设计模式(23) 访问者模式
由于应用开发过程中先前完成的类型会因为需求变化(无论是业务功能,还是技术实现或是出于集成的需要)增加新的方法,如果直接在基类中增加新的方法,其派生类型可能需要相应进行比较繁琐的处理。而使用访问者模式可以做到在不改变既有类型层次的前提下,运行时动态为类型层次的每个类增加新的操作。
访问者模式
GOF对策略模式的描述为:
Represent an operation to be performed on the elements of an object structure. Visitor lets you define a new operation without changing the classes of the elements on which it operates...
— Design Patterns : Elements of Reusable Object-Oriented Software
UML类图
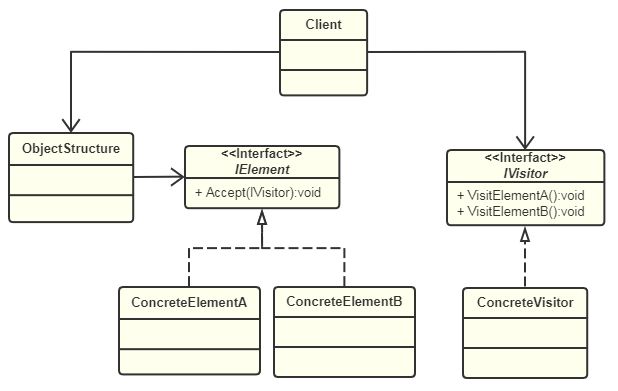
访问者模式包含五种角色:
- IVistor(抽象访问者):为该对象结构中具体元素角色声明一个访问操作接口。
- ConcreteVisitor(具体访问者):每个具体访问者都实现了IVistor中定义的操作。
- IElement(抽象元素):定义了一个accept操作,以IVisitor作为参数。
- ConcreteElement(具体元素):实现了IElement中的accept()方法,调用IVistor的访问方法以便完成对一个元素的操作。
- ObjectStructure(对象结构):可以是组合模式,也可以是集合,能够枚举它包含的元素,并提供一个接口,允许IVistor访问它的元素。
代码示例
设想有这样一个HR系统,系统只能按照标准的工作时间、时薪计算薪金,在系统交付后发现需要提供加班计算功能,而且还需要安排休假、晋升等功能,考虑到类似的需求在将来还会出现,所以改造的时候考虑采用访问者模式。在HR系统的对象上增加了Accept某个IVisistor接口的能力,在添加新功能的时候可以实现IVisitor接口。
public interface IEmployee
{
string Name { get; set; }
double Income { get; set; }
int VacationDays { get; set; }
void Accept(IVisitor visitor);
}
public interface IVisitor
{
void VisitiEmployee(IEmployee employee);
void VisitManager(Manager manager);
}
public class Employee : IEmployee
{
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Income { get; set; }
public int VacationDays { get; set; }
public Employee(string name, double income, int vacationDays)
{
this.Name = name;
this.Income = income;
this.VacationDays = vacationDays;
}
public void Accept(IVisitor visitor)
{
visitor.VisitiEmployee(this);
}
}
public class Manager : IEmployee
{
public string Department { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public double Income { get; set; }
public int VacationDays { get; set; }
public Manager(string name, double income, int vacationDays, string department)
{
this.Name = name;
this.Income = income;
this.VacationDays = vacationDays;
this.Department = department;
}
public void Accept(IVisitor visitor)
{
visitor.VisitManager(this);
}
}
public class EmployeeCollection : List<IEmployee>
{
public void Accept(IVisitor visitor)
{
foreach (IEmployee employee in this)
{
employee.Accept(visitor);
}
}
}
public class ExtraVacationVisitor : IVisitor
{
public void VisitiEmployee(IEmployee employee)
{
employee.VacationDays += 1;
}
public void VisitManager(Manager manager)
{
manager.VacationDays += 2;
}
}
public class RaiseSalaryVisitor : IVisitor
{
public void VisitiEmployee(IEmployee employee)
{
employee.Income *= 1.1;
}
public void VisitManager(Manager manager)
{
manager.Income *= 1.2;
}
}
调用端代码
public class Test
{
public static void Entry()
{
EmployeeCollection employees = new EmployeeCollection();
employees.Add(new Employee("joe", 25000, 14));
employees.Add(new Manager("alice", 22000, 14, "sales"));
employees.Add(new Employee("peter", 15000, 7));
employees.Accept(new ExtraVacationVisitor());
employees.Accept(new RaiseSalaryVisitor());
}
}
Employee类型并没有加薪和修改休假天数的方法,但借助访问者模式,时期具有了对应的功能。访问者模式的关键代码是在数据基础类里面有一个方法接受访问者,将自身引用传入访问者,这样访问者就可以操作数据类了。
访问者模式的适用场景
- 一个类型需要依赖于很多不同接口的类型,在结构尽量松散的前提下,希望可以用到这些类型不同接口方法。
- 经常需要为一个结构相对固定的对象结构添加一些新的操作。
- 需要用一个独立的类型来组织一批不相干的操作,使用它的类型可以根据应用需要进行定制。
访问者模式的特点
优点
- 符合单一职责原则。
- 优秀的扩展性。
- 灵活性。
缺点 - 具体元素对访问者公布细节,违反了迪米特原则。
- 具体元素变更比较困难。
- 违反了依赖倒置原则,依赖了具体类,而不是依赖抽象。
参考书籍:
王翔著 《设计模式——基于C#的工程化实现及扩展》




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号