Android TabHost
1.概念
盛放Tab的容器就是TabHost。TabHost的实现有两种方式:
第一种继承TabActivity,从TabActivity中用getTabHost()方法获取TabHost。各个Tab中的内容在布局文件中定义就行了。
第二种方式,不继承TabActivity,在布局文件中定义TabHost即可,但是TabWidget的id必须是@android:id/tabs,FrameLayout的id必须是@android:id/tabcontent。
Tab应用的结构
TabHost的Activity的结构如下:
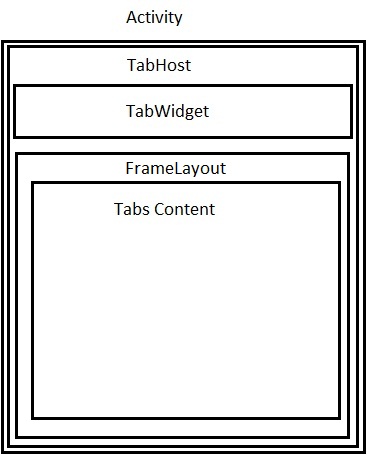
2.案例
1)继承TabActivity
res/layout/main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- 定义TabHost组件 --> <TabHost xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <!-- 定义第一个标签页的内容 --> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/tab01" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <!-- 定义两个TextView用于显示标签页中的内容 --> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="孙悟空-2011/07/12"/> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="猪八戒-2011/07/10"/> </LinearLayout> <!-- 定义第二个标签页的内容 --> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/tab02" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="萨僧-2011/07/11"/> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="唐僧-2011/07/10"/> </LinearLayout> <!-- 定义第三个标签页的内容 --> <LinearLayout android:id="@+id/tab03" android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="孙悟空-2011/07/12"/> <TextView android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="萨僧-2011/07/08"/> </LinearLayout> </TabHost>
HelloTabHost.java
public class HelloTabHost extends TabActivity { @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); //调用TabActivity的getTabHost()方法获取TabHost对象 TabHost tabHost = getTabHost(); //设置使用TabHost布局 LayoutInflater.from(this).inflate(R.layout.main, tabHost.getTabContentView(),true); //添加第一个标签页 tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab01").setIndicator("已接电话").setContent(R.id.tab01)); //添加第二个标签页,并在其标签上添加一个图片 tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab02").setIndicator("未接电话",getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.icon)).setContent(R.id.tab02)); //添加第三个标签页 tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab03").setIndicator("已拨电话").setContent(R.id.tab03)); } }
运行效果:


2)不继承TabActivity
继承普通Activity,<TabWidget>标签id必须为tabs、<FrameLayout>标签id必须为tabcontent.这个方式在通过findViewById获得TabHost之后,必须要调用setup方法。
main.xml代码
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <!-- TabHost必须包含一个 TabWidget和一个FrameLayout--> <TabHost android:id="@+id/tabhost" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content"> <LinearLayout android:orientation="vertical" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <!-- TabWidget的id属性必须为 @android:id/tabs--> <TabWidget android:id="@android:id/tabs" android:orientation="horizontal" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> <!-- FrameLayout的id属性必须为 @android:id/tabcontent--> <FrameLayout android:id="@android:id/tabcontent" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"> <TextView android:id="@+id/view1" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/view2" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"/> <TextView android:id="@+id/view3" android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent"/> </FrameLayout> </LinearLayout> </TabHost> </LinearLayout>
Java代码
public class TabHostTest extends Activity { @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); // 获取TabHost对象 TabHost tabHost = (TabHost) findViewById(R.id.tabhost); // 如果没有继承TabActivity时,通过该种方法加载启动tabHost tabHost.setup(); tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab1").setIndicator("第一个标签", getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.icon)).setContent( R.id.view1)); tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab3").setIndicator("第三个标签") .setContent(R.id.view3)); tabHost.addTab(tabHost.newTabSpec("tab2").setIndicator("第二个标签") .setContent(R.id.view2)); } }
效果图

设置tab的内容
上面的例子展示了使用tab显示不同的layout资源。如果我们需要通过tab导航到不同的Activity,该怎么办?
这种情况,我们需要有一个activity作为应用的根activity。这个Activity包含TabHost,通过intents导航不同的activity。
注意:根Activity必须继承TabActivity。代码如下:
Layout:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <TabHost android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@android:id/tabhost" xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" > <TabWidget android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:id="@android:id/tabs" /> <FrameLayout android:layout_width="fill_parent" android:layout_height="fill_parent" android:id="@android:id/tabcontent" > </FrameLayout> </TabHost>
Activity:
public class TabDemo extends TabActivity { /** Called when the activity is first created. */ @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); setContentView(R.layout.main); TabHost tabHost=getTabHost(); // no need to call TabHost.Setup() //First Tab TabSpec spec1=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab 1"); spec1.setIndicator("Tab 1",getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.sun)); Intent in1=new Intent(this, Act1.class); spec1.setContent(in1); TabSpec spec2=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab 2"); spec2.setIndicator("Tab 2",getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.chart)); Intent in2=new Intent(this,Act2.class); spec2.setContent(in2); tabHost.addTab(spec2); tabHost.addTab(spec3); } }
运行效果

在运行时添加Tab
在运行时我们可以通过调用TabSepc.setContent(TabContentFactory)方法添加Tab。
<span style="white-space:pre"> </span>TabSpec spec1=tabHost.newTabSpec("Tab 1"); spec1.setIndicator("Tab 1",getResources().getDrawable(R.drawable.sun)); spec1.setContent(new TabContentFactory() { <span style="white-space:pre"> </span> @Override <span style="white-space:pre"> </span> public View createTabContent(String tag) { <span style="white-space:pre"> </span> // TODO Auto-generated method stub <span style="white-space:pre"> </span> return (new AnalogClock(TabDemo.this)); <span style="white-space:pre"> </span> } <span style="white-space:pre"> </span> });


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号