实验二、深入理解系统调用
一、实验内容
- 找一个系统调用,系统调用号为学号最后2位相同的系统调用
- 通过汇编指令触发该系统调用
- 通过gdb跟踪该系统调用的内核处理过程
- 重点阅读分析系统调用入口的保存现场、恢复现场和系统调用返回,以及重点关注系统调用过程中内核堆栈状态的变化
二、实验过程
1.环境配置
下载linux5.4.34源码
axel -n 20 https://mirrors.edge.kernel.org/pub/linux/kernel/v5.x/linux-5.4.34.tar.xz xz -d linux-5.4.34.tar.xz tar -xvf linux-5.4.34.tar cd linux-5.4.34
配置内核编译选项
make defconfig make menuconfig
进入如下界面:
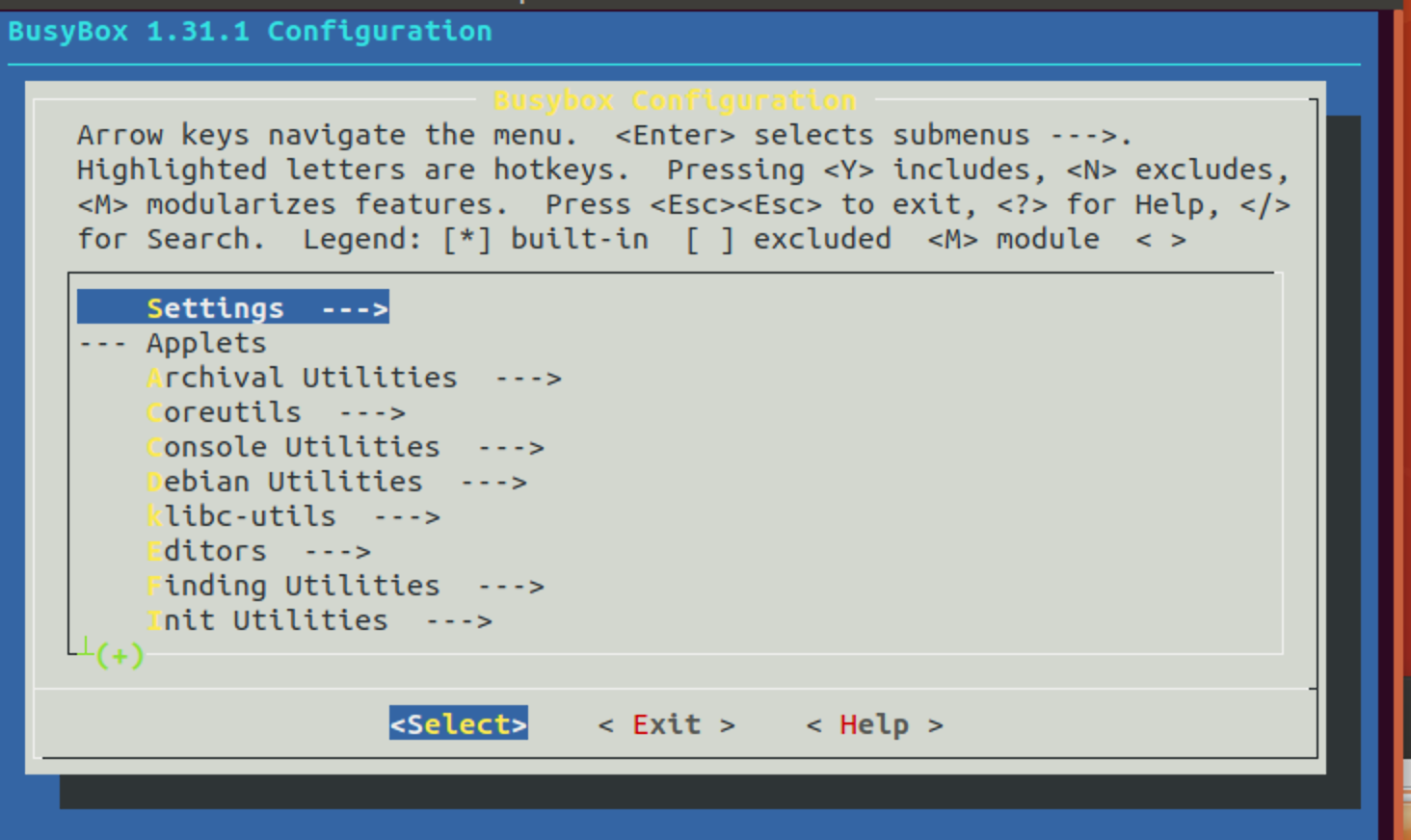
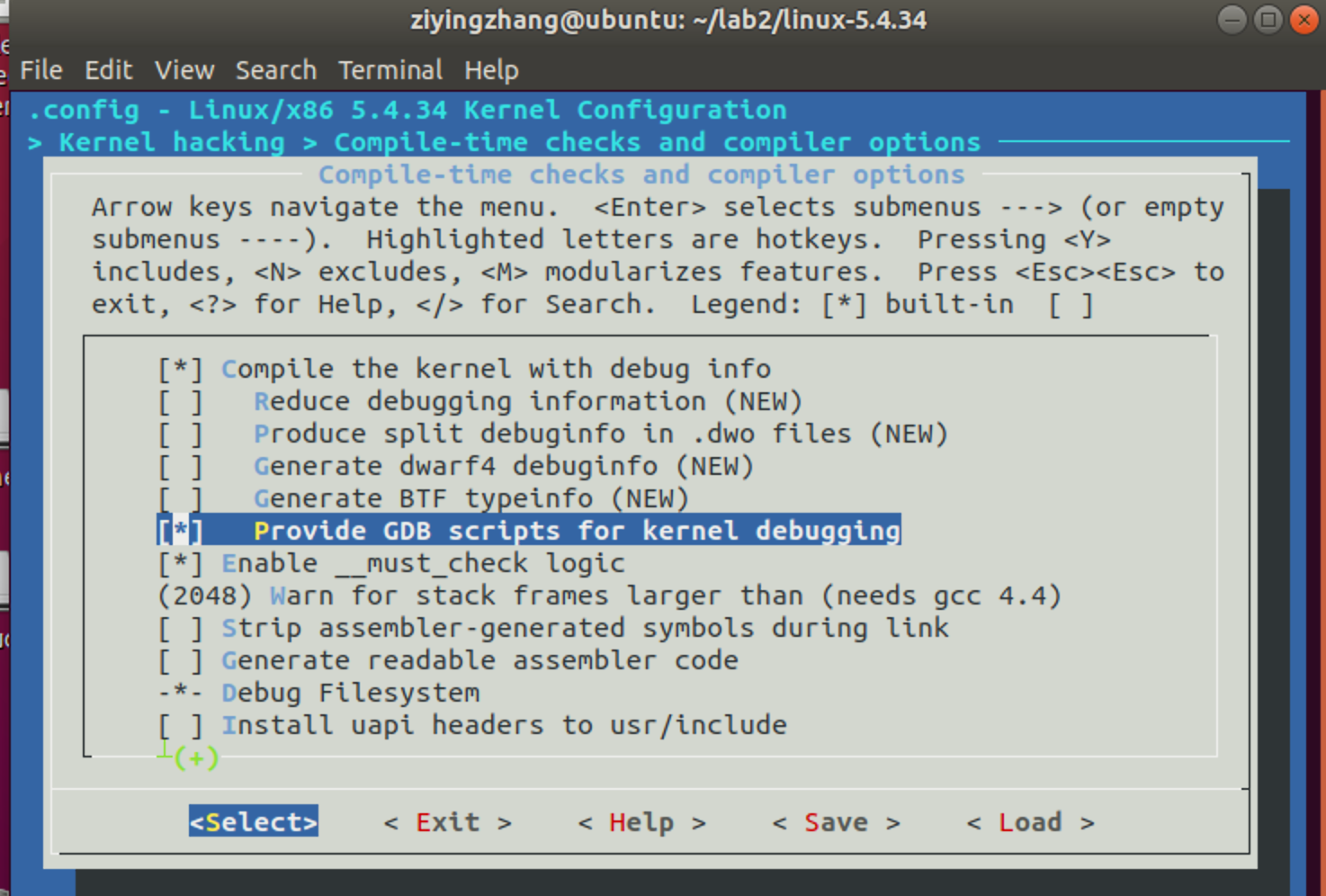
首先选择Kernel hacking 然后选择 Compile-time checks and compiler options ,勾选其中的三个选项
- Compile the kernel with debug info
- Provide GDB scripts for kernel debugging
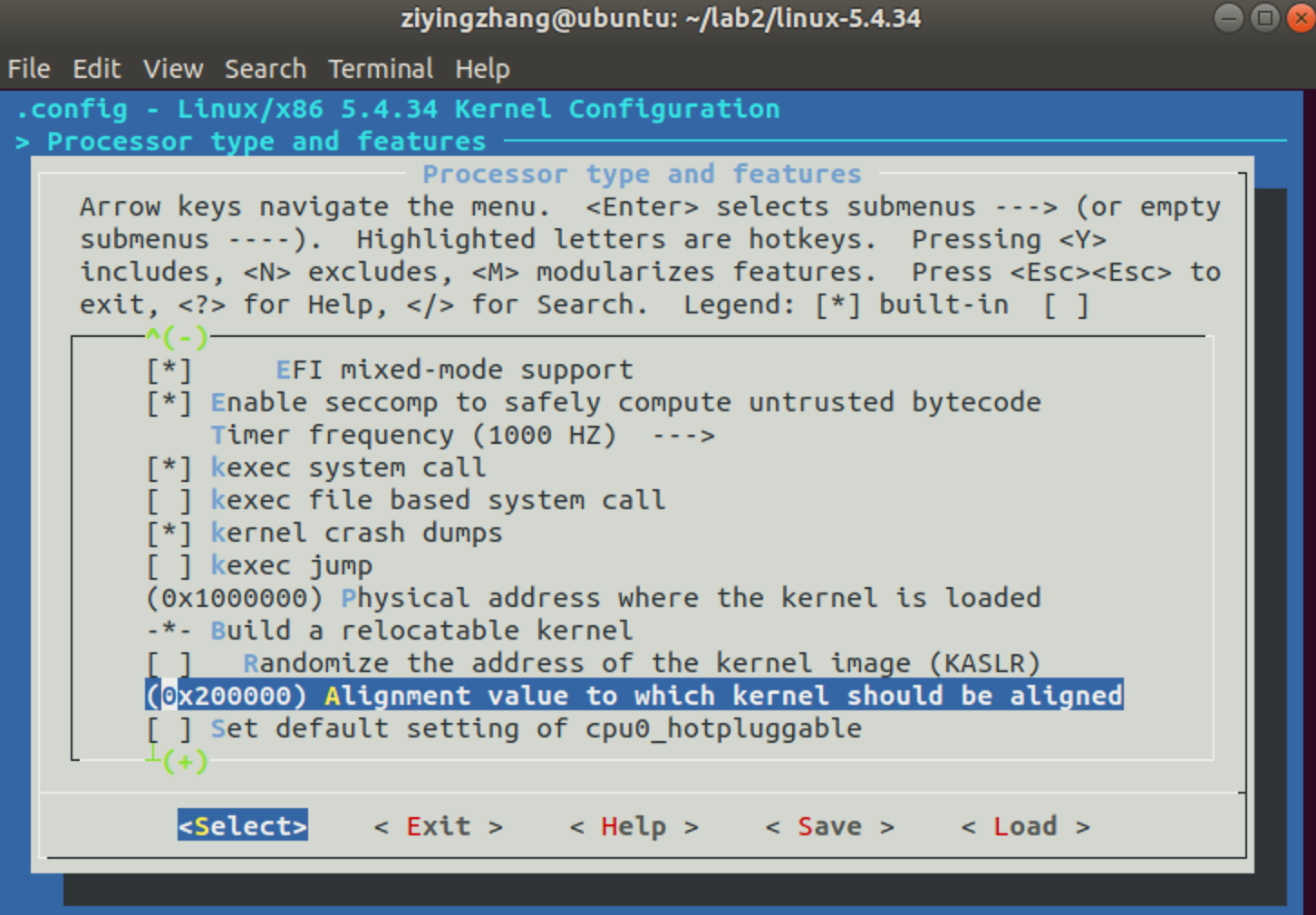
然后返回一级菜单,选择 Processor type and features 去除 Randomize the address of the kernel image (KASLR) 选项。
编译内核
make -j$(nproc) # nproc gives the number of CPU cores/threads available
制作文件系统
axel -n 20 https://busybox.net/downloads/busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2 tar -jxvf busybox-1.31.1.tar.bz2 cd busybox-1.31.1
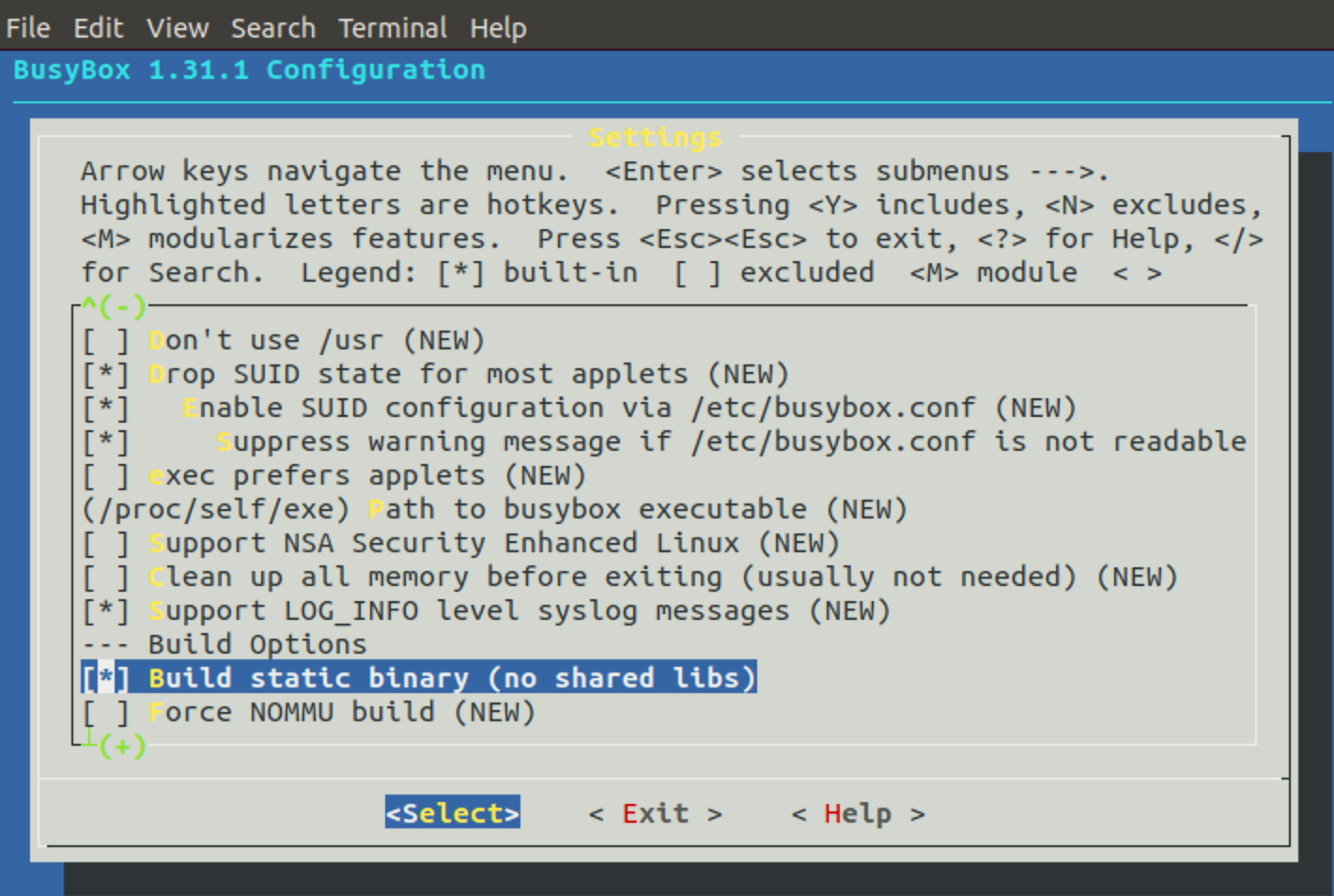
进入配置 make menuconfig
进入 Settings 勾选 Build static binary (no shared libs)
编译安装 make -j$(nproc) && make install
制作文件系统镜像
mkdir rootfs
cd rootfs
cp ../busybox-1.31.1/_install/* ./ -rf
mkdir dev proc sys home
sudo cp -a /dev/{null,console,tty,tty1,tty2,tty3,tty4} dev/
在rootfs下创建init脚本,添加如下内容
#!/bin/sh mount -t proc none /proc mount -t sysfs none /sys echo "Wellcome TestOS!" echo "--------------------" cd home /bin/sh
设置权限 chmod +x init
打包成内存根文件系统镜像 find . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../rootfs.cpio.gz
2.进行gdb调试
在arch/x86/entry/syscalls/syscall_64.tbl中,找到尾号为94的系统调用为lchown
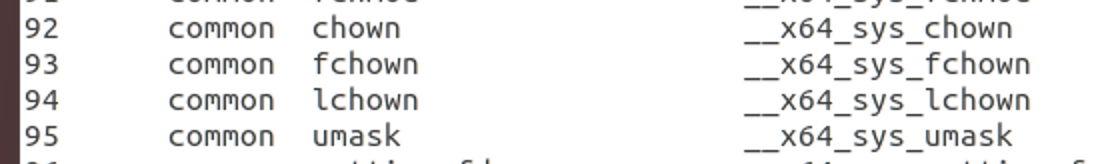
创建test.c
int main()
{
asm volatile(
"movl $0x5E,%eax\n\t" //使⽤EAX传递系统调⽤号94
"syscall\n\t" //触发系统调⽤
);
return 0;
}
编译,将生成的文件拷贝到rootfs/home中
gcc -o test test.c -static
find . -print0 | cpio --null -ov --format=newc | gzip -9 > ../rootfs.cpio.gz
回到linux目录下启动 qemu-system-x86_64 -kernel linux-5.4.34/arch/x86/boot/bzImage -initrd rootfs.cpio.gz -S -s -nographic -append "console=ttyS0"
另开一个命令窗口开启gdb gdb vmlinux
设置断点
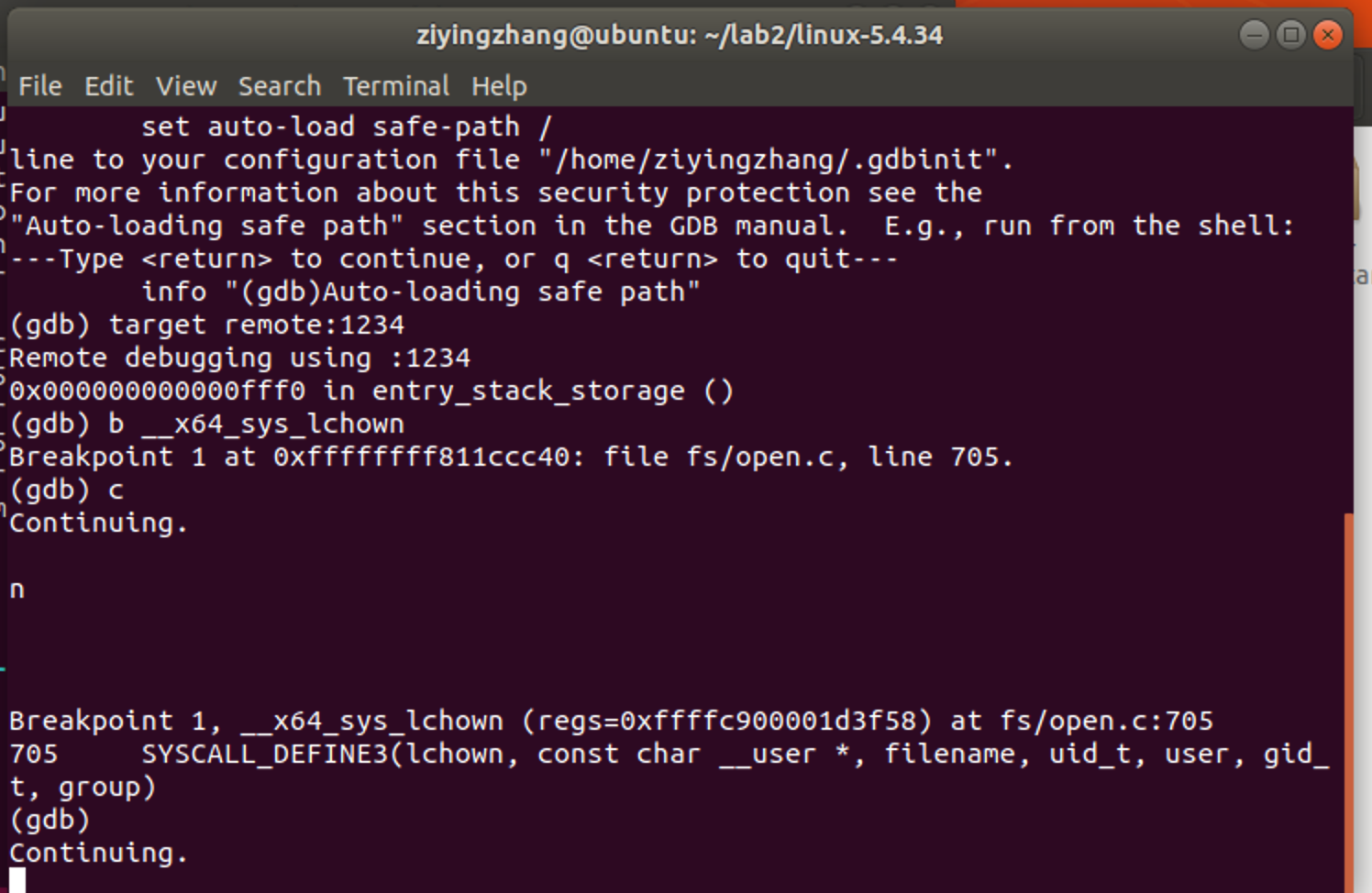
单步调试
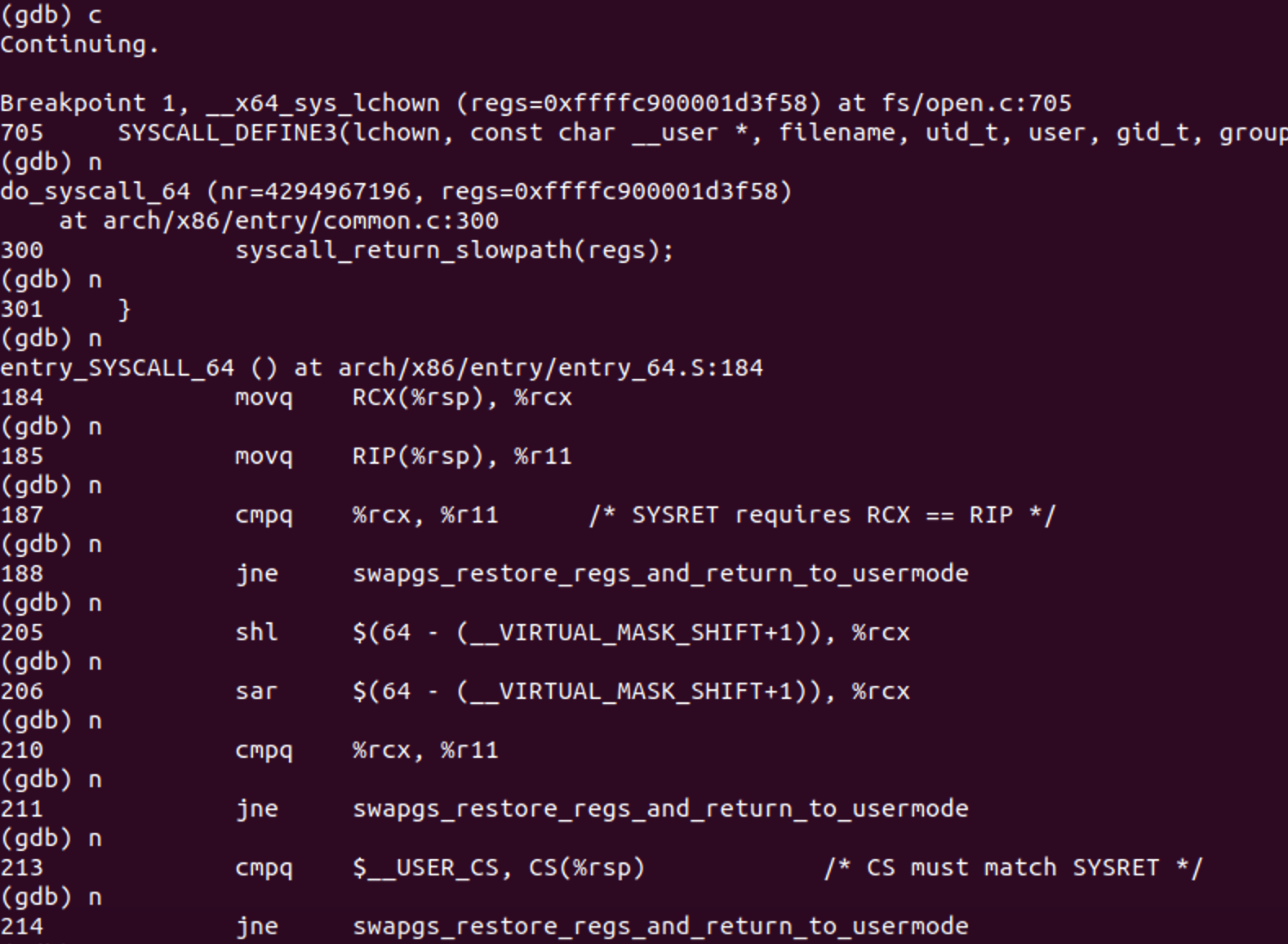
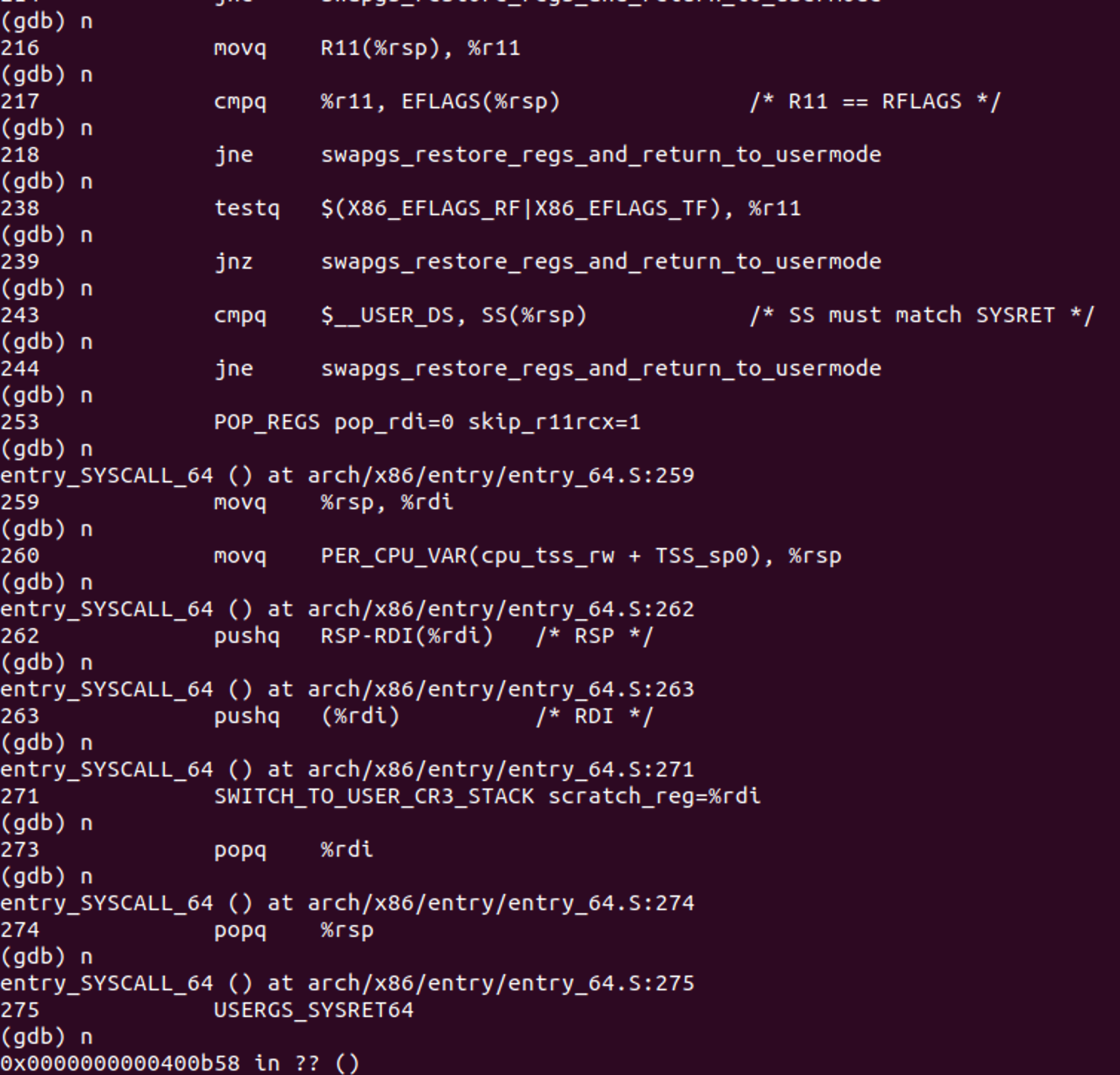
三、分析
用户态程序触发系统调用;然后系统进入内核态,完成内核初始化后,调用entry_SYSCALL_64 ()。通过 swapgs 指令保存现场
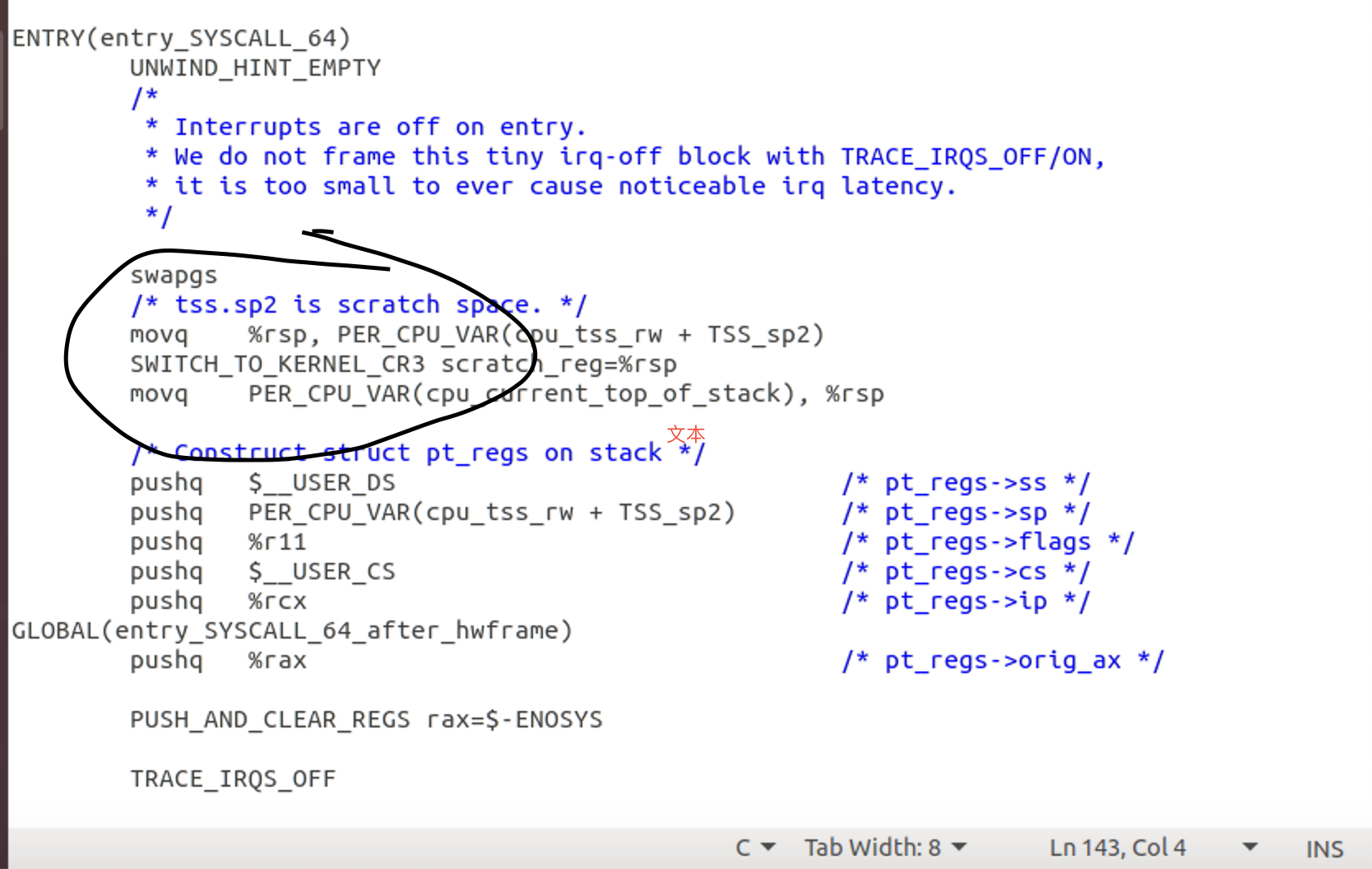
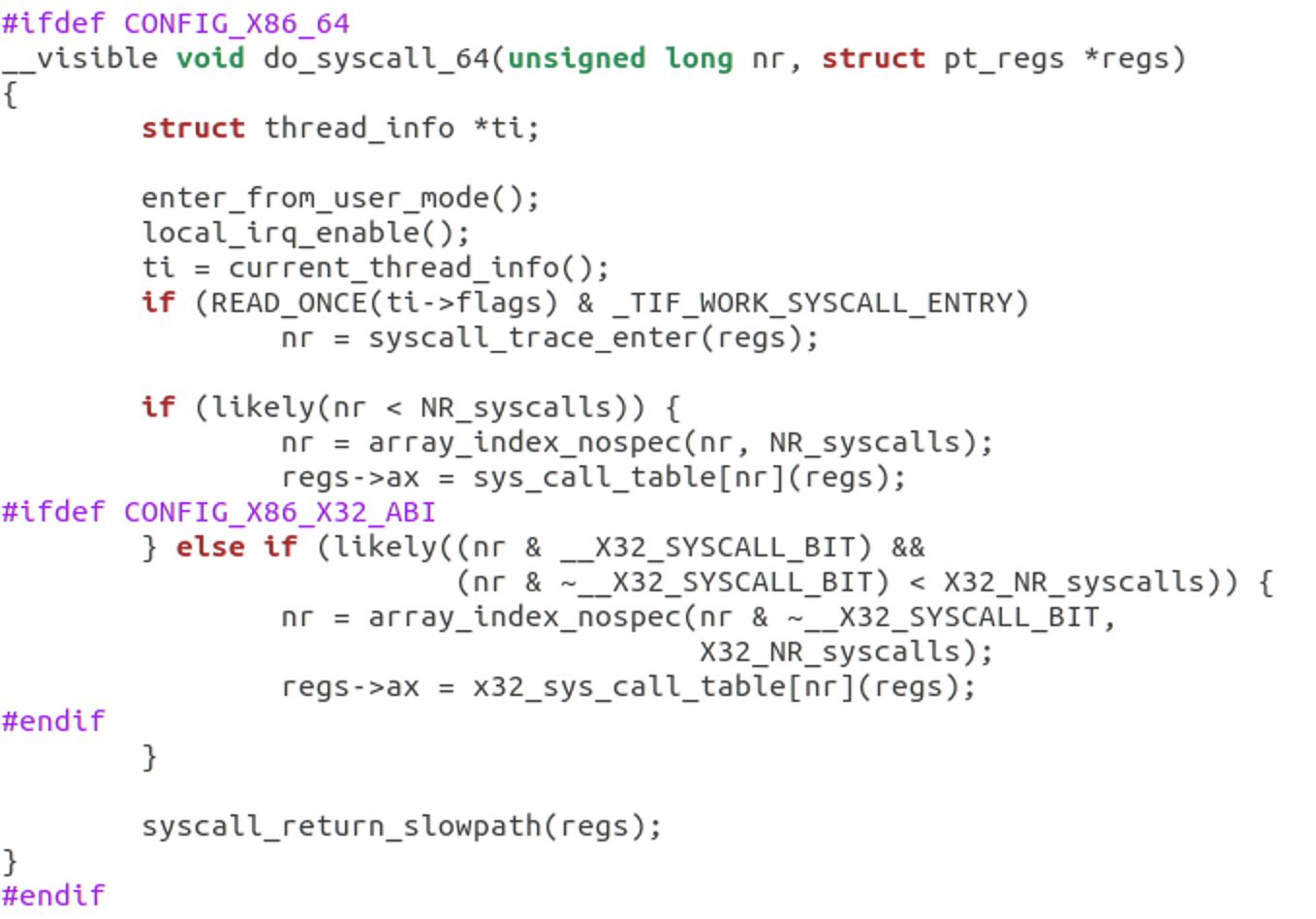
然后从CPU内部的MSR寄存器来查找系统调⽤处理⼊⼝,更改CPU的指令指针(eip/rip)到系统调⽤处理⼊⼝,触发 do_syscall_64。do_syscall_64 根据调用号,执行系统调用相应内容。然后程序跳到 fs/open.c文件,触发了 ksys_chdir() 函数。系统调用完成后执行do_syscall_64 中的 syscall_return_slowpath() ,进行现场恢复操作,然后回用户态。
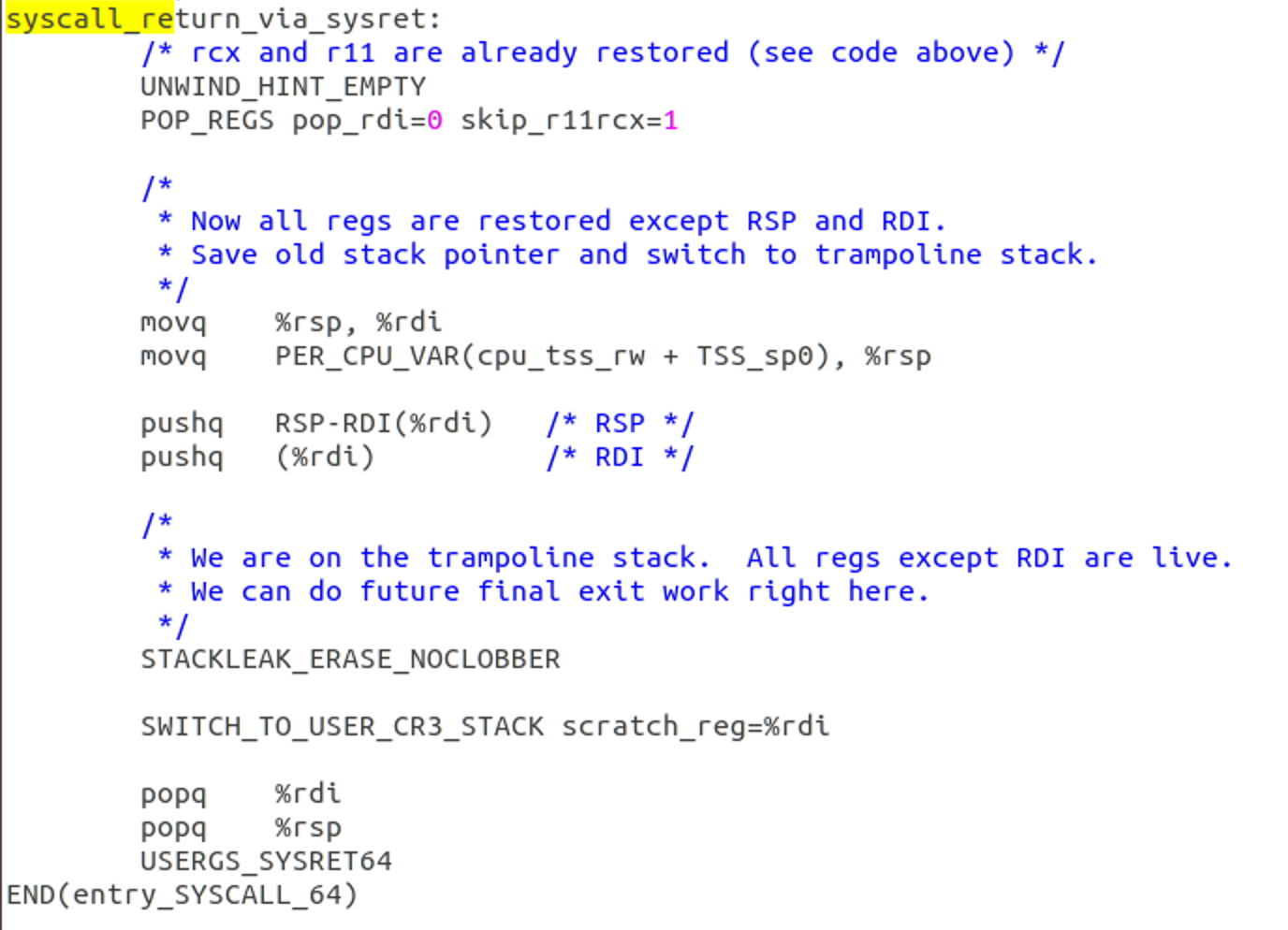
堆栈切换




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号