第四次作业
| 这个作业属于哪个课程 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE |
|---|---|
| 这个作业要求在哪里 | https://edu.cnblogs.com/campus/zswxy/2018SE/homework/11406 |
| 这个作业的目标 | 算法和二叉树的排序和遍历> |
| 其他参考文献 | CSDN |
| 1.寻找数组中第K大是数 | |
| 思路:定义一个数组中的个数,再输入数组,用一个while循环,再定义一个数组,用这个数组来输出,这个数组中的第一个数是第一次数组中的第l个数。 |
`public class four {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] a = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 1 ; i <= n ; i++ ){
a[i] = sc.nextInt();
} int m = sc.nextInt();
while(m-->0){
int l = sc.nextInt();
int r = sc.nextInt();
int k = sc.nextInt();
int[] b = new int[r-l+2];
int len = r - l + 1 ;
for(int i = 1 ; i <=len;i++){
b[i] = a[l];
l++;
}
Arrays.sort(b);
System.out.println(b[b.length-k]);
}
}`
运行结果
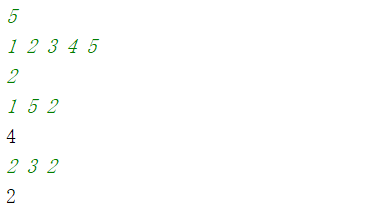
-
二叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历
从csdn博客中学习
https://blog.csdn.net/hongxue8888/article/details/102935259 学习理解递归方法
https://www.cnblogs.com/hezhiyao/p/7550602.html 借助队列来实现层次遍历
先序遍历:⑴访问根结点;⑵遍历左子树;⑶遍历右子树。
中恤遍历:⑴遍历左子树;⑵访问根结点;⑶遍历右子树。
后续遍历:⑴遍历左子树;⑵遍历右子树;⑶访问根结点。
层序遍历:层序遍历就是从所在二叉树的根节点出发,首先访问第一层的树根节点,然后从左到右访问第2层上的节点,接着是第三层的节点。`public class five { public static void main(String[] args) { /* 作业要求:叉树的先、中、后 序遍历与层级遍历 自己实现四个方法,main方法中调用,将结果打印到控制台 */ /* 二叉树的结构 A / \ T 6 / D / \ N 5 / \ / B 4 1 \ 9 */ Node root = into(); // 先序遍历 a(root);System.out.println("先序遍历" ); b(root);System.out.println("中序遍历" ); c(root);System.out.println("后序遍历" ); d(root); System.out.println("层级遍历" ); } private static void a(Node node) { System.out.print(node.data); if (node == null) return; if(node.l != null) a(node.l); if(node.r != null) a(node.r); } private static void b(Node node) { if (node == null) return; if(node.l != null) b(node.l); System.out.print(node.data); if(node.r != null) b(node.r); } private static void c(Node node) { if (node == null) return; if(node.l != null) c(node.l); if(node.r != null) c(node.r); System.out.print(node.data); } private static void d(Node node) { if (node == null) return; LinkedList<Node> queue = new LinkedList<Node>(); Node current; queue.offer(node); while (!queue.isEmpty()) { current = queue.poll(); //取出队列的头节点 System.out.print(current.data );//输出队列的头节点的值 if (current.l != null) { queue.offer(current.l); //如果当前节点的左节点不为空,则左节点入队列 } if (current.r != null) { queue.offer(current.r); //如果当前节点的右节点不为空,则右节点入队列 } } } private static Node into(){ Node root = new Node("A"); Node node1 = new Node("T"); Node node2 = new Node("D"); Node node3 = new Node("N"); Node node4 = new Node("B"); Node node5 = new Node("6"); Node node6 = new Node("5"); Node node7 = new Node("4"); Node node8 = new Node("9"); Node node9 = new Node("1"); root.l = node1; node1.l = node2; node2.l = node3; node2.r = node6; node3.r = node7; node7.r = node8; node6.l = node9; node3.l = node4; root.r = node5; return root; } static class Node{ // 数据 Object data; // 左孩子 Node l; // 右孩子 Node r; public Node(){} public Node(Object data) { this.data = data; this.l = null; this.r = null; } public Node(Object data, Node l, Node r) { this.data = data; this.l = l; this.r = r; } } } `运行结果图
![]()





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号