Soul网关的数据注册和同步数据流探究
Soul网关的Http/SpringMvc 数据注册和同步数据流探究
Soul-Admin端数据的探究
首先启动客户端项目soul-examples-http的过程中看到控制台会输出和

可以很明显的看到这段信息就是我们注解了@SoulSpringMvcClient的接口信息,那么这个操作是在哪里产生的了。
全局搜索了register success 字样。发现在soul-examples-http依赖的子项目soul-client-springmvc中有对应的SpringMvcClientBeanPostProcessor来进行注册的代码,这个SpringMvcClientBeanPostProcessor实现了Spring的BeanPostProcessor接口,如果我们想在Spring容器中完成bean实例化、配置以及其他初始化方法前后要添加一些自己逻辑处理。我们需要定义一个或多个BeanPostProcessor接口实现类,然后注册到Spring IoC容器中。因此这里就是soul的客户端将数据注册到soul-admin的入口,
于是我在注册这里进行了断点调试,看看他到底是在那个接口注册从而将数据传递到soul-admin项目和网关,

可以看到http的项目是在控制台项目的http://localhost:9095/soul-client/springmvc-register 接口进行了注册。
随后我们转到这个接口
/**
* Register spring cloud string.
*
* @param springCloudRegisterDTO the spring cloud register dto
* @return the string
*/
@PostMapping("/springcloud-register")
public String registerSpringCloud(@RequestBody final SpringCloudRegisterDTO springCloudRegisterDTO) {
return soulClientRegisterService.registerSpringCloud(springCloudRegisterDTO);
}
深入到service层可以看到是应用的数据利用到上一节的Spring的事件处理机制来实现了
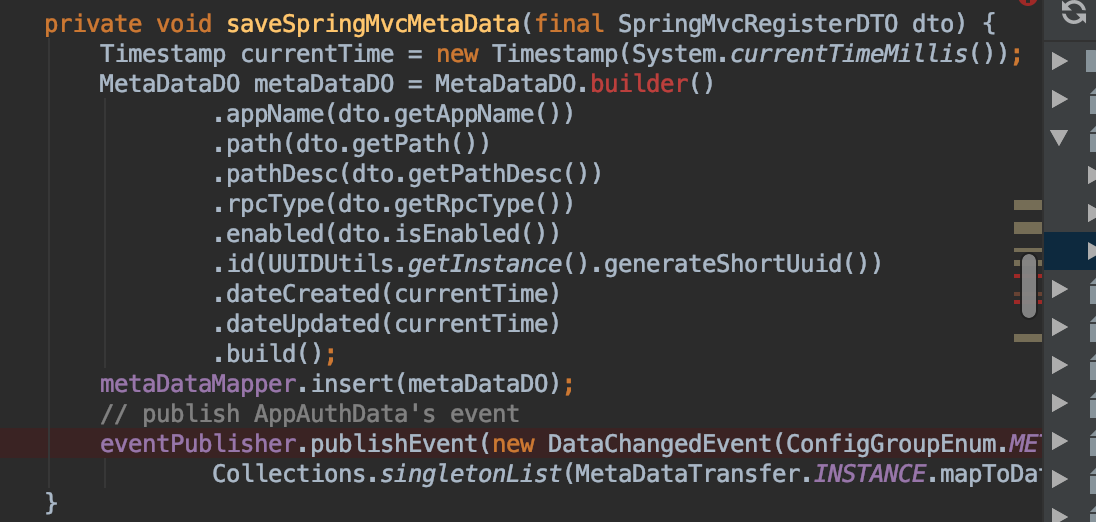
随后断点进入到实现了Spring的事件监听接口ApplicationListener的事件分发类DataChangedEventDispatcher
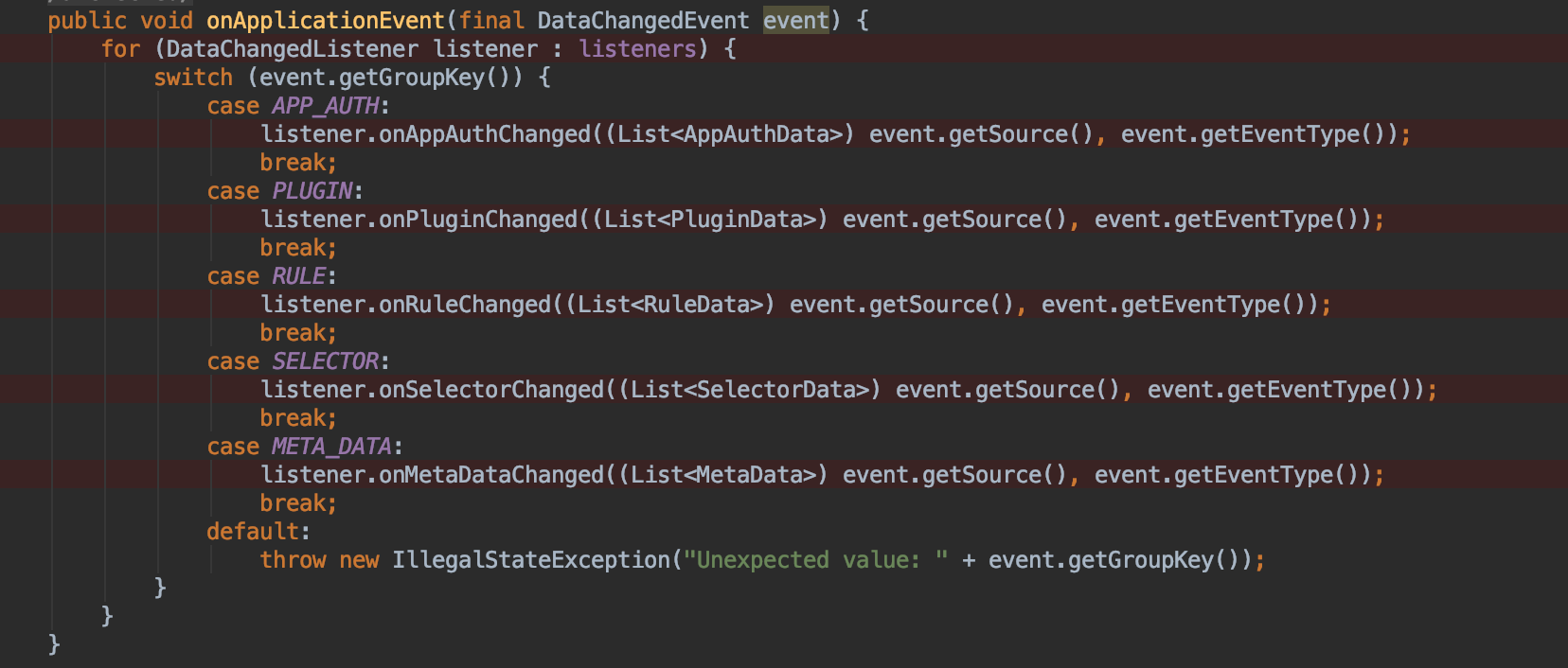
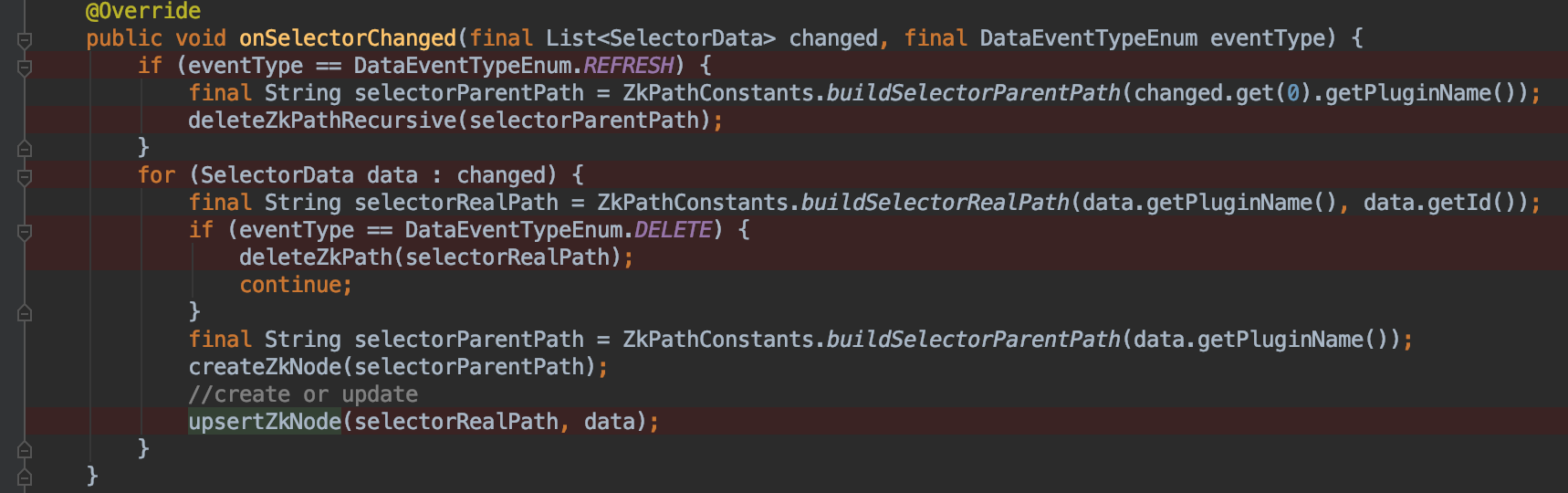
可以看到,我启动的时候因为没有增加插件,所以此时是进入了SELECTOR断点中,由于此时我选择的zookeepr作为数据同步的组件。我找到了ZookeeperDataChangedListener中进行断点 ,发现这里数据同步是将数据放入到zookeeper
private void createZkNode(final String path) {
if (!zkClient.exists(path)) {
zkClient.createPersistent(path, true);
}
}
/**
* create or update zookeeper node.
* @param path node path
* @param data node data
*/
private void upsertZkNode(final String path, final Object data) {
if (!zkClient.exists(path)) {
zkClient.createPersistent(path, true);
}
zkClient.writeData(path, data);
}
private void deleteZkPath(final String path) {
if (zkClient.exists(path)) {
zkClient.delete(path);
}
}
private void deleteZkPathRecursive(final String path) {
if (zkClient.exists(path)) {
zkClient.deleteRecursive(path);
}
}
zookeeper内写入节点和更新数据的流程如上
Soul-Boostrap端数据的探究
打开soul-boostrap可以看到。类很少,只有两个。一个SoulNettyWebServerFactory和HealthFilter。HealthFilter是用来做服务健康检查的。而SoulNettyWebServerFactory就是spring webflux应用的一个响应式Server工厂类。具体的可以去看https://www.jianshu.com/p/ada196969995 这篇文章
但是此时我们还是没有达到我们想要的请求转发的东西。去pom文件中找到了核心的网关的项目soul-spring-boot-starter-gateway但是发现其中一个类都没有,但是其中依赖了soul-web模块,因此对soul-web模块进行了解
首先可以看到配置类SoulConfiguration,
/**
* Init SoulWebHandler.
*
* @param plugins this plugins is All impl SoulPlugin.
* @return {@linkplain SoulWebHandler}
*/
@Bean("webHandler")
public SoulWebHandler soulWebHandler(final ObjectProvider<List<SoulPlugin>> plugins) {
List<SoulPlugin> pluginList = plugins.getIfAvailable(Collections::emptyList);
final List<SoulPlugin> soulPlugins = pluginList.stream()
.sorted(Comparator.comparingInt(SoulPlugin::getOrder)).collect(Collectors.toList());
soulPlugins.forEach(soulPlugin -> log.info("load plugin:[{}] [{}]", soulPlugin.named(), soulPlugin.getClass().getName()));
return new SoulWebHandler(soulPlugins);
}
可以看到这里,加载了一个webhandler的处理器,处理器的主要内容
public SoulWebHandler(final List<SoulPlugin> plugins) {
this.plugins = plugins;
String schedulerType = System.getProperty("soul.scheduler.type", "fixed");
if (Objects.equals(schedulerType, "fixed")) {
int threads = Integer.parseInt(System.getProperty(
"soul.work.threads", "" + Math.max((Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors() << 1) + 1, 16)));
scheduler = Schedulers.newParallel("soul-work-threads", threads);
} else {
scheduler = Schedulers.elastic();
}
}
/**
* Handle the web server exchange.
*
* @param exchange the current server exchange
* @return {@code Mono<Void>} to indicate when request handling is complete
*/
@Override
public Mono<Void> handle(@NonNull final ServerWebExchange exchange) {
MetricsTrackerFacade.getInstance().counterInc(MetricsLabelEnum.REQUEST_TOTAL.getName());
Optional<HistogramMetricsTrackerDelegate> startTimer = MetricsTrackerFacade.getInstance().histogramStartTimer(MetricsLabelEnum.REQUEST_LATENCY.getName());
return new DefaultSoulPluginChain(plugins).execute(exchange).subscribeOn(scheduler)
.doOnSuccess(t -> startTimer.ifPresent(time -> MetricsTrackerFacade.getInstance().histogramObserveDuration(time)));
}
主要内容是利用责任链对请求的线程数进行处理。handle方法用来处理请求
根据soul-example-springmvc的注解进行请求。可以在抽象的基础AbstractSoulPlugin接受到这个请求
@Override
public Mono<Void> execute(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final SoulPluginChain chain) {
String pluginName = named();
final PluginData pluginData = BaseDataCache.getInstance().obtainPluginData(pluginName);
if (pluginData != null && pluginData.getEnabled()) {
final Collection<SelectorData> selectors = BaseDataCache.getInstance().obtainSelectorData(pluginName);
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(selectors)) {
return handleSelectorIsNull(pluginName, exchange, chain);
}
final SelectorData selectorData = matchSelector(exchange, selectors);
if (Objects.isNull(selectorData)) {
return handleSelectorIsNull(pluginName, exchange, chain);
}
selectorLog(selectorData, pluginName);
final List<RuleData> rules = BaseDataCache.getInstance().obtainRuleData(selectorData.getId());
if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(rules)) {
return handleRuleIsNull(pluginName, exchange, chain);
}
RuleData rule;
if (selectorData.getType() == SelectorTypeEnum.FULL_FLOW.getCode()) {
//get last
rule = rules.get(rules.size() - 1);
} else {
rule = matchRule(exchange, rules);
}
if (Objects.isNull(rule)) {
return handleRuleIsNull(pluginName, exchange, chain);
}
ruleLog(rule, pluginName);
return doExecute(exchange, chain, selectorData, rule);
}
return chain.execute(exchange);
}
这里有很明显的规则和选择器比较的相关逻辑,用来判断当前的请求是否位于网关代理的请求中。但是在这里与上面对应的是,我如何取到上文已经设置的选择器数据,这个留到后面继续去探究
紧接着断点来到了具体的业务的请求插件WebClientPlugin执行后面的业务请求
@Override
public Mono<Void> execute(final ServerWebExchange exchange, final SoulPluginChain chain) {
final SoulContext soulContext = exchange.getAttribute(Constants.CONTEXT);
assert soulContext != null;
String urlPath = exchange.getAttribute(Constants.HTTP_URL);
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(urlPath)) {
Object error = SoulResultWrap.error(SoulResultEnum.CANNOT_FIND_URL.getCode(), SoulResultEnum.CANNOT_FIND_URL.getMsg(), null);
return WebFluxResultUtils.result(exchange, error);
}
long timeout = (long) Optional.ofNullable(exchange.getAttribute(Constants.HTTP_TIME_OUT)).orElse(3000L);
int retryTimes = (int) Optional.ofNullable(exchange.getAttribute(Constants.HTTP_RETRY)).orElse(0);
log.info("The request urlPath is {}, retryTimes is {}", urlPath, retryTimes);
HttpMethod method = HttpMethod.valueOf(exchange.getRequest().getMethodValue());
WebClient.RequestBodySpec requestBodySpec = webClient.method(method).uri(urlPath);
return handleRequestBody(requestBodySpec, exchange, timeout, retryTimes, chain);
}
从如上可以看到,网关在代理请求这一块的逻辑
问题
本文还剩下未解决的问题主要是
- 如何从abstractSoulPlugin执行完之后到WebClientPlugin的相同方法,是责任链模式还是其他的加载过程
- abstractSoulPlugin是如何加载注册或修改后的选择器等数据
- plugin 中的执行方法是如何获取到ServerWebExchange的相关请求数据
参考文章 https://blog.csdn.net/u010084384/article/details/113010594
欢迎搜索关注本人与朋友共同开发的微信面经小程序【大厂面试助手】和公众号【微瞰技术】,以及总结的分类面试题https://github.com/zhendiao/JavaInterview






 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号