import cv2
import numpy as np
import math
def fourier_demo():
#1、灰度化读取文件,
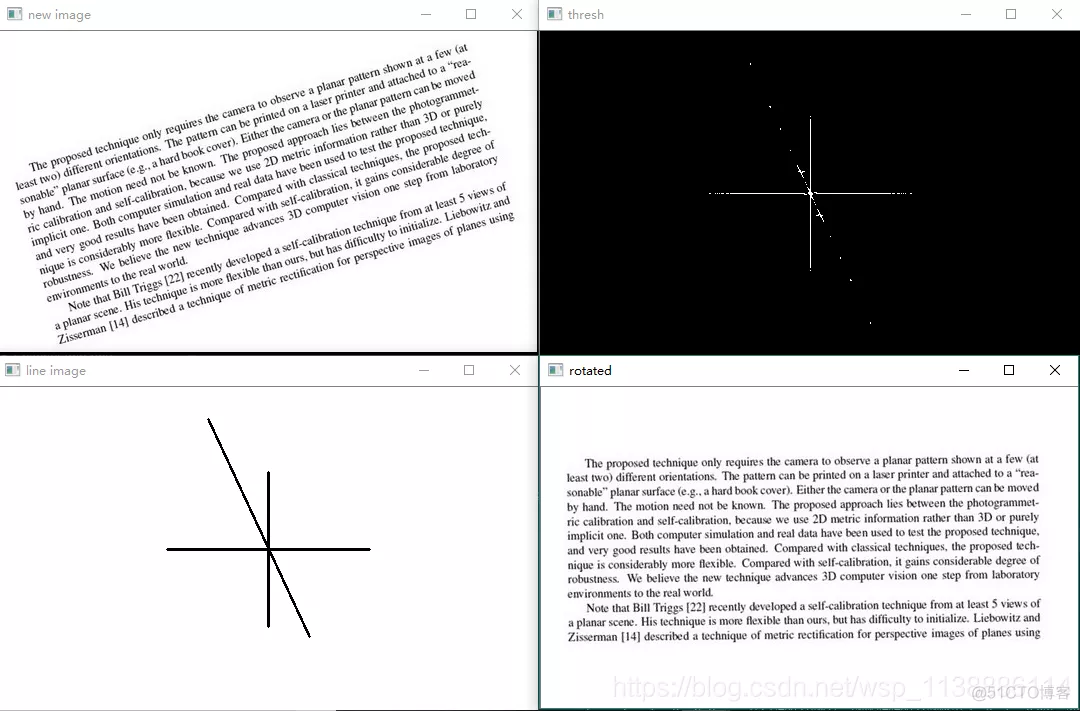
img = cv2.imread('english_rotation.jpg',0)
#2、图像延扩
h, w = img.shape[:2]
new_h = cv2.getOptimalDFTSize(h)
new_w = cv2.getOptimalDFTSize(w)
right = new_w - w
bottom = new_h - h
nimg = cv2.copyMakeBorder(img, 0, bottom, 0, right, borderType=cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=0)
cv2.imshow('new image', nimg)
#3、执行傅里叶变换,并过得频域图像
f = np.fft.fft2(nimg)
fshift = np.fft.fftshift(f)
magnitude = np.log(np.abs(fshift))
#二值化
magnitude_uint = magnitude.astype(np.uint8)
ret, thresh = cv2.threshold(magnitude_uint, 11, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
print(ret)
cv2.imshow('thresh', thresh)
print(thresh.dtype)
#霍夫直线变换
lines = cv2.HoughLinesP(thresh, 2, np.pi/180, 30, minLineLength=40, maxLineGap=100)
print(len(lines))
#创建一个新图像,标注直线
lineimg = np.ones(nimg.shape,dtype=np.uint8)
lineimg = lineimg * 255
piThresh = np.pi/180
pi2 = np.pi/2
print(piThresh)
for line in lines:
x1, y1, x2, y2 = line[0]
cv2.line(lineimg, (x1, y1), (x2, y2), (0, 255, 0), 2)
if x2 - x1 == 0:
continue
else:
theta = (y2 - y1) / (x2 - x1)
if abs(theta) < piThresh or abs(theta - pi2) < piThresh:
continue
else:
print(theta)
angle = math.atan(theta)
print(angle)
angle = angle * (180 / np.pi)
print(angle)
angle = (angle - 90)/(w/h)
print(angle)
center = (w//2, h//2)
M = cv2.getRotationMatrix2D(center, angle, 1.0)
rotated = cv2.warpAffine(img, M, (w, h), flags=cv2.INTER_CUBIC, borderMode=cv2.BORDER_REPLICATE)
cv2.imshow('line image', lineimg)
cv2.imshow('rotated', rotated)
fourier_demo()
cv2.waitKey(0)
cv2.destroyAllWindows()


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号