ResNet 动手实现
参考:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/225597229
前言
ResNet(Residual Neural Network)由微软研究院的Kaiming He等四名华人提出,通过使用ResNet Unit成功训练出了152层的神经网络,并在ILSVRC2015比赛中取得冠军,在top5上的错误率为3.57%,同时参数量比VGGNet低,效果非常突出。ResNet的结构可以极快的加速神经网络的训练,模型的准确率也有比较大的提升。同时ResNet的推广性非常好,甚至可以直接用到InceptionNet网络中。
背景:
当堆叠到一定网络深度时,就会出现两个问题。
- 梯度消失或梯度爆炸。
- 退化问题(degradation problem)。
ReLU和Batch Normalization能解决梯度消失或者梯度爆炸问题;但是对于退化问题(随着网络层数的加深,效果还会变差)并没有很好的解决办法。
理论
ResNet 有很多尺寸,包括 ResNet 18、ResNet 34、ResNet 50、ResNet 101、ResNet 152,网络结构对比如下:
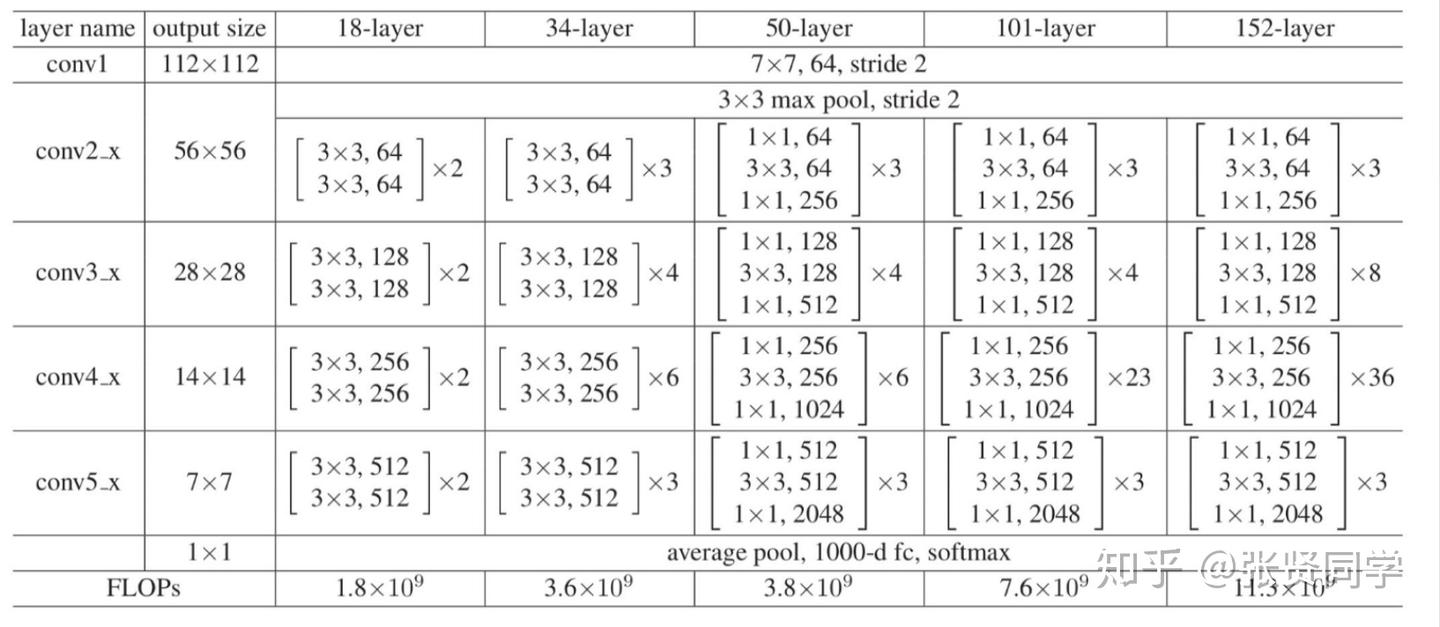
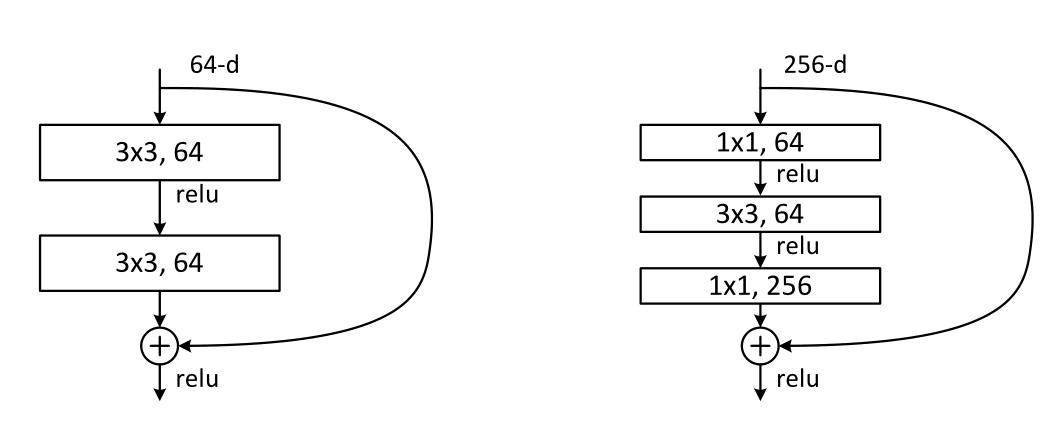
两种基本单元结构:
论文原文中给出了两种ResNet的基本单元结构,其中左边的单元用于较浅的网络(BasicBlock),如ResNet18、ResNet34,右边的单元则用于较深的网络(Bottleneck),如ResNet50、ResNet101等。
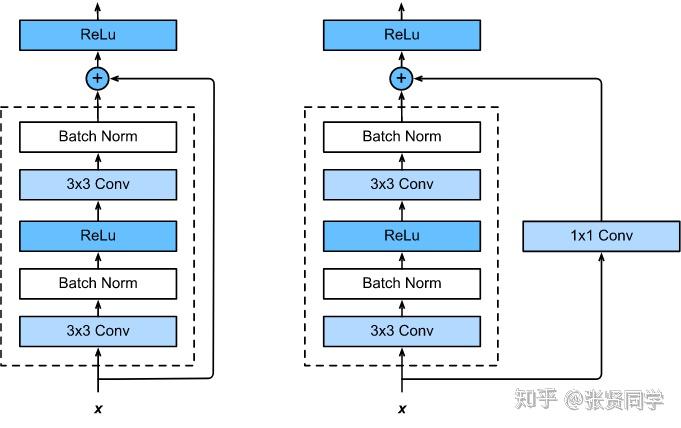
两种残差路径:
shortcut 路径大致可以分成 2 种,取决于残差路径是否改变了feature map数量和尺寸。
- 一种是将输入
x原封不动地输出。 - 另一种则需要经过 1×1 卷积来升维或者降采样,主要作用是将输出与 F(x) 路径的输出保持
shape一致,对网络性能的提升并不明显。(上图只有一条线。下面标注1x1 Conv更明显。)
两种结构如下图所示:
在ResNet 18中,数据变换大致流程如下:
- 输入的图片形状是 3×224×224。
- 图片经过
conv1层,输出图片大小为 64×112×112。(通道64,尺寸/2) - 图片经过
max pool层,输出图片大小为 64×56×56。(通道不变,尺寸/2) - 图片经过
conv2层,输出图片大小为 64×56×56。(通道不变,尺寸不变) - 图片经过
conv3层,输出图片大小为 128×28×28。(通道x2,尺寸/2) - 图片经过
conv4层,输出图片大小为 256×14×14。(通道x2,尺寸/2) - 图片经过
conv5层,输出图片大小为 512×7×7。(通道x2,尺寸/2) - 图片经过
avg pool层,输出大小为 512×1×1。(通道不变) - 图片经过
fc层,输出维度为 numclasses,表示每个分类的logits。
代码实战
模型代码
def conv3x3(in_planes: int, out_planes: int, stride: int = 1) -> nn.Conv2d:
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
def conv1x1(in_planes: int, out_planes: int, stride: int = 1) -> nn.Conv2d:
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes: int, planes: int, stride: int = 1):
super().__init__()
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(in_planes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.stride = stride
self.downsample = None
if in_planes != planes or stride != 1:
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(in_planes, planes, self.stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block: BasicBlock, layers: list[int], num_classes: int = 10):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 64, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 128, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 256, 512, layers[3], stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512, num_classes)
def _make_layer(self, block, in_planes: int, planes: int, blocks: int, stride: int = 1) -> nn.Sequential:
layers = [block(in_planes, planes, stride)]
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(planes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
数据代码
数据来源: https://storage.googleapis.com/download.tensorflow.org/example_images/flower_photos.tgz
总共有5个类别3670张图片,分别为daisy(雏菊)、dandelion(蒲公英)、rose(玫瑰)、sunflower(向日葵)、tulip(郁金香)。
数据预处理:
import json
import os
import random
data = []
for target in os.listdir('data/flower_photos'):
for x in os.listdir(f'data/flower_photos/{target}'):
cur = {
'file': f'data/flower_photos/{target}/{x}',
'label': target
}
data.append(cur)
random.shuffle(data)
n_train = int(len(data) * 0.8)
with open('data/train.jsonl', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for x in data[:n_train]:
f.write(json.dumps(x, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')
with open('data/valid.jsonl', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as f:
for x in data[n_train:]:
f.write(json.dumps(x, ensure_ascii=False) + '\n')
自定义数据集:
class MyDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, filename):
self.data = [json.loads(x) for x in open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8').readlines()]
self.img_map = {
'daisy': 0,
'dandelion': 1,
'roses': 2,
'sunflowers': 3,
'tulips': 4
}
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
image = Image.open(self.data[idx]['file'])
image = transforms.Resize((224, 224))(image)
image = transforms.ToTensor()(image)
label = torch.tensor(self.img_map[self.data[idx]['label']])
return image, label
训练代码(完整代码)
import json
import random
import numpy as np
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from PIL import Image
from torch.optim.lr_scheduler import CosineAnnealingLR, LinearLR, SequentialLR
from torch.utils.data import DataLoader
from torch.utils.data import Dataset
from torchvision import transforms
from torchvision.models import resnet18
seed = 100
torch.manual_seed(seed)
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(seed)
random.seed(seed)
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
def conv3x3(in_planes: int, out_planes: int, stride: int = 1) -> nn.Conv2d:
"""3x3 convolution with padding"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=False)
def conv1x1(in_planes: int, out_planes: int, stride: int = 1) -> nn.Conv2d:
"""1x1 convolution"""
return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=False)
class BasicBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, in_planes: int, planes: int, stride: int = 1):
super().__init__()
# Both self.conv1 and self.downsample layers downsample the input when stride != 1
self.conv1 = conv3x3(in_planes, planes, stride)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.stride = stride
self.downsample = None
if in_planes != planes or stride != 1:
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(in_planes, planes, self.stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class ResNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, block: BasicBlock, layers: list[int], num_classes: int = 10):
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=False)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, 64, layers[0])
self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 64, 128, layers[1], stride=2)
self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 128, 256, layers[2], stride=2)
self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 256, 512, layers[3], stride=2)
self.avgpool = nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d((1, 1))
self.fc = nn.Linear(512, num_classes)
def _make_layer(self, block, in_planes: int, planes: int, blocks: int, stride: int = 1) -> nn.Sequential:
layers = [block(in_planes, planes, stride)]
for _ in range(1, blocks):
layers.append(block(planes, planes))
return nn.Sequential(*layers)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.bn1(x)
x = self.relu(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.layer1(x)
x = self.layer2(x)
x = self.layer3(x)
x = self.layer4(x)
x = self.avgpool(x)
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.fc(x)
return x
class MyDataset(Dataset):
def __init__(self, filename):
self.data = [json.loads(x) for x in open(filename, 'r', encoding='utf-8').readlines()]
self.img_map = {
'daisy': 0,
'dandelion': 1,
'roses': 2,
'sunflowers': 3,
'tulips': 4
}
def __len__(self):
return len(self.data)
def __getitem__(self, idx):
image = Image.open(self.data[idx]['file'])
image = transforms.Resize((224, 224))(image)
image = transforms.ToTensor()(image)
label = torch.tensor(self.img_map[self.data[idx]['label']])
return image, label
def train(epoch, epochs, net, dataloader, loss_fn, optimizer, scheduler):
train_loss = []
net.train()
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
y_hat = net(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_hat, y)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
scheduler.step()
train_loss.append(loss.item())
if step % 1 == 0:
print(f"epoch={epoch}/{epochs}, {step}/{len(dataloader)} of train, loss={loss.item()}")
return train_loss
def valid(epoch, epochs, net, dataloader, loss_fn):
valid_loss = []
net.eval()
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(dataloader):
x, y = x.to(device), y.to(device)
y_hat = net(x)
loss = loss_fn(y_hat, y)
valid_loss.append(loss.item())
if step % 1 == 0:
print(f"epoch={epoch}/{epochs}, {step}/{len(dataloader)} of valid, loss={loss.item()}")
return valid_loss
def main():
# 参数
batch_size = 4
epochs = 1
learning_rate = 0.0001
num_workers = 2
train_dataset = MyDataset('data/train.jsonl')
valid_dataset = MyDataset('data/valid.jsonl')
train_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=train_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=True)
valid_dataloader = DataLoader(dataset=valid_dataset, batch_size=batch_size, num_workers=num_workers, shuffle=False)
net = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2])
model = net.to(device)
loss_fn = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device)
optimizer = torch.optim.AdamW(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
warm_up_iter = 20
scheduler1 = LinearLR(optimizer, start_factor=0.01, end_factor=1, total_iters=warm_up_iter)
scheduler2 = CosineAnnealingLR(optimizer, len(train_dataloader) * epochs - warm_up_iter)
scheduler = SequentialLR(optimizer, schedulers=[scheduler1, scheduler2], milestones=[warm_up_iter])
for epoch in range(epochs):
train_loss = train(epoch, epochs, net, train_dataloader, loss_fn, optimizer, scheduler)
print(f"epoch={epoch}/{epochs}, train epoch loss={np.mean(train_loss)}")
valid_loss = valid(epoch, epochs, net, valid_dataloader, loss_fn)
print(f"epoch={epoch}/{epochs}, valid epoch loss={np.mean(valid_loss)}")
torch.save(net.state_dict(), f"resnet18.pth")
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
# test()
测试代码
def test():
net = resnet18()
net.fc = nn.Linear(in_features=net.fc.in_features, out_features=10)
net.load_state_dict(torch.load('resnet18.pth'))
net.eval()
image = Image.open('data/flower_photos/daisy/5547758_eea9edfd54_n.jpg')
image = transforms.Resize((224, 224))(image)
image = transforms.ToTensor()(image).unsqueeze(0)
y_hat = net(image)
y_hat = torch.argmax(y_hat, dim=1)
print(y_hat)
if __name__ == '__main__':
# main()
test()
补充:Bottleneck
Bottleneck会对通道先降维(1/2),再扩充x4
class Bottleneck(nn.Module):
expansion: int = 4 # Bottleneck层输出通道都是输入的4倍
def __init__(self, in_planes: int, planes: int, stride: int = 1) -> None:
super().__init__()
self.conv1 = conv1x1(in_planes, planes)
self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes, stride)
self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
self.conv3 = conv1x1(planes, planes * self.expansion)
self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * self.expansion)
self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True)
self.downsample = None
if in_planes != planes * self.expansion or stride != 1:
self.downsample = nn.Sequential(
conv1x1(in_planes, planes * self.expansion, stride),
nn.BatchNorm2d(planes)
)
def forward(self, x: torch.Tensor) -> torch.Tensor:
identity = x
out = self.conv1(x)
out = self.bn1(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv2(out)
out = self.bn2(out)
out = self.relu(out)
out = self.conv3(out)
out = self.bn3(out)
if self.downsample is not None:
identity = self.downsample(x)
out += identity
out = self.relu(out)
return out




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号