Java学习笔记70——多态中的转型问题
多态中的转型问题
猫狗案例练习多态版
class Animal{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("狗吃肉");
}
public void lookDoor(){
System.out.println("看门");
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
public void catchMouse(){
System.out.println("猫抓老鼠");
}
}
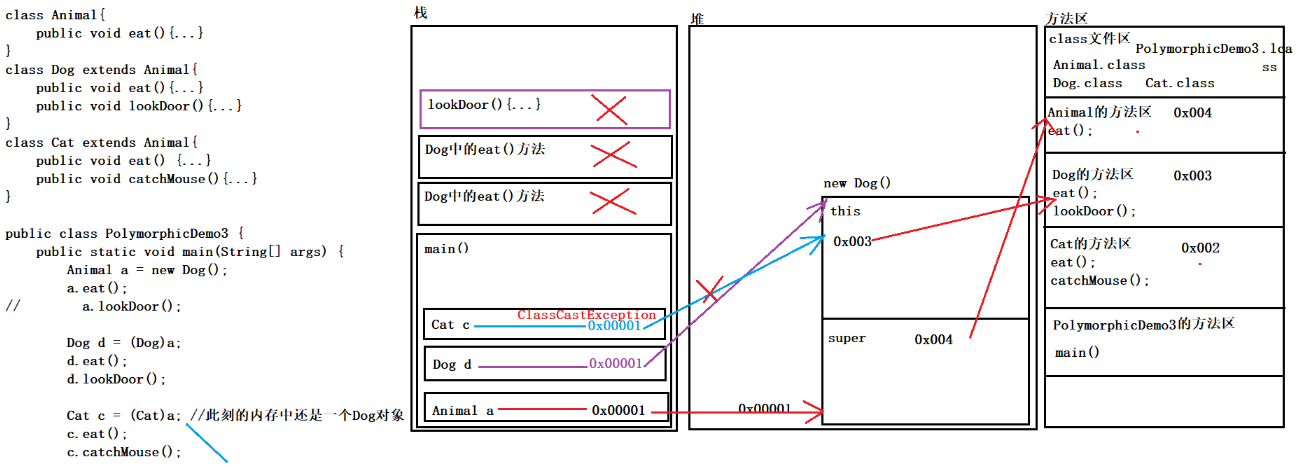
public class PolymorphicDemo3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//多态的形式创建一个对象
Animal a =new Dog();
a.eat();
//向下转型访问子类特有的方法
Dog d=(Dog)a;
d.eat();
d.lookDoor();
//java.lang.ClassCastException 类型转换异常
//Cat c = (Cat)a; //报错。此刻的内存中还是一个Dog对象
//c.eat();
//c.catchMouse();
}
}
多态中类型转换异常图示
class Animal2{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
}
class Dog2 extends Animal2{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("狗吃肉");
}
public void lookDoor(){
System.out.println("狗看门");
}
}
class Cat2 extends Animal2{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("猫吃鱼");
}
public void catchMouse(){
System.out.println("猫抓老鼠");
}
}
public class PolymorphicTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal2 a = new Dog2();
a.eat();
// a.lookDoor();
System.out.println("-----------------");
Dog2 d = (Dog2)a;
d.eat();
d.lookDoor();
System.out.println("------------------");
a = new Cat2();
a.eat();
// a.catchMouse();
System.out.println("------------------");
Cat2 c = (Cat2)a;
c.eat();
c.catchMouse();
// c.lookDoor();
System.out.println("------------------");
// Dog2 dog2 = new Animal2();//报错。子类引用指向父类,反了
// Dog2 dog2 = new Cat2();//报错。两个类之间不存在继承关系
// Dog2 dog2 = (Dog2)a;//报错。Dog类地址值在内存中无法赋值给Cat地址值
// dog2.eat();
}
}
不同地方饮食文化不同的案例
class Person{
public void eat(){
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
}
class SouthPerson extends Person{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃米饭");
}
public void work(){
System.out.println("创业");
}
}
class NorthPerson extends Person{
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃面食");
}
public void bath(){
System.out.println("搓澡");
}
}
public class PolymorphinTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p =new SouthPerson();
p.eat();
System.out.println("===============");
SouthPerson s =(SouthPerson)p;
s.eat();
s.work();
System.out.println("===============");
p=new NorthPerson();
p.eat();
System.out.println("===============");
NorthPerson n =(NorthPerson)p;
n.eat();
n.bath();
}
}
看程序,写结果--1
class Fu {
public void show() {
System.out.println("fu show");
}
}
class Zi extends Fu {
public void show() {
System.out.println("zi show");
}
public void method() {
System.out.println("zi method");
}
}
public class PolymorphicTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Fu f = new Zi();
// f.method();//报错
//向下转型
Zi z = (Zi)f;
z.method();//zi method
}
}
看程序,写结果--2
class A1 {
public void show() {
show2();
}
public void show2() {
System.out.println("我");
}
}
class B1 extends A1 {
//这里隐含了继承过来的show方法,只不过我们没有重写
// public void show() {
// show2();
// }
public void show2() {
System.out.println("爱");
}
}
class C1 extends B1 {
public void show() {
super.show();
}
public void show2() {
System.out.println("你");
}
}
public class PolymorphicTest4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
A1 a = new B1();
a.show(); // 爱(翻译看左,运行看右,找到A1中的show方法,运行B1中隐藏的继承自A1的show方法指向show2方法(就近原则))
B1 b = new C1();
b.show(); // 你(翻译看左,运行看右,找到B1中的show方法,运行C1中的show方法通过super关键字指向B1中的show2方法其实就是C1中继承自B1的show2方法,运行C1中的show2方法(就近原则))
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号