树:剑指 Offer 27. 二叉树的镜像
题目描述:
请完成一个函数,输入一个二叉树,该函数输出它的镜像。
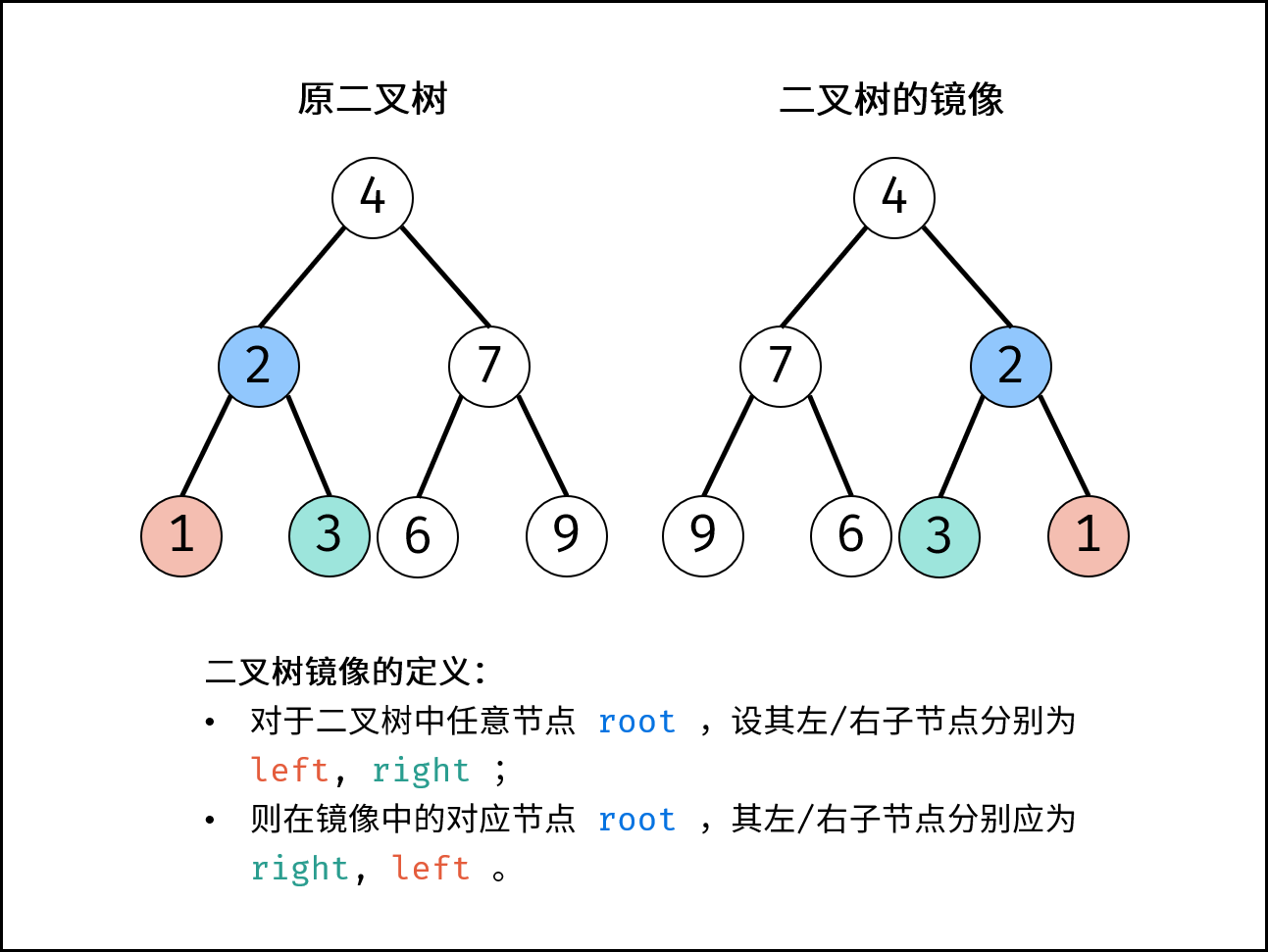
例如输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
镜像输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1
示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
限制:
0 <= 节点个数 <= 1000
二叉树镜像定义: 对于二叉树中任意节点 root ,设其左 / 右子节点分别为 left, right ;
则在二叉树的镜像中的对应 root 节点,其左 / 右子节点分别为 right, left 。
递归法
- 根据二叉树镜像的定义,考虑递归遍历(dfs)二叉树,交换每个节点的左 / 右子节点,即可生成二叉树的镜像。
递归解析:
1.终止条件: 当节点 root 为空时(即越过叶节点),则返回 null ;
2.递推工作:
1).初始化节点 tmp ,用于暂存 root 的左子节点;
2).开启递归 右子节点 mirrorTree(root.right) ,并将返回值作为 root 的 左子节点 。
3).开启递归 左子节点mirrorTree(tmp) ,并将返回值作为 root 的 右子节点 。
3.返回值: 返回当前节点 root ;
Q: 为何需要暂存 rootroot 的左子节点?
A: 在递归右子节点 “root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);” 执行完毕后, root.left 的值已经发生改变,此时递归左子节点 mirrorTree(root.left) 则会出问题。
复杂度分析:
时间复杂度 O(N) : 其中 N 为二叉树的节点数量,建立二叉树镜像需要遍历树的所有节点,占用O(N) 时间。
空间复杂度 O(N) : 最差情况下(当二叉树退化为链表),递归时系统需使用 O(N) 大小的栈空间。
class TreeNode{ int val; TreeNode left; TreeNode right; public TreeNode(int x) { val = x; } }
class Solution { public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) { if(root == null) return null; TreeNode tmp = root.left; root.left = mirrorTree(root.right); root.right = mirrorTree(tmp); return root; } }
另解:
class Solution{ public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root){ if(root==null) return null; TreeNode temp = root.left; root.left = root.right; root.right = temp; mirrorTree(root.left); mirrorTree(root.right); return root; } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号