SpringBoot——入门及原理
SpringBoot 用来简化 Spring应用开发,约定大于配置,去繁从简,是由 Pivotal团队提供的全新框架。其设计目的是用来简化新 Spring应用的初始搭建以及开发过程。该框架使用了特定的方式来进行配置(有特殊需求可以添加自己的配置覆盖默认配置),从而使开发人员不再需要定义样板化的配置。SpringBoot 可以看成是 J2EE的一站式解决方案。
一、SpringBoot 的优点
【1】快速创建独立运行的 Spring项目以及与主流框架集成。
【2】使用嵌入式的 Servlet容器,应用无需打成 war包,可以打成 jar包,通过 java -jar的方式直接运行。
【3】starters(启动器)自动依赖与版本控制。
【4】大量的自动配置,简化开发,也可以修改默认值。
【5】无需配置XML,无代码生成,开箱即用。
【6】准生产环境的运行时应用监控。
【7】与云计算的天然集成。
二、解决微服务部署和运维难的问题:Spring Boot
搭建项目 构建连接 批处理
三、Spring Boot 入门项目
HelloWorld(也可以参考五,快速创建一个 SpringBoot项目)
【1】准备环境:为 Maven 的 settings.xml 配置文件的 profiles 标签添加如下信息:
1 <profile> 2 <id>jdk-1.8</id> 3 <activation> 4 <activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault> 5 <jdk>1.8</jdk> 6 </activation> 7 <properties> 8 <maven.compiler.source>1.8</maven.compiler.source> 9 <maven.compiler.target>1.8</maven.compiler.target> 10 <maven.compiler.compilerVersion>1.8</maven.compiler.compilerVersion> 11 </properties> 12 </profile>
【2】将 IDEA 的 Maven更换为我们自己本地安装的 Maven。(自行百度更换)创建一个 maven工程(jar),在 pom.xml中导入如下依赖:
1 <parent> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 4 <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> 5 </parent> 6 <dependencies> 7 <dependency> 8 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 9 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 10 </dependency> 11 </dependencies>
【3】编写一个主程序,启动 SpringBoot应用
1 @SpringBootApplication 2 public class Hello { 3 public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception { 4 //启动spring应用 5 SpringApplication.run(Hello.class, args); 6 } 7 }
【4】编写相关的 Controller、Service类
1 @Controller 2 public class HelloController { 3 @ResponseBody 4 @RequestMapping("/hello") 5 public String hello(){ 6 return "hello world!"; 7 } 8 }
【5】运行主测试程序。简化部署应用<可以将应用打包成一个可执行的 jar包>:通过 Maven Projects中 的 package(双击)即可。生成 jar的位置:默认在项目的 target目录下的“项目名称.jar”文件。运行jar:在命令行可以通过 “java -jar jar文件名.jar” 命令运行项目。
1 <build> 2 <plugins> 3 <plugin> 4 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 5 <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> 6 </plugin> 7 </plugins> 8 </build>
四、Hello World 探究(POM文件)
【1】父项目(spring-boot-starter-parent):
1 <parent> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 4 <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> 5 </parent>
【2】进入 spring-boot-starter-parent发现它还有一个父项目 :
1 <parent> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId> 4 <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> 5 <relativePath>../../spring-boot-dependencies</relativePath> 6 </parent>
【3】进入 spring-boot-dependencies后,发现如下信息,与之前我们创建的分布式项目继承的 Maven父项目功能是一样的,用来管理所有 jar包依赖的版本。称为 SpringBoot的版本仲裁中心,以后我们导入依赖默认是不需要写版本;(没有在dependencies 里面管理的依赖,需要声明版本号)
1 <properties> 2 <activemq.version>5.15.3</activemq.version> 3 <antlr2.version>2.7.7</antlr2.version> 4 <appengine-sdk.version>1.9.62</appengine-sdk.version> 5 <artemis.version>2.4.0</artemis.version> 6 <aspectj.version>1.8.13</aspectj.version> 7 <assertj.version>3.9.1</assertj.version> 8 <... 此处省略 .../> 9 </properties>
【4】启动器(spring-boot-starter-web)
1 <dependency> 2 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 3 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 4 </dependency>
spring-boot-starter-web:spring-boot-starter 指 spring-boot 场景启动器;进入官网可以到有许多场景启动器,简单点说就是通过此功能将相关 jar包给组合在起来,我们使用时只需要引入一个 Web Starter就可以轻松搞定。Spring Boot 将所有的功能场景都抽取出来,做成一个个的 starters(启动器),只需要在项目里面引入这些 starter相关场景,所有依赖都会导入进来。要用什么功能就导入什么场景启动器。
1 <dependencies> 2 <dependency> 3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId> 5 </dependency> 6 <dependency> 7 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 8 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-tomcat</artifactId> 9 </dependency> 10 <dependency> 11 <groupId>org.hibernate</groupId> 12 <artifactId>hibernate-validator</artifactId> 13 </dependency> 14 <dependency> 15 <groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId> 16 <artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId> 17 </dependency> 18 <dependency> 19 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 20 <artifactId>spring-web</artifactId> 21 </dependency> 22 <dependency> 23 <groupId>org.springframework</groupId> 24 <artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId> 25 </dependency> 26 </dependencies>
【5】主程序类(Java类):@SpringBootApplication:此注解声明的类,是 SpringBoot的主配置类,SpringBoot就应该运行这个类的 main方法来启动 SpringBoot。
1 //@ImportResource(locations={"classpath:bean.xml"}) 2 //@SpringBootApplication 来标注一个主程序类,说明这是一个SpringBoot应用 3 @SpringBootApplication 4 public class HellowordQuickStartApplication { 5 6 public static void main(String[] args) { 7 /*SpringBoot应用启动项 8 HellowordQuickStartApplication.class 参数必须是用@SpringBootApplication注解修饰的类 9 */ 10 SpringApplication.run(HellowordQuickStartApplication.class, args); 11 } 12 }
@SpringBootApplication(主要由:@SpringBootConfiguration/@EnableAutoConfiguration/@ComponentScan 组成)
1 @Target(ElementType.TYPE) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Inherited 5 @SpringBootConfiguration 6 @EnableAutoConfiguration 7 @ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { 8 @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class), 9 @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) }) 10 public @interface SpringBootApplication {
@SpringBootConfiguration:标注在某个类上,表示此类是一个SpringBoot的配置类。由以下注解组合形成:配置类 == 配置文件,配置类也是容器的一个组件,底层由 @Component等等组成。
1 @Target({ElementType.TYPE}) 2 @Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME) 3 @Documented 4 @Configuration //表示此类是一个配置类 是spring的一个组件 5 public @interface SpringBootConfiguration {
@EnableAutoConfiguration:开启自动配置功能。也是一个组合注解,由以下注解组成(部分重要注解):
1 @AutoConfigurationPackage 2 @Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class) 3 public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
@AutoConfigurationPackage:自动依赖相关的配置包,也是一个组合注解,主要由 @import 等注解组合
1 @Import({Registrar.class})//给容器中导入一个组件;导入的组件由此组建决定。 2 public @interface AutoConfigurationPackage {
进入 @Import(Registrar.class) 中的 Registrar类中,通过断点,可以查看到我注释的一些信息。
1 static class Registrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar, DeterminableImports { 2 Registrar() { 3 } 4 //registerBeanDefinitions方法中的metadata可以查看到我们启动类使用的注解 @SpringBootApplication 5 public void registerBeanDefinitions(AnnotationMetadata metadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) { 6 AutoConfigurationPackages.register(registry, new String[]{(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImport(metadata)).getPackageName()}); 7 } 8 //new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImport(metadata) 可以解析出我们当前主启动所在的package包 9 public Set<Object> determineImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) { 10 return Collections.singleton(new AutoConfigurationPackages.PackageImport(metadata)); 11 } 12 }
@Import(Registrar.class)作用:将主配置类的所在包以及下边所有子包里面的所有组件扫描到 Spring容器中。这也就能理解为什么会自动扫描我们写的 @Controller类了。
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class):进入 AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class 类中,查看如下方法:
1 public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) { 2 if(!this.isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) { 3 return NO_IMPORTS; 4 } else { 5 try { 6 AutoConfigurationMetadata autoConfigurationMetadata = AutoConfigurationMetadataLoader.loadMetadata(this.beanClassLoader); 7 AnnotationAttributes attributes = this.getAttributes(annotationMetadata); 8 // 主要用到的是 这个 configurations 后面会有重点说明 9 List<String> configurations = this.getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes); 10 configurations = this.removeDuplicates(configurations); 11 configurations = this.sort(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata); 12 Set<String> exclusions = this.getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes); 13 this.checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions); 14 configurations.removeAll(exclusions); 15 configurations = this.filter(configurations, autoConfigurationMetadata); 16 this.fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions); 17 return StringUtils.toStringArray(configurations); 18 } catch (IOException var6) { 19 throw new IllegalStateException(var6); 20 } 21 } 22 }
这是导入组件的选择器方法,将所有需要导入的组件以全类名的方式返回,这些组件最终被添加到容器中。其中List<String> configurations 会给容器中导入非常多的自动配置类(xxxAutoConfiguration),就是给容器中导入这个场景需要的所有组件,并配置好这些组件。有了自动配置类,免去了我们手动编写配置注入功能组件等的工作;自动配置类共109个,如下部分所示:
1 protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) { 2 // *** 后边需要了解的方法 *** 3 //SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(EnableAutoConfiguration.class,classLoader); 4 List<String> configurations = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(this.getSpringFactoriesLoaderFactoryClass(), this.getBeanClassLoader()); 5 Assert.notEmpty(configurations, "No auto configuration classes found in META-INF/spring.factories. If you are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct."); 6 return configurations; 7 }
进入 SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactoryNames(EnableAutoConfiguration.class,classLoader)方法,具体注释说明:
1 public static List<String> loadFactoryNames(Class<?> factoryClass, @Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { 2 //org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer 3 String factoryClassName = factoryClass.getName(); 4 return (List)loadSpringFactories(classLoader).getOrDefault(factoryClassName, Collections.emptyList()); 5 } 6 private static Map<String, List<String>> loadSpringFactories(@Nullable ClassLoader classLoader) { 7 MultiValueMap<String, String> result = (MultiValueMap)cache.get(classLoader); 8 if(result != null) { 9 return result; 10 } else { 11 try { 12 //通过类加载器(classLoader获取)META-INF/spring.factories(也就是配置了109个自动配置类的文件) 资源 13 Enumeration<URL> urls = classLoader != null?classLoader.getResources("META-INF/spring.factories"):ClassLoader.getSystemResources("META-INF/spring.factories"); 14 LinkedMultiValueMap result = new LinkedMultiValueMap(); 15 16 while(urls.hasMoreElements()) { 17 URL url = (URL)urls.nextElement(); 18 UrlResource resource = new UrlResource(url); 19 //将urls 当做一个properties配置文件 20 Properties properties = PropertiesLoaderUtils.loadProperties(resource); 21 Iterator var6 = properties.entrySet().iterator(); 22 23 while(var6.hasNext()) { 24 Entry<?, ?> entry = (Entry)var6.next(); 25 //将META-INF/spring.factories文件中的EnableAutoConfiguration下的配置进行加载 如下图所示 26 List<String> factoryClassNames = Arrays.asList(StringUtils.commaDelimitedListToStringArray((String)entry.getValue())); 27 result.addAll((String)entry.getKey(), factoryClassNames); 28 } 29 } 30 31 cache.put(classLoader, result); 32 return result; 33 } catch (IOException var9) { 34 throw new IllegalArgumentException("Unable to load factories from location [META-INF/spring.factories]", var9); 35 } 36 } 37 }
1 //这里我就摘出一些重要的配置,来帮我我们观察即可。 2 @Configuration 3 public class WebMvcAutoConfiguration { 4 @Bean 5 @ConditionalOnMissingBean 6 /*视图解析器 , SpringBoot中的所有配置文件都是.java形式,方法的名字,就是以前xml中的id。 7 等等都是用注解表示的,这个我们后面会重点说明,这里就先了解一下*/ 8 //我们可以看到SpringBoot已经帮我们配置好了视图解析器 等等一些功能 我们直接使用就好 9 public InternalResourceViewResolver defaultViewResolver() { 10 InternalResourceViewResolver resolver = new InternalResourceViewResolver(); 11 resolver.setPrefix(this.mvcProperties.getView().getPrefix()); 12 resolver.setSuffix(this.mvcProperties.getView().getSuffix()); 13 return resolver; 14 } 15 }
总结:SpringBoot 在启动的时候从类路径下的 META-INF/spring.factories 中获取 EnableAutoConfiguration 指定的值,将这些值作为自动配置类导入到容器中,自动配置类就生效,帮我们进行自动配置工作。如此一来,就具有我们在 SSM等环境下写了一大堆配置文件后才具有的功能。而这些所有配置文件都在 spring-boot-autoconfigure-2.0.0.RELEASE.jar 中。
五、使用 Spring Initializer 快速创建 Spring Boot 项目
注意:Artifact 中不能大小写混合使用。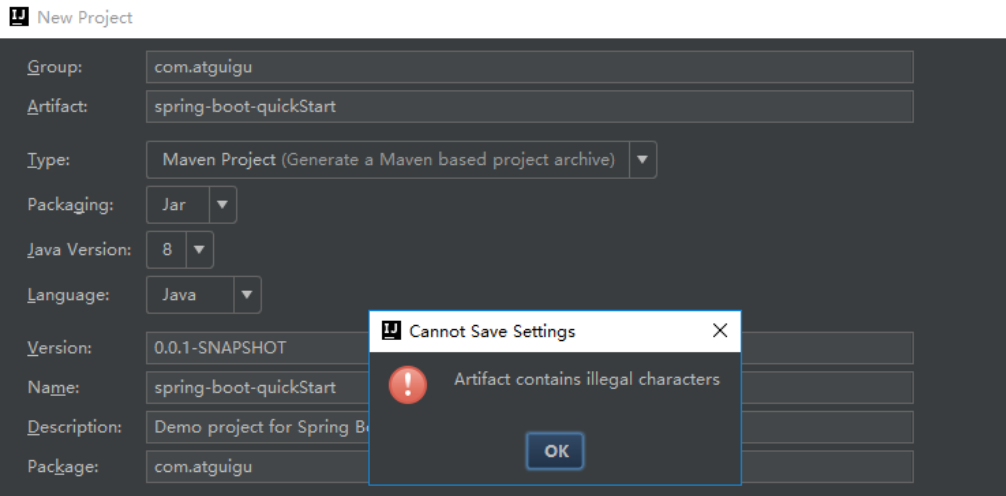
通过需求选择 starts,例如选择 Web。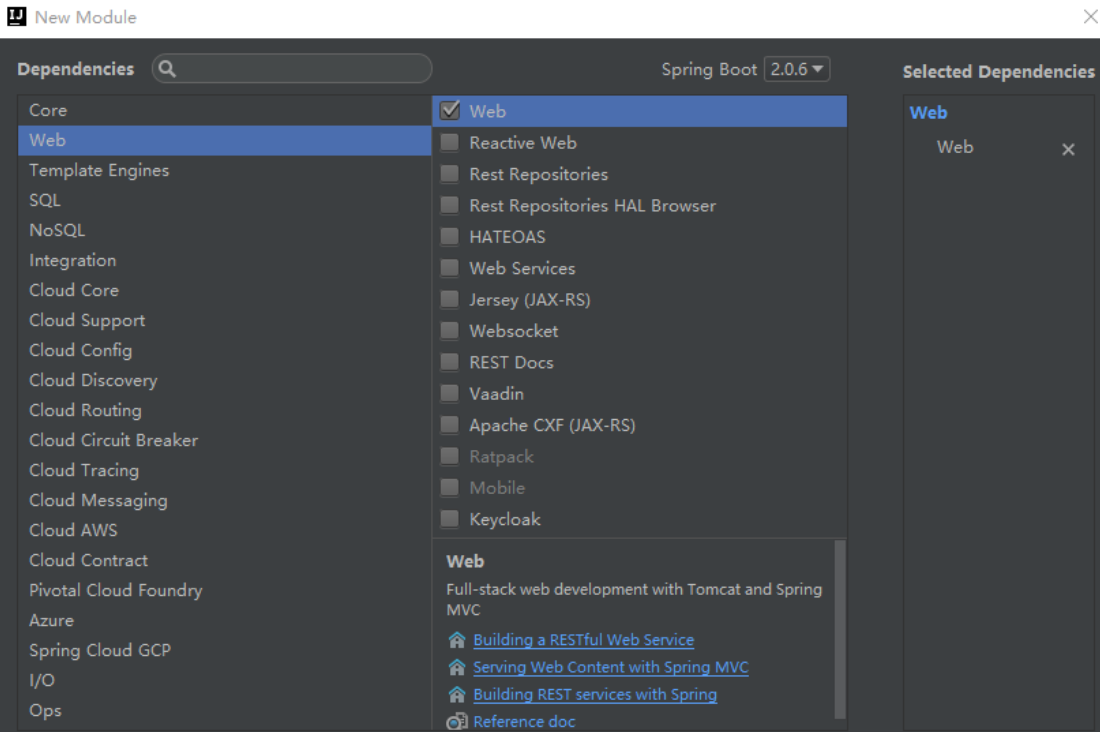
我们就会发现 pom.xml文件中,就会自动配置了我们引入的 starts。
1 <!-- 摘取一部分 --> 2 <parent> 3 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 4 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> 5 <version>2.0.0.RELEASE</version> 6 <relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> 7 </parent> 8 9 <properties> 10 <project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding> 11 <project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding> 12 <java.version>1.8</java.version> 13 </properties> 14 <dependencies> 15 <dependency> 16 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 17 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> 18 </dependency> 19 20 <dependency> 21 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 22 <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> 23 <scope>test</scope> 24 </dependency> 25 26 <dependency> 27 <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> 28 <artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId> 29 <optional>true</optional> 30 </dependency> 31 </dependencies>
添加 controller 层:新注解 @RestController == @ResponseBody 与 @Controller的合体;
1 //这个类的所有方法返回的数据直接写给浏览器(如果是对象转为JSON) 2 //@ResponseBody@Controller 3 @RestController 4 public class HelloWordController { 5 @RequestMapping("/hello") 6 public String hello(){ 7 return "hell"; 8 } 9 }
优点:默认生成的 SpringBoot项目,我们只需要编写自己的逻辑。默认生成的 Resources 配置文件的目录结构:
【1】static:保存所有的静态资源。 (js/css/image)
【2】templates:保存所有的模板页面(SpringBoot默认 jar包使用嵌入式的 Tomcat,默认不支持 JSP页面)但可以使用模板引擎。(freemarker、thymeleaf)
【3】application.properties:SpringBoot 应用的配置文件。默认的配置都在此文件可以修改。








 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号