OGNL,表达式上下文ContextMap
1.OGNL表达式
object graph navigation language:对象图导航语言
存取对象属性;调用对象方法;字段类型转换等。
<input type="text" name="user.username" />
2.OGNL表达式的使用场景
2.1 在jsp中
s1.导入struts标签库:
<%@ taglib prefix="s" uri="/struts-tags" %>
s2. 只能在在struts标签库中使用OGNL表达式,不能再其他地方用
对于property的value默认使用OGNL表达式。
对于radio的list属性默认使用OGNL表达式
纯字符串:
<s:property value="%{'OGNLExpression'}" />
<s:property value="'OGNLExpression'" />
使用OGNL表达式:
<s:textfield value="%{name}" label="姓名" />
调用对象方法:
<s:textfield value="%{'admin'.length()}" label="姓名" />
<s:textfield value="%{'admin'.split('m')}" label="姓名" />
调用静态类的静态成员:
<s:property value="@java.lang.Math@PI" /><br /> 静态成员
<constant name="struts.ognl.allowStaticMethodAccess" value="true" /> 开启允许调用OGNL静态方法【struts.xml中配置】
<s:property value="@java.lang.Math@random()" /> 静态方法
操作List对象:{'',''} -->ArrayList-->['','']
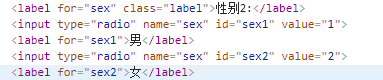
<s:radio name="gender" list="{'male','female'}" label="性别"></s:radio> list属性默认使用OGNL表达式
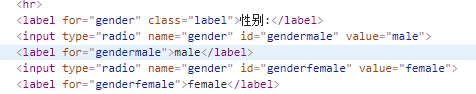
操作Map对象:#{'':'' , '':''} -->Map -->{'':'', '':''}
<s:radio name="sex" list="#{'1':'男','2':'女'}" label="性别2"></s:radio>
3.OGNL表达式上下文:ContextMap
contextMap是struts2封装好的一次请求可能出现的最大的数据容器。
结构:是一个Map结构 {String:Object}
里面存的数据:
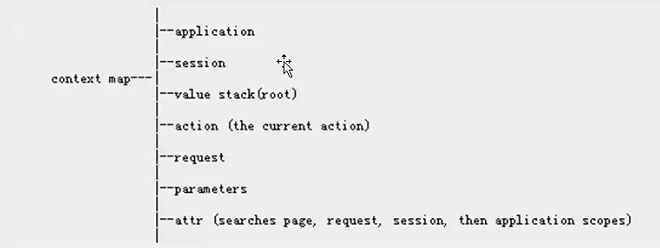
- application:ServletContext应用对象
- session:HttpSession
- valueStack:值栈 List类型
- action:当前执行的动作类相关数据 【不是Map类型】
- request:HttpServletRequest
- parameters:请求参数
- attr:四大域的属性数据
除了ValueStack和action不是Map类型的,其他的都是Map类型{String : Object}
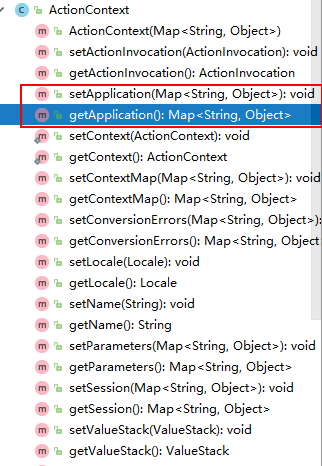
4.ActionContext和ContextMap的关系
ActionContext可以获取四大域对象,他是个工具类。

// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package com.opensymphony.xwork2; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.inject.Container; import com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack; import java.io.Serializable; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Locale; import java.util.Map; public class ActionContext implements Serializable { static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> actionContext = new ThreadLocal(); public static final String ACTION_NAME = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name"; public static final String VALUE_STACK = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"; public static final String SESSION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session"; public static final String APPLICATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application"; public static final String PARAMETERS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters"; public static final String LOCALE = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale"; public static final String TYPE_CONVERTER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.typeConverter"; public static final String ACTION_INVOCATION = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation"; public static final String CONVERSION_ERRORS = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors"; public static final String CONTAINER = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container"; private Map<String, Object> context; public ActionContext(Map<String, Object> context) { this.context = context; } public void setActionInvocation(ActionInvocation actionInvocation) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation", actionInvocation); } public ActionInvocation getActionInvocation() { return (ActionInvocation)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.actionInvocation"); } public void setApplication(Map<String, Object> application) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application", application); } public Map<String, Object> getApplication() { return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application"); } public static void setContext(ActionContext context) { actionContext.set(context); } public static ActionContext getContext() { return (ActionContext)actionContext.get(); } public void setContextMap(Map<String, Object> contextMap) { getContext().context = contextMap; } public Map<String, Object> getContextMap() { return this.context; } public void setConversionErrors(Map<String, Object> conversionErrors) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors", conversionErrors); } public Map<String, Object> getConversionErrors() { Map<String, Object> errors = (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.conversionErrors"); if (errors == null) { errors = new HashMap(); this.setConversionErrors((Map)errors); } return (Map)errors; } public void setLocale(Locale locale) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale", locale); } public Locale getLocale() { Locale locale = (Locale)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.locale"); if (locale == null) { locale = Locale.getDefault(); this.setLocale(locale); } return locale; } public void setName(String name) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name", name); } public String getName() { return (String)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.name"); } public void setParameters(Map<String, Object> parameters) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters", parameters); } public Map<String, Object> getParameters() { return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.parameters"); } public void setSession(Map<String, Object> session) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session", session); } public Map<String, Object> getSession() { return (Map)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.session"); } public void setValueStack(ValueStack stack) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack", stack); } public ValueStack getValueStack() { return (ValueStack)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"); } public void setContainer(Container cont) { this.put("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container", cont); } public Container getContainer() { return (Container)this.get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.container"); } public <T> T getInstance(Class<T> type) { Container cont = this.getContainer(); if (cont != null) { return cont.getInstance(type); } else { throw new XWorkException("Cannot find an initialized container for this request."); } } public Object get(String key) { return this.context.get(key); } public void put(String key, Object value) { this.context.put(key, value); } }
ContextMap是一个Map类型的对象,key为application等,value为Map类型的数据,但是通过ContextMap.get(application)返回的是Object类型的对象。因此可以通过ActionContext工具类直接获取Map对象。
域对象:
com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletxxx
ContextMap中的数据:
com.opensymphony.xwork2.ActionContext.application
源码分析:ActionContext.java
static ThreadLocal<ActionContext> actionContext = new ThreadLocal();
private Map<String, Object> context; //传说中的ContextMap
public static ActionContext getContext() {
return (ActionContext)actionContext.get(); }
获取线程安全的ActionContext对象
ServletActionContext.java
public static HttpServletRequest getRequest() { return (HttpServletRequest)ActionContext.getContext().get("com.opensymphony.xwork2.dispatcher.HttpServletRequest"); }
通过ActionContext.getContext()静态方法可以获取一个线程安全的ActionContext对象,然后再调用里面的get方法:

由此可知:域对象(ServletContext)、域对象数据(Map)都是存在context(Map<String, Object>)属性中的
注意:ActionContext的声明周期为一次请求。
ContextMap: {key: value}
application:Map
ActionContext.application:Map
servlet.ServletContext:ServletContext
往ContextMap中存入数据:
public class UserAction extends ActionSupport { public String index(){ ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext(); actionContext.put("contextMapKey","this is ContextMap value"); //底层:ActionContext.context.put() return SUCCESS; } }
往ServletContext域中存入数据:application,
取值:#ContextMap的key.key
<s:property value="#application.application1" />
5.ValueStack
值栈中的数据不需要使用#访问。而ContextMap中的Value需要使用#Key
valueStack是一个List集合

// // Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA // (powered by Fernflower decompiler) // package com.opensymphony.xwork2.util; import java.util.Map; public interface ValueStack { String VALUE_STACK = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ValueStack"; String REPORT_ERRORS_ON_NO_PROP = "com.opensymphony.xwork2.util.ValueStack.ReportErrorsOnNoProp"; Map<String, Object> getContext(); void setDefaultType(Class var1); void setExprOverrides(Map<Object, Object> var1); Map<Object, Object> getExprOverrides(); CompoundRoot getRoot(); void setValue(String var1, Object var2); void setParameter(String var1, Object var2); void setValue(String var1, Object var2, boolean var3); String findString(String var1); String findString(String var1, boolean var2); Object findValue(String var1); Object findValue(String var1, boolean var2); Object findValue(String var1, Class var2); Object findValue(String var1, Class var2, boolean var3); Object peek(); Object pop(); void push(Object var1); void set(String var1, Object var2); int size(); }
方法:

OGNLValueStack:继承ValueStack
CompoundRoot root; public Object peek() { return this.root.peek(); } public Object pop() { return this.root.pop(); } public void push(Object o) { this.root.push(o); }
使用valueStack存入数据:User1Action.java

public class User1Action extends ActionSupport { public String login(){ ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext(); //valueStack ValueStack valueStack = actionContext.getValueStack(); Student student = new Student(); student.setId(1); student.setUsername("张三"); student.setAge(21); valueStack.push(student); return SUCCESS; } }
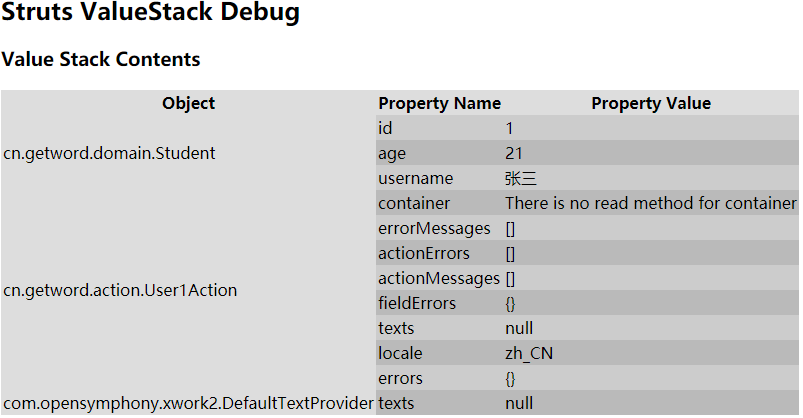
不建议把Map和List加到值栈中,建议存入到ContextMap。对于POJO建议存入到值栈中
取值:先从栈顶找,有没有username的对象,再看有没有username的属性
<s:property value="username" />
栈顶:
<s:property value="[0].username" />
<s:property value="[1].username" />
OGNL通过ValueStack.findValue方法找值
6.struts2中使用EL
(1)struts2中的EL :由于request对象被增强了,valueStack和ContextMap本质上是存入到request对象中,因此ActionContext是每次请求实例化一次。
page --> request --> valueStack --> ContextMap --> session --> application
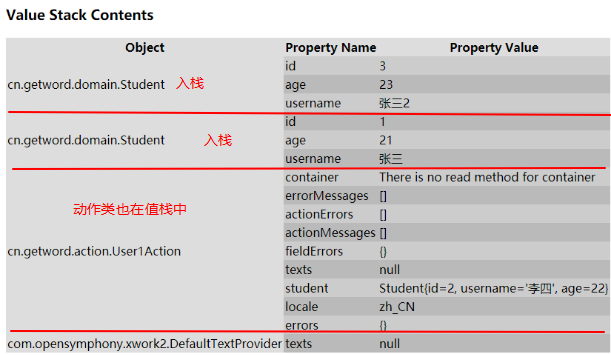
案例:

public class User2Action extends ActionSupport { public String index(){ ActionContext actionContext = ActionContext.getContext(); //valueStack Student student1 = new Student(); student1.setId(1); student1.setUsername("张三"); student1.setAge(21); Student student2 = new Student(); student2.setId(3); student2.setUsername("张三2"); student2.setAge(23); Map<String, Object> contextMap = actionContext.getContextMap(); List<Student> list = new ArrayList<Student>(); list.add(student1); list.add(student2); contextMap.put("students", list); return SUCCESS; } }
EL :查找顺序 page>request>valueStack>ContextMap>session >application
<table border="1">
<tr>
<th>姓名</th>
<th>年龄</th>
</tr>
<c:forEach items="${students}" var="s">
<tr>
<td>${s.username}</td>
<td>${s.age}</td>
</tr>
</c:forEach>
</table>
end



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号