Git的配置
2.1、查看配置
git config -l 查看详细配置
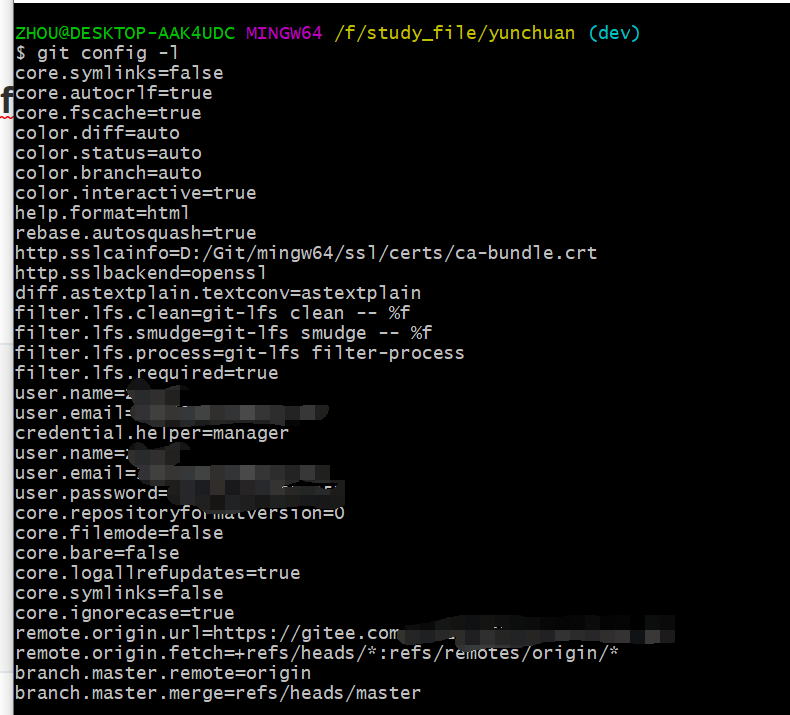
查看不同级别的配置文件:
#查看系统config git config --system --list #查看当前用户(global)配置 git config --global --list #查看当前仓库配置信息 git config --local --list
2.2、Git配置文件分类
Git相关的配置文件有三个:
1)、 /etc/gitconfig:包含了适用于系统所有用户和所有项目的值。注是git的安装目录(Win:D:\Git\mingw64\etc\gitconfig) --system 系统级
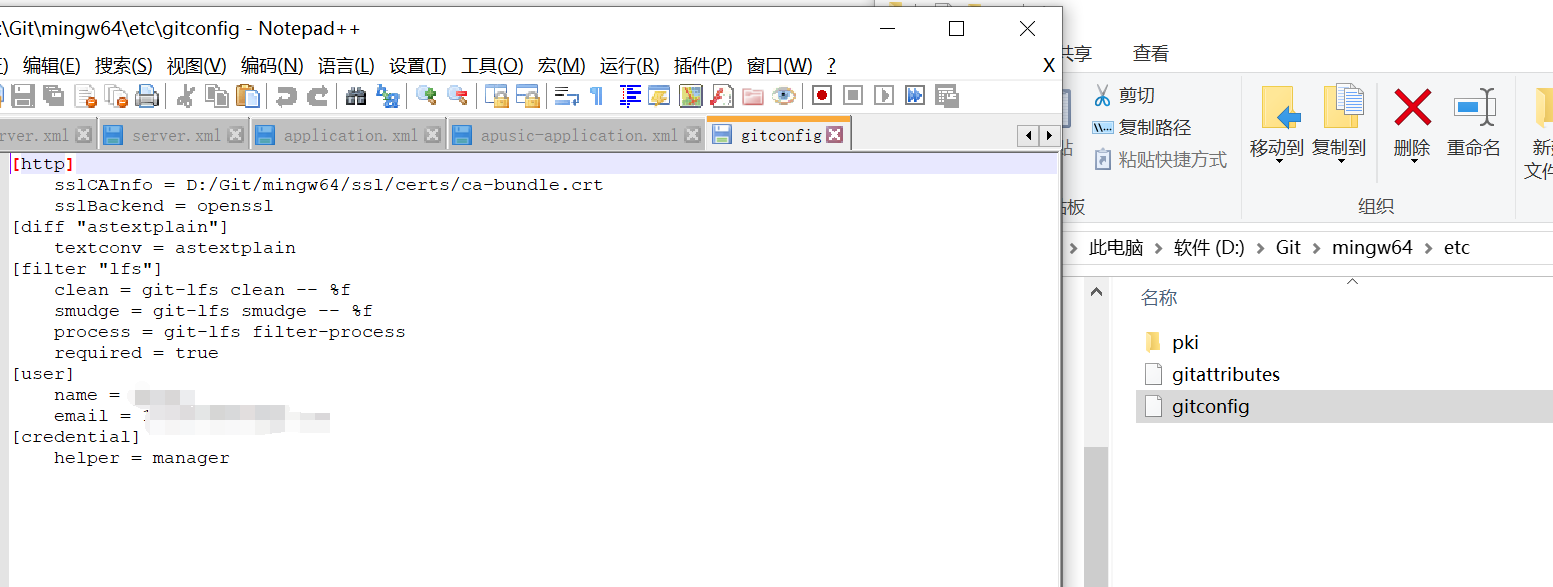
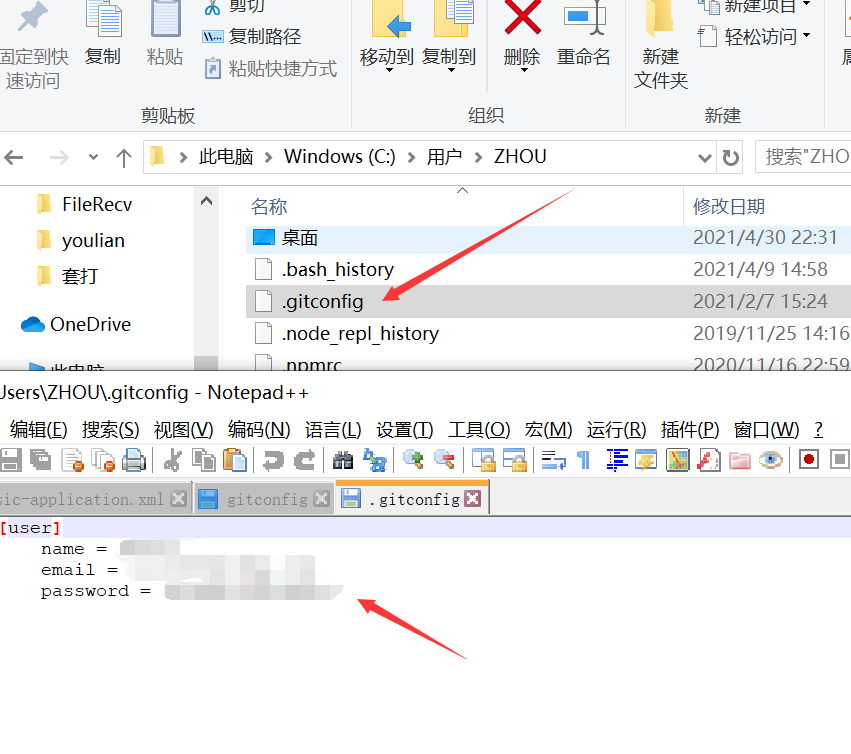
2)、~/.gitconfig:只适用于当前登录用户的配置。(Win:C:\Users\Administrator.gitconfig) --global 全局
3)、位于git项目目录中的.git/config:适用于特定git项目的配置。--local当前项目
注意:对于同一配置项,三个配置文件的优先级是1<2<3
2.3、设置用户名与邮箱(用户标识,必要)
当你安装Git后首先要做的事情是设置你的用户名称和e-mail地址。这是非常重要的,因为每次Git提交都会使用该信息。它被永远的嵌入到了你的提交中:
$ git config --global user.name "***" #名称
$ git config --global user.email ****@qq.com #邮箱
只需要做一次这个设置,如果你传递了--global 选项,因为Git将总是会使用该信息来处理你在系统中所做的一切操作。如果你希望在一个特定的项目中使用不同的名称或e-mail地址,你可以在该项目中运行该命令而不要--global选项。 总之--global为全局配置,不加为某个项目的特定配置。修改如上图2所示;
2.4、添加或删除配置项
1)、添加配置项
git config [--local|--global|--system] section.key value
[--local|--global|--system] #可选的,对应本地,全局,系统不同级别的设置
section.key #区域下的键
value #对应的值
--local 项目级
--global 当前用户级
--system 系统级
2)、删除配置项
git config [--local|--global|--system] --unset section.key
2.5、更多配置项
git config --global color.ui true #打开所有的默认终端着色
git config --global alias.ci commit #别名 ci 是commit的别名
[alias]
co = checkout
ci = commit
st = status
pl = pull
ps = push
dt = difftool
l = log --stat
cp = cherry-pick
ca = commit -a
b = branch
user.name #用户名
user.email #邮箱
core.editor #文本编辑器
merge.tool #差异分析工具
core.paper "less -N" #配置显示方式
color.diff true #diff颜色配置
alias.co checkout #设置别名
git config user.name #获得用户名
git config core.filemode false #忽略修改权限的文件
所有config命令参数
语法: git config [<options>]
文件位置
--global #use global config file 使用全局配置文件
--system #use system config file 使用系统配置文件
--local #use repository config file 使用存储库配置文件
-f, --file <file> #use given config file 使用给定的配置文件
--blob <blob-id> #read config from given blob object 从给定的对象中读取配置
动作
--get #get value: name [value-regex] 获得值:[值]名[正则表达式]
--get-all #get all values: key [value-regex] 获得所有值:[值]名[正则表达式]
--get-regexp #get values for regexp: name-regex [value-regex] 得到的值根据正则
--get-urlmatch #get value specific for the URL: section[.var] URL 为URL获取特定的值
--replace-all #replace all matching variables: name value [value_regex] 替换所有匹配的变量:名称值[ value_regex ]
--add #add a new variable: name value 添加一个新变量:name值
--unset #remove a variable: name [value-regex] 删除一个变量名[值]:正则表达式
--unset-all #remove all matches: name [value-regex] 删除所有匹配的正则表达式:名称[值]
--rename-section #rename section: old-name new-name 重命名部分:旧名称 新名称
--remove-section #remove a section: name 删除部分:名称
-l, --list #list all 列出所有
-e, --edit #open an editor 打开一个编辑器
--get-color #find the color configured: slot [default] 找到配置的颜色:插槽[默认]
--get-colorbool #find the color setting: slot [stdout-is-tty] 发现颜色设置:槽[ stdout是TTY ]
类型
--bool #value is "true" or "false" 值是“真”或“假”。
--int #value is decimal number 值是十进制数。
--bool-or-int #value is --bool or --int 值--布尔或int
--path #value is a path (file or directory name) 值是路径(文件或目录名)
其它
-z, --null #terminate values with NUL byte 终止值与null字节
--name-only #show variable names only 只显示变量名
--includes #respect include directives on lookup 尊重包括查找指令
--show-origin #show origin of config (file, standard input, blob, command line) 显示配置(文件、标准输入、数据块、命令行)的来源




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号