Java异常
目录
1 异常(记忆)
异常的概述
异常就是程序出现了不正常的情况
异常的体系结构
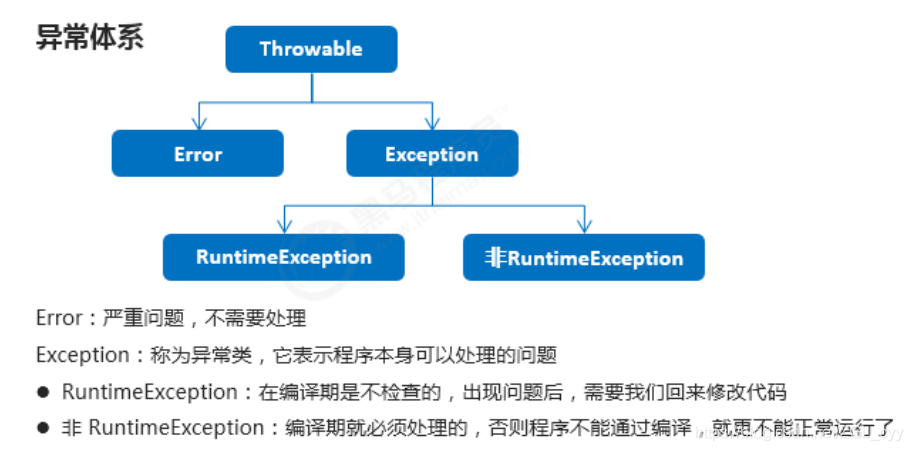
2 JVM默认处理异常的方式(理解)
如果程序出现了问题,我们没有做任何处理,最终
JVM
会做默认的处理,处理方式有如下两个步骤:
把异常的名称,错误原因及异常出现的位置等信息输出在了控制台
程序停止执行
3 try-catch方式处理异常(应用)
定义格式
try {
可能出现异常的代码;
} catch(异常类名 变量名) {
异常的处理代码;
}
执行流程
程序从 try 里面的代码开始执行
出现异常,就会跳转到对应的 catch 里面去执行
执行完毕之后,程序还可以继续往下执行
示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
method();
System.out.println("结束");
}
public static void method() {
try {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(arr[3]);
System.out.println("这里能够访问到吗");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
// System.out.println("你访问的数组索引不存在,请回去修改为正确的索引");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}4 Throwable成员方法(应用)
常用方法
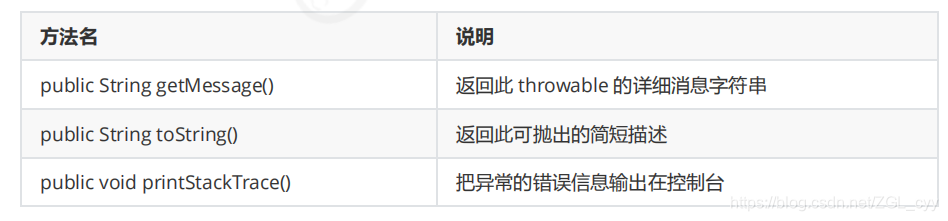
示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
method();
System.out.println("结束");
}
public static void method() {
try {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(arr[3]); //new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
System.out.println("这里能够访问到吗");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { //new
ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException();
// e.printStackTrace();
//public String getMessage():返回此 throwable 的详细消息字符串
// System.out.println(e.getMessage());
//Index 3 out of bounds for length 3
//public String toString():返回此可抛出的简短描述
// System.out.println(e.toString());
//java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 3 out of bounds
for length 3
//public void printStackTrace():把异常的错误信息输出在控制台
e.printStackTrace();
// java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: Index 3 out of bounds
for length 3
// at com.itheima_02.ExceptionDemo02.method(ExceptionDemo02.java:18)
// at com.itheima_02.ExceptionDemo02.main(ExceptionDemo02.java:11)
}
}
}
5 编译时异常和运行时异常的区别(记忆)
编译时异常
都是
Exception
类及其子类
必须显示处理,否则程序就会发生错误,无法通过编译
运行时异常
都是
RuntimeException
类及其子类
无需显示处理,也可以和编译时异常一样处理
6 throws方式处理异常(应用)
定义格式
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
public void 方法() throws 异常类名 {
}
示例代码
public class ExceptionDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("开始");
// method();
try {
method2();
}catch (ParseException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("结束");
}
//编译时异常
public static void method2() throws ParseException {
String s = "2048-08-09";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date d = sdf.parse(s);
System.out.println(d);
}
//运行时异常
public static void method() throws ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException {
int[] arr = {1, 2, 3};
System.out.println(arr[3]);
}
}
注意事项
这个
throws
格式是跟在方法的括号后面的
编译时异常必须要进行处理,两种处理方案:
try...catch …
或者
throws
,如果采用
throws
这种方案,
将来谁调用谁处理
运行时异常可以不处理,出现问题后,需要我们回来修改代码
7 throws和throw的区别(记忆)

8 自定义异常(应用)

抛出相应的异常
![]()
自定义异常类
public class ScoreException extends Exception {
public ScoreException() {}
public ScoreException(String message) {
super(message);
}
}老师类
public class Teacher {
public void checkScore(int score) throws ScoreException {
if(score<0 || score>100) {
// throw new ScoreException();
throw new ScoreException("你给的分数有误,分数应该在0-100之间");
} else {
System.out.println("成绩正常");
}
}
}测试类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入分数:");
int score = sc.nextInt();
Teacher t = new Teacher();
try {
t.checkScore(score);
} catch (ScoreException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}在try-catch-finally 的模式中
try里面是你没有出现异常,也就是你的程序正常执行的处理部分
catch里面是在try出现异常后转到的部分,不出现异常的话,这部分不会执行
finally则是顺序下来的,一定汇报执行的部分,通常我们在这里执行一些程序
必须要执行的当作。好像有关关闭数据库的操作那,不管你的数据库操作是否正确
最后你必须释放连接以及一些资源,否则会出问题,这样我们就把这些操作放在finally做一定处理。
9 异常的产生原理

10 执行流程
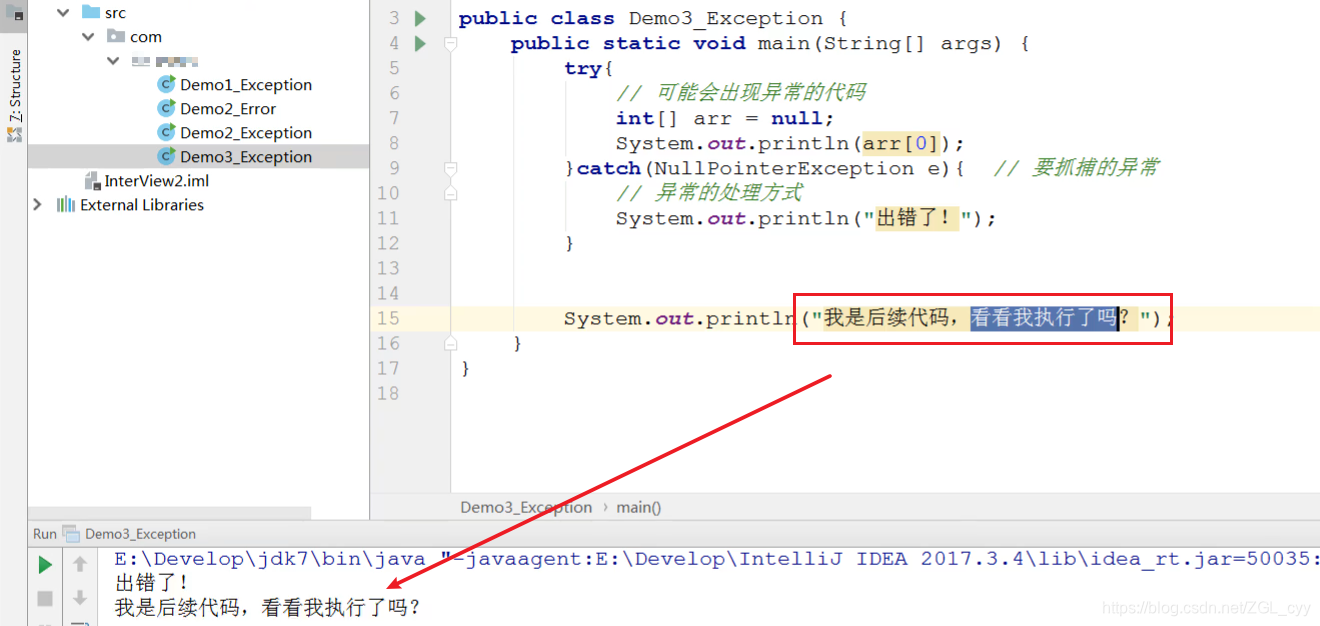
10 异常的处理方式


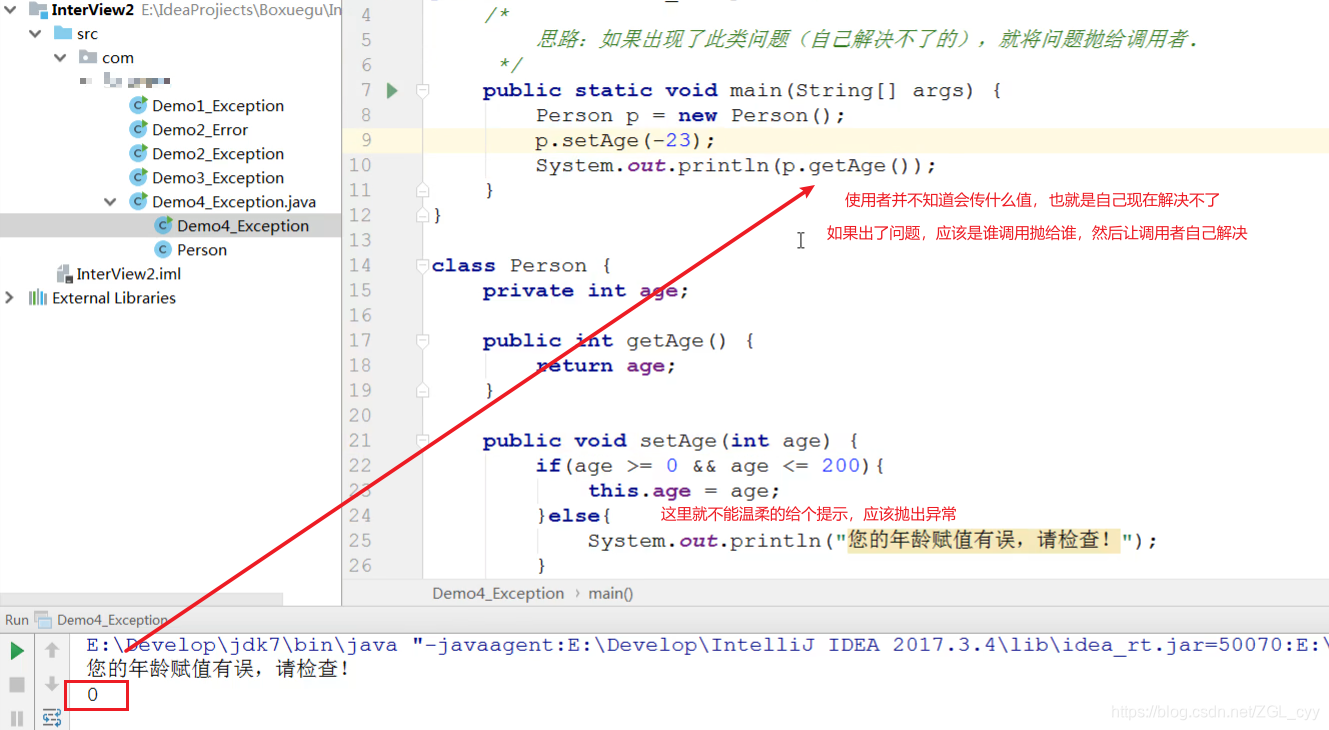
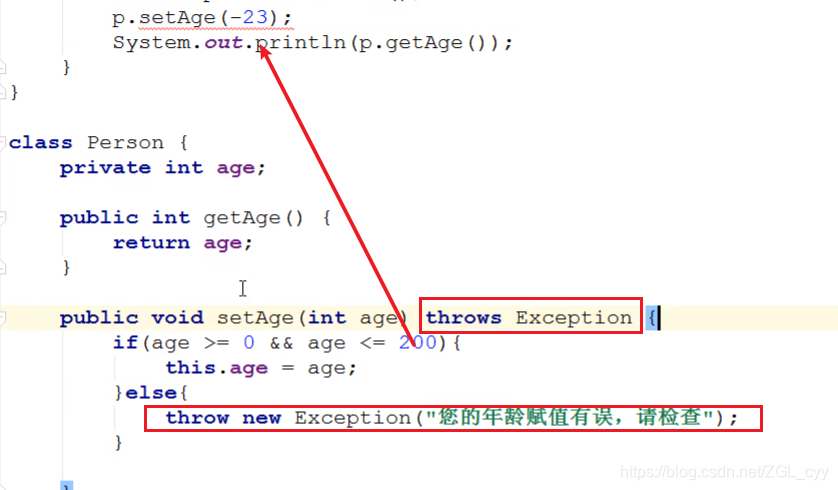
11 问题扩展




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号