管道传输
提交运行 ls | sort -r的结果,总结管道的功能
管道的功能总结:
数据流传输: 管道允许将一个命令的输出直接传输到另一个命令的输入,无需中间文件。
命令组合: 可以组合多个命令,实现复杂的数据处理流程。
效率提升: 由于数据在内存中直接传输,避免了磁盘 I/O,提高了处理速度
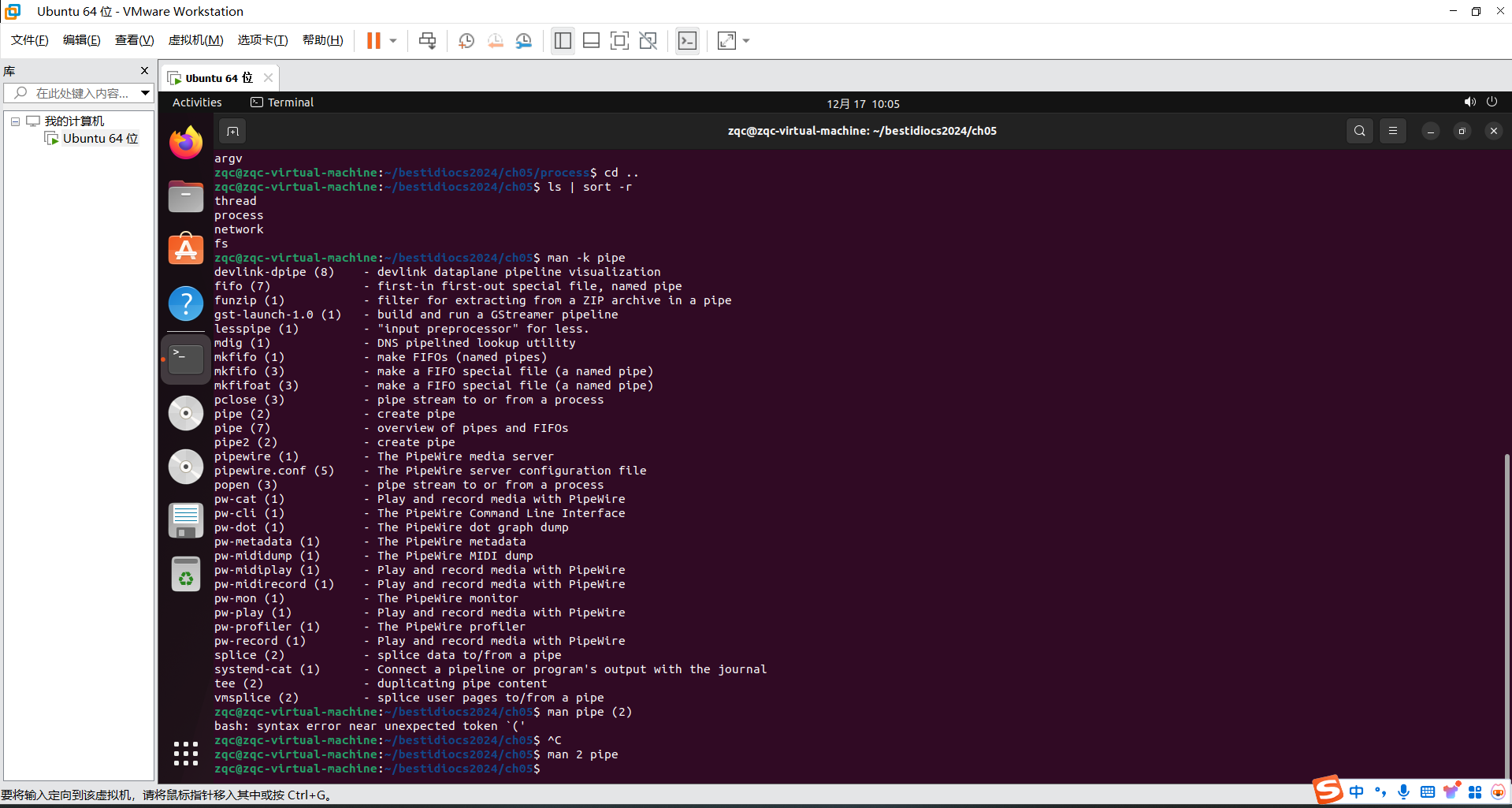
使用Linux系统调用编写实现管道(pipe)功能时,需要什么系统调用?提交man -k 相关截图。
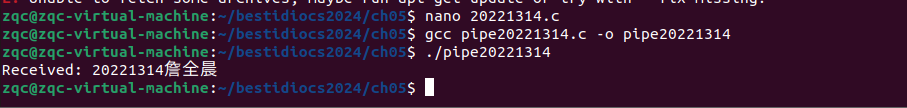
使用系统调用创建一个管道,父进程向管道写入数据,子进程从管道读取数据。在父进程中使用 write 系统调用写入字符串 “你的八位学号+姓名” ,并在子进程中使用 read 系统调用读取数据并打印。提交代码,编译运行过程截图(可文本)
`#include <stdio.h>
include <unistd.h>
include <stdlib.h>
include <sys/wait.h>
int main() {
int pipefd[2];
pid_t pid;
char message[] = "20221314詹全晨"; // 写入管道的字符串
// 创建管道
if (pipe(pipefd) == -1) {
perror("pipe");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 创建子进程
pid = fork();
if (pid == -1) {
perror("fork");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
if (pid == 0) { // 子进程
// 子进程关闭写端,只保留读端
close(pipefd[1]);
// 读取数据
char buffer[128];
int bytes_read = read(pipefd[0], buffer, sizeof(buffer));
if (bytes_read == -1) {
perror("read");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
buffer[bytes_read] = '\0'; // 确保字符串以空字符结尾
// 打印接收到的数据
printf("Received: %s\n", buffer);
// 关闭读端
close(pipefd[0]);
exit(EXIT_SUCCESS);
} else { // 父进程
// 父进程关闭读端,只保留写端
close(pipefd[0]);
// 写入数据到管道
int bytes_written = write(pipefd[1], message, sizeof(message));
if (bytes_written == -1) {
perror("write");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
// 关闭写端
close(pipefd[1]);
// 等待子进程结束
wait(NULL);
}
return 0;
}
`
gitlog
commit 64bb38900e690643ee682669f09724e833b649e7
Author: zqc zqc@zqc-virtual-machine
Date: Tue Dec 17 08:43:56 2024 +0800
管道传输


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号