线程安全
如果有多个线程在同时运行,而这些线程可能会同时运行这段代码。程序每次运行结果和单线程运行的结果是一样的,而且其他的变量的值也和预期的是一样的,就是线程安全的。
线程同步(线程安全处理Synchronized)
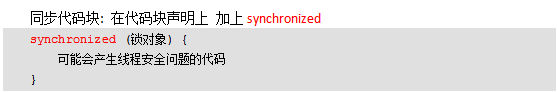
同步代码块
![]()
//同步代码块
public class MyTicket3 implements Runnable{
private int ticket=100;
Object obj=new Object();//锁对象
public void run() {
while(true){
synchronized (obj) {//扩起可能产生问题的代码块
if(ticket>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖第"+ticket--+"张票");
}
}
}
}
}
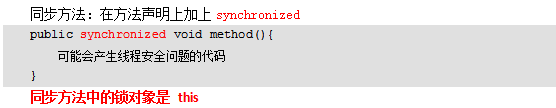
同步方法
![]()
//同步方法 锁对象:this
//静态同步方法 锁对象:MyTicket2.class
//加了同步安全 但是运行速度会下降 StringBuffer就是加了同步 StringBuilder没加
public class MyTicket2 implements Runnable{
private static int ticket=100;
public static synchronized void method(){
if(ticket>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖第"+ticket--+"张票");
}
}
public void run() {
while(true){
method();
}
}
}
Lock接口
Lock接口中的常用方法
![]()
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantLock;
//Lock接口
public class MyTicket implements Runnable{
private int ticket=100;
private Lock lock=new ReentrantLock();//创建Lock接口实现类对象
public void run() {
while(true){
lock.lock();//获取锁
if(ticket>0){
try {
Thread.sleep(10);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖第"+ticket--+"张票");
}
lock.unlock();//释放锁
}
}
}
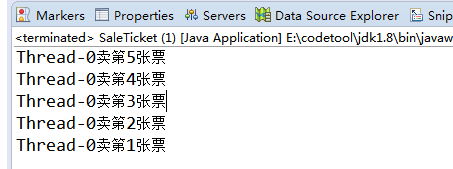
public class SaleTicket {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyTicket mt=new MyTicket();
//创建线程
Thread t0=new Thread(mt);
Thread t1=new Thread(mt);
Thread t2=new Thread(mt);
//开启线程
t0.start();
t1.start();
t2.start();
}
}
![]()
死锁
同步锁使用的弊端:当线程任务中出现了多个同步(多个锁)时,如果同步中嵌套了其他的同步。这时容易引发一种现象:程序出现无限等待,这种现象我们称为死锁。这种情况能避免就避免掉。
public class LockA {
private LockA(){}
public final static LockA locka=new LockA();
}
public class LockB {
private LockB(){}
public final static LockB lockb=new LockB();
}
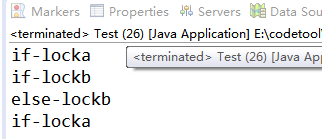
public class DeadLock implements Runnable{
private int i=0;
public void run() {
while(true){
if(i%2==0){
synchronized (LockA.locka) {
System.out.println("if-locka");
synchronized (LockB.lockb) {
System.out.println("if-lockb");
}
}
}else{
synchronized (LockB.lockb) {
System.out.println("else-lockb");
synchronized (LockA.locka) {
System.out.println("else-locka");
}
}
}
i++;
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
DeadLock dl=new DeadLock();
Thread t0=new Thread(dl);
Thread t1=new Thread(dl);
t0.start();
t1.start();
}
}
![]()
等待唤醒机制
等待唤醒机制所涉及到的方法:
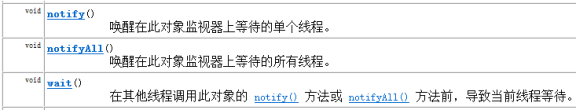
wait() :等待,将正在执行的线程释放其执行资格 和 执行权,并存储到线程池中。
notify():唤醒,唤醒线程池中被wait()的线程,一次唤醒一个,而且是任意的。
notifyAll(): 唤醒全部:可以将线程池中的所有wait() 线程都唤醒。
![]()
示例
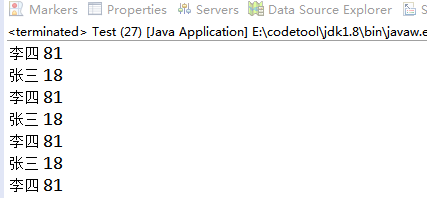
1.当input发现Resource中没有数据时,开始输入,输入完成后,叫output来输出。如果发现有数据,就wait();
2.当output发现Resource中没有数据时,就wait() ;当发现有数据时,就输出,然后,叫醒input来输入数据。
public class Resource {
public String name;
public int age;
//添加标记:true:赋值完成 false:输出完成
public boolean flag=false;
}
public class Input implements Runnable{
//对Resource进行赋值
private Resource r;
public Input(){}
public Input(Resource r){
this.r=r;
}
public void run() {
int i=0;
while(true){
//添加同步代码块
synchronized (r) {
//判断标记
if(r.flag){
try {
r.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(i%2==0){
r.name="张三";
r.age=18;
}else{
r.name="李四";
r.age=81;
}
r.flag=true;
r.notify();
}
i++;
}
}
}
public class Output implements Runnable{
private Resource r;
public Output(){}
public Output(Resource r){
this.r=r;
}
public void run() {
//对Resourse进行输出
while(true){
synchronized (r) {
//判断标记
if(!r.flag){
try {
r.wait();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
System.out.println(r.name+" "+r.age);
//改标记 唤醒input
r.flag=false;
r.notify();
}
}
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Resource r=new Resource();
Input in=new Input(r);
Output out=new Output(r);
Thread tin=new Thread(in);
Thread tout=new Thread(out);
tin.start();
tout.start();
}
}
![]()
![]()
![]()





 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号