TreeMap简介
在Map集合框架中,除了HashMap以外,TreeMap也是常用到的集合对象之一。
与HashMap相比,TreeMap是一个能比较元素大小的Map集合,会对传入的key进行了大小排序。其中,可以使用元素的自然顺序,也可以使用集合中自定义的比较器来进行排序;
不同于HashMap的哈希映射,TreeMap实现了红黑树的结构,形成了一颗二叉树。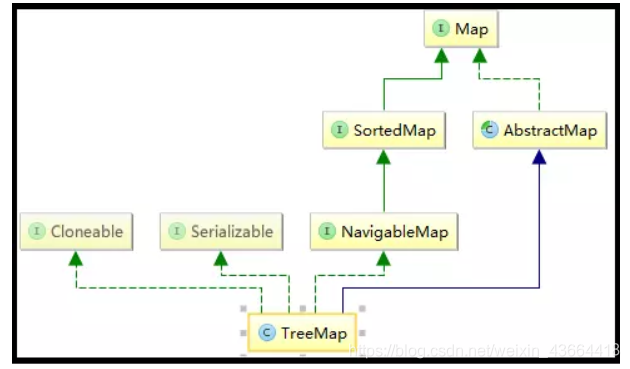
TreeMap继承于AbstractMap,实现了Map, Cloneable, NavigableMap, Serializable接口。
(1)TreeMap 继承于AbstractMap,而AbstractMap实现了Map接口,并实现了Map接口中定义的方法,减少了其子类继承的复杂度;
(2)TreeMap 实现了Map接口,成为Map框架中的一员,可以包含着key-value形式的元素;
(3)TreeMap 实现了NavigableMap接口,意味着拥有了更强的元素搜索能力;
(4)TreeMap 实现了Cloneable接口,实现了clone()方法,可以被克隆;
(5)TreeMap 实现了Java.io.Serializable接口,支持序列化操作;
TreeMap具有如下特点:
不允许出现重复的key;
可以插入null键,null值;
可以对元素进行排序;
无序集合(插入和遍历顺序不一致);
TreeMap基本操作
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
|
public class TreeMapTest { public static void main(String[] agrs){ //创建TreeMap对象: TreeMap<String,Integer> treeMap = new TreeMap<String,Integer>(); System.out.println("初始化后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size()); //新增元素: treeMap.put("hello",1); treeMap.put("world",2); treeMap.put("my",3); treeMap.put("name",4); treeMap.put("is",5); treeMap.put("huangqiuping",6); treeMap.put("i",6); treeMap.put("am",6); treeMap.put("a",6); treeMap.put("developer",6); System.out.println("添加元素后,TreeMap元素个数为:" + treeMap.size()); //遍历元素: Set<Map.Entry<String,Integer>> entrySet = treeMap.entrySet(); for(Map.Entry<String,Integer> entry : entrySet){ String key = entry.getKey(); Integer value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println("TreeMap元素的key:"+key+",value:"+value); } //获取所有的key: Set<String> keySet = treeMap.keySet(); for(String strKey:keySet){ System.out.println("TreeMap集合中的key:"+strKey); } //获取所有的value: Collection<Integer> valueList = treeMap.values(); for(Integer intValue:valueList){ System.out.println("TreeMap集合中的value:" + intValue); } //获取元素: //获取集合内元素key为"huangqiuping"的值 Integer getValue = treeMap.get("huangqiuping"); //获取集合内第一个元素 String firstKey = treeMap.firstKey(); //获取集合内最后一个元素 String lastKey =treeMap.lastKey(); //获取集合内的key小于"huangqiuping"的key String lowerKey =treeMap.lowerKey("huangqiuping"); //获取集合内的key大于等于"huangqiuping"的key String ceilingKey =treeMap.ceilingKey("huangqiuping"); //获取集合的key从"a"到"huangqiuping"的元素 SortedMap<String,Integer> sortedMap =treeMap.subMap("a","my"); //删除元素: //删除集合中key为"huangqiuping"的元素 Integer removeValue = treeMap.remove("huangqiuping"); //清空集合元素: treeMap.clear(); //判断方法: //判断集合是否为空 boolean isEmpty = treeMap.isEmpty(); //判断集合的key中是否包含"huangqiuping" boolean isContain = treeMap.containsKey("huangqiuping"); }} |
TreeMap排序
(1)使用元素自然排序
在使用自然顺序排序时候,需要区分两种情况:一种是Jdk定义的对象,一种是自己定义的对象;
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
|
<font style="color:rgb(77, 77, 77)"><font face="""><font style="font-size:16px">public class SortedTest implements Comparable<SortedTest> { private int age; public SortedTest(int age){ this.age = age; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } //自定义对象,实现compareTo(T o)方法: public int compareTo(SortedTest sortedTest) { int num = this.age - sortedTest.getAge(); //为0时候,两者相同: if(num==0){ return 0; //大于0时,传入的参数小: }else if(num>0){ return 1; //小于0时,传入的参数大: }else{ return -1; } }}public class TreeMapTest { public static void main(String[] agrs){ //自然顺序比较 naturalSort(); } //自然排序顺序: public static void naturalSort(){ //第一种情况:Integer对象 TreeMap<Integer,String> treeMapFirst = new TreeMap<Integer, String>(); treeMapFirst.put(1,"huangqiuping"); treeMapFirst.put(6,"huangqiuping"); treeMapFirst.put(3,"huangqiuping"); treeMapFirst.put(10,"huangqiuping"); treeMapFirst.put(7,"huangqiuping"); treeMapFirst.put(13,"huangqiuping"); System.out.println(treeMapFirst.toString()); //第二种情况:SortedTest对象 TreeMap<SortedTest,String> treeMapSecond = new TreeMap<SortedTest, String>(); treeMapSecond.put(new SortedTest(10),"huangqiuping"); treeMapSecond.put(new SortedTest(1),"huangqiuping"); treeMapSecond.put(new SortedTest(13),"huangqiuping"); treeMapSecond.put(new SortedTest(4),"huangqiuping"); treeMapSecond.put(new SortedTest(0),"huangqiuping"); treeMapSecond.put(new SortedTest(9),"huangqiuping"); System.out.println(treeMapSecond.toString()); }}</font></font></font> |
在自然顺序比较中,需要让被比较的元素实现Comparable接口,否则在向集合里添加元素时报:"java.lang.ClassCastException: com.huangqiuping.collection.map.SortedTest cannot be cast to java.lang.Comparable"异常;
这是因为在调用put()方法时,会将传入的元素转化成Comparable类型对象,所以当你传入的元素没有实现Comparable接口时,就无法转换,遍会报错;
(2)使用自定义比较器排序
使用自定义比较器排序,需要在创建TreeMap对象时,将自定义比较器对象传入到TreeMap构造方法中;
自定义比较器对象,需要实现Comparator接口,并实现比较方法compare(To1,To2);
使用自定义比较器排序的话,被比较的对象无需再实现Comparable接口了;
|
01
02
03
04
05
06
07
08
09
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
|
public class SortedTest { private int age; public SortedTest(int age){ this.age = age; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }}public class SortedTestComparator implements Comparator<SortedTest> { //自定义比较器:实现compare(To1,To2)方法: public int compare(SortedTest sortedTest1, SortedTest sortedTest2) { int num = sortedTest1.getAge() - sortedTest2.getAge(); if(num==0){//为0时候,两者相同: return 0; }else if(num>0){//大于0时,后面的参数小: return 1; }else{//小于0时,前面的参数小: return -1; } }} |



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号