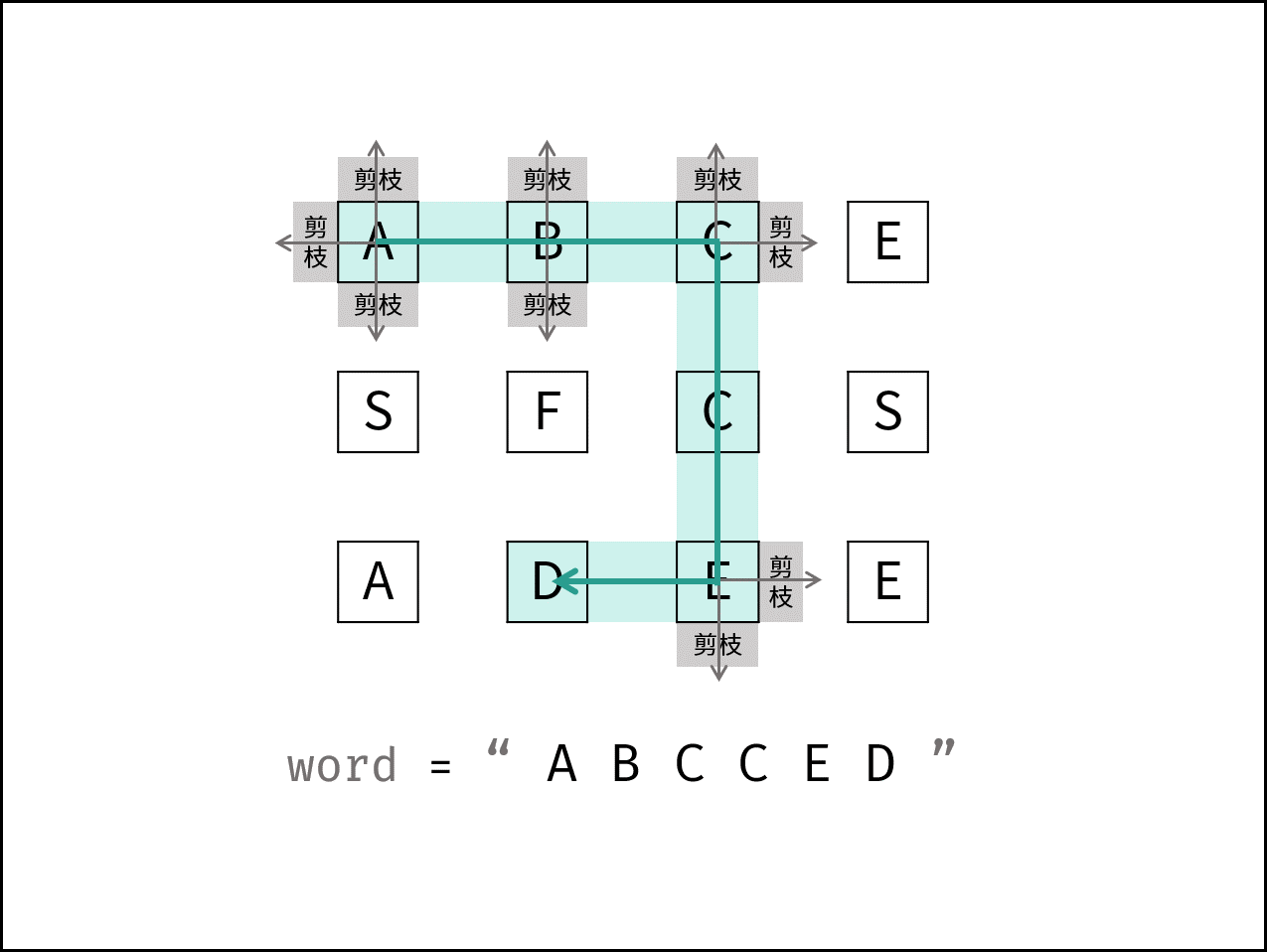
时间复杂度:O(\(3^kMN\))
class Solution {
public boolean exist(char[][] board, String word) {
char []words = word.toCharArray();
for(int i = 0; i< board.length;i++){
for(int j =0;j<board[0].length;j++){
if(dfs(board, words, i, j,0)) return true;
}
}
return false;
}
boolean dfs(char[][]board, char[]words, int i, int j, int k){
if(i>=board.length||i<0||j>=board[0].length||j<0||board[i][j] != words[k]) return false;
if(k == words.length -1) return true;
board[i][j] = '\0';
boolean res = dfs(board, words, i+1, j, k+1)||dfs(board, words, i-1, j, k+1)||dfs(board, words, i, j+1, k+1)||dfs(board, words, i, j-1, k+1);
board[i][j] = words[k];
return res;
}
}
题10 机器人的运动范围
地上有一个m行n列的方格,从坐标 [0,0] 到坐标 [m-1,n-1] 。一个机器人从坐标 [0, 0] 的格子开始移动,它每次可以向左、右、上、下移动一格(不能移动到方格外),也不能进入行坐标和列坐标的数位之和大于k的格子。例如,当k为18时,机器人能够进入方格 [35, 37] ,因为3+5+3+7=18。但它不能进入方格 [35, 38],因为3+5+3+8=19。请问该机器人能够到达多少个格子?
思路:遇到矩阵搜索问题,第一个就要想到的是DFS,本题中因为从左上角开始进行遍历,所以只需要考虑向下或者向右就可以了。
class Solution {
public int movingCount(int m, int n, int k) {
boolean [][] visited = new boolean[m][n];
return dfs(0, 0,m, n,k,visited);
}
int dfs(int i, int j, int m, int n, int k, boolean [][]visited){
if(i<0||i>=m||j<0||j>=n||(i/10+i%10+j/10+j%10) > k||visited[i][j]){
return 0;
}
visited[i][j] = true;
return dfs(i+1,j,m,n,k,visited)+dfs(i,j+1,m,n,k,visited)+1;
}
}
题11合并两个排序的链表
输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的节点仍然是递增排序的。
思路:链表的题目一般设置一个伪头节点,便于后续遍历可以直接找到链表的头,创建一个链表,将输入的两个链表作比较,谁小先放谁,然后移动。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0);
ListNode pre = head;
while( l1!=null && l2!=null){
if(l1.val <= l2.val){
pre.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
}else{
pre.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
pre = pre.next;
}
pre.next = l1 !=null? l1:l2;
return head.next;
}
}
题12: *剑指 Offer 07. 重建二叉树
题目:输入某二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果,请构建该二叉树并返回其根节点。假设输入的前序遍历和中序遍历的结果中都不含重复的数字。
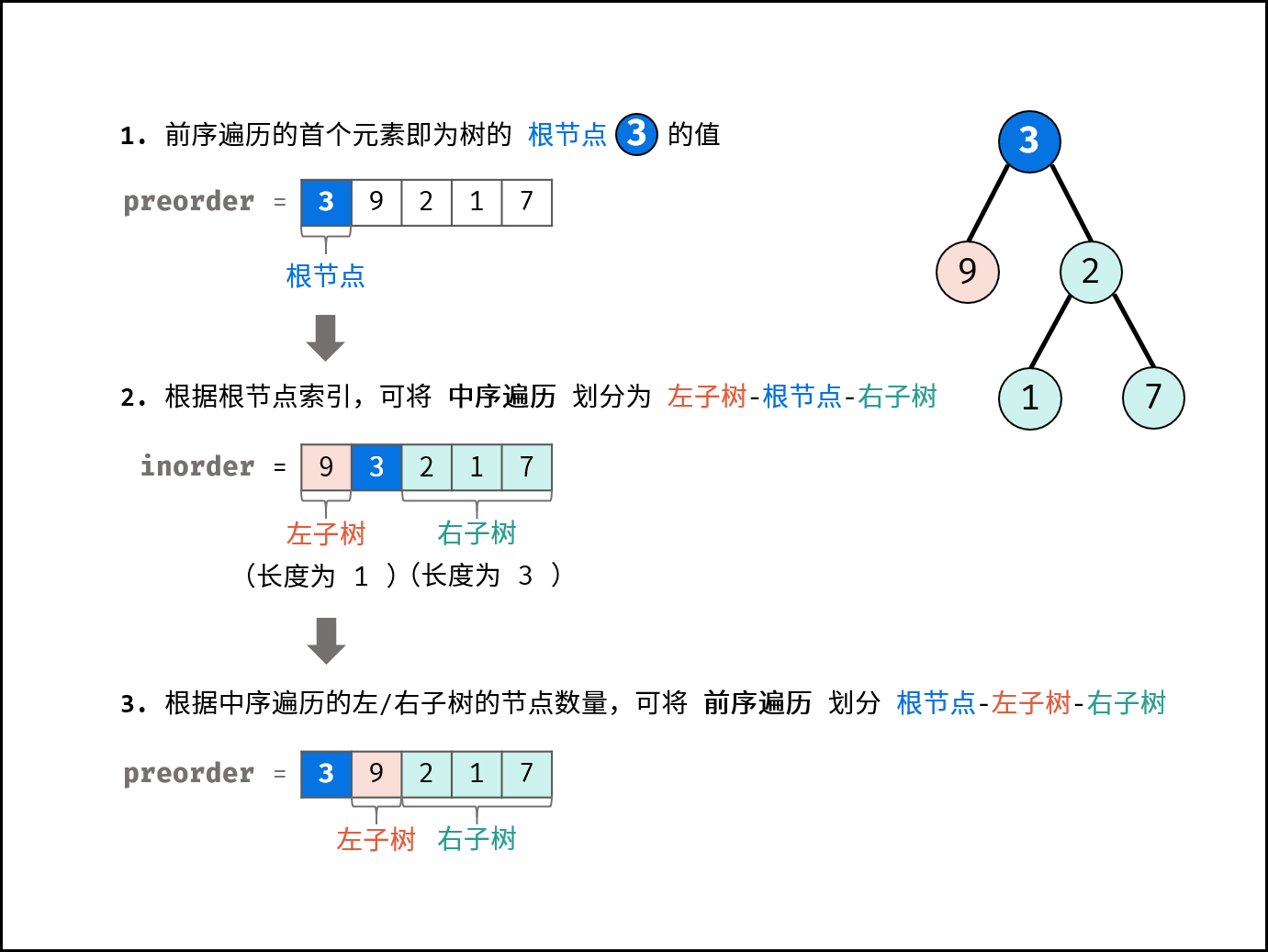
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
HashMap<Integer, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();//标记中序遍历
int[] preorder;//保留的先序遍历,方便递归时依据索引查看先序遍历的值
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
this.preorder = preorder;
//将中序遍历的值及索引放在map中,方便递归时获取左子树与右子树的数量及其根的索引
for (int i = 0; i < inorder.length; i++) {
map.put(inorder[i], i);
}
//三个索引分别为
//当前根的的索引
//递归树的左边界,即数组左边界
//递归树的右边界,即数组右边界
return recur(0,0,inorder.length-1);
}
TreeNode recur(int pre_root, int in_left, int in_right){
if(in_left > in_right) return null;// 相等的话就是自己
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(preorder[pre_root]);//获取root节点
int idx = map.get(preorder[pre_root]);//获取在中序遍历中根节点所在索引,以方便获取左子树的数量
//左子树的根的索引为先序中的根节点+1
//递归左子树的左边界为原来的中序in_left
//递归右子树的右边界为中序中的根节点索引-1
root.left = recur(pre_root+1, in_left, idx-1);
//右子树的根的索引为先序中的 当前根位置 + 左子树的数量 + 1
//递归右子树的左边界为中序中当前根节点+1
//递归右子树的有边界为中序中原来右子树的边界
root.right = recur(pre_root + (idx - in_left) + 1, idx+1, in_right);
return root;
}
}
题13:调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有偶数位于数组的后半部分。
示例:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[1,3,2,4]
注:[3,1,2,4] 也是正确的答案之一。
//自己想法
class Solution {
public int[] exchange(int[] nums) {
int []arr = new int[nums.length];
int j=0;
int k = nums.length -1;
for(int i = 0; i< nums.length; i++){
if(nums[i]%2 == 1){
arr[j] = nums[i];
j++;
}else{
arr[k] = nums[i];
k--;
}
}
return arr;
}
}
//头尾双指针
class Solution{
public int[] exchange(int[] nums) {
int left = 0, right = nums.length -1;
while(left <= right){
while(left<=right&&nums[left]%2==1){
left++;
}
while(left<=right&&nums[right]%2==0){
right--;
}
if(left>right) break;
int temp = nums[left];
nums[left] = nums[right];
nums[right] = temp;
}
return nums;
}
}
题14:* 剑指 Offer 14- I. 剪绳子(同15题比较)
给你一根长度为 n 的绳子,请把绳子剪成整数长度的 m 段(m、n都是整数,n>1并且m>1),每段绳子的长度记k[0],k[1]...k[m-1] 。请问 k[0]*k[1]*...*k[m-1] 可能的最大乘积是多少?例如,当绳子的长度是8时,我们把它剪成长度分别为2、3、3的三段,此时得到的最大乘积是18。
思路:动态规划
这题用动态规划是比较好理解的
- 我们想要求长度为
n的绳子剪掉后的最大乘积,可以从前面比n小的绳子转移而来 - 用一个
dp数组记录从0到n长度的绳子剪掉后的最大乘积,也就是dp[i]表示长度为i的绳子剪成m段后的最大乘积,初始化dp[2] = 1 - 我们先把绳子剪掉第一段
(长度为j),如果只剪掉长度为1,对最后的乘积无任何增益,所以从长度为2开始剪 - 剪了第一段后,剩下
(i - j)长度可以剪也可以不剪。如果不剪的话长度乘积即为j * (i - j);如果剪的话长度乘积即为j * dp[i - j]。取两者最大值max(j * (i - j), j * dp[i - j]) - 第一段长度
j可以取的区间为[2,i),对所有j不同的情况取最大值,因此最终dp[i]的转移方程为
dp[i] = max(dp[i], max(j * (i - j), j * dp[i - j])) - 最后返回
dp[n]即可
//动态规划
class Solution {
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
int []dp = new int[n+1];
dp[2] = 1;
for(int i = 3;i<n+1;i++){
for(int j = 2; j<i; j++){
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i], Math.max(j*(i-j), j*dp[i-j]));
}
}
return dp[n];
}
}
题15:剑指 Offer 14- II. 剪绳子 II
给你一根长度为 n 的绳子,请把绳子剪成整数长度的 m 段(m、n都是整数,n>1并且m>1),每段绳子的长度记为 k[0],k[1]...k[m - 1] 。请问 k[0]*k[1]*...*k[m - 1] 可能的最大乘积是多少?例如,当绳子的长度是8时,我们把它剪成长度分别为2、3、3的三段,此时得到的最大乘积是18。
答案需要取模 1e9+7(1000000007),如计算初始结果为:1000000008,请返回 1。
//循环取余法
class Solution {
public int cuttingRope(int n) {
if(n < 4) return n-1;
if(n == 4) return n;
long res = 1;
while(n > 4){
res *=3;
res %= 1000000007;
n -= 3;
}
res = (res*n)%1000000007;
return (int)res;
}
}
题16:剑指 Offer 15. 二进制中1的个数
编写一个函数,输入是一个无符号整数(以二进制串的形式),返回其二进制表达式中数字位数为 '1' 的个数(也被称为 汉明重量).)。
思路:java中无符号右移为>>>;
public class Solution {
// you need to treat n as an unsigned value
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
int k = 0;
while(n != 0){
if((n&1) == 1) k++;
n >>>= 1;
}
return k;
}
//等同于 return Integer.bitCount(n);
}
//另外,java中引用数据类型还提供了如下方法统计汉明距离,Integer.bitCount()
题17剑指 Offer 16. 数值的整数次方
实现$ pow(x, n)$ ,即计算 x 的 n 次幂函数(即,\(x^n\))。不得使用库函数,同时不需要考虑大数问题。
思路:快速幂

class Solution {
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
double res = 1.0;
long b = n;
if(b<0){
x = 1/x;
b = -b;
}
while(b>0){
if((b&1)==1) res*=x;
x*=x;
b>>=1;
}
return res;
}
}
题18剑指 Offer 17. 打印从1到最大的n位数
输入数字 n,按顺序打印出从 1 到最大的 n 位十进制数。比如输入 3,则打印出 1、2、3 一直到最大的 3 位数 999。
示例 1:
输入: n = 1
输出: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
思路:这道题目没有讲考虑到大数的情况,也就是溢出的情况,直接得到\(end=10^{n}-1\),创建数组int[]nums = new int[end],遍历就可以了
class Solution {
public int[] printNumbers(int n) {
int m = print(n);
int []num = new int[m];
for(int i = 0;i< m;i++){
num[i] = i+1;
}
return num;
}
private int print(int n){
String a = "";
while(n>0){
a += "9";
n--;
}
return Integer.valueOf(a);
}
}
大数遍历:
面试的时候不会问你这么简单的题目,会问你大数怎么解决;
暂时看不懂
题19剑指 Offer 18. 删除链表的节点
给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。返回删除后的链表的头节点。
示例 1:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
解法一:哨兵节点
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
ListNode tmp = head;
ListNode right = tmp.next;
if(tmp.val == val) return head.next;
while(right.val != val){
tmp = right;
right = right.next;
}
if(right.next == null){
tmp.next = null;
}else{
tmp.next = right.next;
}
return head;
}
}
解法二:递归
题20剑指 Offer 20. 表示数值的字符串
思路
首先定义了四个flag,对应四种字符
是否有数字:hasNum
是否有e:hasE
是否有正负符号:hasSign
是否有点:hasDot
其余还定义了字符串长度n以及字符串索引index
先处理一下开头的空格,index相应的后移
然后进入循环,遍历字符串
如果当前字符c是数字:将hasNum置为true,index往后移动一直到非数字或遍历到末尾位置;如果已遍历到末尾(index == n),结束循环
如果当前字符c是'e'或'E':如果e已经出现或者当前e之前没有出现过数字,返回fasle;否则令hasE = true,并且将其他3个flag全部置为false,因为要开始遍历e后面的新数字了
如果当前字符c是+或-:如果已经出现过+或-或者已经出现过数字或者已经出现过'.',返回flase;否则令hasSign = true
如果当前字符c是'.':如果已经出现过'.'或者已经出现过'e'或'E',返回false;否则令hasDot = true
如果当前字符c是' ':结束循环,因为可能是末尾的空格了,但也有可能是字符串中间的空格,在循环外继续处理
如果当前字符c是除了上面5种情况以外的其他字符,直接返回false
处理空格,index相应的后移
如果当前索引index与字符串长度相等,说明遍历到了末尾,但是还要满足hasNum为true才可以最终返回true,因为如果字符串里全是符号没有数字的话是不行的,而且e后面没有数字也是不行的,但是没有符号是可以的,所以4个flag里只要判断一下hasNum就行;所以最后返回的是hasNum && index == n
如果字符串中间有空格,按以上思路是无法遍历到末尾的,index不会与n相等,返回的就是false
class Solution {
public boolean isNumber(String s) {
char []charArray = s.toCharArray();
int n = s.length();
int index = 0;
boolean hasNum = false, hasE = false,
hassSign = false, hasDot = false;
while(index < n && charArray[index] == ' '){
index++;
}
while(index<n){
char c = charArray[index];
if(c >= '0' && c<='9'){
hasNum = true;
}else if(c == 'e' || c=='E'){
if(hasE || !hasNum) return false;
hasE = true;
hasNum = hasDot = hassSign = false;
}else if(c == '+' ||c=='-'){
if(hassSign||hasDot||hasNum) return false;
hassSign = true;
}else if(c=='.'){
if(hasDot||hasE) return false;
hasDot = true;
}else if(c==' '){
break;
}else{
return false;
}
index++;
}
for(; index<n;index++){
if(charArray[index] != ' ') return false;
}
return hasNum;
}
}
题21剑指 Offer 24. 反转链表
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
思路:双指针 或者 递归(递归还不是很懂)
//指针
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = head, pre = null;
while(cur != null){
ListNode tmp = cur.next;
cur.next = pre;
pre = cur;
cur = tmp;
}
return pre;
}
}
题22剑指 Offer 29. 顺时针打印矩阵
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字。( 回形针)。
示例 1:
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
思路:
根据题目示例 matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]] 的对应输出 [1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5] 可以发现,顺时针打印矩阵的顺序是 “从左向右、从上向下、从右向左、从下向上” 循环。
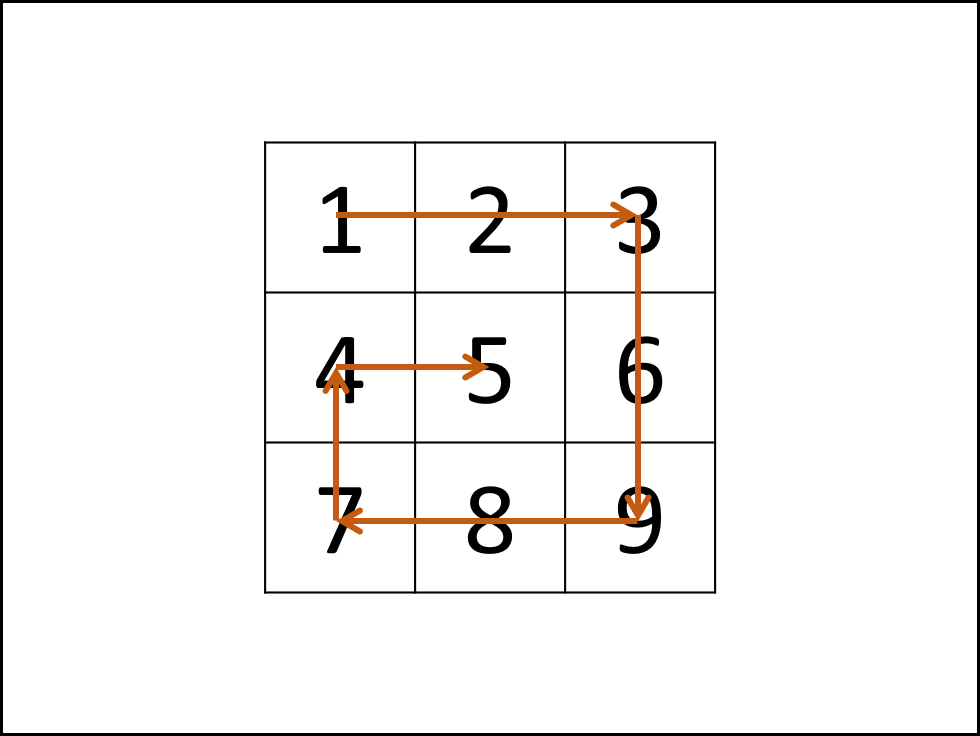
- 因此,考虑设定矩阵的“左、上、右、下”四个边界,模拟以上矩阵遍历顺序。
class Solution {
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
if(matrix.length == 0) return new int[0];
int rows = matrix.length, columms = matrix[0].length;
int start = 0;
int []res = new int[rows*columms];
int k=0;
while(columms > (start*2) && rows >(start*2)){
int endX = columms - start-1;
int endY =rows - start-1;
//从左到右
for(int i = start; i<=endX;i++){
res[k]=matrix[start][i];
k++;
}
//从上到下打印数组
if(start < endY){
for(int i=start+1;i<=endY;i++){
res[k]= matrix[i][endX];
k++;
}
}
//从右到左
if(start<endX && start < endY){
for(int i = endX-1;i>=start;i--){
res[k]=matrix[endY][i];
k++;
}
}
//从下到上
if(start < endY-1&&start<endX){
for(int i = endY-1;i>=start+1;i--){
res[k]= matrix[i][start];
k++;
}
}
start++;
}
return res;
}
}
题22剑指 Offer 32 - I. 从上到下打印二叉树
从上到下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同一层的节点按照从左到右的顺序打印。
思路:BFS,广度遍历;
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
ArrayList<Integer> res = new ArrayList<>();
if(root == null) return new int[0];
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<>();
TreeNode p = root;
queue.add(root);
while(!queue.isEmpty()){
p = queue.poll();
res.add(p.val);
if(p.left != null){
queue.add(p.left);
}if(p.right != null){
queue.add(p.right);
}
}
int i = 0;
int []result = new int[res.size()];
for(int a: res){
result[i++] = a;
}
return result;
}
}
剑指 Offer 43. 1~n 整数中 1 出现的次数
解题思路:
将 11 ~ nn 的个位、十位、百位、...的 11 出现次数相加,即为 11 出现的总次数。
设数字 nn 是个 xx 位数,记 nn 的第 ii 位为 n_in**i ,则可将 nn 写为 n_{x} n_{x-1} \cdots n_{2} n_{1}nxn**x−1⋯n2n1 :
- 称 " n_in**i " 为 当前位 ,记为 curcur ,
- 将 " n_{i-1} n_{i-2} \cdots n_{2} n_{1}n**i−1n**i−2⋯n2n1 " 称为 低位 ,记为 lowlow ;
- 将 " n_{x} n_{x-1} \cdots n_{i+2} n_{i+1}nxn**x−1⋯n**i+2n**i+1 " 称为 高位 ,记为 highhig**h 。
- 将 10^i10i 称为 位因子 ,记为 digitdigit 。
某位中 11 出现次数的计算方法:
根据当前位 curcur 值的不同,分为以下三种情况:
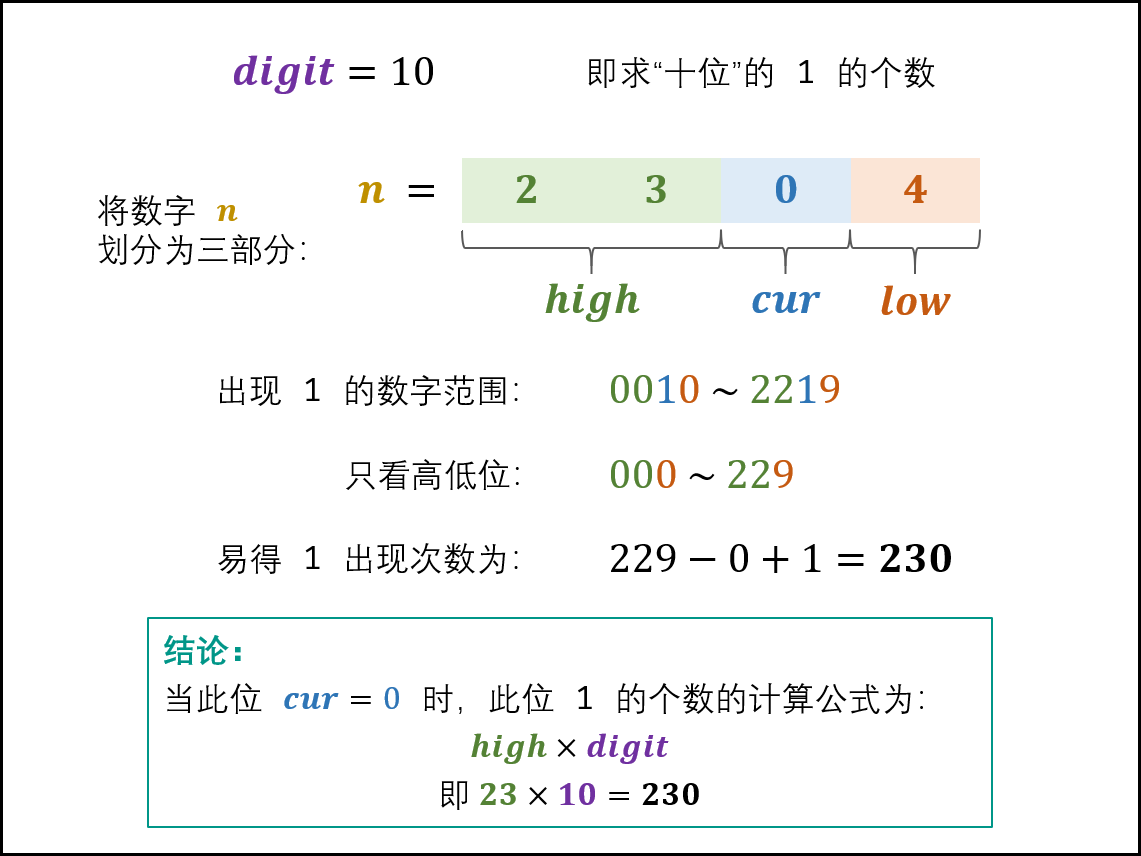
- 当 cur = 0*c*u*r*=0 时: 此位 11 的出现次数只由高位 highhig**h 决定,计算公式为:
high \times digithig**h×digit
如下图所示,以 n = 2304n=2304 为例,求 digit = 10digit=10 (即十位)的 11 出现次数。
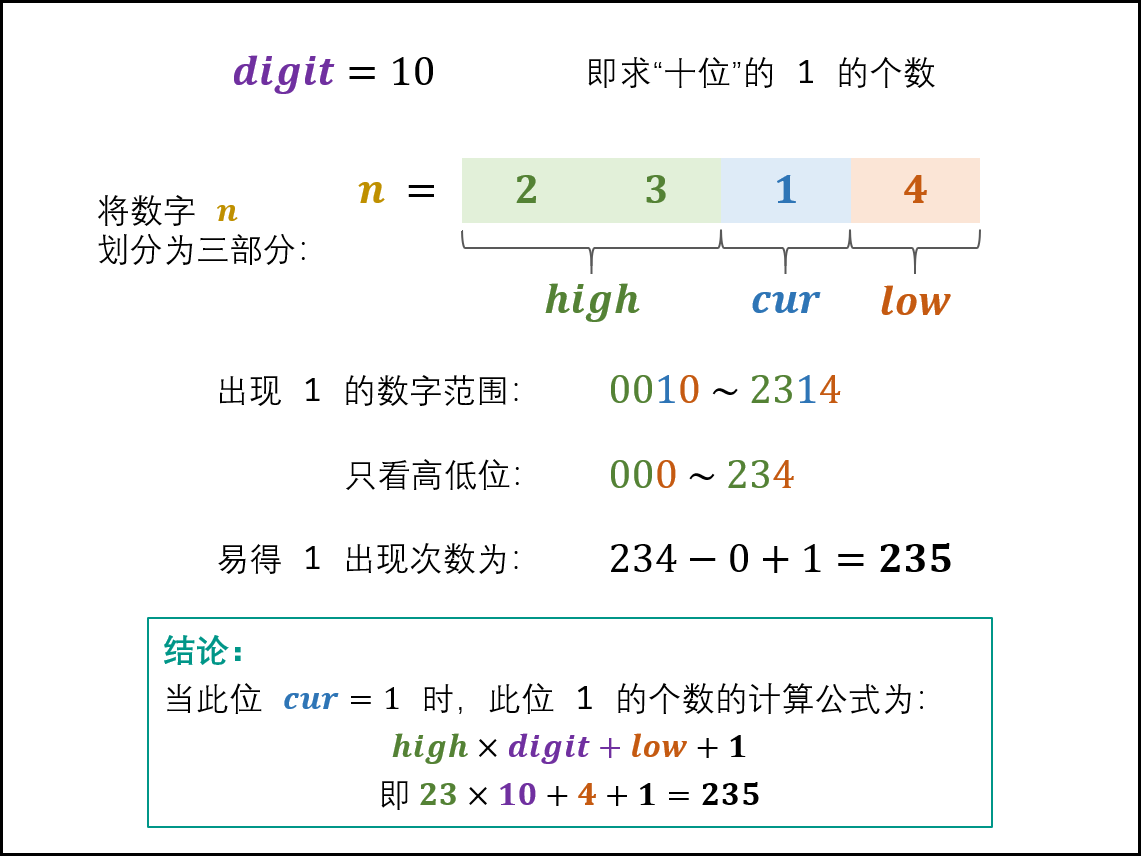
- 当 cur = 1*c*u*r*=1 时: 此位 11 的出现次数由高位 highhig**h 和低位 lowlow 决定,计算公式为:
high \times digit + low + 1hig**h×digit+low+1
如下图所示,以 n = 2314n=2314 为例,求 digit = 10digit=10 (即十位)的 11 出现次数。
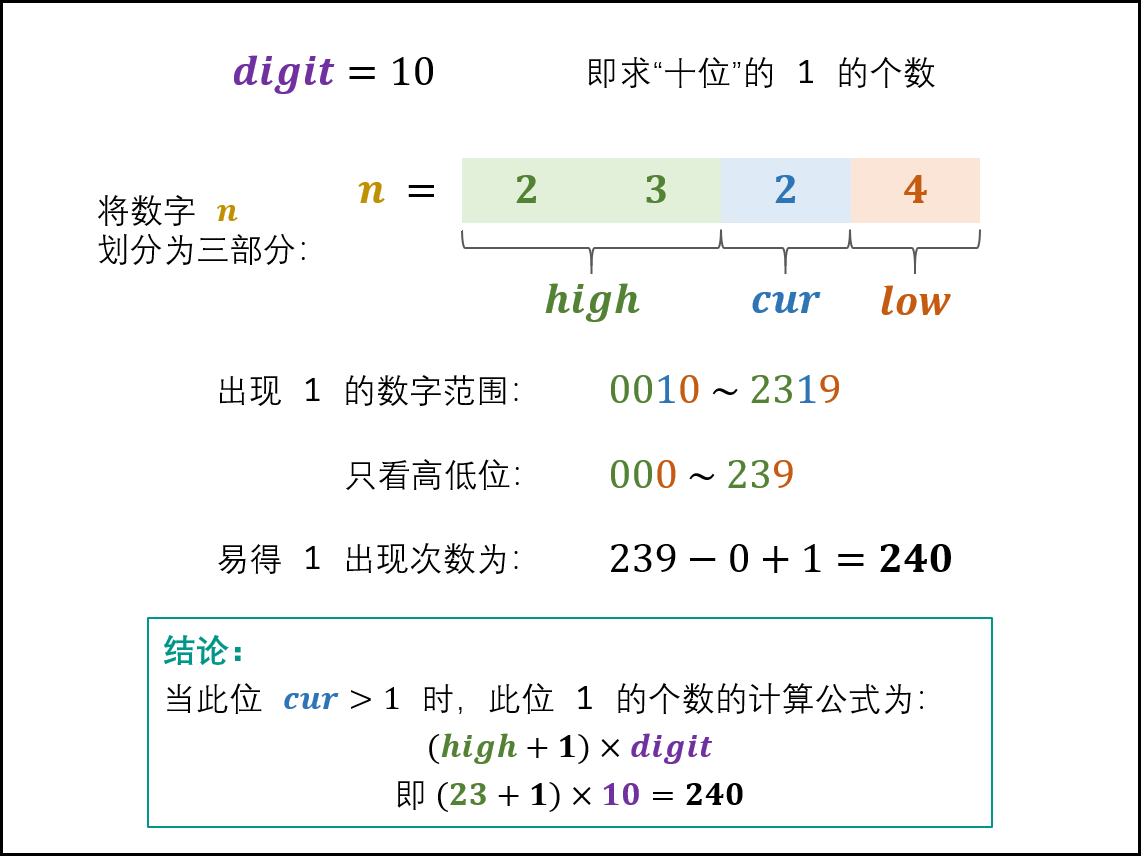
- 当 cur = 2, 3, \cdots, 9*c*u*r*=2,3,⋯,9 时: 此位 11 的出现次数只由高位 highhig**h 决定,计算公式为:
(high + 1) \times digit(hig**h+1)×digit
如下图所示,以 n = 2324n=2324 为例,求 digit = 10digit=10 (即十位)的 11 出现次数。
变量递推公式:
设计按照 “个位、十位、...” 的顺序计算,则 high / cur / low / digithig**h/cur/low/digit 应初始化为:
high = n // 10
cur = n % 10
low = 0
digit = 1 # 个位
因此,从个位到最高位的变量递推公式为:
while high != 0 or cur != 0: # 当 high 和 cur 同时为 0 时,说明已经越过最高位,因此跳出
low += cur * digit # 将 cur 加入 low ,组成下轮 low
cur = high % 10 # 下轮 cur 是本轮 high 的最低位
high //= 10 # 将本轮 high 最低位删除,得到下轮 high
digit *= 10 # 位因子每轮 × 10
复杂度分析:
- 时间复杂度 O(\log n)*O*(log*n*) : 循环内的计算操作使用 O(1)O(1) 时间;循环次数为数字 nn 的位数,即 \log_{10}{n}log10n ,因此循环使用 O(\log n)O(logn) 时间。
- 空间复杂度 O(1)*O*(1) : 几个变量使用常数大小的额外空间。
1 / 7
代码:
class Solution {
public int countDigitOne(int n) {
int digit = 1, res = 0;
int high = n / 10, cur = n % 10, low = 0;
while(high != 0 || cur != 0) {
if(cur == 0) res += high * digit;
else if(cur == 1) res += high * digit + low + 1;
else res += (high + 1) * digit;
low += cur * digit;
cur = high % 10;
high /= 10;
digit *= 10;
}
return res;
}
}
剑指 Offer 52. 两个链表的第一个公共节点
我们使用两个指针 node1,node2 分别指向两个链表 headA,headB 的头结点,然后同时分别逐结点遍历,当 node1 到达链表 headA 的末尾时,重新定位到链表 headB 的头结点;当 node2 到达链表 headB 的末尾时,重新定位到链表 headA 的头结点。
这样,当它们相遇时,所指向的结点就是第一个公共结点
备注:
看到一个评论,就像《你的名字一样》,
你变成我,走过我走过的路。
我变成你,走过你走过的路。
然后我们便相遇了..这就是题目唯美的样子
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) {
* val = x;
* next = null;
* }
* }
*/
public class Solution {
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
ListNode tempA = headA;
ListNode tempB = headB;
while(tempA != tempB){
tempA = tempA== null? headB:tempA.next;
tempB = tempB == null? headA:tempB.next;
}
return tempA;
}
}
位运算的巧妙之处,用异或
相同数字异或为0;所以先异或,得到两个出现一次的数字异或后的结果,再找到一个两个出现一次数字不同结果的位数,利用这位进行分组,将两个数字分开,为别异或,找到结果。
class Solution {
public int[] singleNumbers(int[] nums) {
int x = 0,y=0,n=0,m=1;
for(int num: nums){
n ^= num;
}
while((n&m) == 0)
m <<= 1;
for(int num:nums){
if((m&num) == 0) x^= num;
else y^=num;
}
return new int[]{x,y};
}
}
剑指 Offer 56 - II. 数组中数字出现的次数 II
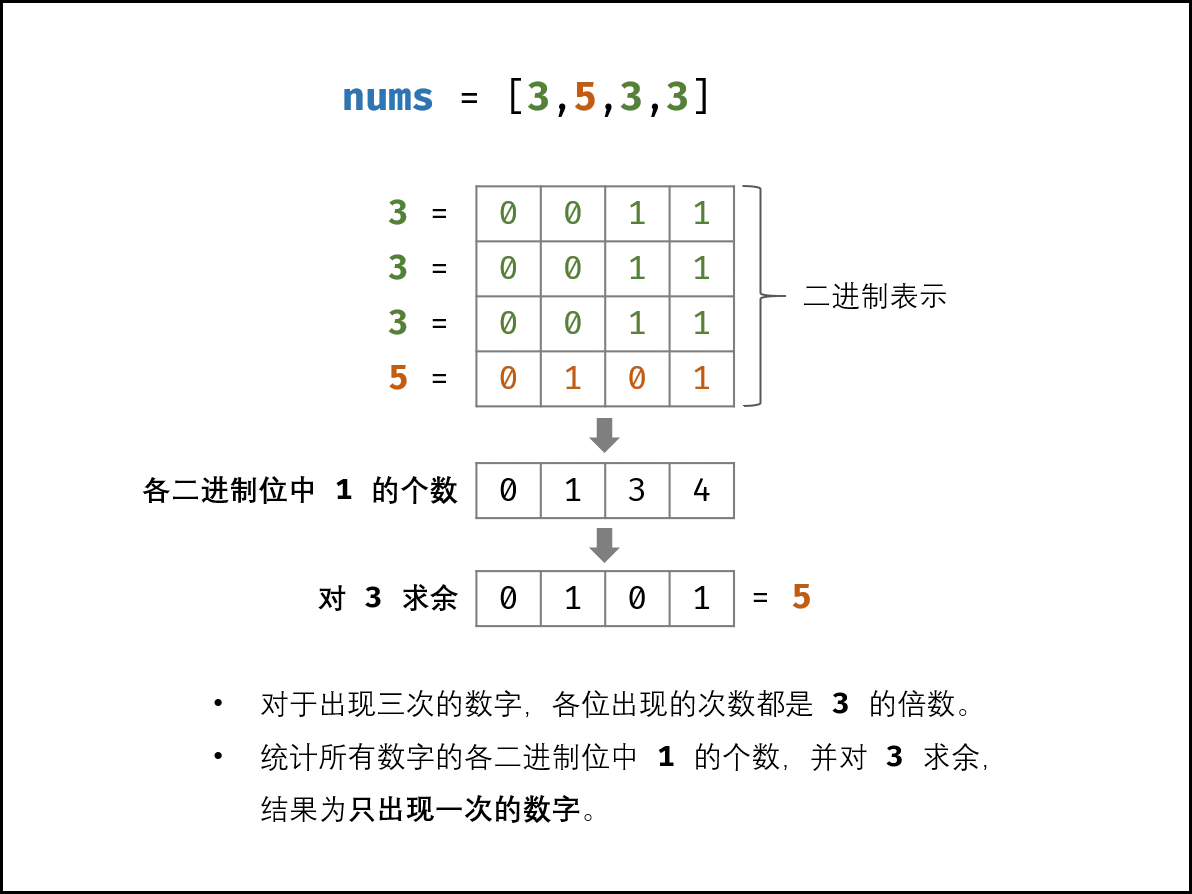
解析:理解简单的位运算方法;
如下图所示,考虑数字的二进制形式,对于出现三次的数字,各 二进制位 出现的次数都是 33 的倍数。
因此,统计所有数字的各二进制位中 11 的出现次数,并对 33 求余,结果则为只出现一次的数字
class Solution {
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int[] counts = new int[32];
for(int num : nums) {
for(int j = 0; j < 32; j++) {
counts[j] += num & 1;
num >>>= 1;
}
}
int res = 0, m = 3;
for(int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
res <<= 1;
res |= counts[31 - i] % m;
}
return res;
}
}
滑动窗口加双指针;
class Solution {
public int[][] findContinuousSequence(int target) {
int i = 1, j = 2, s = 3;
List<int[]> res = new ArrayList<>();
while(i < j) {
if(s == target) {
int[] ans = new int[j - i + 1];
for(int k = i; k <= j; k++)
ans[k - i] = k;
res.add(ans);
}
if(s >= target) {
s -= i;
i++;
} else {
j++;
s += j;
}
}
return res.toArray(new int[0][]);
}
}
剑指 Offer 58 - I. 翻转单词顺序
双指针从后往前,先去掉首尾空格,再倒序
class Solution {
public String reverseWords(String s) {
s = s.trim(); // 删除首尾空格
int j = s.length() - 1, i = j;
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
while(i >= 0) {
while(i >= 0 && s.charAt(i) != ' ') i--; // 搜索首个空格
res.append(s.substring(i + 1, j + 1) + " "); // 添加单词
while(i >= 0 && s.charAt(i) == ' ') i--; // 跳过单词间空格
j = i; // j 指向下个单词的尾字符
}
return res.toString().trim(); // 转化为字符串并返回
}
}
剑指 Offer 44. 数字序列中某一位的数字
1.确定 n所在 数字 的 位数 ,记为digit ;
2.确定 n 所在的 数字 ,记为 num ;
3.确定 nn是 num 中的哪一数位,并返回结果。
class Solution {
public int findNthDigit(int n) {
int digit = 1;
long count = 9;
long start = 1;
//得到n所在的位数
while(n > count){
n -= count;
digit++;
start *= 10;
count = digit*start*9;
}
//确定n所在的数字
long num = start + (n - 1)/digit;
return Long.toString(num).charAt((n-1)%digit) - '0';
}
}
剑指 Offer 59 - I. 滑动窗口的最大值
单调队列算法:

class Solution {
public int[] maxSlidingWindow(int[] nums, int k) {
if(nums.length == 0|| k == 0) return new int[0];
int res[] = new int[nums.length -k +1];
Deque<Integer>deque = new LinkedList<>();
//未形成窗口
for(int i = 0;i<k;i++){
while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekLast() < nums[i]){
deque.removeLast();
}
deque.addLast(nums[i]);
}
res[0] = deque.peekFirst();
//形成窗口后
for(int i = k;i< nums.length;i++){
if(deque.peekFirst() == nums[i-k])
deque.removeFirst();
while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekLast() < nums[i]){
deque.removeLast();
}
deque.addLast(nums[i]);
res[i-k+1] = deque.peekFirst();
}
return res;
}
}
剑指 Offer 38. 字符串的排列
回溯+剪枝
1.终止条件:当已经排列了x-1个字符的时候,所有位置已经固定,将结果添加到res中;
- 递推参数:固定当前位:x;
- 递推工作: 初始化一个 Set ,用于排除重复的字符;将第 x 位字符与 x后面字符分别交换,并进入下层递归;
剪枝: 若 c[i] 在 Set 中,代表其是重复字符,因此 “剪枝” ;
将 c[i] 加入 Set ,以便之后遇到重复字符时剪枝;
固定字符: 将字符 c[i] 和 c[x] 交换,即固定 c[i] 为当前位字符;
开启下层递归: 调用 dfs(x + 1) ,即开始固定第 x + 1 个字符;
还原交换: 将字符 c[i] 和 c[x] 交换(还原之前的交换);
看第二种代码;
class Solution {
int N = 10;
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
boolean[] vis = new boolean[N];
public String[] permutation(String s) {
char[] cs = s.toCharArray();
dfs(cs, 0, "");
String[] ans = new String[set.size()];
int idx = 0;
for (String str : set) ans[idx++] = str;
return ans;
}
void dfs(char[] cs, int u, String cur) {
int n = cs.length;
if (u == n) {
set.add(cur);
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!vis[i]) {
vis[i] = true;
dfs(cs, u + 1, cur + String.valueOf(cs[i]));
vis[i] = false;
}
}
}
}
//回溯剪枝
class Solution {
List<String> res = new LinkedList<>();
char[] c;
public String[] permutation(String s) {
c = s.toCharArray();
dfs(0);//开始递归
return res.toArray(new String[res.size()]);
}
void dfs(int x) {
if(x == c.length - 1) {//已经排列好一种组合,输出结果
res.add(String.valueOf(c)); // 添加排列方案
return;
}
HashSet<Character> set = new HashSet<>();
for(int i = x; i < c.length; i++) {
if(set.contains(c[i])) continue; // 防止同个字符重复,因此剪枝
set.add(c[i]);
swap(i, x); // 交换,将 c[i] 固定在第 x 位
dfs(x + 1); // 开启固定第 x + 1 位字符
swap(i, x); // 恢复交换
}
}
void swap(int a, int b) {
char tmp = c[a];
c[a] = c[b];
c[b] = tmp;
}
}
剑指 Offer 55 - II. 平衡二叉树
得出左右子树的深度,
当左右子树的深度差>2,则返回-1;
终止条件:root为空,则已经遍历完树,返回0;
左右子树的深度为-1:则此节点后面的左右子树已经不是平衡二叉树了,直接返回-1;
class Solution {
public boolean isBalanced(TreeNode root) {
return dfs(root) != -1;
}
int dfs(TreeNode root){
if(root == null) return 0;
int left = dfs(root.left);
if( left == -1) return -1;
int right = dfs(root.right);
if( right == -1) return -1;
if(Math.abs(left - right)>1) return -1;
return Math.max(left,right)+1;
}
}
剑指 Offer 32 - III. 从上到下打印二叉树 III
设立奇偶层标志位,奇数层则倒序输出;
class Solution {
public List<List<Integer>> levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
List<List<Integer>> res = new ArrayList<>();
Deque<TreeNode> deque = new LinkedList<>();
if(root == null) return res;
deque.add(root);
while(!deque.isEmpty()){
LinkedList<Integer> ans = new LinkedList<>();
int count = deque.size();
for(int i = 0;i<count ;i++){
TreeNode temp = deque.poll();
if(res.size()%2 == 0) ans.addLast(temp.val);
else ans.addFirst(temp.val);
if(temp.left != null) deque.add(temp.left);
if(temp.right != null) deque.add(temp.right);
}
res.add(new ArrayList(ans));
}
return res;
}
}
剑指 Offer 59 - II. 队列的最大值
class MaxQueue {
Queue<Integer> queue;
Deque<Integer> deque;
public MaxQueue() {
queue = new LinkedList<>();
deque = new LinkedList<>();
}
public int max_value() {
if(deque.isEmpty()) return -1;
return deque.peekFirst();
}
public void push_back(int value) {
queue.offer(value);
while(!deque.isEmpty() && deque.peekLast() < value){
deque.pollLast();
}
deque.offerLast(value);
}
public int pop_front() {
if(queue.isEmpty()) return -1;
if(queue.peek().equals(deque.peekFirst()))
deque.pollFirst();
return queue.poll();
}
}
剑指 Offer 60. n个骰子的点数
动态规划,先求出n=1的概率,然后再递推;
class Solution {
public double[] dicesProbability(int n) {
double []dp = new double[6];
Arrays.fill(dp, 1.0/6.0);
for(int i =2;i <= n; i++){
double[] tmp = new double[5*i+1];
for(int j = 0;j<dp.length;j++){
for(int k = 0;k<6;k++){
tmp[j+k] += dp[j]/6;
}
}
dp = tmp;
}
return dp;
}
}
剑指 Offer 65. 不用加减乘除做加法
循环求 n 和 c,直至进位 c = 0 ;此时 s = n,返回 n 即可。
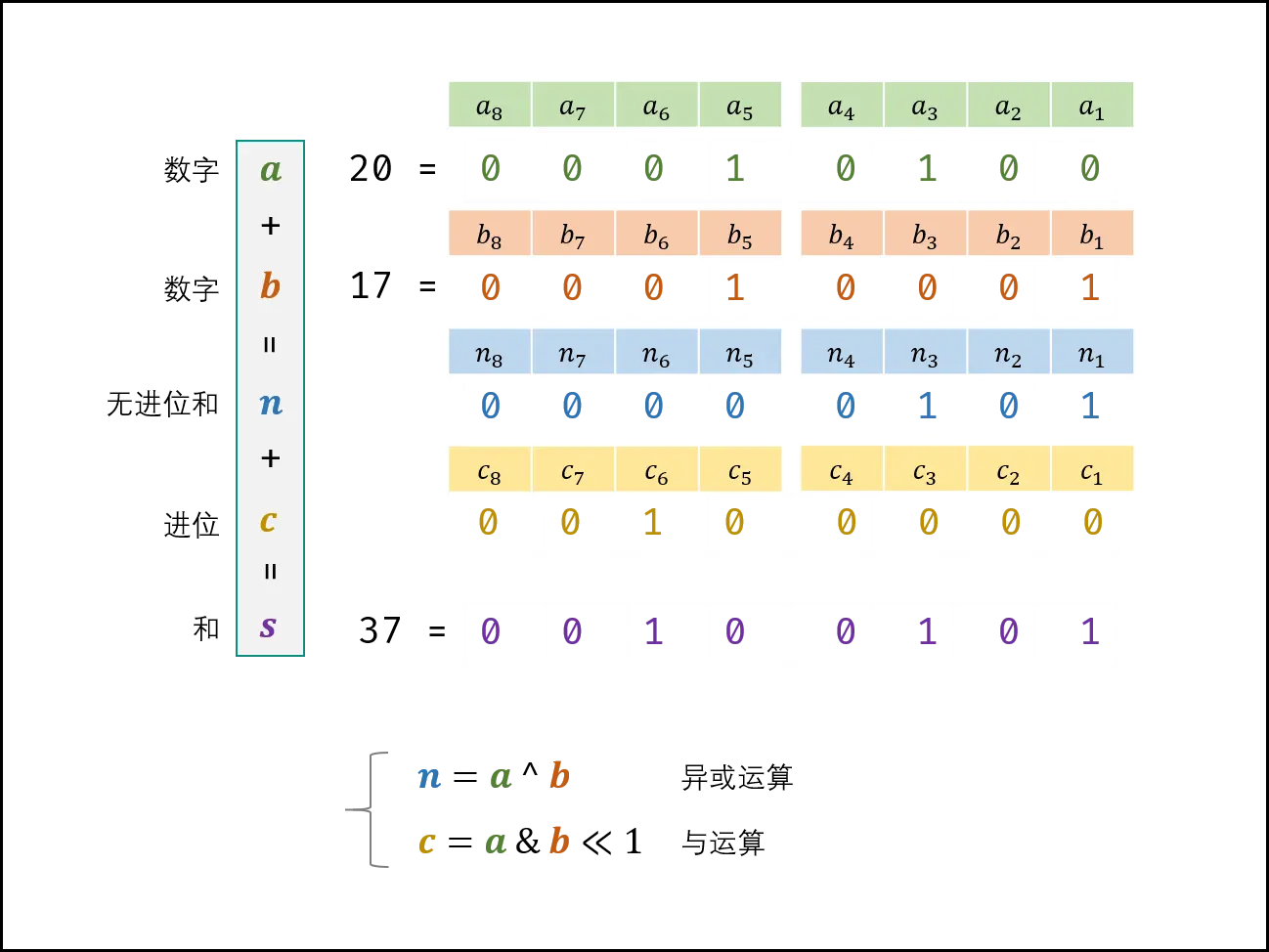
class Solution {
public int add(int a, int b) {
while(b!=0){
int c = (a&b)<<1;
a ^= b;
b = c;
}
return a;
}
}
剑指 Offer 63. 股票的最大利润
动态规划五部曲:
- 确定dp数组(dp table)以及下标的含义
- 确定递推公式
- dp数组如何初始化
- 确定遍历顺序
- 举例推导dp数组
//自己的想出来的一维数组动态规划
class Solution {
public int maxProfit(int[] prices) {
if(prices.length == 0) return 0;
int[] dp = new int[prices.length];
int min = prices[0];
for(int i =1;i<dp.length;i++){
dp[i] = Math.max(dp[i-1],prices[i]-min);
min = Math.min(min, prices[i]);
}
return dp[prices.length-1];
}
}
剑指 Offer 67. 把字符串转换成整数
考虑边界条件
class Solution {
public int strToInt(String str) {
char[] c = str.trim().toCharArray();
if(c.length == 0) return 0;
int res = 0, bndry = Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10;
int i = 1, sign = 1;
if(c[0] == '-') sign = -1;
else if(c[0] != '+') i = 0;
for(int j = i; j < c.length; j++) {
if(c[j] < '0' || c[j] > '9') break;
if(res > bndry || res == bndry && c[j] > '7') return sign == 1 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
res = res * 10 + (c[j] - '0');
}
return sign * res;
}
}
剑指 Offer 67. 把字符串转换成整数
class Solution {
public int strToInt(String str) {
//去前后空格
char[] chars = str.trim().toCharArray();
if (chars.length == 0) return 0;
//记录第一个符合是否为负数
int sign = 1;
//开始遍历的位置
int i = 1;
//如果首个非空格字符为负号,那么从位置1开始遍历字符串,并且结果需要变成负数
if (chars[0] == '-') {
sign = -1;
} else if (chars[0] != '+') { //如果首个非空格字符不是负号也不是加号,那么从第一个元素开始遍历
i = 0;
}
int number = Integer.MAX_VALUE / 10;
//结果
int res = 0;
for (int j = i; j < chars.length; j++) {
//遇到非数字直接退出
if (chars[j] > '9' || chars[j] < '0') break;
/*
这里这个条件的意思为,因为题目要求不能超过int范围,所以需要判断结果是否越界
因为res每次都会 * 10 ,所以外面定义了一个int最大值除以10的数字
此时只需要保证本次循环的res * 10 + chars[j] 不超过 int 即可保证不越界
res > number 意思是,此时res已经大于number了,他 * 10 一定越界
res == number && chars[j] > '7' 的意思是,当res == number时,即:214748364
此时res * 10 变成 2147483640 此时没越界,但是还需要 + chars[j],
而int最大值为 2147483647,所以当chars[j] > 7 时会越界
*/
if (res > number || (res == number && chars[j] > '7')) {
//根据字符串首负号判断返回最大值还是最小值
return sign == 1 ? Integer.MAX_VALUE : Integer.MIN_VALUE;
}
//字符获取数字需要 - '0' 的位移
res = res * 10 + (chars[j] - '0');
}
//返回结果,需要判断正负
return res * sign;
}
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号