前端可视化echarts和three
canvas画一条直线
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas')
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d')
ctx.beginPath()//绘制都用beginPath和closePath包裹
ctx.lineWidth = 4
ctx.strokeStyle = 'orange'
// 起点 终点 中间点
ctx.moveTo(100, 100)
ctx.lineTo(300, 300)
ctx.lineTo(500, 200)
ctx.stroke()//添上才能显示出来
ctx.closePath()
canvas绘制实心空心文字
// 实心文字 描边文字
ctx.fillStyle = 'orange'
ctx.strokeStyle = "hotpink"
ctx.font = 'bold 60px 微软雅黑'
ctx.fillText('拉勾教育', 100, 100, 100)
ctx.strokeText('前端', 100, 240)
// 对齐属性设置
ctx.textAlign = 'center' // left right start end center
ctx.textBaseline = "middle" // top bottom middle
ctx.fillText('拉勾教育', 450, 300)
canvas实现动画及碰撞检测
实现动画的原理时不停地改变物体的x,y值,记得每次都要有清空画布的操作,碰撞检测原理就是物体的坐标减去物体一半的宽度小于等于0或者物体的坐标加上物体一半的宽度大于等于画布的宽度时,让坐标的变化速度值取反
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas')
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d')
canvas.style.width = canvas.width + 'px'
canvas.style.height = canvas.height + 'px'
canvas.width = canvas.width * 1.5
canvas.height = canvas.height * 1.5
const drawCircle = (x, y, r) => {
ctx.beginPath()
ctx.fillStyle = 'orange'
ctx.arc(x, y, r, 0, Math.PI * 2)
ctx.fill()
ctx.closePath()
}
// 配置属性
const wd = canvas.clientWidth * 1.5
const ht = canvas.clientHeight * 1.5
let x = y = 100
const r = 20
let xSpeed = 6
let ySpeed = 4
drawCircle(x, y, r)
setInterval(() => {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, wd, ht) // 清空画布
if (x - r <= 0 || x + r >= wd) {
xSpeed = -xSpeed
}
if (y - r <= 0 || y + r >= ht) {
ySpeed = -ySpeed
}
x += xSpeedjiang
y += ySpeed
drawCircle(x, y, r)
}, 20)
将一个会变颜色,不同大小,不同速率走的球写成一个类,然后遍历添加
const canvas = document.getElementById('canvas')
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d')
canvas.style.width = canvas.width + 'px'
canvas.style.height = canvas.height + 'px'
canvas.width = canvas.width * 1.5
canvas.height = canvas.height * 1.5
class Ball {
constructor(canvas) {
this.canvas = canvas
this.ctx = this.canvas.getContext('2d')
this.wd = this.canvas.clientWidth * 1.5
this.ht = this.canvas.clientHeight * 1.5
this.r = Math.random() * 40 + 10
this.x = Math.random() * (this.wd - (this.r * 2)) + this.r
this.y = Math.random() * (this.ht - (this.r * 2)) + this.r
this.color = '#' + parseInt(Math.random() * 0xFFFFFF).toString(16)
this.xSpeed = Math.random() * 4 + 6
this.ySpeed = Math.random() * 6 + 4
this.init()
}
init() {
this.run()
this.draw()
}
draw() {
this.ctx.beginPath()
this.ctx.fillStyle = this.color
this.ctx.arc(this.x, this.y, this.r, 0, 2 * Math.PI)
this.ctx.fill()
this.ctx.closePath()
}
run() {
if (this.x - this.r <= 0 || this.x + this.r >= this.wd) {
this.xSpeed = -this.xSpeed
}
if (this.y - this.r <= 0 || this.y + this.r >= this.ht) {
this.ySpeed = -this.ySpeed
}
this.x += this.xSpeed
this.y += this.ySpeed
}
}
let ballArr = []
for (let i = 0; i < 100; i++) {
let ball = new Ball(canvas)
ballArr.push(ball)
}
// 动画
setInterval(() => {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, canvas.clientWidth * 1.5, canvas.clientHeight * 1.5)
for (let i = 0; i < ballArr.length; i++) {
let ball = ballArr[i]
ball.init()
}
}, 15)
canva实现每个圆连线并且能够添加文字的思路
将绘制文字和绘制线的方法添加到球的类中,
然后在定时器中循环遍历ball数组,先画线,然后再画球
动态设置rem全局实现
在public中的index下添加
<title>可视化插件封装</title>
<script>
document.documentElement.style.fontSize = document.documentElement.clientWidth / 10 + 'px'
window.addEventListener('resize', () => {
document.documentElement.style.fontSize = document.documentElement.clientWidth / 10 + 'px'
})
</script>
动画函数从0到指定值方法的实现
export default function myAnimation(param) {
let current = 0
let looped
const ctx = this.ctx
const _canvas = this._canvas
const callback = param.render
const successCb = param.success;
(function looping() {
looped = requestAnimationFrame(looping)
if (current < param.percent) {
ctx.clearRect(0, 0, _canvas.width, _canvas.height)
current = current + 4 > param.percent ? param.percent : current + 4
callback(current)
} else {
window.cancelAnimationFrame(looping)
looped = null
successCb && successCb()
}
})()
}
函数调用
myAnimation.call(this, {
percent: 100,
render: (current) => {
console.log(current)
}
})
svg绘制图形
1.D3.js底层采用svg来完成图像的绘制
<script src="./d3.min.js"></script>
// 01 d3 获取元素
console.log(d3.select('#box p'))
console.log(d3.selectAll('#box p'))
// 02 获取元素属性
console.log(+d3.select('rect').attr('width') === 300)
// 03 设置属性
// d3.select('rect')
// .attr('transform', 'translate(100, 100)')
// 04 添加删除元素
d3.select('svg').append('rect')
.attr('x', 100)
.attr('y', '200')
.attr('width', '200')
.attr('height', '100')
.attr('fill', 'lightblue')
.text('拉勾教育')
// 05 删除元素
d3.selectAll('rect').remove()
D3数据绑定
const data = [
{ cx: 100, cy: 100, r: 10, fill: 'orange' },
{ cx: 130, cy: 140, r: 20, fill: 'seagreen' },
{ cx: 230, cy: 240, r: 19, fill: 'lightblue' },
]
d3.select('svg').selectAll('circle')
.data(data)
.enter()//没有circle,添加circle
.append('circle')//必加
.attr('cx', d => d.cx)
.attr('cy', d => d.cy)
.attr('r', d => d.r)
.attr('fill', d => d.fill)
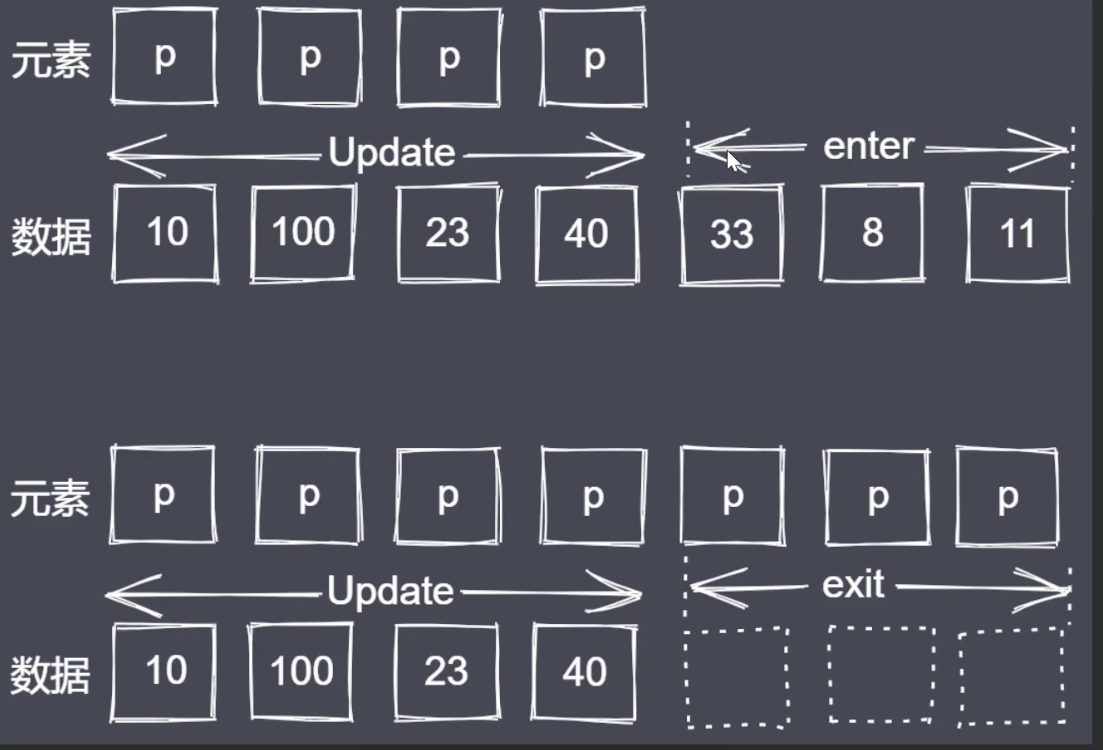
// update(数据和元素<svg,circle>一一对应) enter (有数据但是没有元素) exit (有元素没有数据)
线性比例尺映射关系
输入输出连续
若数据中有一个特别大,有一个过于小就会导致小的看不见,大的看不完,所有需要把数据映射在一个范围,就是比例尺
// 定义线性比例尺
const linear = d3.scaleLinear()
.domain([0, d3.max(data)])
.range([0, 300])
//线性比例尺的使用是在数据data表示高度或者坐标的时候将将data作为linear的参数即linear(data)
序列比例尺
输入输出离散,相等间隔
.domain([1, 2, 3, 4])//输入
.range([0, 100])//输出
D3绘制坐标轴
// 定义坐标刻度生成器
const xAxis = d3.axisBottom(xScale)
// 绘制X轴具体的刻度内容
d3.select('svg').append('g')
.call(xAxis)
.attr('transform', `translate(0, ${height - margin.bottom})`)
.attr('font-size', 14)
D3过渡
// transition duration delay ease
// 初始状态 结束状态
circle.attr('cx', 100).attr('cy', 100)
// 结束状态
circle.transition()
.duration(3000)
.delay(1000)
.ease(d3.easeBounce)
.attr('cx', 500)
.attr('cy', 300)
D3交互
svg可以直接添加事件监听,对其进行类操作样式
添加提示框,显示柱状图数据,有过渡效果
//这是一个让元素缓慢平滑动画的类
class EaseObj {
constructor(target) {
this.target = target
this.pos = { x: width / 2, y: height / 2 }
this.endPos = { x: 0, y: 0 }
this._play = false
this.fm = 0
this.speed = 0.1
}
set animate(value) {
if (value !== this._play) {
if (value) {
this.render()
} else {
this.cancel()
}
this._play = value
}
}
render() {
const { pos, endPos, speed, target } = this
pos.x += (endPos.x - pos.x) * speed
pos.y += (endPos.y - pos.y) * speed
target.style('left', `${pos.x}px`)
.style('top', `${pos.y}px`)
this.fm = requestAnimationFrame(() => {
this.render()
})
}
cancel() {
cancelAnimationFrame(this.fm)
}
}
// 10 定义提示框元素
const tip = d3.select('body').append('div').attr('id', 'tip')
// 11 鼠标移上
rects.on('mouseover', ({ clientX, clientY }, data) => {
tip.style('left', `${clientX}px`)
.style('top', `${clientY}px`)
.style('display', 'block')
.html(`
<p>此项平均值:${data}</p>
`)
})
const tipObj = new EaseObj(tip)
rects.on('mousemove', ({ clientX, clientY }, data) => {
tipObj.endPos = { x: clientX, y: clientY }
tipObj.animate = true
})
rects.on('mouseout', () => {
tipObj.animate = false
tip.style('display', 'none')
})
webGL和Three.js
场景显示呈现舞台,相机眼睛,透视相机似人的眼睛,渲染器决定内容如何呈现至屏幕,材质,threejs中面是由三个点构造而成
光源操作初始在场景中
const scene = new THREE.Scene();
const camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera( 75, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 0.1, 1000 );//视角,所在元素的纵横比,相机距近截面(屏幕)的距离,相机距远截面距离
const renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({
antialias: true//让物体更平滑
})
renderer.setClearColor(0xffffff)
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
const geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(1, 1, 1)
const material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
color: 0x285b41,
wireframe: true//线条渲染
})
const cube = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material)
scene.add(cube)//将几何体添加到场景中
camera.position.z = 4//默认相机和物体都会渲染到中心点(0,0,0)位置,屏幕上看不到物体,移动相机位置可看到物体
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
cube.rotation.y += 0.01
cube.rotation.x += 0.01//做动画
renderer.render(scene, camera)//渲染到屏幕上
}
animate()
相机控制来看为物体四周
材质外部内部贴图来看物体内外部
// 定义全局变量
let scene, camera, geometry, mesh, renderer, controls
// 初始化渲染器
function initRenderer() {
renderer = new THREE.WebGLRenderer({ antialias: true })
renderer.setSize(window.innerWidth, window.innerHeight)
renderer.setPixelRatio(window.devicePixelRatio)
document.body.appendChild(renderer.domElement)
}
// 初始化场景
function initScene() {
scene = new THREE.Scene()
const axesHelper = new THREE.AxesHelper(100)//用于简单模拟3个坐标轴的对象.
scene.add(axesHelper)
// const directionalLight = new THREE.DirectionalLight('red')
// const ambientLight = new THREE.AmbientLight('orange')
// const pointLight = new THREE.PointLight('green')
// const spotLight = new THREE.SpotLight('lightblue')
const hemisphereLight = new THREE.HemisphereLight('red')
hemisphereLight.position.set(0, 30, 0)
scene.add(hemisphereLight)
}
// 初始化相机
function initCamera() {
camera = new THREE.PerspectiveCamera(45, window.innerWidth / window.innerHeight, 1, 1000)
camera.position.set(0, 0, 15)
controls = new THREE.TrackballControls(camera, renderer.domElement)//控制器,控制物体旋转
}
// 初始化模型
function initMesh() {
geometry = new THREE.BoxGeometry(2, 2, 2)
// material = new THREE.MeshNormalMaterial()//把法向量映射到RGB颜色的材质
const texture = new THREE.TextureLoader().load('img/crate.gif')//加载器,加载文件
material = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: texture,
side: THREE.DoubleSide//控制贴图里外都加上
})//立即使用加载器制造纹理进行材质创建
mesh = new THREE.Mesh(geometry, material)
scene.add(mesh)
}
// 初始化动画
function animate() {
requestAnimationFrame(animate)
controls.update()//必有,让物体能够从多角度观察
renderer.render(scene, camera)
}
// 定义初始化方法
function init() {
initRenderer()
initScene()
initCamera()
initMesh()
animate()
}
init()
精灵材质及交互
应用全景看房点击精灵图(箭头)时场景切换到指定位置
光线投射Raycaster
光线投射用于进行鼠标拾取(在三维空间中计算鼠标移动过什么物体)
const raycaster = new THREE.Raycaster()
const mouse = new THREE.Vector2()
function onMouseMove(event) {
// 将鼠标位置归一化为设备坐标。x 和 y 方向的取值范围是 (-1 to +1)
mouse.x = (event.clientX / window.innerWidth) * 2 - 1;
mouse.y = - (event.clientY / window.innerHeight) * 2 + 1;
}
window.addEventListener('mousemove', onMouseMove, false)
window.addEventListener('click', function () {
// 计算物体和射线的焦点
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects([mesh])//mesh是想要点击有操作的物体
if (intersects.length > 0) {
mesh.rotation.x += 0.1
}
}, false)
全景看房的实现
- 全景图片进行拼凑
function initMesh() {
// 前面
const geometryF = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(4, 4)
const materialF = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: new THREE.TextureLoader().load('img/0_f.jpg'),
side: THREE.DoubleSide
})
const meshF = new THREE.Mesh(geometryF, materialF)
meshF.rotation.y = 180 * Math.PI / 180
meshF.position.z = 2
scene.add(meshF)
// 后面
const geometryB = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(4, 4)
const materialB = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: new THREE.TextureLoader().load('img/0_b.jpg'),
side: THREE.DoubleSide
})
const meshB = new THREE.Mesh(geometryB, materialB)
// meshB.rotation.y = 180 * Math.PI / 180
meshB.position.z = -2
scene.add(meshB)
// 左侧
const geometryL = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(4, 4)
const materialL = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: new THREE.TextureLoader().load('img/0_l.jpg'),
side: THREE.DoubleSide
})
const meshL = new THREE.Mesh(geometryL, materialL)
meshL.rotation.y = (-90) * Math.PI / 180
meshL.position.x = 2
scene.add(meshL)
// 右侧
const geometryR = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(4, 4)
const materialR = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: new THREE.TextureLoader().load('img/0_r.jpg'),
side: THREE.DoubleSide
})
const meshR = new THREE.Mesh(geometryR, materialR)
meshR.rotation.y = (90) * Math.PI / 180
meshR.position.x = -2
scene.add(meshR)
// 上面
const geometryU = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(4, 4)
const materialU = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: new THREE.TextureLoader().load('img/0_u.jpg'),
side: THREE.DoubleSide
})
const meshU = new THREE.Mesh(geometryU, materialU)
meshU.rotation.x = (90) * Math.PI / 180
meshU.rotation.z = (180) * Math.PI / 180
meshU.position.y = 2
scene.add(meshU)
// 下面
const geometryD = new THREE.PlaneGeometry(4, 4)
const materialD = new THREE.MeshBasicMaterial({
map: new THREE.TextureLoader().load('img/0_d.jpg'),
side: THREE.DoubleSide
})
const meshD = new THREE.Mesh(geometryD, materialD)
meshD.rotation.x = (-90) * Math.PI / 180
meshD.rotation.z = (180) * Math.PI / 180
meshD.position.y = -2
scene.add(meshD)
}
- 相机视角直接进入到内部
controls = new THREE.TrackballControls(camera, renderer.domElement)
controls.maxDistance = 2//六面体宽度为4,所以最大选择2
controls.minDistance = 0
3.利用精灵材质引入地面标记,固定在地面
new THREE.TextureLoader().load('img/icon.png', (texture) => {
const spriteMaterial = new THREE.SpriteMaterial({
map: texture
})
spriteArrow = new THREE.Sprite(spriteMaterial)
spriteArrow.scale.set(0.1, 0.1, 0.1)
spriteArrow.position.set(0.5, -1, -1.5)
scene.add(spriteArrow)
})
4.点击精灵图时视角往前拉,进入另一个立方体看里面内容
使用Raycaster类,让mouse获取到当前位置信息
// 鼠标点击
function mouseClickEvent(ev) {
ev.preventDefault();
// 射线捕获
raycaster.setFromCamera(mouse, camera)
const intersects = raycaster.intersectObjects([spriteArrow])
if (intersects.length > 0) {
changeScene()
}
}
window.addEventListener('click', mouseClickEvent, false)
function changeScene() {
// 创建六个面
const sixBox = createPlane(2)
const timer = setInterval(() => {
camera.fov -= 1//视角变小
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()//让相机能不
if (camera.fov == 20) {
clearInterval(timer)
camera.fov = 45
camera.updateProjectionMatrix()
for (let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
scene.remove(sixPlane[i])
}//将之前绘制的6个面清除
sixPlane = sixBox
for (let i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
scene.add(sixPlane[i])//添加新绘制的6个面
}
spriteArrow.visible = false
}
}, 50)
}




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号