通用近似定理(Universal Approximation Theorem)
定力内容:一个 两层的前馈神经网络(只要隐藏层足够大,且使用非线性激活函数),就可以逼近任意连续函数。
• 对分类问题的启示:
分类其实就是在寻找一个函数 \(f(x)\),让它在不同类别上输出不同的值。
接下来我们通过代码演示 激活函数引入非线性 → 决策边界可以弯曲;
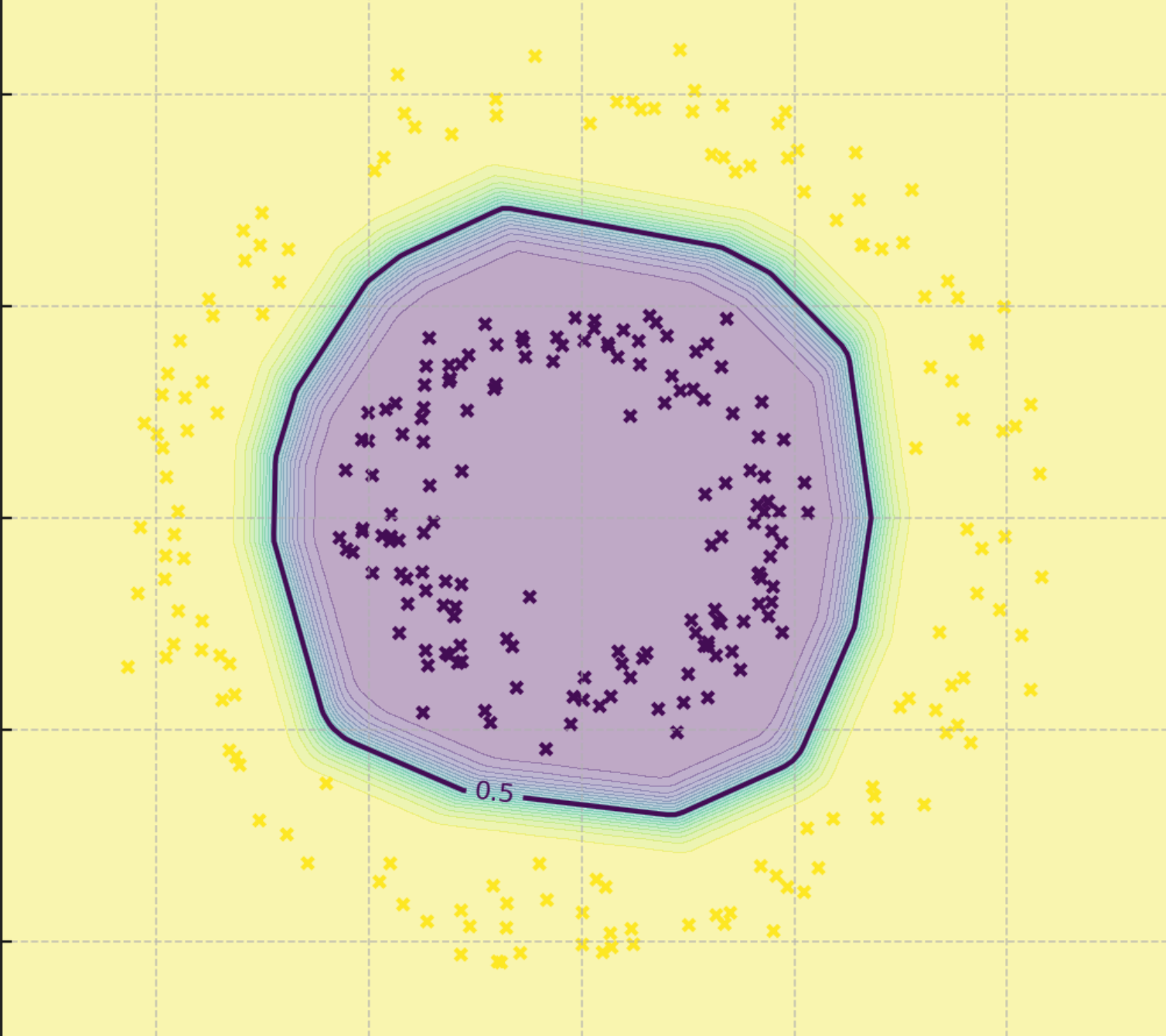
如图所示的问题我们通过原有的线性方程就无法对我们想要的数据进行隔离,我们需要引入损失函数来让增加函数的曲线特性。
# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-
# Demo: 激活函数引入非线性 → 决策边界可以弯曲(PyTorch,无 sklearn 依赖)
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# 1) 生成非线性可分数据:同心圆(inner circle vs outer ring)
def make_concentric_circles(n_samples=300, inner_r=0.5, outer_r=1.0, noise=0.08, seed=42):
rng = np.random.default_rng(seed)
n_inner = n_samples // 2
n_outer = n_samples - n_inner
# 内圈(类0)
angles_inner = rng.uniform(0, 2*np.pi, size=n_inner)
r_inner = rng.normal(inner_r, noise, size=n_inner)
x_inner = np.stack([r_inner * np.cos(angles_inner), r_inner * np.sin(angles_inner)], axis=1)
y_inner = np.zeros((n_inner, 1), dtype=np.float32)
# 外环(类1)
angles_outer = rng.uniform(0, 2*np.pi, size=n_outer)
r_outer = rng.normal(outer_r, noise, size=n_outer)
x_outer = np.stack([r_outer * np.cos(angles_outer), r_outer * np.sin(angles_outer)], axis=1)
y_outer = np.ones((n_outer, 1), dtype=np.float32)
X = np.vstack([x_inner, x_outer]).astype(np.float32)
y = np.vstack([y_inner, y_outer]).astype(np.float32)
# 打乱
idx = rng.permutation(n_samples)
return X[idx], y[idx]
X_np, y_np = make_concentric_circles(
n_samples=300, inner_r=0.45, outer_r=1.0, noise=0.07, seed=7
)
X = torch.tensor(X_np)
y = torch.tensor(y_np)
# 2) 定义两个模型:
# (A) 线性模型(无隐藏层 → 线性边界)
linear_model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
# (B) 带非线性激活的 MLP(隐藏层 + ReLU → 非线性弯曲边界)
mlp_model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(2, 16),
nn.ReLU(),
nn.Linear(16, 1),
nn.Sigmoid()
)
# 3) 训练函数
def train(model, X, y, lr=0.02, epochs=500):
criterion = nn.BCELoss()
optimizer = optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=lr)
for _ in range(epochs):
optimizer.zero_grad()
out = model(X)
loss = criterion(out, y)
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
with torch.no_grad():
pred = (model(X) >= 0.5).float()
acc = (pred.eq(y)).float().mean().item()
return acc
# 分别训练
acc_linear = train(linear_model, X, y, lr=0.05, epochs=250)
acc_mlp = train(mlp_model, X, y, lr=0.02, epochs=500)
# 4) 可视化决策边界
def plot_decision_boundary(model, X_np, y_np, title):
x_min, x_max = X_np[:,0].min() - 0.3, X_np[:,0].max() + 0.3
y_min, y_max = X_np[:,1].min() - 0.3, X_np[:,1].max() + 0.3
xx, yy = np.meshgrid(np.linspace(x_min, x_max, 150),
np.linspace(y_min, y_max, 150))
grid = torch.tensor(np.c_[xx.ravel(), yy.ravel()], dtype=torch.float32)
with torch.no_grad():
zz = model(grid).reshape(xx.shape).numpy()
plt.figure(figsize=(6, 6))
# 决策区域
plt.contourf(xx, yy, zz, levels=np.linspace(0, 1, 21), alpha=0.35)
# 0.5 的等高线作为分类边界
CS = plt.contour(xx, yy, zz, levels=[0.5])
plt.clabel(CS, inline=1, fontsize=8)
# 训练样本散点(颜色用类别值)
plt.scatter(X_np[:,0], X_np[:,1], c=y_np.squeeze(), s=12, edgecolors='none')
plt.title(title)
plt.xlabel("x1")
plt.ylabel("x2")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.show()
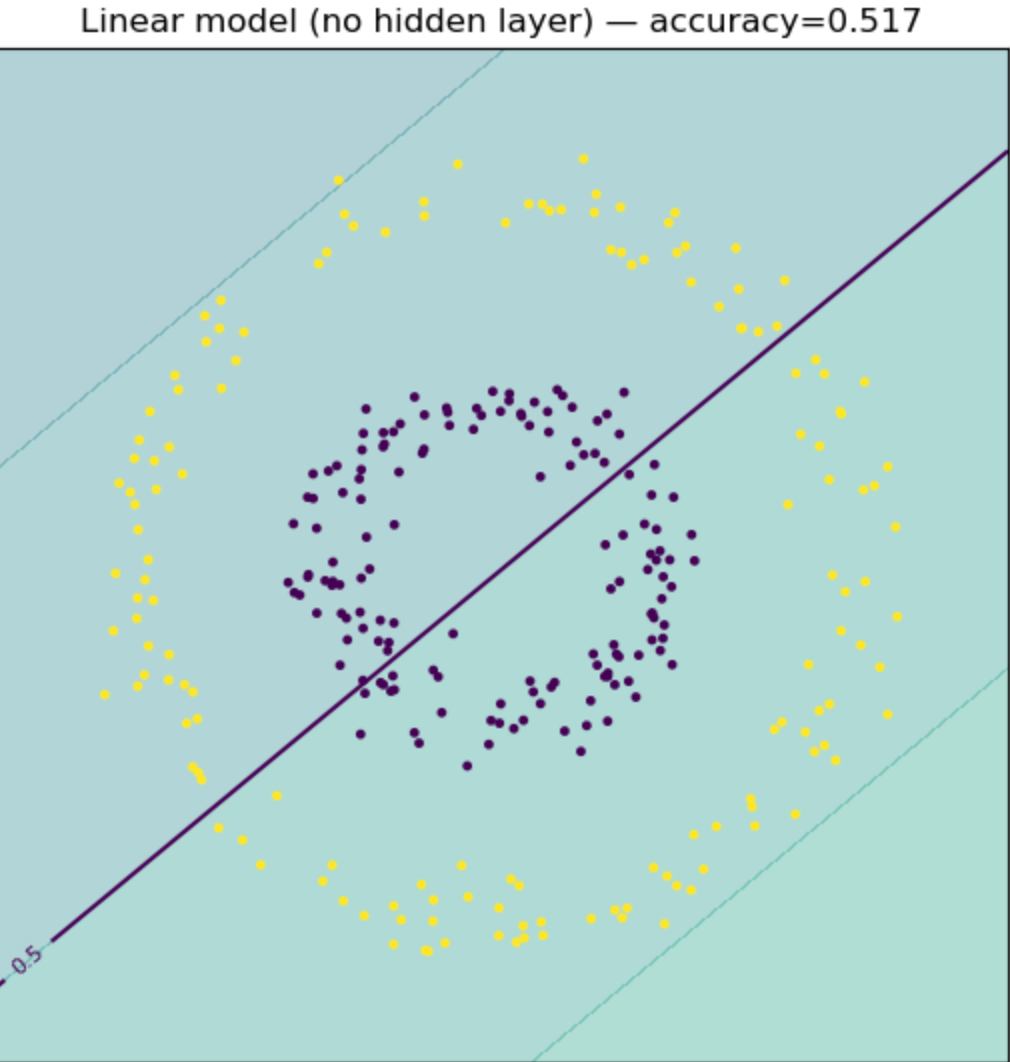
plot_decision_boundary(linear_model, X_np, y_np, f"Linear model (no hidden layer) — accuracy={acc_linear:.3f}")
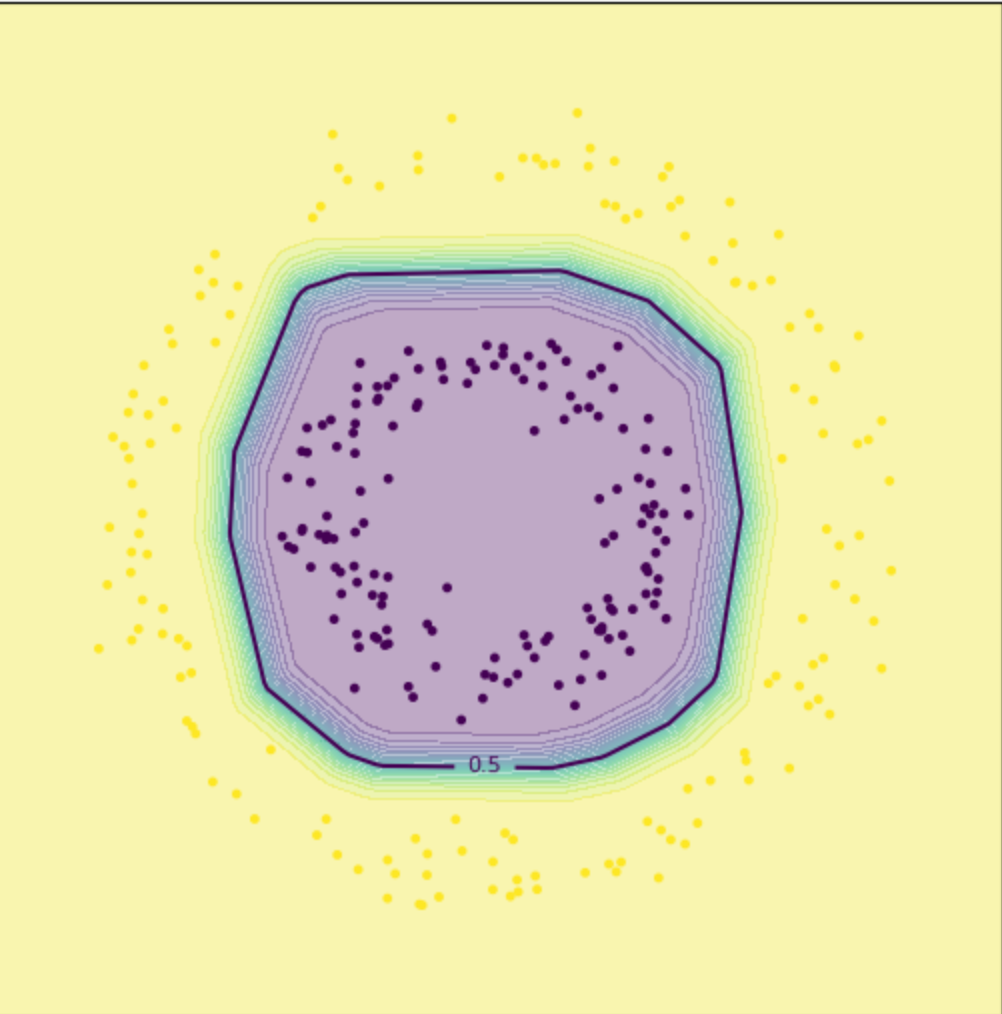
plot_decision_boundary(mlp_model, X_np, y_np, f"MLP with ReLU (curved boundary) — accuracy={acc_mlp:.3f}")
训练结束之后训练出的图形做个对比,没有损失函数,只能获取线性的函数,无法有效区分和圈定隔离数据
加入损失函数之后我们就可以让函数表现出曲线的特性
思维试验:根据之前学习的数学概念,其实圆形的图形或者圆形的平面我们可以通过根据所需要的数据精确度来创建多条圆形上的点的切线来模拟,在进行函数角度的延伸我们也可以通过函数的泰勒展开式对函数进行展开,只需要确定多项式的系数即可,但是这样学习的问题是会无线的把问题无线的方法,且想要达到的较高的精度需要相当很多项,借用pytorch封装好的工具和函数获取训练之后的网络模型。
直观演示可以通过html的动态动画进行展示
import React, { useState, useEffect, useRef } from 'react';
import { Play, Pause, RotateCcw, Zap } from 'lucide-react';
const CircularMLPDemo = () => {
const [training, setTraining] = useState(false);
const [epoch, setEpoch] = useState(0);
const [loss, setLoss] = useState(1.0);
const [accuracy, setAccuracy] = useState(0.5);
const [speed, setSpeed] = useState(50);
const canvasRef = useRef(null);
// 生成圆形数据
const generateCircularData = () => {
const data = [];
const nSamples = 100;
// 内圈(紫色,类别0)
for (let i = 0; i < nSamples; i++) {
const r = Math.random() * 0.5;
const theta = Math.random() * 2 * Math.PI;
data.push({
x: r * Math.cos(theta),
y: r * Math.sin(theta),
label: 0
});
}
// 外圈(黄色,类别1)
for (let i = 0; i < nSamples; i++) {
const r = 0.7 + Math.random() * 0.5;
const theta = Math.random() * 2 * Math.PI;
data.push({
x: r * Math.cos(theta),
y: r * Math.sin(theta),
label: 1
});
}
return data;
};
const [data] = useState(generateCircularData());
// He初始化 - 更稳定的权重初始化方法
const heInit = (fanIn) => {
const std = Math.sqrt(2.0 / fanIn);
return (Math.random() - 0.5) * 2 * std;
};
// 初始化权重(改进版)
const initWeights = () => ({
// 第一层:2 -> 8
w1: Array(16).fill(0).map(() => heInit(2)),
b1: Array(8).fill(0),
// 第二层:8 -> 8
w2: Array(64).fill(0).map(() => heInit(8)),
b2: Array(8).fill(0),
// 输出层:8 -> 1
w3: Array(8).fill(0).map(() => heInit(8)),
b3: 0
});
const [weights, setWeights] = useState(initWeights());
const [lossHistory, setLossHistory] = useState([]);
// ReLU激活函数
const relu = (x) => Math.max(0, x);
// Sigmoid激活函数(带数值稳定性)
const sigmoid = (x) => {
if (x >= 0) {
return 1 / (1 + Math.exp(-x));
} else {
const exp_x = Math.exp(x);
return exp_x / (1 + exp_x);
}
};
// 前向传播
const forward = (x, y) => {
// 第一层:2 -> 8
const hidden1 = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
const z = x * weights.w1[i*2] + y * weights.w1[i*2+1] + weights.b1[i];
hidden1.push(relu(z));
}
// 第二层:8 -> 8
const hidden2 = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
let z = weights.b2[i];
for (let j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
z += hidden1[j] * weights.w2[i*8 + j];
}
hidden2.push(relu(z));
}
// 输出层:8 -> 1
let output = weights.b3;
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
output += hidden2[i] * weights.w3[i];
}
return sigmoid(output);
};
// 梯度裁剪
const clipGrad = (grad, maxNorm = 1.0) => {
return Math.max(-maxNorm, Math.min(maxNorm, grad));
};
// 训练一步(改进版)
const trainStep = () => {
const lr = 0.01; // 降低学习率
const newWeights = JSON.parse(JSON.stringify(weights));
let totalLoss = 0;
let correct = 0;
// Mini-batch训练
const batchSize = 32;
const indices = Array.from({length: data.length}, (_, i) => i)
.sort(() => Math.random() - 0.5)
.slice(0, batchSize);
indices.forEach(idx => {
const point = data[idx];
const pred = forward(point.x, point.y);
// 检查预测值是否有效
if (isNaN(pred) || !isFinite(pred)) {
console.error('Invalid prediction:', pred);
return;
}
const error = pred - point.label;
totalLoss += error * error;
if ((pred > 0.5 && point.label === 1) || (pred <= 0.5 && point.label === 0)) {
correct++;
}
// 重新前向传播获取中间值
const input = [point.x, point.y];
// 第一层
const hidden1 = [];
const z1 = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
const z = input[0] * weights.w1[i*2] + input[1] * weights.w1[i*2+1] + weights.b1[i];
z1.push(z);
hidden1.push(relu(z));
}
// 第二层
const hidden2 = [];
const z2 = [];
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
let z = weights.b2[i];
for (let j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
z += hidden1[j] * weights.w2[i*8 + j];
}
z2.push(z);
hidden2.push(relu(z));
}
// 反向传播
const dL_dout = 2 * error / batchSize; // 除以batch size
// 输出层梯度
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
const grad = clipGrad(dL_dout * hidden2[i]);
newWeights.w3[i] -= lr * grad;
}
newWeights.b3 -= lr * clipGrad(dL_dout);
// 第二层梯度
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
const dL_dh2 = dL_dout * weights.w3[i];
const dh2_dz2 = z2[i] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
const dL_dz2 = dL_dh2 * dh2_dz2;
for (let j = 0; j < 8; j++) {
const grad = clipGrad(dL_dz2 * hidden1[j]);
newWeights.w2[i*8 + j] -= lr * grad;
}
newWeights.b2[i] -= lr * clipGrad(dL_dz2);
}
// 第一层梯度
for (let i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
let dL_dh1 = 0;
for (let k = 0; k < 8; k++) {
const dL_dz2 = dL_dout * weights.w3[k] * (z2[k] > 0 ? 1 : 0);
dL_dh1 += dL_dz2 * weights.w2[k*8 + i];
}
const dh1_dz1 = z1[i] > 0 ? 1 : 0;
const dL_dz1 = dL_dh1 * dh1_dz1;
newWeights.w1[i*2] -= lr * clipGrad(dL_dz1 * input[0]);
newWeights.w1[i*2+1] -= lr * clipGrad(dL_dz1 * input[1]);
newWeights.b1[i] -= lr * clipGrad(dL_dz1);
}
});
const avgLoss = totalLoss / batchSize;
const acc = correct / batchSize;
// 检查损失是否有效
if (isNaN(avgLoss) || !isFinite(avgLoss)) {
console.error('Invalid loss, resetting weights');
setWeights(initWeights());
setLossHistory([]);
return;
}
setWeights(newWeights);
setLoss(avgLoss);
setAccuracy(acc);
setLossHistory(prev => [...prev.slice(-99), avgLoss]);
};
// 训练循环
useEffect(() => {
let interval;
if (training) {
interval = setInterval(() => {
trainStep();
setEpoch(e => e + 1);
}, 100 - speed);
}
return () => clearInterval(interval);
}, [training, weights, speed]);
// 绘制可视化
useEffect(() => {
const canvas = canvasRef.current;
if (!canvas) return;
const ctx = canvas.getContext('2d');
const width = canvas.width;
const height = canvas.height;
ctx.fillStyle = '#ffffff';
ctx.fillRect(0, 0, width, height);
// 绘制决策边界
const resolution = 60;
for (let i = 0; i < resolution; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < resolution; j++) {
const x = -1.5 + (i / resolution) * 3;
const y = -1.5 + (j / resolution) * 3;
const pred = forward(x, y);
const px = (x + 1.5) / 3 * width;
const py = height - (y + 1.5) / 3 * height;
if (!isNaN(pred) && isFinite(pred)) {
if (pred > 0.5) {
ctx.fillStyle = `rgba(255, 215, 0, ${Math.min(pred * 0.6, 0.6)})`;
} else {
ctx.fillStyle = `rgba(147, 112, 219, ${Math.min((1-pred) * 0.6, 0.6)})`;
}
ctx.fillRect(px, py, width/resolution + 1, height/resolution + 1);
}
}
}
// 绘制决策边界线
ctx.strokeStyle = '#1e3a8a';
ctx.lineWidth = 2.5;
ctx.beginPath();
const contourPoints = [];
for (let i = 0; i < resolution; i++) {
for (let j = 0; j < resolution; j++) {
const x = -1.5 + (i / resolution) * 3;
const y = -1.5 + (j / resolution) * 3;
const pred = forward(x, y);
if (Math.abs(pred - 0.5) < 0.08 && !isNaN(pred)) {
const px = (x + 1.5) / 3 * width;
const py = height - (y + 1.5) / 3 * height;
contourPoints.push({px, py});
}
}
}
if (contourPoints.length > 0) {
ctx.moveTo(contourPoints[0].px, contourPoints[0].py);
contourPoints.forEach(p => ctx.lineTo(p.px, p.py));
ctx.stroke();
}
// 绘制数据点
data.forEach(point => {
const px = (point.x + 1.5) / 3 * width;
const py = height - (point.y + 1.5) / 3 * height;
ctx.beginPath();
ctx.arc(px, py, 3.5, 0, 2 * Math.PI);
ctx.fillStyle = point.label === 0 ? '#9370DB' : '#FFD700';
ctx.fill();
ctx.strokeStyle = '#000';
ctx.lineWidth = 0.5;
ctx.stroke();
});
}, [weights, data]);
// 重置
const reset = () => {
setWeights(initWeights());
setEpoch(0);
setLoss(1.0);
setAccuracy(0.5);
setLossHistory([]);
setTraining(false);
};
return (
<div className="p-6 max-w-7xl mx-auto bg-gradient-to-br from-blue-50 to-purple-50 min-h-screen">
<div className="mb-6">
<h1 className="text-3xl font-bold mb-2 text-gray-800">
🎯 MLP圆形决策边界实时训练演示
</h1>
<p className="text-gray-600">观察神经网络如何通过ReLU激活函数学习非线性的圆形边界</p>
</div>
<div className="grid grid-cols-1 lg:grid-cols-3 gap-6">
{/* 主可视化区域 */}
<div className="lg:col-span-2 space-y-4">
<div className="bg-white p-4 rounded-xl shadow-lg">
<div className="flex justify-between items-center mb-3">
<h3 className="font-semibold text-lg">决策边界可视化</h3>
<div className="text-sm bg-green-100 text-green-800 px-3 py-1 rounded-full font-mono">
Accuracy: {(accuracy * 100).toFixed(1)}%
</div>
</div>
<canvas
ref={canvasRef}
width={600}
height={600}
className="border border-gray-200 rounded-lg w-full"
/>
<div className="mt-3 flex justify-center gap-6 text-sm">
<div className="flex items-center gap-2">
<div className="w-4 h-4 rounded-full bg-purple-400"></div>
<span>类别 0 (内圈)</span>
</div>
<div className="flex items-center gap-2">
<div className="w-4 h-4 rounded-full bg-yellow-400"></div>
<span>类别 1 (外圈)</span>
</div>
<div className="flex items-center gap-2">
<div className="w-8 h-1 bg-blue-900"></div>
<span>决策边界</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
{/* 损失曲线 */}
<div className="bg-white p-4 rounded-xl shadow-lg">
<h3 className="font-semibold mb-3">训练损失曲线</h3>
<svg width="100%" height="150" className="border border-gray-200 rounded" viewBox="0 0 600 150">
<line x1="0" y1="150" x2="600" y2="150" stroke="#e5e7eb" strokeWidth="1"/>
<line x1="0" y1="0" x2="0" y2="150" stroke="#e5e7eb" strokeWidth="1"/>
{lossHistory.length > 1 && (
<polyline
points={lossHistory.map((l, i) =>
`${i * 600 / Math.max(lossHistory.length, 1)},${Math.max(0, 150 - Math.min(l * 100, 145))}`
).join(' ')}
fill="none"
stroke="#3b82f6"
strokeWidth="2"
/>
)}
<text x="10" y="20" className="text-xs" fill="#666">Loss: {loss.toFixed(4)}</text>
</svg>
</div>
</div>
{/* 控制面板 */}
<div className="space-y-4">
<div className="bg-white p-4 rounded-xl shadow-lg">
<h3 className="font-semibold mb-3">🧠 网络架构(优化版)</h3>
<div className="space-y-2 text-sm">
<div className="bg-blue-50 p-3 rounded-lg border border-blue-200">
<div className="font-mono text-xs space-y-1">
<div>📥 <strong>输入层</strong>: 2神经元 (x, y)</div>
<div>🔄 <strong>隐藏层1</strong>: 8神经元 + ReLU</div>
<div>🔄 <strong>隐藏层2</strong>: 8神经元 + ReLU</div>
<div>📤 <strong>输出层</strong>: 1神经元 + Sigmoid</div>
</div>
</div>
<div className="text-xs bg-green-50 text-green-700 p-2 rounded border border-green-200">
✅ 使用He初始化 | 学习率0.01 | Mini-batch=32
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div className="bg-white p-4 rounded-xl shadow-lg">
<h3 className="font-semibold mb-3">⚙️ 训练控制</h3>
<div className="space-y-3">
<div className="flex gap-2">
<button
onClick={() => setTraining(!training)}
className={`flex-1 py-3 rounded-lg font-medium flex items-center justify-center gap-2 transition-all ${
training
? 'bg-orange-500 hover:bg-orange-600 text-white'
: 'bg-green-500 hover:bg-green-600 text-white'
}`}
>
{training ? <><Pause size={18} /> 暂停</> : <><Play size={18} /> 开始训练</>}
</button>
<button
onClick={reset}
className="px-4 py-3 bg-gray-500 hover:bg-gray-600 text-white rounded-lg flex items-center gap-2 transition-all"
>
<RotateCcw size={18} />
</button>
</div>
<div>
<label className="text-sm text-gray-600 mb-1 block">训练速度</label>
<input
type="range"
min="0"
max="90"
value={speed}
onChange={(e) => setSpeed(Number(e.target.value))}
className="w-full"
/>
<div className="flex justify-between text-xs text-gray-500 mt-1">
<span>慢</span>
<span>快</span>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div className="bg-white p-4 rounded-xl shadow-lg">
<h3 className="font-semibold mb-3">📊 训练状态</h3>
<div className="space-y-3">
<div className="flex justify-between items-center">
<span className="text-gray-600">训练轮次</span>
<span className="font-mono text-lg font-bold text-blue-600">{epoch}</span>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-between items-center">
<span className="text-gray-600">损失值</span>
<span className="font-mono text-lg font-bold text-purple-600">
{isNaN(loss) ? '错误' : loss.toFixed(4)}
</span>
</div>
<div className="flex justify-between items-center">
<span className="text-gray-600">准确率</span>
<span className="font-mono text-lg font-bold text-green-600">
{(accuracy * 100).toFixed(1)}%
</span>
</div>
{/* 进度条 */}
<div className="mt-4">
<div className="h-2 bg-gray-200 rounded-full overflow-hidden">
<div
className="h-full bg-gradient-to-r from-blue-500 to-green-500 transition-all duration-300"
style={{ width: `${accuracy * 100}%` }}
/>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
<div className="bg-gradient-to-r from-purple-100 to-blue-100 p-4 rounded-xl border border-purple-200">
<h3 className="font-semibold mb-2 flex items-center gap-2">
<Zap className="text-yellow-600" size={18} />
优化要点
</h3>
<ul className="text-sm space-y-1 text-gray-700">
<li>• <strong>He初始化</strong>:更稳定的权重</li>
<li>• <strong>降低学习率</strong>:0.01防止梯度爆炸</li>
<li>• <strong>Mini-batch</strong>:批量训练更稳定</li>
<li>• <strong>梯度裁剪</strong>:防止NaN出现</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
</div>
);
};
export default CircularMLPDemo;



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号